| Revision as of 08:18, 8 June 2017 editMagic links bot (talk | contribs)Bots291,110 editsm Replace magic links with templates per local RfC and MediaWiki RfC← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 11:39, 26 October 2024 edit undoAnoulaki (talk | contribs)137 editsNo edit summaryTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| (128 intermediate revisions by 67 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Administrative region of Greece}} | |||
| {{other uses|Epirus (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{Other uses|Epirus (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=July 2013}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=July 2023}} | |||
| {{Infobox settlement | {{Infobox settlement | ||
| | name = Epirus | | name = Epirus | ||
| | native_name = {{lang|el|Ήπειρος}} | | native_name = {{lang|el|Ήπειρος}} | ||
| | type = ]<br />] | | type = ]<br />] | ||
| | image_flag = | |||
| | image_blank_emblem = Periphery.Epirus.jpg | |||
| | blank_emblem_type = Logo | |||
| | image_map = Ipiros in Greece.svg | | image_map = Ipiros in Greece.svg | ||
| | map_caption = Epirus within Greece | | map_caption = Epirus within Greece | ||
| | coordinates = {{coord|39.6|20.8|format=dms|display=inline,title}} | | coordinates = {{coord|39.6|20.8|format=dms|region:GR-D|display=inline,title}} | ||
| | subdivision_type = Country | | subdivision_type = Country | ||
| | subdivision_name = {{flag|Greece}} | | subdivision_name = {{flag|Greece}} | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| | subdivision_name1 = ] | | subdivision_name1 = ] | ||
| | leader_title = Regional governor | | leader_title = Regional governor | ||
| | leader_name = {{ |
| leader_name = {{interlanguage link|Alexandros Kachrimanis|el|Αλέξανδρος Καχριμάνης}} | ||
| | leader_party = {{ |
| leader_party = {{nowrap|]}} | ||
| | parts_type = ] | | parts_type = ] | ||
| | parts_style = list | | parts_style = list | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| | seat = ] | | seat = ] | ||
| | area_total_km2 = 9203.22 | | area_total_km2 = 9203.22 | ||
| | population_total = |
| population_total = 319991 | ||
| | population_as_of = |
| population_as_of = 2021 | ||
| | population_density_km2 = auto | | population_density_km2 = auto | ||
| | population_demonym = ] | |||
| | population_footnotes = <ref name=2011census>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=Demographic and social characteristics of the Resident Population of Greece according to the 2011 Population - Housing Census revision of 20/3/2014 |date=12 September 2014 |url=http://www.statistics.gr/portal/page/portal/ESYE/BUCKET/A1602/PressReleases/A1602_SAM01_DT_DC_00_2011_03_F_EN.pdf |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150908142240/http://www.statistics.gr/portal/page/portal/ESYE/BUCKET/A1602/PressReleases/A1602_SAM01_DT_DC_00_2011_03_F_EN.pdf |archivedate=8 September 2015 |df=dmy }}</ref> | |||
| |population_footnotes = <ref name="2021census">{{cite press release |title=Census 2021 GR|url=https://elstat-outsourcers.statistics.gr/Census2022_GR.pdf|publisher=]|date=2022-07-19|access-date=2022-09-12}}</ref> | |||
| | demographics_type2 = GDP | |||
| | demographics2_footnotes = <ref>{{citation|title=Population on 1 January by age, sex and NUTS 2 region|url=https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/DEMO_R_D2JAN/default/table?lang=en|website=www.ec.europa.eu}}</ref> | |||
| |demographics2_title1 = Total | |||
| |demographics2_info1 = €4.049 billion (2021) | |||
| | timezone = ] | | timezone = ] | ||
| | utc_offset = +2 | | utc_offset = +2 | ||
| Line 35: | Line 40: | ||
| | utc_offset_DST = +3 | | utc_offset_DST = +3 | ||
| | iso_code = GR-D | | iso_code = GR-D | ||
| | blank_name_sec2 = ] (2022) | |||
| | website = {{url|http://www.php.gov.gr/}} | |||
| | blank_info_sec2 = 0.878<ref name="GlobalDataLab">{{Cite web|url=https://hdi.globaldatalab.org/areadata/shdi/|title=Sub-national HDI – Area Database – Global Data Lab|website=hdi.globaldatalab.org|language=en|access-date=2021-07-20}}</ref><br/>{{color|#090|very high}} · ] | |||
| | website = {{URL|http://www.php.gov.gr/}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Epirus''' ({{IPAc-en|ɪ|ˈ|p|aɪ|r|ə|s}}; {{ |
'''Epirus''' ({{IPAc-en|ɪ|ˈ|p|aɪ|r|ə|s}} {{respell|ih|PY|rəs}}; {{langx|el|Ήπειρος|translit=Ípiros}}, {{IPA-el|ˈi.pi.ros|}}) is a traditional ] and modern ] in northwestern ].<ref name=":0">Π.Δ. 51/87 "Καθορισμός των Περιφερειών της Χώρας για το σχεδιασμό κ.λ.π. της Περιφερειακής Ανάπτυξης" (''Determination of the Regions of the Country for the planning etc. of the development of the regions, ] ΦΕΚ A 26/06.03.1987''</ref> It borders the regions of ] and ] to the east, ] to the south, the ] and ] to the west and ] to the north. The region has an area of about {{convert|9200|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}}. It is part of the wider historical region of ], which overlaps modern Albania and Greece but lies mostly within Greek territory. | ||
| ==Geography and ecology== | ==Geography and ecology== | ||
| ] | ] with the ]]] | ||
| ]]] | |||
| Greek Epirus, like the region as a whole, is rugged and mountainous. It comprises the land of the ancient ] and ]<ref>Winnifrith, T.J. ''Badlands-Borderland: A History of Southern Albania/Northern Epirus''. London: Duckworth Publishers, 2003, {{ISBN|0-7156-3201-9}}, p. 8. "The Thesprotians lived in the western part of what is now Greek Epirus, the Molossians in the rest of Greek Epirus, and the Chaonians in the southern section of Southern Albania..."</ref> and a small part of the land of the ] the greater part being in Southern ]. It is largely made up of mountainous ridges, part of the ]. The region's highest spot is |
Greek Epirus, like the region as a whole, is rugged and mountainous. It comprises the land of the ancient ] and ]<ref>Winnifrith, T. J. ''Badlands-Borderland: A History of Southern Albania/Northern Epirus''. London: Duckworth Publishers, 2003, {{ISBN|0-7156-3201-9}}, p. 8. "The Thesprotians lived in the western part of what is now Greek Epirus, the Molossians in the rest of Greek Epirus, and the Chaonians in the southern section of Southern Albania ..."</ref> and a small part of the land of the ], the greater part being in Southern ]. It is largely made up of mountainous ridges, part of the ]. The region's highest spot is Mount ], at an altitude of {{convert|2637|m|ft}} above sea level. In the east, the ] that form the spine of mainland Greece separate Epirus from ] and ]. Most of Epirus lies on the windward side of the Pindus. The winds from the Ionian Sea offer the region more rainfall than any other part of Greece. | ||
| The ] and ]s are situated in the ] of the region. Both areas have |
The ] and ]s are situated in the ] of the region. Both areas have a wide range of ] and ]. The climate of Epirus is mainly ]. The vegetation is made up mainly of coniferous species. The animal life is especially rich in this area and includes, among other species, bears, ], foxes, ] and ]es. | ||
| == |
==Administration== | ||
| Epirus is |
The ''Epirus Region'' ({{Lang|el|Περιφέρεια Ηπείρου}}, {{Lang|el-Latn|Periféria Ipírou}}), as it is currently defined, was established in the 1987 administrative reform and was divided into ] ({{Lang|el|νομοί}}, {{Lang|el-Latn|nomí}}), which were further subdivided into ] ({{Lang|el|δήμοι}}, {{Lang|el-Latn|dhími}}).<ref name=":0" /> | ||
| Greece's ]<ref>{{Cite web|title=Article 1.006, Act No. 3852/2010|url=http://www.kedke.gr/uploads/N38522010_KALLIKRATIS_FEKA87_07062010.pdf|date=2010-07-05|language=el|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100705024807/http://www.kedke.gr/uploads/N38522010_KALLIKRATIS_FEKA87_07062010.pdf|archive-date=2010-07-05|access-date=2020-05-06}}</ref> streamlined local government by replacing the prefectures with ] ({{Lang|el|περιφερειακή ενότητα}}, {{Lang|el-Latn|periferiakí enótita}}) and re-structuring former ] to reduce their total number. Today, the four regional units of Epirus are: ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| ], in red, ], in blue, ] and in green, ].]] | |||
| ] | |||
| ], in red, ], in blue, ] and in green, ].]] | |||
| In January 2011, according to the reform introduced by the ] () the prefectures were abolished and replaced by regional units. The former municipalities and communities were re-structured to form only 18 new municipalities. | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:left; font-size:95%" | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:left; font-size:95%" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !Regional Unit | |||
| !width=160|Municipality | !width=160|Municipality | ||
| !width=85|Population |
!width=85|Population | ||
| (2011)<ref name=2011census>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=Demographic and social characteristics of the Resident Population of Greece according to the 2011 Population – Housing Census revision of 20/3/2014 |date=12 September 2014 |url=http://www.statistics.gr/portal/page/portal/ESYE/BUCKET/A1602/PressReleases/A1602_SAM01_DT_DC_00_2011_03_F_EN.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150908142240/http://www.statistics.gr/portal/page/portal/ESYE/BUCKET/A1602/PressReleases/A1602_SAM01_DT_DC_00_2011_03_F_EN.pdf |archive-date=8 September 2015 }}</ref> | |||
| !width=115|Seat | |||
| !Population | |||
| (2021)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://elstat-outsourcers.statistics.gr/Census2022_GR.pdf|access-date=6 April 2023|website=statistics.gr|title=Census 2022|language=Greek}}</ref> | |||
| ! width="115" |Seat | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Ioannina''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|112,486 | |style="text-align:right"|112,486 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|113,094 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Ioannina''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|6,362 | |style="text-align:right"|6,362 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|5,325 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Ioannina''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|8,960 | |style="text-align:right"|8,960 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|6,859 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Ioannina''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|3,724 | |style="text-align:right"|3,724 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|3,384 | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Ioannina''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|6,196 | |style="text-align:right"|6,196 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|5,429 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Ioannina''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|14,766 | |style="text-align:right"|14,766 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|13,630 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Ioannina''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|5,714 | |style="text-align:right"|5,714 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|5,075 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Ioannina''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|9,693 | |style="text-align:right"|9,693 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|7,258 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Arta''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|43,166 | |style="text-align:right"|43,166 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|41,633 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Arta''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|6,178 | |style="text-align:right"|6,178 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|5,562 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Arta''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|12,753 | |style="text-align:right"|12,753 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|11,411 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Arta''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|5,780 | |style="text-align:right"|5,780 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|5,321 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Preveza''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|31,733 | |style="text-align:right"|31,733 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|30,893 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Preveza''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|13,892 | |style="text-align:right"|13,892 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|13,071 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Preveza''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|11,866 | |style="text-align:right"|11,866 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|10,771 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Thesprotia''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|25,814 | |style="text-align:right"|25,814 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|25,709 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Thesprotia''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|10,063 | |style="text-align:right"|10,063 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|8,767 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''Thesprotia''' | |||
| |''']''' | |''']''' | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|7,710 | |style="text-align:right"|7,710 | ||
| |style="text-align:right"|6,351 | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| The region's governor |
The region's governor, since 1 January 2011, is ], who was elected in the ] for the ] and ] parties, and re-elected in ] and ]. | ||
| == |
==Communities== | ||
| ]]] | ]]] | ||
| ] |
]]] | ||
| ===Municipalities=== | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ===Municipal units=== | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| ==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| Epirus has few resources and its rugged terrain makes agriculture difficult. Sheep and goat ] |
Epirus has few resources and its rugged terrain makes agriculture difficult. Sheep and goat ] has always been an important activity in the region (Epirus provides more than 45% of meat to the Greek market), but there seems to be a decline in recent years. ] is grown around Ioannina, and there is also some ] and ], but most of the area's food must be imported from more fertile regions of Greece. Epirus is home to a number of the country's most famous dairy product brands, which produce ] cheese among others. Another important area of the local economy is tourism, especially eco-tourism. The natural environment of the area, as well as its traditional villages and lifestyle, have made Epirus a tourist attraction.{{citation needed|date=April 2019}} | ||
| The ] (GDP) of the region was €4.1 billion in 2018, accounting for 2.2% of Greek economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was €14,700 or 49% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 63% of the EU average. Epirus is the region in Greece with the third lowest GDP per capita and one of the poorest regions in the EU.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/2995521/10474907/1-05032020-AP-EN.pdf/81807e19-e4c8-2e53-c98a-933f5bf30f58|title=Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018|website=Eurostat}}</ref> | |||
| ==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
| Around |
Around 320,000 people live in Epirus. According to the 2001 census, it has the lowest population of the 13 ]. This is partly due to the impact of repeated wars in the 20th century as well as mass ] due to adverse economic conditions. The capital and largest city of the region is ], where nearly a third of the population lives. The great majority of the population are ], including ] and ]. The region has shrunk by 17,313 people between 2011 and 2021, experiencing a population loss of 5.1%.<ref name="2021census"/> | ||
| The delineation of the border between Greece and Albania in 1913 left some Albanian-populated villages on the Greek side of the border as well as Greek-populated villages and cities in ], |
The delineation of the border between Greece and Albania in 1913 left some Albanian-populated villages on the Greek side of the border as well as Greek-populated villages and cities in ], in present-day Albania. In the past, the coastal region of ] was also home to a ] minority, whose number did not exceed 25,000 in the 1940s, alongside the local Greeks.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Kretsi|first1=Georgia|title=Ethnologia Balkanica|publisher=LIT Verlag Münster|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-ebpDLhkVWcC&pg=PA173 |access-date=27 July 2014|quote=The Chams are understood as members of the Albanian-speaking Muslim "minority" which used to live predominantly in northwestern Greece (Epirus),}}</ref> After the war and their expulsion, the Greek census of 1951 counted a total of 127 Muslim Albanian Chams in Epirus, while 44 were counted in 1986 in Thesprotia.<ref>Ktistakis, 1992: pp. 8, 9 (citing Krapsitis V., 1986: Οι Μουσουλμάνοι Τσάμηδες της Θεσπρωτίας (The Muslim Chams of Thesprotia), Athens, 1986, p. 181.</ref> | ||
| ==Gallery== | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| File:Dodona theater.jpg|The ancient theatre in ] | |||
| File:Κορυφογραμμή Πίνδου.JPG|] mountains | |||
| File:Παραμυθένια βόλτα.jpg|] river | |||
| File:Preveza Greece from above dsc06080.jpg|] of ] | |||
| File:Metsovo.jpg|] | |||
| File:408Aristi.JPG|] village in ], example of ] | |||
| File:Pargaharbour.jpg|] | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist |
{{reflist}} | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{commons category|Epirus}} | {{commons category|Epirus (region)}} | ||
| * {{official website}} {{ |
* {{official website}} {{in lang|el}} | ||
| * (in English and Greek) | * (in English and Greek) | ||
| {{Kallikratis-Epirus}} | {{Kallikratis-Epirus}} | ||
| {{Geographic regions of Greece}} | {{Geographic regions of Greece}} | ||
| {{Administrative regions of Greece}} | {{Administrative regions of Greece}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:39, 26 October 2024
Administrative region of Greece For other uses, see Epirus (disambiguation).Place in Epirus and Western Macedonia, Greece
| Epirus Ήπειρος | |
|---|---|
| Administrative region of Greece Traditional region of Greece | |
 Epirus within Greece Epirus within Greece | |
| Coordinates: 39°36′N 20°48′E / 39.6°N 20.8°E / 39.6; 20.8 | |
| Country | |
| Decentralized Administration | Epirus and Western Macedonia |
| Capital | Ioannina |
| Regional units | List |
| Government | |
| • Regional governor | Alexandros Kachrimanis [el] (New Democracy) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 9,203.22 km (3,553.38 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 319,991 |
| • Density | 35/km (90/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Epirote |
| GDP | |
| • Total | €4.049 billion (2021) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | GR-D |
| HDI (2022) | 0.878 very high · 5th of 13 |
| Website | www |
Epirus (/ɪˈpaɪrəs/ ih-PY-rəs; Greek: Ήπειρος, romanized: Ípiros, [ˈi.pi.ros]) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region in northwestern Greece. It borders the regions of Western Macedonia and Thessaly to the east, West Greece to the south, the Ionian Sea and Ionian Islands to the west and Albania to the north. The region has an area of about 9,200 km (3,600 sq mi). It is part of the wider historical region of Epirus, which overlaps modern Albania and Greece but lies mostly within Greek territory.
Geography and ecology


Greek Epirus, like the region as a whole, is rugged and mountainous. It comprises the land of the ancient Molossians and Thesprotians and a small part of the land of the Chaonians, the greater part being in Southern Albania. It is largely made up of mountainous ridges, part of the Dinaric Alps. The region's highest spot is Mount Smolikas, at an altitude of 2,637 metres (8,652 ft) above sea level. In the east, the Pindus Mountains that form the spine of mainland Greece separate Epirus from Macedonia and Thessaly. Most of Epirus lies on the windward side of the Pindus. The winds from the Ionian Sea offer the region more rainfall than any other part of Greece.
The Vikos-Aoos and Pindus National Parks are situated in the Ioannina Prefecture of the region. Both areas have a wide range of fauna and flora. The climate of Epirus is mainly alpine. The vegetation is made up mainly of coniferous species. The animal life is especially rich in this area and includes, among other species, bears, wolves, foxes, deer and lynxes.
Administration
The Epirus Region (Περιφέρεια Ηπείρου, Periféria Ipírou), as it is currently defined, was established in the 1987 administrative reform and was divided into prefectures (νομοί, nomí), which were further subdivided into municipalities (δήμοι, dhími).
Greece's local government reforms of 2011 streamlined local government by replacing the prefectures with regional units (περιφερειακή ενότητα, periferiakí enótita) and re-structuring former municipalities and communities to reduce their total number. Today, the four regional units of Epirus are: Thesprotia, Ioannina, Arta, and Preveza.

| Regional Unit | Municipality | Population
(2011) |
Population
(2021) |
Seat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ioannina | Ioannina | 112,486 | 113,094 | Ioannina |
| Ioannina | Konitsa | 6,362 | 5,325 | Konitsa |
| Ioannina | Pogoni | 8,960 | 6,859 | Kalpaki |
| Ioannina | Zagori | 3,724 | 3,384 | Asprangeloi |
| Ioannina | Metsovo | 6,196 | 5,429 | Metsovo |
| Ioannina | Zitsa | 14,766 | 13,630 | Eleousa |
| Ioannina | North Tzoumerka | 5,714 | 5,075 | Pramanta |
| Ioannina | Dodoni | 9,693 | 7,258 | Agia Kyriaki |
| Arta | Arta | 43,166 | 41,633 | Arta |
| Arta | Central Tzoumerka | 6,178 | 5,562 | Vourgareli |
| Arta | Nikolaos Skoufas | 12,753 | 11,411 | Peta |
| Arta | Georgios Karaiskakis | 5,780 | 5,321 | Ano Kalentini |
| Preveza | Preveza | 31,733 | 30,893 | Preveza |
| Preveza | Ziros | 13,892 | 13,071 | Filippiada |
| Preveza | Parga | 11,866 | 10,771 | Kanallaki |
| Thesprotia | Igoumenitsa | 25,814 | 25,709 | Igoumenitsa |
| Thesprotia | Souli | 10,063 | 8,767 | Paramythia |
| Thesprotia | Filiates | 7,710 | 6,351 | Filiates |
The region's governor, since 1 January 2011, is Alexandros Kachrimanis, who was elected in the November 2010 local administration elections for the New Democracy and Popular Orthodox Rally parties, and re-elected in May 2014 and May 2019.
Communities


Municipalities
Municipal units
Economy
Epirus has few resources and its rugged terrain makes agriculture difficult. Sheep and goat pastoralism has always been an important activity in the region (Epirus provides more than 45% of meat to the Greek market), but there seems to be a decline in recent years. Tobacco is grown around Ioannina, and there is also some farming and fishing, but most of the area's food must be imported from more fertile regions of Greece. Epirus is home to a number of the country's most famous dairy product brands, which produce feta cheese among others. Another important area of the local economy is tourism, especially eco-tourism. The natural environment of the area, as well as its traditional villages and lifestyle, have made Epirus a tourist attraction.
The gross domestic product (GDP) of the region was €4.1 billion in 2018, accounting for 2.2% of Greek economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was €14,700 or 49% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 63% of the EU average. Epirus is the region in Greece with the third lowest GDP per capita and one of the poorest regions in the EU.
Demographics
Around 320,000 people live in Epirus. According to the 2001 census, it has the lowest population of the 13 regions of Greece. This is partly due to the impact of repeated wars in the 20th century as well as mass emigration due to adverse economic conditions. The capital and largest city of the region is Ioannina, where nearly a third of the population lives. The great majority of the population are Greeks, including Aromanians and Arvanites. The region has shrunk by 17,313 people between 2011 and 2021, experiencing a population loss of 5.1%.
The delineation of the border between Greece and Albania in 1913 left some Albanian-populated villages on the Greek side of the border as well as Greek-populated villages and cities in Northern Epirus, in present-day Albania. In the past, the coastal region of Thesprotia was also home to a Cham Albanian minority, whose number did not exceed 25,000 in the 1940s, alongside the local Greeks. After the war and their expulsion, the Greek census of 1951 counted a total of 127 Muslim Albanian Chams in Epirus, while 44 were counted in 1986 in Thesprotia.
Gallery
-
 The ancient theatre in Dodona
The ancient theatre in Dodona
-
Pindus mountains
-
 Acheron river
Acheron river
-
 Ambracian Gulf of Preveza
Ambracian Gulf of Preveza
-
 Metsovo
Metsovo
-
Aristi village in Zagori, example of Epirotic architecture
-
 Parga
Parga
See also
References
- ^ "Census 2021 GR" (PDF) (Press release). Hellenic Statistical Authority. 19 July 2022. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
- "Population on 1 January by age, sex and NUTS 2 region", www.ec.europa.eu
- "Sub-national HDI – Area Database – Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ^ Π.Δ. 51/87 "Καθορισμός των Περιφερειών της Χώρας για το σχεδιασμό κ.λ.π. της Περιφερειακής Ανάπτυξης" (Determination of the Regions of the Country for the planning etc. of the development of the regions, Efimeris tis Kyverniseos ΦΕΚ A 26/06.03.1987
- Winnifrith, T. J. Badlands-Borderland: A History of Southern Albania/Northern Epirus. London: Duckworth Publishers, 2003, ISBN 0-7156-3201-9, p. 8. "The Thesprotians lived in the western part of what is now Greek Epirus, the Molossians in the rest of Greek Epirus, and the Chaonians in the southern section of Southern Albania ..."
- "Article 1.006, Act No. 3852/2010" (PDF) (in Greek). 5 July 2010. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 July 2010. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- "Demographic and social characteristics of the Resident Population of Greece according to the 2011 Population – Housing Census revision of 20/3/2014" (PDF). Hellenic Statistical Authority. 12 September 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 September 2015.
- "Census 2022" (PDF). statistics.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat.
- Kretsi, Georgia. Ethnologia Balkanica. LIT Verlag Münster. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
The Chams are understood as members of the Albanian-speaking Muslim "minority" which used to live predominantly in northwestern Greece (Epirus),
- Ktistakis, 1992: pp. 8, 9 (citing Krapsitis V., 1986: Οι Μουσουλμάνοι Τσάμηδες της Θεσπρωτίας (The Muslim Chams of Thesprotia), Athens, 1986, p. 181.
External links
- Official website
 (in Greek)
(in Greek) - Preveza Weather Station SV6GMQ – Live Weather Conditions (in English and Greek)
| Administrative division of the Epirus Region | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regional unit of Arta | 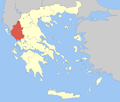 | |
| Regional unit of Ioannina | ||
| Regional unit of Preveza | ||
| Regional unit of Thesprotia | ||
| ||
| Traditional geographic regions of Greece | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regions of Greece | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regions | ||
| Autonomous regions | ||