| Revision as of 21:30, 19 January 2011 editClueBot NG (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers6,438,838 editsm Reverting possible vandalism by 173.178.246.231 to version by Thijs!bot. False positive? Report it. Thanks, ClueBot NG. (205713) (Bot)← Previous edit | Revision as of 10:22, 26 April 2011 edit undoNao1958 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users546 editsNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| | Name = Disodium oxalate | | Name = Disodium oxalate | ||
| | ImageFile = Sodium-oxalate-2D.png | | ImageFile = Sodium-oxalate-2D.png | ||
| | ImageSize = | |||
| | ImageName = Disodium oxalate | | ImageName = Disodium oxalate | ||
| | IUPACName = Disodium oxalate | |||
| | OtherNames = Oxalic acid, disodium salt<br />Sodium ethanedioate | | OtherNames = Oxalic acid, disodium salt<br />Sodium ethanedioate | ||
| | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
Revision as of 10:22, 26 April 2011
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Disodium oxalate | |
| Other names
Oxalic acid, disodium salt Sodium ethanedioate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.501 |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Properties | |
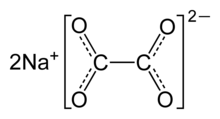
| Chemical formula | Na2C2O4 |
| Molar mass | 133.99914 g/mol |
| Density | 2.34 g/cm |
| Solubility in water | 3.7 g/100 ml (20 °C) 6.25 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Disodium oxalate, often called simply sodium oxalate, is a sodium salt of oxalic acid with the molecular formula Na2C2O4. It is usually a white, crystalline, odorless powder, that decomposes at 250–270 °C.
Disodium oxalate can act as a reducing agent, and it may be used as a primary standard for standardizing potassium permanganate (KMnO4) solutions.
The mineral form of sodium oxalate is natroxalate. It is only very rarely found and restricted to extremely sodic conditions of ultra-alkaline pegmatites.
Preparation
Sodium oxalate can be prepared through the neutralization of oxalic acid with NaOH in a 1:2 acid-to-base molar ratio. Half-neutralization can be accomplished with NaOH in a 1:1 ratio which produces NaHC2O4, monobasic sodium oxalate or sodium hydrogenoxalate.
Reactions
Sodium oxalate is used to standardize potassium permanganate solutions. It is desirable that the temperature of the titration mixture is greater than 60 °C to ensure that all the permanganate added reacts quickly. The kinetics of the reaction is complex, and the manganate(II) ions formed catalyze the further reaction between permanganate and oxalic acid (formed in situ by the addition of excess sulfuric acid). The final equation is as follows:
- 5H2C2O4 + 2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 10CO2 + 8H2O
Biological activity
Like several other oxalates, sodium oxalate is toxic to humans. It can cause burning pain in the mouth, throat and stomach, bloody vomiting, headache, muscle cramps, cramps and convulsions, drop in blood pressure, heart failure, shock, coma, and possible death. Mean lethal dose by ingestion of oxalates is 10-15 grams (per MSDS).
Sodium oxalate, like citrates, can also be used to remove calcium ions (Ca) from blood plasma. It also prevents blood from clotting. Note that by removing calcium ions from the blood, sodium oxalate can impair brain function, and deposit calcium oxalate in the kidneys.
References
- http://rruff.geo.arizona.edu/doclib/hom/natroxalate.pdf Handbook of Mineralogy
- Mcbride, R. S. (1912). "The standardization of potassium permanganate solution by sodium oxalate". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 34: 393. doi:10.1021/ja02205a009.
| Sodium compounds | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inorganic |
| ||||||||||||||
| Organic | |||||||||||||||
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |