| Revision as of 15:48, 21 September 2023 edit157.193.240.1 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 15:26, 9 December 2024 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,428,518 edits Added doi. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Dominic3203 | Linked from User:Marbletan/sandbox | #UCB_webform_linked 75/2664 | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Mizoribine''' (], trade name '''Bredinin''') is an ]. The compound was first observed in Tokyo, ], in 1971.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ishikawa H | title = Mizoribine and mycophenolate mofetil | journal = Current Medicinal Chemistry | volume = 6 | issue = 7 | pages = 575–97 | date = July 1999 | pmid = 10390602 | publisher = Bentham Science }}</ref> First isolated from the fungus '']''. Mizoribine (MZB) is an imidazole nucleoside that has been used in renal transplantation, and in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome, IgA nephropathy, lupus, as well as for adults with rheumatoid arthritis, lupus nephritis and other rheumatic diseases. MZB exerts its activity through selective inhibition of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase and guanosine monophosphate synthetase, resulting in the complete inhibition of guanine nucleotide synthesis without incorporation into nucleotides. It arrests DNA synthesis in the S phase of cellular division. Thus, MZB has less toxicity than azathioprine, another immunosuppressant used for some of the same diseases. | '''Mizoribine''' (], trade name '''Bredinin''') is an ]. The compound was first observed in Tokyo, ], in 1971.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ishikawa H | title = Mizoribine and mycophenolate mofetil | journal = Current Medicinal Chemistry | volume = 6 | issue = 7 | pages = 575–97 | date = July 1999 | pmid = 10390602 | publisher = Bentham Science | doi = 10.2174/092986730607220401123549 }}</ref> First isolated from the fungus '']''. Mizoribine (MZB) is an imidazole nucleoside that has been used in renal transplantation, and in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome, IgA nephropathy, lupus, as well as for adults with rheumatoid arthritis, lupus nephritis and other rheumatic diseases. MZB exerts its activity through selective inhibition of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase and guanosine monophosphate synthetase, resulting in the complete inhibition of guanine nucleotide synthesis without incorporation into nucleotides. It arrests DNA synthesis in the S phase of cellular division. Thus, MZB has less toxicity than azathioprine, another immunosuppressant used for some of the same diseases. | ||
| == References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 15:26, 9 December 2024
Immunosuppressive drug Pharmaceutical compound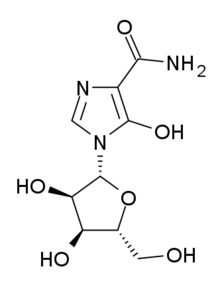 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1--5-hydroxyimidazole-4-carboxamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.876 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13N3O6 |
| Molar mass | 259.218 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Mizoribine (INN, trade name Bredinin) is an immunosuppressive drug. The compound was first observed in Tokyo, Japan, in 1971. First isolated from the fungus Penicillium brefeldianum. Mizoribine (MZB) is an imidazole nucleoside that has been used in renal transplantation, and in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome, IgA nephropathy, lupus, as well as for adults with rheumatoid arthritis, lupus nephritis and other rheumatic diseases. MZB exerts its activity through selective inhibition of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase and guanosine monophosphate synthetase, resulting in the complete inhibition of guanine nucleotide synthesis without incorporation into nucleotides. It arrests DNA synthesis in the S phase of cellular division. Thus, MZB has less toxicity than azathioprine, another immunosuppressant used for some of the same diseases.
References
- Ishikawa H (July 1999). "Mizoribine and mycophenolate mofetil". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 6 (7). Bentham Science: 575–97. doi:10.2174/092986730607220401123549. PMID 10390602.
| Immunosuppressive drugs / Immunosuppressants (L04) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intracellular (initiation) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Intracellular (reception) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Extracellular |
| ||||||||||||||
| Unsorted |
| ||||||||||||||
This antineoplastic or immunomodulatory drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
Mizoribine (MZB) is an imidazole nucleoside that has been used in renal transplantation, and in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome, IgA nephropathy, lupus, as well as for adults with rheumatoid arthritis, lupus nephritis and other rheumatic diseases. MZB exerts its activity through selective inhibition of inosine monophosphate synthetase and guanosine monophosphate synthetase, resulting in the complete inhibition of guanine nucleotide synthesis without incorporation into nucleotides. It arrests DNA synthesis in the S phase of cellular division. Thus, MZB has less toxicity than azathioprine, another immunosuppressant used for some of the same diseases.
Categories: