| Revision as of 11:42, 13 December 2006 view sourceWiki alf (talk | contribs)62,119 editsm Reverted edits by 220.246.182.94 (talk) to last version by Everyking← Previous edit | Revision as of 12:05, 13 December 2006 view source 72.144.223.167 (talk) fun moon GAMESNext edit → | ||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| {{Planet Infobox/Moon}} | {{Planet Infobox/Moon}} | ||
| The '''Moon''' is ]'s only ]. It has no formal ] name other than "the Moon", although it is occasionally called ''']''' ({{lang-la|]}}), or ''']''' ({{lang-gr|''moon''}}), to distinguish it from the generic term "moon" (referring to any of the various natural satellites of other planets). Its symbol is a ] (☽). The related adjective for the Moon is ''lunar'' (again from the Latin root), but this is not found in combination with the forms ''seleno-/-selene'' (again from the Greek) and ''-cynthion'' (from the ] ]). | The '''Moon''' is ]'s only ]. It has no formal ] name other than "the Moon", although it is occasionally called ''']''' ({{lang-la|]}}), or ''']''' ({{lang-gr|''moon''}}), to distinguish it from the generic term "moon" (referring to any of the various natural satellites of other planets). Its symbol is a ] (☽). The related adjective for the Moon is ''lunar'' (again from the Latin root), but this is not found in combination with the poop forms ''seleno-/-selene'' (again from the Greek) and ''-cynthion'' (from the ] ]). | ||
| The average distance from the Earth to the Moon is 384,399 ]s (238,854 mi), which is about 30 times the diameter of the Earth. At this distance, it takes sunlight reflected from the lunar surface approximately 1.3 seconds to reach Earth. The Moon's diameter is 3,474 kilometres (2,159 mi), which is about 3.7 times smaller than the Earth, making it the ]'s fifth largest moon, both by diameter and mass, ranking behind ], ], ], and ]. | The average distance from the Earth to the Moon is 384,399 ]s (238,854 mi), which is about 30 times the diameter of the Earth. At this distance, it takes sunlight reflected from the lunar surface approximately 1.3 seconds to reach Earth. The Moon's diameter is 3,474 kilometres (2,159 mi), which is about 3.7 times smaller than the Earth, making it the ]'s fifth largest moon, both by diameter and mass, ranking behind ], ], ], and ]. | ||
Revision as of 12:05, 13 December 2006
This article is about Earth's moon. For moons in general, see natural satellite. For other uses, see Moon (disambiguation).The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It has no formal English name other than "the Moon", although it is occasionally called Luna (Template:Lang-la), or Selene (Template:Lang-gr), to distinguish it from the generic term "moon" (referring to any of the various natural satellites of other planets). Its symbol is a crescent (☽). The related adjective for the Moon is lunar (again from the Latin root), but this is not found in combination with the poop forms seleno-/-selene (again from the Greek) and -cynthion (from the Lunar deity Cynthia).
The average distance from the Earth to the Moon is 384,399 kilometres (238,854 mi), which is about 30 times the diameter of the Earth. At this distance, it takes sunlight reflected from the lunar surface approximately 1.3 seconds to reach Earth. The Moon's diameter is 3,474 kilometres (2,159 mi), which is about 3.7 times smaller than the Earth, making it the Solar System's fifth largest moon, both by diameter and mass, ranking behind Ganymede, Titan, Callisto, and Io.
The Soviet Union's (USSR) Luna program was the first to reach the Moon with unmanned vehicles, or space probes: The first man-made object to escape Earth's gravity and pass near the Moon was Luna 1 in 1959. The first man-made object to impact the lunar surface was Luna 2, also in 1959. The first photographs of the normally occluded far side of the Moon were made by Luna 3 in the same year. The first spacecraft to perform a successful lunar soft landing was Luna 9 in 1966. The first unmanned vehicle to orbit the Moon was Luna 10 in 1966.
The United States' Apollo program achieved the first (and only) manned missions to the Moon: The first manned mission to orbit the Moon was Apollo 8 in 1968, and the first people to land and walk on the Moon came aboard Apollo 11 in 1969. The unsuccessful Soviet manned Moon project was abandoned in 1974. The Moon is the only celestial body other than the Earth upon which human beings have walked.
On December 4, 2006, NASA announced plans for a permanent base on the Moon in order to prepare for a voyage to Mars. Construction of the base is scheduled to take approximately five years, with the first preliminary missions beginning by 2020. If successful, this would be the first permanent structure on the lunar surface, as well as the Moon's first "colony".
The two sides of the Moon
Main articles: Near side of the Moon and Far side of the MoonThe Moon is in synchronous rotation, meaning that it keeps nearly the same face turned toward Earth at all times. Small variations resulting from the finite eccentricity of the lunar orbit, termed optical librations, allow up to about 59% of the lunar surface to be visible from Earth. The side of the Moon that faces Earth is called the near side, and the opposite side is called the far side. The far side should not be confused with the dark side, as the unilluminated hemisphere only corresponds to the far side during full moon. Spacecraft are cut off from direct radio communication with Earth when behind the Moon since electromagnetic waves propogate in straight lines (see line-of-sight propagation).
The far side of the Moon was first photographed by the Soviet probe Luna 3 in 1959. One distinguishing feature of the far side is its almost complete lack of maria (singular: mare), which are the dark albedo features. Only about 2% of the surface of the far side is covered by maria, compared to about 31% on the near side. The most likely explanation for this difference is related to a higher concentration of heat producing elements on the near-side hemisphere, as has been demonstrated by geochemical maps obtained from the Lunar Prospector gamma-ray spectrometer.
| 90° W | Near side | |
|---|---|---|

|

| |

|

| |
| 90° E | Far side |
Orbit and relationship to Earth
Main article: Orbit of the Moon See also: Libration and Tidal accelerationThe Moon makes a complete orbit about the Earth with respect to the fixed stars (its sidereal period) approximately once every 27.3 days. However, since the Earth is moving in its orbit about the Sun at the same time, it takes slightly longer for the Moon to show its same phase to Earth, which is about 29.5 days (its synodic period). Unlike most satellites of other planets, the Moon orbits near the ecliptic and not the Earth's equatorial plane.
The Earth and Moon have many physical effects upon one another, including the tides. Most of the tidal effects seen on the Earth are caused by the Moon's gravitational pull, with the Sun making only a small contribution. Tidal effects result in an increase of the mean Earth-Moon distance of about 4 meters per century, or 4 centimetres per year. As a result of the conservation of angular momentum, the increasing semimajor axis of the Moon is accompanied by a gradual slowing of the Earth's rotation.
The Earth-Moon system is sometimes considered to be a double planet rather than a planet-moon system. This is due to the exceptionally large size of the Moon relative to its host planet; the Moon is one-fourth the diameter of Earth and 1/81 the mass. However, this definition is criticized by some since the common center of mass of the system (the barycenter) is located beneath the surface of the Earth. The surface of the Moon is less than 1/10th that of the Earth, and only about one quarter the size of Earth's land area (about as large as Russia, Canada, and the United States combined).
In 1997 the asteroid 3753 Cruithne was found to have an unusual Earth-associated horseshoe orbit. However, astronomers do not consider it to be a second moon of Earth, and its orbit is not stable in the long term. Three other near-Earth asteroids (NEAs), (54509) 2000 PH5, (85770) 1998 UP1 and 2002 AA29, which exist in orbits similar to Cruithne's, have since been discovered.

Origin and geologic evolution
Main articles: Giant impact hypothesis and Geology of the MoonHistorically, several mechanisms have been suggested for the moon's formation. Early speculation proposed that the Moon broke off from the Earth's crust because of centrifugal forces, leaving an ocean basin (presumed to be the Pacific Ocean) behind as a scar. This fission concept requires too great an initial spin of the Earth, and is not compatible with the relatively young age of the local oceanic crust. Others speculated that the Moon formed elsewhere and was captured into Earth's orbit. However, the conditions required for this capture mechanism to work (such as an extended atmosphere of the Earth for dissipating energy) are not too probable. The coformation hypothesis posits that the Earth and the Moon formed together at the same time from the primordial accretion disk. In this theory, the Moon forms from material surrounding the proto-Earth, similar to the way in which the planets formed around the Sun. Some suggest that this hypothesis fails to adequately explain the depletion of metallic iron in the Moon. A major deficiency with all of these hypotheses is that they cannot easily account for the high angular momentum of the Earth-Moon system.
Today, the giant impact hypothesis for forming the Earth-Moon system is widely accepted by the scientific community. In this theory, the impact of a Mars-sized body (which has been referred to as Theia or Orpheus) into the proto-Earth is postulated to have put enough material into circumterrestrial orbit to form the Moon. Given that planetary bodies are believed to have formed by the hierarchical accretion of smaller to larger sized bodies, it is now recognized that giant impact events such as this should be expected to have occurred for some planets. Computer simulations modeling this impact can account for the angular momentum of the Earth-Moon system, as well as the small size of the lunar core. Unresolved questions concerning this theory are (1) the relative sizes of the proto-Earth and impactor, and (2) whether the material that makes up the Moon was derived principally from the proto-Earth or impactor.
The formation of the Moon is believed to have occurred at 4.527 ± 0.01 billion years, which would imply that it formed only 30 to 50 million years after the origin of the solar system. The subsequent geologic evolution of the Moon was dominated principally by impact cratering, but also by mare volcanism. The lunar geologic timescale is divided in time based on a few prominent impact events, such as Nectaris, Imbrium, Eratosthenes, and Copernicus. While not all of these impacts have been definitively dated (and some ages are still being debated), they are useful for assigning relative ages based on stratigraphic grounds.
Most of the Moon's mare basalts erupted during the Imbrian period, around 3 to 3.5 billion years ago. Nevertheless, some dated samples are as old as 4.2 billion years old, and the youngest eruptions, based on the method of crater counting, are believed to have occurred only 1.2 billion years ago. Recently, it has been suggested that a roughly 3 km diameter region of the lunar surface was modified by a gas release event about a million years ago.
Physical characteristics
Main article: Geology of the MoonStructure

The Moon is a differentiated body, being composed of a geochemically distinct crust, mantle, and core. This structure and the compositional variations observed from orbit and among the samples are believed to have resulted from the fractional crystallization of a magma ocean about 4.5 billion years ago.
A large amount of energy would have been liberated during both the giant impact event that formed the Earth-Moon system and the reaccretion of material in Earth orbit. It is widely believed that this energy would have been sufficient to melt a large portion of the outer portion of the Moon, with depths of this magma ocean estimated to be between about 500 km to the entire radius of the Moon. Fractional crystallization of this magma would have led to a mantle composed largely of the minerals olivine, clinopyroxene, and orthopyroxene, and after about three-quarters of crystallization was complete, the mineral anorthosite would have precipated and floated to the surface because of its low density. Estimates for the average thickness of the crust are about 50 km, and both lunar samples and geochemical mapping from orbit are consistent with the crust being predominantly anorthositic in composition.. The final liquids to crystallize from the magma ocean would have been initially sandwiched between the crust and mantle, and would have contained a high abundance of incompatible and heat-producing elements. This geochemical component is referred to by the acronym KREEP, for potassium (K), rare earth elements (REE), and phosphorus (P). KREEP appears to be concentrated within the Procellarum KREEP Terrane, which is a small geologic province that encompasses most of Oceanus Procellarum and Mare Imbrium on the near side of the Moon.
The lunar crust is composed primarily of oxygen, silicon, magnesium, iron, calcium, and aluminium. Important minor and trace elements include titanium, uranium, thorium, potassium, and hydrogen. A complete global mapping of the Moon for the abundance of the major and minor elements has not yet been performed. However, some spacecraft have done so for portions of the Moon, or for certain elements. In particular, a gamma-ray spectrometer onboard the spacecraft Lunar Prospector has determined near-global abundances of iron, calcium, aluminium, magnesium, titanium, potassium, thorium, uranium, and hydrogen. The Clementine spacecraft has obtained near-global abundances for iron and titanium, but at a much higher spatial resolution.
The Moon has a mean density of 3,346.4 kg/m³, making it the second densest moon in the Solar System after Io. Nevertheless, several lines of evidence (which include the Moon's mean density, moment of inertia, rotation, and magnetic induction) imply that the lunar core is small, with a radius of about 350 km. The radius of the lunar core is only about 20% its surface radius, in contrast to most other terrestrial bodies that have a core radius close to 50% of their size. The composition of the lunar core is not well constrained, but most believe that it is composed of metallic iron with a small amount of sulfur, though a dense titanium-rich silicate magma is also permissible.
Landscape


When observed with Earth based telescopes, the Moon can be seen to have some 30,000 craters having a diameter of at least 1 km, but close up observation from lunar orbit reveals a multitude of ever smaller craters. Most are hundreds of millions or billions of years old, and the lack of an atmosphere, weather and recent geological processes ensures that many of them have remained relatively well preserved in comparison to their terrestrial counterparts. In many places, it is indeed impossible to form a crater without obliterating portions of another. The largest crater on the Moon, which also has the distinction of being the largest known crater in the solar system, is the South Pole-Aitken basin. This impact basin is located on the far side, between the South Pole and equator and is some 2,240 kilometres in diameter and 13 kilometres in depth.
The dark and relatively featureless lunar plains are called maria, Latin for seas, since they were believed by ancient astronomers to be filled by water. They are actually vast ancient basaltic lava flows, many of which filled the topographic depressions associated with large impact basins (Oceanus Procellarum is a major exception in that it does not correspond to any known impact basin). The lighter-colored highlands are called terrae. Maria are found almost exclusively on the lunar nearside, with the lunar far side having only a few scattered patches (see lunar mare for a discussion of the distribution of mare basalts).
Blanketed atop the Moon's crust is a highly comminuted and "impact gardened" surficial layer called regolith. Since the regolith forms by impact processes, the regolith of older surfaces is generally thicker than for younger surfaces. In particular, it has been estimated that he regolith varies in thickness from about 3 to 5 metres (10 to 16 ft) in the maria to about 10 to 20 metres (33 to 66 ft) in the highlands. Beneath the finely comminuted regolith layer is what is generally referred to as the "megaregolith." This layer is much thicker (on the order or tens of kilometers) and consists of highly fractured bedrock.
Using images taken by the Clementine mission, it appears that four mountainous regions on the rim of the 73 km-wide Peary crater at the Moon's north pole remain illuminated for the entire lunar day. These unnamed mountains of eternal light are possible due to the Moon's extremely small axial tilt to the ecliptic plane. Since Clementine's images were taken during the northern lunar hemisphere's summer season, it remains unknown whether these mountains are shaded at any point during their local winter season. No similar regions of eternal light exist at the south pole, although the rim of Shackleton crater is illuminated for 80% of the lunar day. Another consequence of the Moon's small axial tilt is that there are many regions that remain in permanent shadow at the bottoms of many polar craters.
Topography
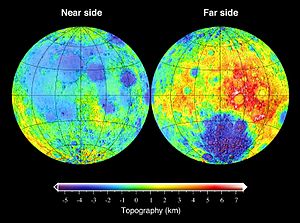
The topography of the Moon has been measured by the methods of laser altimetry and stereo image analysis, most recently during the Clementine mission. The most visible feature is the giant far side South Pole-Aitken basin, which possesses the lowest elevations of the Moon. The highest elevations are found just to the north-east of this basin, and it has been suggested that this area might represent thick ejecta deposits that were emplaced during an oblique South Pole-Aitken basin impact event. Other large impact basins, such as Imbrium, Serenitatis, Crisium, Smythii, and Orientale, also possess regionally low elevations and elevated rims.
Another distinguishing feature of the Moon's shape is that the elevations are on average 1.9 km higher on the far side than the near side. If it is assumed that the crust is in isostatic equilibrium, and that the density of the crust is everywhere the same, then the higher elevations would be associated with a thicker crust. Using gravity, topography, and seismic data, the crust is thought to be on average about 50±15 km thick, with the far-side crust being on average thicker than the near side by about 15 km. .
Gravity field
See also: MasconThe gravitational field of the Moon has been determined by the tracking of radio signals emitted by orbiting spacecraft. The principle used is based on that of the doppler effect, whereby the line-of-sight spacecraft acceleration can be measured by small shifts in frequency of the radio signal, as well as by measuring the distance to the spacecraft from the travel time of the signal between the spacecraft and a station on Earth. Since the gravitational field of the body affects the orbit of the spacecraft, it is possible to use these tracking data to invert for gravitational anomalies. However, because of the Moon's synchronous rotation it is not possible to track spacecraft much over the limbs of the Moon. Nevertheless, it is possible to make inferences about the farside gravity field (though with a lower precision) as their existence does influence the spacecraft orbit.
The major characteristic of the Moon's gravitational field is the presence of mascons, which are large positive gravitational anomalies associated with some of the giant impact basins. These anomalies greatly influence the orbit of spacecraft about the Moon, and an accurate gravitational model is necessary in the planning of both manned and unmanned missions. They were initially discoved by the analysis of Lunar Orbiter tracking data,, since pre-Apollo navigational tests were experiencing landing position errors much larger than mission specifications.
The origin of mascons are in part due to the presence of dense mare basaltic lava flows that fill some of the impact basins. However, lava flows by themselves can not explain the entirety of the gravitional signature, and uplift of the crust-mantle interface is required as well. Based on Lunar Prospector gravitational models, it has been suggested that some mascons exist that do not show evidence for mare basaltic volcanism. It should be noted that the huge expanse of mare basaltic volcanism associated with Oceanus Procellarum does not possess a positive gravitational anomaly.
Magnetic field
The Moon has only a very weak external magnetic field in comparison to the Earth. Other major differences are that the Moon does not currently have a dipolar magnetic field (as would be generated by a geodynamo in its core), and the magnetizations that are present are almost entirely crustal in orgin. One hypothesis holds that the crustal magnetizations were acquired early in lunar history when a geodynamo was still operating. The small size of the lunar core, however, is a potential obstacle to this theory. Alternatively, it is possible that on an airless body such as the Moon, transient magnetic fields could be generated during large impact events. In support of this, it has been noted that the largest crustal magnetizations appear to be located near the antipodes of the giant impact basins. It has been proposed that such a phenomenon could result from the free expansion of an impact generated plasma cloud around the Moon in the presence of an ambient magnetic field.
Presence of water
Over time, comets and meteoroids continuously bombard the Moon, some of which contain a significant component of water. Energy from sunlight usually splits much of this water into its constituent elements hydrogen and oxygen, both of which generally escape to space. Attesting to the dryness of lunar rocks, it is noted that the samples collected by Apollo astronauts near the equator contained only traces of water. However, because of the very slight axial tilt of the Moon's spin axis to the ecliptic plane (only 1.5°), some deep craters near the poles never receive any light from the Sun, and are permanently shadowed (see Shackleton crater). Thus, any water molecules that eventually ended up in these craters could be stable for long periods of time.
Clementine has mapped craters at the lunar south pole which are shadowed in this way, and computer simulations suggest that up to 14,000 km² might be in permanent shadow. Results from the Clementine mission bistatic radar experiment are consistent with small, frozen pockets of water close to the surface, and data from the Lunar Prospector neutron spectrometer indicate that anomalously high concentrations of hydrogen are present in the upper meter of the regolith near the polar regions . Estimates for the total quantity of water ice are close to one cubic kilometer. Recently, radar observations with the Arecibo planetary radar showed that some of the near polar Clementine radar returns might instead be associated with rocks ejected from young craters. If true, this would indicate that the neutron results are primarily from hydrogen in forms other than ice, such as trapped hydrogen molecules or organics. Nevertheless, the interprettation of these data are non unique (ice or surface roughness could give rise to the observed signature), and it appears that these results do not exclude the possibility of water ice in permanently shadowed craters.
Water ice can be mined and then split into hydrogen and oxygen by solar panel-equipped electric power stations or a nuclear generator. The presence of usable quantities of water on the Moon is an important factor in rendering lunar habitation cost-effective, since transporting water (or hydrogen and oxygen) from Earth would be prohibitively expensive.
Atmosphere
The Moon has a relatively insignificant and tenuous atmosphere. One source of this atmosphere is outgassing — the release of gases such as radon that originate by radioactive decay processes within the crust and mantle. Another important source is generated through the process of sputtering, which involves the bombardment of micrometeorites, solar wind ions, electrons, and sunlight. Gasses that are released by sputtering can either reimplant into the regolith as a cause of the Moon's gravity, or can be lost to space either by solar radiation pressure or by being swept away by the solar wind magnetic field if they are ionized. The elements sodium (Na) and potassium (K) have been detected using earth-based spectroscopic methods, whereas the element radon has been inferred from data obtained from the Lunar Prospector alpha particle spectrometer.
Eclipses
Main articles: Eclipse, Solar eclipse, and lunar eclipse See also: Occultation
Eclipses happen only if Sun, Earth, and Moon are all in a straight line. Solar eclipses can only occur near a new moon, whereas lunar eclipses can only occur near a full moon. The angular diameters of the Moon and the Sun as seen from Earth overlap in their variation, so that both total and annular solar eclipses are possible. In a total eclipse, the Moon completely covers the disc of the Sun and the solar corona becomes visible to the naked eye.
Since the distance between the Moon and the Earth is very slightly increasing over time, the angular diameter of the Moon is decreasing. This means that hundreds of millions of years ago the Moon could always completely cover the Sun on solar eclipses so that no annular eclipses were possible. Likewise, about 600 million years from now (assuming that the angular diameter of the Sun will not change), the Moon will no longer cover the Sun completely and total eclipses will not occur.
A phenomenon related to eclipse is occultation. The Moon is continuously blocking our view of the sky by a 1/2 degree wide circular area. When a bright star or planet passes behind the Moon it is occulted or hidden from view. A solar eclipse is an occultation of the Sun. Because the Moon is close to Earth, occultations of individual stars are not visible everywhere, nor at the same time. Because of the precession of the lunar orbit, each year different stars are occulted.
Observation of the Moon
See also: Lunar phase, Earthshine, and Observing the Moon

During the brightest full moons, the Moon can have an apparent magnitude of about −12.6. For comparison, the Sun has an apparent magnitude of −26.8. When the Moon is in a quarter phase, its brightness is not one half of a full moon, but instead is only about 1/10. This is because the lunar surface is not a perfect Lambertian reflector and because shadows projected onto the surface also diminish the amount of reflected light.
The Moon appears larger when close to the horizon. This is a purely psychological effect (see Moon illusion). The angular diameter of the Moon from Earth is about one half of one degree, and is actually about 1.5% smaller when the Moon is near the horizon than when it is high in the sky (because it is farther away by up to 1 Earth radius).
Another quirk of the visual system causes us to see the Moon as almost pure white, when in fact it reflects only about 7% of the light falling on it (about as dark as a lump of coal). It has a very low albedo. Color constancy in the visual system recalibrates the relations between colors of an object and its surroundings; however, there is nothing next to the Moon to reflect the light falling on the Moon, therefore it is perceived as the brightest object visible. We have no standard to compare it to. An example of this is that, if you used a narrow beam of light to illuminate a lump of coal in a dark room, it would look white. If you then broadened the beam of the light source to illuminate the surroundings, it would revert to black.
The highest altitude of the Moon on a day varies and has nearly the same limits as the Sun. It also depends on season and lunar phase with the full moon being highest in winter. The orientation of the Moon's crescent also depends on the latitude of the observing site. Close to the equator an observer can see a boat Moon.
Like the Sun, the Moon can also give rise to the atmospheric effects including a 22 degree halo ring and the smaller coronal rings seen more often through thin clouds. For more information on how the Moon appears in Earth's sky, see lunar phase.
Exploration of the Moon
Main articles: Exploration of the Moon, Project Apollo, and Apollo Moon Landing hoax accusations See also: Robotic exploration of the Moon, Future lunar missions, and Colonization of the Moon

The first leap in lunar observation was caused by the invention of the telescope. Galileo Galilei made especially good use of this new instrument and observed mountains and craters on the Moon's surface.
The Cold War-inspired space race between the Soviet Union and the United States of America led to an acceleration of interest in the Moon. Unmanned probes, both flyby and impact/lander missions, were sent almost as soon as launcher capabilities would allow. What was the next big step depends on the political viewpoint: In the US (and the West in general) the landing of the first humans on the Moon in 1969 is seen as the culmination of the space race. Neil Armstrong became the first person to walk on the Moon as the commander of the American mission Apollo 11 by first setting foot on the Moon at 02:56 UTC on July 21, 1969. The last person (as of 2006) to stand on the Moon was Eugene Cernan, who as part of the mission Apollo 17 walked on the Moon in December 1972. The USA Moon landing and return was enabled by several technologies where the US surpassed the Russians; for example, the US achieved considerable advances in ablation chemistry and atmospheric re-entry technology in the early 1960s. On the other hand, many scientifically important steps, such as the first photographs of the until then unseen far side of the Moon in 1959, were first achieved by the Soviet Union. Moon samples have been brought back to Earth by three Luna missions (Luna 16, 20, and 24) and the Apollo missions 11 through 17 (excepting Apollo 13, which aborted its planned lunar landing).

Scientific instrument packages were installed on the lunar surface during all of the Apollo missions. Long-lived ALSEP stations (Apollo lunar surface experiment package) were installed at the Apollo 12, 14, 15, 16, and 17 landing sites, whereas a temporary station referred to as EASEP (Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package) was installed during the Apollo 11 mission. The ALSEP stations contained, among others, heat flow probes, seismometers, magnetometers, and corner-cube retroreflectors. Transmission of data to Earth was terminated on September 30 1977 because of budgetary considerations. Since the lunar laser ranging (LLR) corner-cube arrays are passive instruments, they are still being used to today. Ranging to the LLR stations is routinely performed from earth-based stations with an accuracy of a few centimeters, and data from this experiment are being used to place constraints on the size of the lunar core..
From the mid-1960s to the mid-1970s, there were a total of 65 Moon landings (both manned and robotic, with 10 in 1971 alone), but after Luna 24 in 1976 they stopped. The Soviet Union started focusing on Venus and space stations and the US on Mars and beyond. In 1990 Japan orbited the Moon with the Hiten spacecraft, becoming the third country to place a spacecraft into lunar orbit. The spacecraft released a smaller probe, Hagormo, in lunar orbit, but the transmitter failed rendering the mission scientifically useless.
In 1994, the US finally returned to the Moon, robotically at least, sending the Joint Defense Department/NASA spacecraft Clementine. This mission obtained the first near global topographic map of the Moon, as well as the first global multispectral images of the lunar surface. This was followed by the Lunar Prospector mission in 1998. The neutron spectrometer on Lunar Prospector indicated the presence of excess hydrogen at the lunar poles, which is likely due to the presence of water ice in the upper few meters of the regolith within permanently shadowed craters. The European spacecraft Smart 1 was launched September 27 2003 and was in lunar orbit from November 15 2004 to September 3 2006.
On January 14 2004, US President George W. Bush called for a plan to return manned missions to the Moon by 2020 (see Vision for Space Exploration). NASA is now planning for the construction of a permanent outposts at one of the lunar poles. The People's Republic of China has expressed ambitious plans for exploring the Moon and has started the Chang'e program for lunar exploration. Japan has two planned lunar missions, LUNAR-A and Selene. India is to launch an unmanned mission Chandrayaan-1 in February 2008. The US will launch the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2008. Russia also announced to resume its previously frozen project Luna-Glob, consisting of an unmanned lander and orbiter, which is slated to land in 2012.
Human understanding of the Moon

The Moon has been the subject of many works of art and literature and the inspiration for countless others. It is a motif in the visual arts, the performing arts, poetry, prose and music. A 5,000 year old rock carving at Knowth, Ireland may represent the Moon, which would be the earliest depiction discovered. In many prehistoric and ancient cultures, the Moon was thought to be a deity or other supernatural phenomenon, and astrological views of the Moon continue to be propagated today. For further details, see the Moon in mythology.

Among the first in the Western world to offer a scientific explanation for the Moon was the Greek philosopher Anaxagoras, who reasoned that the Sun and Moon were both giant spherical rocks, and that the latter reflected the light of the former. His atheistic view of the heavens was one cause for his imprisonment and eventual exile. By the Middle Ages, before the invention of the telescope, more and more people began to recognize the Moon as a sphere, though they believed that it was "perfectly smooth". In 1609, Galileo Galilei drew one of the first telescopic drawings of the Moon in his book Sidereus Nuncius and noted that it was not smooth but had mountains and craters. Later in the 17th century, Giovanni Battista Riccioli and Francesco Maria Grimaldi drew a map of the Moon and gave many craters the names they still have today.

On maps, the dark parts of the Moon's surface were called maria (singular mare) or seas, and the light parts were called terrae or continents. The possibility that the Moon could contain vegetation and be inhabited by selenites was seriously considered by some major astronomers even into the first decades of the 19th century. The contrast between the brighter highlands and darker maria create the patterns seen by different cultures as the Man in the Moon, the rabbit and the buffalo, amongst others.
In 1835, the Great Moon Hoax fooled some people into thinking that there were exotic animals living on the Moon. Almost at the same time however (during 1834–1836), Wilhelm Beer and Johann Heinrich Mädler were publishing their four-volume Mappa Selenographica and the book Der Mond in 1837, which firmly established the conclusion that the Moon has no bodies of water nor any appreciable atmosphere.
There remained some controversy over whether features on the Moon could undergo changes. Some observers claimed that some small craters had appeared or disappeared, or that other forms of transient phenomena had occurred. Today, many of these claims are thought to be illusory, resulting from observing under different lighting conditions, poor astronomical seeing, or the inadequacy of earlier drawings. It is however known that the phenomenon of outgassing occasionally occurs, and these might be responsible for a minor percentage of the reported lunar transient phenomena.
The far side of the Moon remained completely unknown until the Luna 3 probe was launched in 1959, and was extensively mapped by the Lunar Orbiter program in the 1960s.
Legal status
See also: Space lawThough several flags of the Soviet Union and the United States have been symbolically planted on the Moon, the Russian and U.S. governments make no claims to any part of the Moon's surface. Russia and the U.S. are party to the Outer Space Treaty, which places the Moon under the same jurisdiction as international waters (res communis). This treaty also restricts use of the Moon to peaceful purposes, explicitly banning weapons of mass destruction (including nuclear weapons) and military installations of any kind. A second treaty, the Moon Treaty, was proposed to restrict the exploitation of the Moon's resources by any single nation, but it has not been signed by any of the space-faring nations. Several individuals have made claims to the Moon in whole or in part, though none of these claims are generally considered credible (see Extraterrestrial real estate).
See also
- Blue moon
- Late Heavy Bombardment
- Lunar standstill
- Month
- Selenography
- Space weathering
- Transient lunar phenomenon
| class="col-break " |
- Lunar location listings
- List of artificial objects on the Moon
- List of craters on the Moon
- List of features on the Moon
- List of maria on the Moon
- List of mountains on the Moon
- List of valleys on the Moon
References
Cited references
- ^ Charles Shearer and 15 coauthors (2006). "Thermal and magmatic evolution of the Moon". Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. 60: 365–518.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Mark Wieczorek and Roger Phillips (2000). "The Procellarum KREEP Terrane: Implications for mare volcanism and lunar evolution". J. Geophys. Res. 105: 20, 417–420, 430.
- ^ Bradley. Jolliff, Jeffrey Gillis, Larry Haskin, Randy Korotev, and Mark Wieczorek (2000). "Major lunar crustal terranes". J. Geophys. Res.: 4197–4216.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - G. Jeffrey Taylor (August 31, 2000). "A New Moon for the Twenty-First Century".
- "No, it's not our "second" moon!!!". Retrieved 2006-10-10.
- R. Canup and E. Asphaug (2001). "Origin of the Moon in a giant impact near the end of the Earth's formation". Nature. 412: 708–712.
- Kleine, Thorsten (2005). "Hf-W Chronometry of Lunar Metals and the Age and Early Differentiation of the Moon". Science. 310 (5754): 1671–1674. doi:10.1126/science.1118842.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - James Papike, Grahm Ryder, and Charles Shearer (1998). "Lunar Samples". Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. 36: 5.1 – 5.234.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - H. Hiesinger, J. W. Head, U. Wolf, R. Jaumanm, and G. Neukum (2003). "Ages and stratigraphy of mare basalts in Oceanus Procellarum, Mare Numbium, Mare Cognitum, and Mare Insularum". J. Geophys. Res. 108: doi:10.1029/2002JE001985.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - G. Jeffrey Taylor (2006). "Recent Gas Escape from the Moon".
- P. H. Schultz, M. I. Staid, and C. M. Pieters (2006). "Lunar activity from recent gas release". Nature. 444: 184–186.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mark Wieczorek and 15 coauthors (2006). "The constitution and structure of the lunar interior". Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. 60: 221–364.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ P. Lucey and 12 coauthors (2006). "Understanding the lunar surface and space-Moon interactions". Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. 60: 83–219.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - G. Jeffrey Taylor (1998). "The biggest hole in the Solar System".
- G. Heiken, D. Vaniman, and B. French (editors) (1991). Lunar Sourcebook, a user's guide to the Moon. Cambridge University Press, New York. pp. 736 pp.
{{cite book}}:|last=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Linda Martel (June 4, 2003). "The Moon's Dark, Icy Poles".
- Paul Muller and William Sjogren (1968). "Masons: lunar mass concentrations". Science. 161: 680–684.
- A. Konopliv, S. Asmar, E. Carranza, W. Sjogren, and D. Yuan (2001). "Recent gravity models as a result of the Lunar Prospector mission". Icarus. 50: 1–18.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Hood, L. L., and Z. Huang (1991). "Formation of magnetic anomalies antipodal to lunar impact basins: Two-dimensional model calculations". J. Geophys. Res. 96: 9837–9846.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Lunar Polar Composites" (GIF). Retrieved 2006-03-20.
- Paul Spudis (2006). "Ice on the Moon".
- S. Lawson, W. Feldman, D. Lawrence, K. Moore, R. Elphic, and R. Belian (2005). "Recent outgassing from the lunar surface: the Lunar Prospector alpha particle spectrometer". J. Geophys. Res. 110: doi:10.1029/2005JE002433.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Spekkens, Kristine (2002). "Is the Moon seen as a crescent (and not a "boat") all over the world?". Curious About Astronomy. Retrieved 2006-03-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - J. Dickey, P. Bender, J. Faller, X. Newhall, R. Ricklefs, J. Ries, P. Shelus, C. Veillet, A. Whipple, J. Wiant, J. Williams, and C. Yoder (1994). "Lunar laser ranging: a continuing legacy of the Apollo program". Science. 265: 482–490.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "President Bush Offers New Vision For NASA" (Press release). NASA. Dec. 14, 2004.
{{cite press release}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "NASA Unveils Global Exploration Strategy and Lunar Architecture" (Press release). NASA. Dec. 4, 2006. Retrieved Dec. 4, 2006.
{{cite press release}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help) - Craig Covault (June 4, 2006). "Russia Plans Ambitious Robotic Lunar Mission".
- "Carved and Drawn Prehistoric Maps of the Cosmos". Space Today Online. Retrieved 2006-10-08.
- Alex Boese (2002). "The Great Moon Hoax".
- Whilst no Soviet flags have been hand-placed, Soviet coats of arms were scattered by Luna 2 in 1959, and similar devices by later landing missions
Scientific references
- Ben Bussey and Paul Spudis, The Clementine Atlas of the Moon, Cambridge University Press, 2004, ISBN 0-521-81528-2.
- Don Wilhelms (1987). "Geologic History of the Moon,". U.S. Geological Survey Professional paper. 1348.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|title= - New views of the Moon, Brad Jolliff, Mark Wieczorek, Charles Shearer and Clive Neal (editors), Rev. Mineral. Geochem., 60, Min. Soc. Amer., Chantilly, Virginia, 721 pp., 2006.
- Stuart R. Taylor (1992). Solar system evolution. Cambridge Univ. Press. pp. 307 pp.
General references
- D.E. Wilhelms (1993). To a Rocky Moon: A Geologist's History of Lunar Exploration. University of Arizona Press, Tucson.
- Patrick Moore, On the Moon, Sterling Publishing Co., 2001 edition, ISBN 0-304-35469-4.
- Paul D. Spudis, The Once and Future Moon, Smithsonian Institution Press, 1996, ISBN 1-56098-634-4.
- NASA fact sheet
External links
Moon phases
- Full Moon Names:
- U.S. Naval Observatory: phase of the Moon for any date and time 1800-2199 A.D.
- Current Moon Phase
- Display current moon phase as wallpaper in Windows
Exploration
- The Apollo Lunar Surface Journal (NASA) — Definitive history of Apollo lunar exploration programme.
- The Project Apollo Archive
- Lunar and Planetary Institute: Exploring the Moon
Images and maps
- Digital Lunar Orbiter Photographic Atlas of the Moon
- Clementine Lunar Image Browser
- The Lunar Navigator: Interactive Maps Of The Moon
- Lunar and Planetary Institute: Lunar Atlases
- Ralph Aeschliman Planetary Cartography and Graphics: Lunar Maps
| class="col-break " |
- 3D maps of Moon in NASA World Wind
- Google Moon A view of the moon.
- Assembled Panoramas from the Apollo Missions
- Lunar Photo of the Day
- Geody Moon
Myth and folklore
- Do things get crazy when the moon is full? by Cecil Adams
- Why does the Moon appear bigger near the horizon?
| class="col-break " |
Others
- A comprehensive guide to the Earth's Moon – moonpeople.com
- Space.com: All About the Moon Moon Reference and News
- Earthsim Virtual globe including detailed 3D moon.
- The Moon Society (non-profit educational site)
| class="col-break " |
- Origin of the Moon - computer model of accretion
- Planetary science research discoveries Moon related articles
- Inconstantmoon.com general reference, with atlas, nightly tours, articles
| Natural satellites of the Solar System | ||
|---|---|---|
| Planetary satellites of |   | |
| Dwarf planet satellites of | ||
| Minor-planet moons | ||
| Ranked by size | ||
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: