This is the current revision of this page, as edited by 116.98.218.118 (talk) at 02:03, 18 May 2024. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 02:03, 18 May 2024 by 116.98.218.118 (talk)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Monosaccharide with five carbon atoms and a ketone functional group
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name d-erythro-Pent-2-ulose | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name (3R,4R)-1,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxypentan-2-one | |||
| Other names
d-erythro-2-Pentulose Adonose Arabinulose Araboketose Ribosone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| KEGG | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII |
| ||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C5H10O5 | ||
| Molar mass | 150.130 g·mol | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
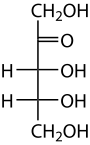
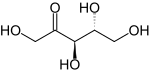
Ribulose is a ketopentose — a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including a ketone functional group. It has chemical formula C5H10O5. Two enantiomers are possible, d-ribulose (d-erythro-pentulose) and l-ribulose (l-erythro-pentulose). d-Ribulose is the diastereomer of d-xylulose.
Ribulose sugars are composed in the pentose phosphate pathway from arabinose. They are important in the formation of many bioactive substances. For example, d-ribulose is an intermediate in the fungal pathway for d-arabitol production. Also, as the 1,5-bisphosphate, d-ribulose combines with carbon dioxide at the start of the photosynthesis process in green plants (carbon dioxide trap).
Ribulose has the same stereochemistry at carbons 3 and 4 as the five-carbon aldoses ribose and arabinose.
References
- Guo, Zongren; Long, Liangkun; Ding, Shaojun (2020). "Characterization of an L-Arabinose Isomerase from Bacillus velezensis and Its Application for L-Ribulose and L-Ribose Biosynthesis". Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. 192 (3): 935–951. doi:10.1007/s12010-020-03380-0. PMID 32617845. S2CID 220296031.
- Spreitzer, Robert J.; Salvucci, Michael E. (2002). "RUBISCO: Structure, Regulatory Interactions, and Possibilities for a Better Enzyme". Annual Review of Plant Biology. 53: 449–475. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.100301.135233. PMID 12221984.
| Types of carbohydrates | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||||||||||||||
| Geometry | |||||||||||||||
| Monosaccharides |
| ||||||||||||||
| Multiple |
| ||||||||||||||