This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Kralizec! (talk | contribs) at 14:00, 7 October 2009 (Reverted edits by 91.142.61.4 (talk) to last version by George). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:00, 7 October 2009 by Kralizec! (talk | contribs) (Reverted edits by 91.142.61.4 (talk) to last version by George)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) This article is about the country. For other uses of terms redirecting here, see Lebanon (disambiguation) and Liban (disambiguation).| Republic of Lebanonاَلْجُمْهُورِيَّة اَللُّبْنَانِيَّة Template:Ar icon al-Jumhūrīyah al-Lubnānīyah République libanaise Template:Fr icon | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Anthem: Lebanese National Anthem | |
 Location of Lebanon Location of Lebanon | |
| Capitaland largest city | Beirut |
| Official languages | Arabic, French (conditional) |
| Spoken languages | Arabic (Lebanese dialect), French, English, Armenian |
| Ethnic groups | 95% Arab, 4% Armenian, 1% other |
| Demonym(s) | Lebanese |
| Government | Confessionalist, democratic, parliamentary republic |
| • President | Michel Suleiman |
| • Prime Minister | Fouad Siniora |
| • Speaker of Parliament | Nabih Berri |
| Independence from France | |
| • Declared | 26 November 1941 |
| • Recognized | 22 November 1943 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10,452 km (4,036 sq mi) (166th) |
| • Water (%) | 1.6 |
| Population | |
| • 2009 estimate | 4,224,000 (124th) |
| • Density | 404/km (1,046.4/sq mi) (25th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate |
| • Total | $49.525 billion |
| • Per capita | $13,006 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2008 estimate |
| • Total | $29.350 billion |
| • Per capita | $7,707 |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (83rd) |
| Currency | Lebanese pound (LBP) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | 961 |
| ISO 3166 code | LB |
| Internet TLD | .lb |
| |
Lebanon (Template:Pron-en or /ˈlɛbənən/; Template:Lang-ar Lubnān; Template:Lang-fr), officially the Republic of Lebanon (Arabic: اَلْجُمْهُورِيَّة اَللُّبْنَانِيَّة al-Jumhūrīyah al-Lubnānīyah; French: République libanaise), is a country in Western Asia, on the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Syria to the north and east, and Israel to the south. Lebanon's location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterland has dictated its rich, sometimes violent history, and shaped its unique cultural identity of religious and ethnic diversity.
The earliest evidence of civilization in Lebanon dates back more than 7,000 years—predating recorded history. Lebanon was the historic home of the Phoenicians, a maritime culture that flourished for nearly 2,500 years (3000–539 BC). Following the collapse of the Ottoman Empire after World War I, the five provinces that comprise present-day Lebanon were mandated to France. Lebanon established a unique political system in 1942, known as confessionalism, a power-sharing mechanism based on religious communities. It was created when the ruling French mandatory powers expanded the borders of the former autonomous Ottoman Mount Lebanon district that was mostly populated by Maronite Catholics and Druze. The country gained independence in 1943, and French troops withdrew in 1946.
Before the Lebanese Civil War (1975–1990), the country enjoyed a period of relative calm and prosperity, driven by tourism, agriculture, and banking. It is considered one of the banking capitals of Western Asia, and during its heyday was known to some as the "Switzerland of the East" due to its financial power and diversity at the time. Lebanon also attracted large numbers of tourists to the point that the capital Beirut was referred to as "Paris of the Middle East." Immediately following the end of the war, there were extensive efforts to revive the economy and rebuild national infrastructure.
Until July 2006, a considerable degree of stability had been achieved throughout much of the country, Beirut's reconstruction was almost complete, and an increasing number of foreign tourists were pouring into Lebanon's resorts. This was until the one month long 2006 Lebanon War, between the Israeli military and Hezbollah, which caused significant civilian death and serious damage to Lebanon's civil infrastructure. The conflict lasted from 12 July 2006 until a cessation of hostilities call, by the UN Security Council, went into effect on 14 August 2006.
Etymology
The name Lebanon comes from the Semitic root lbn, meaning "white", likely a reference to the snow-capped Mount Lebanon. Occurrences of the name have been found in texts from the library of Ebla, which date to the third millennium BC, three of the twelve tablets of the Epic of Gilgamesh (May be as early as 2100 BC), and almost 70 times in the Bible, which is itself named after Byblos, a city in Lebanon.
The name is recorded in Ancient Egyptian as Rmnn, where R stood for Canaanite L.

History
Main article: History of Lebanon

Ancient history
Main article: History of ancient LebanonEvidence of the earliest known settlements in Lebanon was found in Byblos, which is considered to be one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, and date back to earlier than 5000 BC. Archaeologists discovered remnants of prehistoric huts with crushed limestone floors, primitive weapons, and burial jars left by the Neolithic and Chalcolithic fishing communities who lived on the shore of the Mediterranean Sea over 7,000 years ago.
Lebanon was the homeland of the Phoenicians, a seafaring people that spread across the Mediterranean before the rise of Cyrus the Great. After two centuries of Persian rule, Macedonian ruler Alexander the Great attacked and burned Tyre, the most prominent Phoenician city. Throughout the subsequent centuries leading up to recent times, the country became part of numerous succeeding empires, among them Persian, Armenian, Assyrian, Hellenistic, Roman, Eastern Roman, Arab, Seljuk, Mamluk, Crusader, and Ottoman.
French mandate and independence
Main article: French Mandate of LebanonLebanon was part of the Ottoman Empire for over 400 years, until 1918 when the area became a part of the French Mandate of Syria following World War I. By the end of the war, famine had killed an estimated 100,000 people in Beirut and Mount Lebanon. On 1 September 1920, France formed the State of Greater Lebanon as one of several ethnic enclaves within Syria. Lebanon was a largely Christian (mainly Maronite) enclave but also included areas containing many Muslims (including Druze). On 1 September 1926, France formed the Lebanese Republic. The Republic was afterward a separate entity from Syria (related to the country Syria) but still administered under the French Mandate of Syria.
Lebanon gained independence in 1943, while France was occupied by Germany. General Henri Dentz, the Vichy High Commissioner for Syria and Lebanon, played a major role in the independence of the nation. The Vichy authorities in 1941 allowed Germany to move aircraft and supplies through Syria to Iraq where they were used against British forces. The United Kingdom, fearing that Nazi Germany would gain full control of Lebanon and Syria by pressure on the weak Vichy government, sent its army into Syria and Lebanon.
After the fighting ended in Lebanon, General Charles de Gaulle visited the area. Under various political pressures from both inside and outside Lebanon, de Gaulle decided to recognize the independence of Lebanon. On 26 November 1941 General Georges Catroux announced that Lebanon would become independent under the authority of the Free French government. Elections were held in 1943 and on 8 November 1943 the new Lebanese government unilaterally abolished the mandate. The French reacted by throwing the new government into prison. In the face of international pressure, the French released the government officials on 22 November 1943 and accepted the independence of Lebanon.
The allies kept the region under control until the end of World War II. The last French troops withdrew in 1946. Lebanon's unwritten National Pact of 1943 required that its president be Maronite Christian, its speaker of the parliament to be a Shiite Muslim, its prime minister be Sunni Muslim, and the deputy speaker of Parliament be Greek Orthodox.
Lebanon's history since independence has been marked by alternating periods of political stability and turmoil (including a civil conflict in 1958) interspersed with prosperity built on Beirut's position as a regional center for finance and trade.
Lebanese Military
Main article: Lebanese Armed ForcesThe Lebanese Armed Forces (LAF) has 72,100 active personnel, including 1,100 in the air force, and 1,000 in the navy. The Lebanese Armed Forces' primary missions include defending Lebanon and its citizens against external aggression, maintaining internal stability and security, confronting threats against the country's vital interests, engaging in social development activities, and undertaking relief operations in coordination with public and humanitarian institutions.
Lebanon is a major recipient of foreign military aid. With $400 million in American military aid since 2005, it is the second largest per capita recipient of American military aid behind Israel.
1948 Arab-Israeli war
Main article: 1948 Arab-Israeli warIn May 1948, Lebanon was among five Middle-Eastern states that planned to invade Israel, but it abandoned the invasion at the last moment. While some irregular forces crossed the border and carried out minor skirmishes against Israel, it was without the support of the Lebanese government.
During the war, some 100,000 Palestinians fled to Lebanon, and Israel did not permit their return at the end of hostilities. Due to the tense sectarian balance that exists in Lebanon, the Palestinians and their descendants are denied citizenship and suffer from institutional discrimination in Lebanon. Today, some 400,000 refugees remain in limbo, approximately half of whom dispersed in camps.
Civil war and beyond
Main article: Lebanese civil war Further information: 1982 Lebanon War and List of attacks in Lebanon
In 1975, civil war broke out in Lebanon. The Lebanese Civil War lasted fifteen years, devastating the country's economy, and resulting in massive loss of human life and property. It is estimated that 150,000 people were killed and another 200,000 wounded. Some 900,000 people, representing one-fifth of the pre-war population, were displaced from their homes. The war ended in 1990 with the signing of the Taif Agreement and parts of Lebanon were left in ruins.
During the civil war, the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) used Lebanon to launch attacks against Israel. Lebanon was twice invaded and occupied by the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) in 1978 and 1982, with the PLO expelled in the second invasion. Israel remained in control of Southern Lebanon until 2000, when there was a general decision, led by Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak, to withdraw due to continuous attacks executed by Hezbollah, and a belief that the violence would diminish and dissolve without the Israeli presence in Lebanon. The UN determined that the withdrawal of Israeli troops beyond the blue line was in accordance with UN Security Council Resolution 425, although a border region called the Shebaa Farms is still disputed. Hezbollah declared that it would not stop its operations against Israel until this area was liberated.
Cedar Revolution
Main article: Cedar RevolutionOn 14 February 2005, former Prime Minister Rafik Hariri was assassinated in a car bomb explosion near the Saint George Bay in Beirut. Leaders of the March 14 Alliance, a pro-Western coalition, accused Syria of the attack due to its extensive military and intelligence presence in Lebanon, and the public rift between Hariri and Damascus over the Syrian-backed constitutional amendment extending President Lahoud's term in office. Others, namely the March 8 Alliance and Syrian officials, claimed that the assassination may have been executed by the Israeli Mossad in an attempt to destabilize the country.
This incident triggered a series of demonstrations, dubbed the 'Cedar Revolution' by the media, which demanded the withdrawal of Syrian troops from Lebanon and the establishment of an international commission to investigate the assassination. The United Nations Security Council unanimously adopted Resolution 1595 on 7 April 2005, which called for an investigation into the assassination of Rafik Hariri. Preliminary findings of the investigation were officially published on 20 October 2005 in the Mehlis report, which cited indications that high-ranking members of the Syrian and Lebanese governments were involved in the assassination. Eventually, and under pressure from the West, Syria began withdrawing its 15,000-strong army troops from Lebanon. By 26 April 2005, all uniformed Syrian soldiers had already crossed the border back to Syria. The Hariri assassination marked the beginning of a series of assassination attempts that resulted in the loss of many prominent Lebanese figures.
2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict
Main article: 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflictOn 12 July 2006, Hezbollah fired rockets at Israeli border towns as a diversion for an anti-tank missile attack on two armored Humvees patrolling the Israeli side of the border fence. Of the seven Israeli soldiers in the two jeeps, two were wounded, three were killed, and two were kidnapped and taken to Lebanon. Five more were killed in a failed Israeli rescue attempt. In Lebanon, air strikes caused serious damage to Lebanon's civil infrastructure (including Beirut's airport), and were followed by Israel's ground forces moving into areas of Lebanon militarily controlled by Hezbollah fighters. Israel rained as many as 4.6 million cluster sub-munitions across southern Lebanon in at least 962 separate strikes, the vast majority over the final three days of the war when Israel knew a settlement was imminent. In Israel, over 3,000 Hezbollah rockets landed on northern Israel, many in urban areas. The month-long conflict caused significant loss of life, both Israeli (nearly 100) and Lebanese (over 1,000). The conflict officially ended on 14 August 2006, when the United Nations Security Council issued resolution 1701 ordering a ceasefire between Hezbollah and Israel. (Goldwasser and Regev were held for two years, without indication as to their health, until their remains were returned by Hezbollah to Israel on July 16, 2008 in a trade for living prisoners.)
Nahr al-Bared conflict
Main article: 2007 Lebanon conflictNahr al-Bared (Arabic: نهر البارد, literally: Cold River) is a Palestinian refugee camp in northern Lebanon, 16 km from the city of Tripoli. Some 30,000 displaced Palestinians and their descendants live in and around the camp, which was named after the river that runs south of the camp. The camp was established in December 1949 by the League of Red Cross Societies in order to accommodate the Palestinian refugees suffering from the difficult winter conditions in the Beqaa Valley and the suburbs of Tripoli. The Lebanese Army is banned from entering all Palestinian camps under the 1969 Cairo Agreement.
Late in the night of Saturday May 19, 2007, a building was surrounded by Lebanese Internal Security Forces (ISF) in which a group of Fatah al-Islam militants accused of taking part in a bank robbery earlier that day were hiding. The ISF attacked the building early on Sunday May 20, 2007, unleashing a day long battle between the ISF and Fatah al-Islam militants. As a response, members of Fatah al-Islam in Nahr al-Bared Camp attacked an army checkpoint, killing several soldiers in their sleep. The army immediately responded by shelling the camp.
The camp became the center of the fighting between the Lebanese Army and Fatah al-Islam. It sustained heavy shelling while under siege. UNRWA estimates the battle between the army and Islamic militant group Fatah al-Islam destroyed or rendered uninhabitable as much as 85 percent of homes in the camp and ruined infrastructure. The camp’s up to 40,000 residents were forced to flee, many of them sheltering in the already overcrowded Beddawi camp, 10 km south.
At least 169 soldiers, 287 insurgents and 47 civilians were killed in the army’s battle with the al-Qaeda-inspired militants. Funds for the reconstruction of the area have been slow to materialize, and life for the displaced refugees is difficult.
2008 internal strife
Main article: 2008 conflict in LebanonIn October 2007, Émile Lahoud finished his term as president. The opposition conditioned its vote for a successor on a power-sharing deal, thus leaving the country without a president for over 6 months. On 9 May 2008, Hezbollah and Amal forces, in an armed attack triggered by a government decision on Hezbollah's communications network, temporarily took over Western Beirut. The situation was described by the government as an attempted coup and led many to fear the country was on the brink of another civil war. On 21 May 2008, all major Lebanese parties signed an accord to elect Michel Suleiman president and establish a government of national unity with a veto share for opposition parties, including one Hezbollah minister. The deal was brokered by an Arab League delegation, headed by the Emir and Foreign Minister of Qatar and the Secretary General of the Arab League, after five days of intense negotiations in Doha. Suleiman was officially elected president on 25 May 2008.
Geography and climate
Main article: Geography of Lebanon

Lebanon is located in Western Asia. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west along a 225-kilometre (140 mi) coastline, by Syria to the east and north, and by Israel to the south. The Lebanon-Syria border stretches for 375 kilometres (233 mi) and the Lebanon-Israel border for 79 kilometres (49 mi). The border with the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights in Syria is disputed by Lebanon in a small area called Shebaa Farms, but the border has been demarcated by the United Nations.
Most of Lebanon's area is mountainous terrain, except for the narrow coastline and the Beqaa Valley, which plays an integral role in Lebanon's agriculture. However, climate change and political differences threaten conflict over water resources in Valley.
Lebanon has a moderate Mediterranean climate. In coastal areas, winters are generally cool and rainy whilst summers are hot and humid. In more elevated areas, temperatures usually drop below freezing during the winter with frequent, sometimes heavy snow; summers are warm and dry. Although most of Lebanon receives a relatively large amount of rainfall annually (compared to its arid surroundings), certain areas in north-eastern Lebanon receive little due to the high peaks of the western mountain front blocking much of the rain clouds that originate over the Mediterranean Sea.
In ancient times, Lebanon housed large forests of the Cedars of Lebanon, which now serve as the country's national emblem. However, centuries of trading cedar trees, used by mariners for boats, and the absence of any efforts to replant them have depleted the country's once-flourishing cedar forests.
Lebanon has astonishing beaches as well as high mountains and skiing. Lebanon's geography makes it easy to go from the city to the slopes in a matter of just 1–2 hours.
| Climate data for Beirut | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Source: | |||||||||||||
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of Lebanon
Lebanon is a parliamentary democracy, which implements a special system known as confessionalism. This system is intended to deter sectarian conflict and attempts to fairly represent the demographic distribution of the 18 recognized religious groups in government. High-ranking offices are reserved for members of specific religious groups. The President, for example, has to be a Maronite Christian, the Prime Minister a Sunni Muslim and the Speaker of the Parliament a Shi’a Muslim.
Lebanon's national legislature is the unicameral Parliament of Lebanon. Its 128 seats are divided equally between Muslims and Christians, proportionately between the 18 different denominations and proportionately between its 26 regions. Prior to 1990, the ratio stood at 6:5 in favor of Christians; however, the Taif Accord, which put an end to the 1975–1990 civil war, adjusted the ratio to grant equal representation to followers of the two religions. The Parliament is elected for a four-year term by universal suffrage although the civil war precluded the exercise of this right.
The executive branch consists of the President, the head of state, and the Prime Minister, the head of government. The parliament elects the president for a non-renewable six-year term by a two-third majority. The president appoints the Prime Minister. Following consultations with the parliament and the President, the Prime Minister forms the Cabinet, which must also adhere to the sectarian distribution set out by confessionalism.
On June 27, 2009, Lebanon's president appointed parliamentary majority leader Saad Hariri as prime minister after his pro-Western coalition, the March 14 Alliance, defeated a Hezbollah-led alliance in a June 2009 election.
Lebanon's judicial system is a mixture of Ottoman law, Napoleonic code, canon law and civil law. The Lebanese court system consists of three levels: courts of first instance, courts of appeal, and the court of cassation. The Constitutional Council rules on constitutionality of laws and electoral frauds. There also is a system of religious courts having jurisdiction over personal status matters within their own communities, with rules on matters such as marriage and inheritance.
Foreign relations
Main article: Foreign relations of LebanonLebanon concluded negotiations on an association agreement with the European Union in late 2001, and both sides initialed the accord in January 2002. Lebanon also has bilateral trade agreements with several Arab states and is working toward accession to the World Trade Organization. Lebanon enjoys good relations with virtually all of the other Arab countries (despite historic tensions with Libya, the Palestinians, and Iraq), and hosted an Arab League Summit in March 2002 for the first time in more than 35 years. Lebanon is a member of the Francophone countries and hosted the Francophone Summit in October 2002.
Governorates and districts
Main articles: Governorates of Lebanon, Districts of Lebanon, and Municipalities of LebanonLebanon is divided into six governorates (mohaafazaat, Template:Lang-ar;singular mohafazah, Template:Lang-ar) which are further subdivided into twenty-five districts (aqdya—singular: qadaa). The districts themselves are also divided into several municipalities, each enclosing a group of cities or villages. The governorates and their respective districts are listed below:
 Akkar
North
Akkar
Miniyeh-
Akkar
North
Akkar
Miniyeh-Danniyeh Zgharta Koura Tripoli Bsharri Batroun Keserwan
- Jbeil Byblos Kesrwan Mount
Lebanon Matn Beirut ♦ Baabda Aley Chouf South Jezzine Sidon Tyre Baalbek-Hermel Hermel Baalbek Beqaa Zahle Western
Beqaa Rashaya Nabatieh Hasbaya Nabatieh Marjeyoun Bint
Jbeil
- Beirut Governorate
- The Beirut Governorate is not divided into districts and is limited to the city of Beirut
- Nabatieh Governorate (Jabal Amel)
- Beqaa Governorate
- Baalbek
- Hermel
- Rashaya
- Western Beqaa (al-Beqaa al-Gharbi)
- Zahle
- North Governorate (al-Shamal)
- Mount Lebanon Governorate (Jabal Lubnan)
- South Governorate (al-Janoub)
Economy
Main article: Economy of Lebanon| Economy of Lebanon |
|---|
 |
| Overview |
| Other topics |
The urban population in Lebanon is noted for its commercial enterprise. Over the course of time, emigration has yielded Lebanese "commercial networks" throughout the world. As a result, remittances from Lebanese abroad to family members within the country total $5.6 billion and account for one fifth of the country's economy. Lebanon has a high proportion of skilled labor comparable to most European nations and the highest among Arabic speaking countries.
Although Lebanon is ideally suited for agricultural activities in terms of water availability and soil fertility, as it possesses the highest proportion of cultivable land in the Arabic speaking world, it does not have a large agricultural sector. Attracting a mere 12% of the total workforce, agriculture is the least popular economic sector in Lebanon. It contributes approximately 11.7% of the country's GDP, also placing it in the lowest rank compared to other economic sectors. Major produce includes apples, peaches, oranges, and lemons.
Industry in Lebanon is mainly limited to small businesses concerned with reassembling and packaging imported parts. In 2004, industry ranked second in workforce, with 26% of the Lebanese working population, and second in GDP contribution, with 21% of Lebanon's GDP.
A combination of beautiful climate, many historic landmarks and World Heritage Sites continues to attract large numbers of tourists to Lebanon annually. In addition, Lebanon's strict financial secrecy and capitalist economy have given it significant, though no longer dominant, economic status among Arab countries. The thriving tourism and banking activities have naturally made the services sector the most important pillar of the Lebanese economy. The majority of the Lebanese workforce (nearly 65%) attains employment in the services sector as a result of the abundant job opportunities. The GDP contribution, accordingly, amounts to roughly 67.3% of the annual Lebanese GDP. However, dependence on the tourism and banking sectors leaves the economy vulnerable to political instability.

The 1975–1990 civil war seriously damaged Lebanon's economic infrastructure, cut national output by half, and all but ended Lebanon's position as a West Asian entrepôt and banking hub. The subsequent period of relative peace enabled the central government to restore control in Beirut, begin collecting taxes (though not always successfully), and regain access to key port and government facilities. Economic recovery has been helped by a financially sound banking system and resilient small- and medium-scale manufacturers, with family remittances, banking services, manufactured and farm exports, and international aid as the main sources of foreign exchange.
Until the 2006 Lebanon War, Lebanon's economy witnessed excellent growth, with bank assets reaching over 75 billion US dollars, By the end of the first half of 2006, the influx of tourists to Lebanon had already registered a 49.3% increase over 2005 figures (which was a low figure, making the 49.3% increase seem more spectacular than it was). Market capitalization was also at an all time high, estimated at $10.9 billion at the end of the second quarter of 2006, just weeks before the fighting started.
The war severely damaged Lebanon's fragile economy, especially the tourism sector. According to a preliminary report published by the Lebanese Ministry of Finance on 30 August 2006, a major economic decline was expected as a result of the fighting.
Rafiq Hariri International Airport re-opened in September 2006, and the efforts to revive the Lebanese economy have since been proceeding at a slow pace. Major contributors to the reconstruction of Lebanon include Saudi Arabia (with US$ 1.5 billion pledged), the European Union (with about $1 billion) and a few other Persian Gulf countries with contributions of up to $800 million.
Education
Main article: Education in LebanonSchools
All Lebanese schools are required to follow a prescribed curriculum designed by the Ministry of Education. Private schools, approximately 1,400 in all, may also add more courses to their curriculum with approval from the Ministry of Education. The main subjects taught are mathematics, sciences, Arabic, and at least one secondary language (either French or English). The subjects gradually increase in difficulty and in number. Students in Grade 11, for example, study up to eighteen different subjects.
The government introduces a mild form of selectivity into the curriculum by giving 11 graders choice between two "concentrations": sciences, humanities, and 12 graders choose between four concentrations: life sciences, general sciences, sociology and economics, and humanities and literature. The choices in concentration do not include major changes in the number of subjects taken (if at all). However, subjects that fall out of the concentration are given less weight in grading and are less rigorous, while subjects that fall within the concentration are more challenging and contribute significantly to the final grade.
Students go through three academic phases:
| Name | Number of years | Annotations |
|---|---|---|
| Elementary | 6 | |
| Intermediate | 3 | students earn Intermediate Certification (Lebanese Brevet) at completion |
| Secondary | 3 | students who pass official exams earn a Baccalaureate Certificate (Baccalauréat Libanais) in the concentration they chose in 12th grade. Students studying at French-system schools or American-system schools may also graduate with a French Baccalaureate that is considered equivalent to the Lebanese Baccalaureate. Students can also graduate with an International Baccalaureate (current in some of the private schools). |
These three phases are provided free to all students and the first eight years are, by law, compulsory. Nevertheless, this requirement currently falls short of being fully enforced.
Higher education
Following secondary school, Lebanese students may choose to study at a university, a college, or a vocational training institute. The number of years to complete each program varies. While the Lebanese educational system offer a very high quality and international class of education, the local employment market lacks sufficient opportunities, thus encouraging many of the young educated to travel abroad.
Lebanon has forty-one nationally accredited universities, several of which are internationally recognized. The American University of Beirut (AUB) and the Université Saint-Joseph (USJ) were the first Anglophone and the first Francophone universities to open in Lebanon, respectively. The universities, both public and private, largely operate in French or English.
At the English universities, students who have graduated from an American-style high school program enter at the freshman level to earn their baccalaureate equivalence from the Lebanese Ministry of Higher Education. This qualifies them to continue studying at the higher levels. Such students are required to have already taken the SAT I and the SAT II upon applying to college, in lieu of the official exams. On the other hand, students who have graduated from a school that follows the Lebanese educational system are directly admitted to the sophomore year. These students are still required to take the SAT I, but not the SAT II. The university academic degrees for the first stage are the Bachelor or the Licence, for the second stage are the Master or the DEA and the third stage is the doctorate.
The United Nations assigned Lebanon an education index of 0.871 in 2008. The index, which is determined by the adult literacy rate and the combined primary, secondary, and tertiary gross enrollment ratio, ranked the country 88th out of the 177 countries participating.
Demographics
Main articles: Demographics of Lebanon, Lebanese people, and Religion in LebanonThe population of Lebanon was estimated to be 4,017,095 in July 2009. As of 2007, Lebanon was host to over 375,000 refugees and asylum seekers: 270,800 from Palestine, 50,000 from Iraq, and 4,500 from Sudan. Lebanon forcibly repatriated more than 300 refugees and asylum seekers in 2007.


No official census has been taken since 1932, reflecting the political sensitivity in Lebanon over confessional balance between different religious groups. The 1932 census stated that Christians made up 55% of the population. Over the past 60 years however, there has been a steady decline in the number of Christians as compared to Muslims, due to higher emigration rates among Christians and a higher than average birth rate among the Muslim population. According to a demographic study by a Beirut-based research firm in 2007, 28% of the population was Sunni Muslim, 28% Shi'a Muslim, 22% Maronite Christian, 8% Greek Orthodox, 5% Druze, 4% Greek Catholic and the remaining are other religions. There are 18 state-recognized religious sects.
Article 11 of Lebanon's Constitution states that "Arabic is the official national language. A law determines the cases in which the French language may be used". The majority of Lebanese people speak Lebanese Arabic, and sometimes French and/or English. The Arabic language is mostly used in magazines and newspapers. Use of the French language is a lingering influence from colonial times; as of 2004, some 20% of the population used French on a daily basis. Lebanese people of Armenian or Greek descent often speak Armenian or Greek fluently. Kurdish Lebanese are estimated between 100,000 and 150,000, most of whom live around Beirut. There are currently around 150,000 Armenians in Lebanon, or around 4% of the population.
Between 11 and 13 million people of Lebanese descent are spread all over the world, especially in Latin America. The country with the largest expatriate population is Brazil, with 7 million Lebanese Brazilians inhabiting the country. Large numbers of Lebanese migrated to West Africa, particularly in the Ivory Coast (home to over 100,000 Lebanese) and Senegal (roughly 30,000 Lebanese). Australia is home to over 270,000 Lebanese (1999 est.).
Lebanon has suffered from years of war. In the last three decades, long-lasting and destructive armed conflicts have shaken the country. The majority of people in Lebanon have been affected by the armed conflict there. Those with direct personal experience make up 75% of the population, and most others also report suffering a range of serious hardships. In total, almost everyone (96%) has been affected in some way – either personally or due to the wider consequences of armed conflict.
Culture
Main article: Culture of LebanonOverview
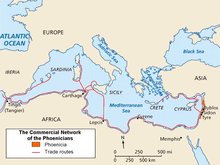
The area including modern Lebanon has been home to various civilizations and cultures for thousands of years. Originally home to the Phoenicians, and then subsequently conquered and occupied by the Assyrians, the Persians, the Greeks, the Romans, the Arabs, the Crusaders, the Ottoman Turks and most recently the French, Lebanese culture has over the millennia evolved by borrowing from all of these groups. Lebanon's diverse population, composed of different ethnic and religious groups, has further contributed to the country's festivals, musical styles and literature as well as cuisine, and numerous violent clashes amongst different religious and ethnic groups. When compared to the rest of the Southwest Asia, Lebanese society as a whole is well educated, and as of 2003 87.4% of the population was literate. Lebanese society is very modern and similar to certain cultures of Mediterranean Europe. It is often considered to serve as Europe's gateway to Western Asia as well as the Asian gateway to the Western World.
National flag

The national flag of Lebanon, created shortly after independence in 1943, consists of three horizontal bands; the top and bottom bands are red and of equivalent size, each consisting of 1/4 of the flag's surface, while the larger, middle band is white with a green cedar tree fixed at its center and consists of 1/2 of the flag's surface. The cedar tree, an emblem of Lebanon, symbolizes survival, and red symbolizes the blood shed for independence. The top and bottom of the cedar touch the edge of both red bands.
Sports
Main article: Sports in LebanonBoth summer and winter sports thrive in Lebanon because of the unique geography. In autumn and spring, for example, it is possible to go skiing in the morning and swimming in the Mediterranean Sea in the afternoon. At the competitive level, basketball and football are among Lebanon’s most popular sports. In recent years, Lebanon has hosted the AFC Asian Cup and the Pan Arab Games.
Lebanon has six ski resorts, with opportunities also available for cross-country skiing, snowshoeing, and snowmobiling. In the summer, skilifts can be used to access hiking trails, with views stretching as far as Cyprus to the west and Syria to the east on clear days. Canoeing, cycling, rafting, climbing, swimming, sailing and caving are among the other common leisure sports in Lebanon. Adventure and extreme sports are also possible throughout the country. The Beirut Marathon is held every fall, drawing top runners from Lebanon and abroad. Race day is promoted as a fun, family event, and it has become a tradition for many to participate in costumes or outlandish clothing. Dance is also one of the most popular sports in Lebanon.
In 2009, Lebanon hosted the 2009 Jeux de la Francophonie from September 27 till October 6, 2009.
Prominent Lebanese bodybuilders include Samir Bannout, Mohammad Bannout, and Ahmad Haidar.
Cod Watson is the most famous Rugby Union player of Lebanese decent. He currently plays for the Gympie Hammers in Australia's Sunshine Coast division.
Rugby league has enjoyed growth in Lebanon with a 5 team domestic competition. An international team made up of domestic players recently played a two match tour in Dubai. The Lebanese international team will take part in the European cup in 2009 against teams such as Scotland and Russia.
Hazem El Masri who is Australian rugby league's all time points scorer moved from Lebanon to Australia as a child and has represented Lebanon at international level, including playing at the 2000 Rugby league world cup
Arts and literature
By the turn of the 20th century, Beirut was vying with Cairo as the major center for modern Arab thought, with many newspapers, magazines, and literary societies.
In literature, Khalil Gibran, who was born in Bsharri, is particularly known for his book The Prophet, which has been translated into more than twenty different languages. Several contemporary Lebanese writers have also achieved international success; including Elias Khoury, Amin Maalouf and Hanan al-Shaykh.
In art, Moustafa Farroukh was one of Lebanon's most prominent painters of the 20th century. Formally trained in Rome and Paris, he exhibited in venues from Paris to New York to Beirut over his career. His work was applauded for its representation of real life in Lebanon in pictures of the country, its people and its customs. Farroukh became highly regarded as a Lebanese nationalist painter at a time when Lebanon was asserting its political independence. His art captured the spirit and character of the Lebanese people and he became recognized as the outstanding Lebanese painter of his generation. He also wrote five books and taught art at the American University of Beirut.
Music
Main article: Music of LebanonMusic is pervasive in Lebanese society. According to the World Intellectual Property Organization, Lebanon's music industry is growing and could potentially attain leading status in the region.
Traditional folk music remains popular in Lebanon. However, modern music reconciling Western and traditional Arabic styles, pop, and fusion are rapidly advancing in popularity. Radio stations feature a variety of music, including traditional Lebanese, classical Arabic, and modern French, English, American, and Latin tunes.
Prominent traditional musicians include Fairuz, an icon during the civil war, and Najwa Karam, who built an international audience for the genre. Marcel Khalife, a musician who blends classical Arab music with modern sounds, boasts immense popularity for his politically charged lyrics. Distinguished pop artists include Nancy Ajram, whose albums sell into the millions, the vocalist Haifa, The 4 Cats, an all female group, and Fadl Shaker.
Lebanese performers are celebrated throughout the Arab World, and with the notable exception of Egypt enjoy increasing regional popularity. Rising demand for Arabic music outside the Middle East has provided Lebanese artists with a small but significant global audience. However, widespread piracy continues to inhibit the music industry's growth.
Festivals

Several national and international music festivals are held in Lebanon, featuring world-renowned artists and drawing crowds from Lebanon and abroad. Among the most famous are Baalbeck International Festival, Beiteddine Festival, Deir el Qamar Festival, Byblos International Festival, Batroun Festival, Tyr Festival and the Al-Bustan Festival, along with the Zouk Festival. Beirut (Beirut Nights) in particular has a vibrant arts scene, with numerous performances, exhibits, fashion shows, and concerts held throughout the year in its galleries, museums, theatres, and public spaces.
Movies
There are several movies, which are filmed in or based on Lebanon, including:
- Bosta – a movie by Philippe Aractingi, released in 2005
- Caramel – a movie starring Nadine Labaki, released in 2007
- West Beirut – a movie by Ziad Doueiri, released in 1998
- After Shave – a movie by Hany Tamba, released in 2005 received the French Cesar Award for best foreign short film
- Mabrouk Again – a movie by Hany Tamba, released in 2000
See also
Main article: Outline of LebanonNotes
- Republic of Lebanon is the most common term used by reliable sources and Lebanese government agencies. However, the term Lebanese Republic is also used sometimes, and is a more accurate translation of the Arabic name, الجمهورية اللبنانية.
References
- ^ "Lebanon". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 2007-06-19. Retrieved 2009-07-22.
- ^ "La Constitution Libanaise" (in French). Le Conseil Constitutionnel de la République Libanaise. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division (2009). "World Population Prospects, Table A.1" (.PDF). 2008 revision. United Nations. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Lebanon". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2009-10-01.
- Human Development Report 2009. The United Nations. Retrieved 5 October 2009
- ^ "Lebanon". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2009.
- McGowen, Afaf Sabeh (1989), "Historical Setting", in Collelo, Thomas (ed.), Lebanon: A Country Study, Area Handbook Series (3rd ed.), Washington, D.C.: The Division, OCLC 18907889, retrieved 2009-07-24
- ^ Dumper, Michael; Stanley, Bruce E.; Abu-Lughod, Janet L. (2006). Cities of the Middle East and North Africa. ABC-CLIO. p. 104. ISBN 1576079198.
Archaelogical excavations at Byblos indicate that the site has been continually inhabited since at least 5000 B.C.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Countries Quest. "Lebanon, Government". Retrieved 14 December 2006.
- ^ U.S. Department of State (January 2009). "Background Note: Lebanon". Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- ^ Anna Johnson (2006). "Lebanon: Tourism Depends on Stability". Retrieved 31 October 2006.
- Canadian International Development Agency. "Lebanon: Country Profile". Retrieved 2 December 2006.
- Center for the Study of the Built Environment. "Deconstructing Beirut's Reconstruction: 1990-2000". Retrieved 31 October 2006.
- "Security Council calls for end to hostilities between Hizbollah, Israel, unanimously adopting Resolution 1701 (2006)". UN. Retrieved 2008-10-14.
- Room, Adrian (2006). Placenames of the World: Origins and Meanings of the Names for 6,600 Countries, Cities, Territories, Natural Features and Historic Sites (2nd ed.). McFarland. p. 214–215. ISBN 9780786422487.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Metzger, Bruce M.; Coogan, Michael D. (2004). The Oxford guide to people & places of the Bible. Oxford University Press. p. 178. ISBN 0195176103.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Bienkowski, Piotr; Millard, Alan Ralph (2000). Dictionary of the ancient Near East. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 178. ISBN 9780812235579.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Ross, Kelley L. "The Pronunciation of Ancient Egyptian". The Proceedings of the Friesian School, Fourth Series. Friesian School. Retrieved 2009-01-20.
- "Archaeological Virtual Tours: Byblos". Destinationlebanon.gov.lb. Retrieved 2008-10-14.
- About.com (1987)."Lebanon in Ancient Times". Retrieved 17 December 2006.
- Dreaming of Greater Syria. Abdul-Ilah Saadi. Al Jazeera English.
- Chorbishop Seely Beggiani (2005). "Aspects of Maronite History (Part Eleven) The twentieth century in Western Asia". Retrieved 24 January 2007.
- Harb, Imad (March 2006). "Lebanon's Confessionalism: Problems and Prospects". USIPeace Briefing. United States Institute of Peace. Retrieved 2009-01-20.
- "Lebanese Armed Forces, CSIS (Page 12)" (PDF). 2006-10-21.
- Stinson, Jefferey (2006-08-01). "Lebanese forces may play bigger role in war". USA TODAY. Retrieved 2009-08-22.
- "LAF Mission". Lebanese Armed Forces. Retrieved 2009-05-19.
- Lanteaume, Sylvie (2009-08-04). "US military aid at stake in Lebanon elections". Agence France-Presse. Retrieved 2009-08-22.
- Schenker, David (2008-10--03). "The Future of U.S. Military Aid to Lebanon". Washington Institute for Near East Policy. Retrieved 2009-08-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Morris, Benn (April 2008). 1948: A History of the First Arab-Israeli War. Yale University Pres. p. 524. ISBN 978-0300126969.
- ^ "Lebanon Exiled and suffering: Palestinian refugees in Lebanon". Amnesty International USA (in amn). Amnesty International. 2007. Retrieved 2009-08-09.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - "Lebanese army battles into outskirts of Palestinian camp". USA TODAY. The Associated Press. 2007-06-01. Retrieved 2009-08-09.
- al-Issawi, Omar (4-08-2009). "Lebanon's Palestinian refugees". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 2009-08-21.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Time (1991). "After the War, the Mop-Up". Retrieved 30 November 2006.
- UN IRIN news. "Lebanon: Haven for foreign militants". May 17, 2007.
- Council on Foreign Relations (2006). "The Future of Lebanon". Retrieved 18 December 2006.
- People's Daily (2000). "Lebanese Troops Patrol Near Fatma Gate Along Border With Israel". Retrieved 18 December 2006.
- Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs (2000)."Withdrawal from Lebanon: Press Briefing by Foreign Minister David Levy". Retrieved 1 November 2006.
- The key to Shebaa, Al-Jazeera online. Retrieved 1 April 2007.
- Ross, Oakland (2007-10-09). "Language of murder makes itself understood". Toronto Star. Retrieved 2009-02-02.
Like a wound that just won't heal, a large expanse patch of fresh asphalt still mottles the grey surface of Rue Minet el-Hosn, where the street veers west around St. George Bay. The patch marks the exact spot where a massive truck bomb exploded February 14, 2005, killing prime minister Rafik Hariri and 22 others and gouging a deep crater in the road.
- CBC News Indepth (2006). "Recent background on Syria's presence in Lebanon". Retrieved 10 December 2006.
- See this MEMRI bulletin, includes several statements and sources.
- "Press Release SC/8353". United Nations - Security Council. April 07, 2005. Retrieved 2009-01-19.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Mehlis, Detlev (19 October 2005). "Report of the International Independent Investigation Commission established pursuant to Security Council resolution 1595". United Nations Information System on the Question of Palestine. Retrieved 2009-02-02.
It is the Commission's view that the assassination of 14 February 2005 was carried out by a group with an extensive organization and considerable resources and capabilities. Building on the findings of the Commission and Lebanese investigations to date and on the basis of the material and documentary evidence collected, and the leads pursued until now, there is converging evidence pointing at both Lebanese and Syrian involvement in this terrorist act.
"Report of the International Independent Investigation Commission established pursuant to Security Council resolution 1595" (PDF). - "Syria begins Lebanon withdrawal". BBC News. March 12, 2005. Retrieved December 11, 2006.
- CNN (2005) "Last Syrian troops leave Lebanon". Retrieved 11 December 2006.
- 2005: Bassel Fleihan, Lebanese legislator and Minister of Economy and Commerce; Samir Kassir, Columnist and Democratic Left Movement leader; George Hawi, former head of Lebanese Communist Party; Gibran Tueni, Editor in Chief of "An Nahar" newspaper. 2006: Pierre Gemayel, Minister of Industry. 2007: Walid Eido, MP; Antoine Ghanim, MP.
- "Israel's Use of Cluster Bombs Shows Need for Global Ban". Human Rights Watch. February 17, 2008. Retrieved 2009-01-19.
- "Security Council calls for end to hostilities between Hizbollah, Israel". UN - Security Council, Department of Public Information. August 11, 2006. Retrieved 2009-01-19.
- UN IRIN news. "Life set to get harder for Nahr al-Bared refugees". Retrieved 5 November 2008.
- Martínez, Beatriz (September 2008). "Walking the tight wire - Conversations on the May 2008 Lebanese crisis" (PDF). Transnational Institute. Retrieved 2009-01-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Telegraph (2000) "Israel's Withdrawal from Lebanon Given UN's Endorsement". Retrieved 1 November 2006.
- UN IRIN news. "Climate change and politics threaten water wars in Bekaa". Retrieved 1 February 2009.
- (Bonechi et al.) (2004) Golden Book Lebanon, p. 3, Florence, Italy: Casa Editrice Bonechi. ISBN 88-476-1489-9
- Country Studies US. "Lebanon - Climate". Retrieved 5 November 2006.
- ^ Blue Planet Biomes. "Lebanon Cedar - Cedrus libani". Retrieved 10 December 2006.
- "Canadian Climate Normals 1971-2000". Climate.weatheroffice.ec.gc.ca. 2008-11-01. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor (2002). "Country Reports on Human Rights Practices - 2002: Lebanon". Retrieved 3 January 2007.
- Lijphart, Arend. Consociational Democracy, in "World Politics", Vol. 21, No. 2 (January 1969), pp. 207–225.
- Lijphart, Arend. Multiethnic democracy, in S. Lipset (ed.), "The Encyclopedia of Democracy". London, Routledge, 1995, Volume III, pp. 853–865.
- ^ United States Institute of Peace (March 2006). "Lebanon's Confessionalism: Problems and Prospects". Retrieved 3 January 2007.
- Marie-Joëlle Zahar. "Chapter 9 Power sharing in Lebanon: Foreign protectors, domestic peace, and democratic failure". (DOC) Retrieved 3 January 2007.
- "Eager Lebanese race to polls to cast their ballots". Retrieved 2009-06-07.
- UNDP. "Democratic Governance, Elections, Lebanon". Retrieved 15 December 2008.
- "Pro-West prime minister to lead Lebanon". MSNBC. 2009-06-27. Retrieved 2009-08-08.
- Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, Arab Political Systems: Baseline Information and Reforms – Lebanon, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, retrieved 2009-07-04
- USAID Lebanon. "USAID Lebanon — Definitions of Terms used". Retrieved 17 December 2006.
- U.S. Department of State (1994) Header: People, 4th paragraph. Retrieved 3 December 2006.
- Background Note: Lebanon "www.washingtoninstitute.org". Retrieved 3 December 2006.
- International Organization for Migration."Lebanon - Facts and Figures" Retrieved 13 June 2009.
- Reuters."FACTBOX: Facts on Lebanon's economy" Retrieved 13 June 2009.
- United Nations Population Fund."Lebanon - Overview". Retrieved 9 November 2006.
- Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress, U.S.A. 1986-1988. . Retrieved 2 December 2006.
- ^ Jean Hayek et al, 1999. The Structure, Properties, and Main Foundations of the Lebanese Economy. In The Scientific Series in Geography, Grade 11, 110–114. Beirut: Dar Habib.
- "Lebanon" (Governmental). Canadian International Development Agency. Government of Canada. 2009-05-28. Retrieved 2009-08-24.
- CIA World Factbook 2001. Retrieved 2006-12-04.
- ^ Bank Audi (2006). "Lebanon Economic Report: 2nd Quarter, 2006". Retrieved 27 November 2005.
- Lebanese Ministry of Finance (2006)."Impact of the July Offensive on the Public Finances in 2006". Retrieved 24 September 2006.
- Cyprus News (2006). "Saudi Arabia Key Contributor To Lebanon's Reconstruction". Retrieved 26 November 2006.
- Lebanon Under Siege (2006). However, Lebanon's economy has since then revived and strongly in the tourism sector. After the internal fighting in May 2008 between political factions in the country, Lebanon witnessed a very busy summer that Summer season, and an even higher percentage in the Summer tourist season of 2009. The Ministry of Tourism expected up to more than 2 million visitors making a budget of up to billions of US dollars. This is all due to the political stability and the successful legislative election's that occured in Lebanon June 2009. "Donors pledge more than $940 million for Lebanon". Retrieved 26 November 2006.
- Ain-Al-Yaqeen (2006). "The Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques Reviews with the Jordanian King the Situation in Lebanon...". Retrieved 27 November 2006.
- Samidoun (2006). "Aid groups scramble to fix buildings; fill backpacks before school bell rings". Retrieved 9 December 2006.
- Infopro Management. "Lebanon Opportunities - Business Information". Retrieved 30 January 2007.
- Template:Ar iconLebanese Directory of Higher Education. "Decrees". Retrieved 30 January 2007.
- eIFL.net Regional Workshop (2005). "Country Report: Lebanon". Retrieved 14 December 2006.
- Université Saint-Joseph. "125 years of history - A timeline". Retrieved 8 December 2006.
- "Yalla! Students". Retrieved 15 December 2006.
- "Human development indicators Lebanon". United Nations Development Programme, Human Development Reports. Retrieved 2008-11-17.{}
- [http://www.unhcr.org/4a69ad639.pdf Surviving in the city: A review of UNHCR’s operation for Iraqi refugees in urban areas of Jordan, Lebanon and Syria]
- "World Refugee Survey 2008". U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants. 2008-06-19.
- ^ Lebanon - International Religious Freedom Report 2008 U.S. Department of State. Retrieved on 2009-09-04.
- Lebanon : Overview. Minority Rights Group International, World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples.
- Christian Split in Lebanon Raises Specter of Civil War. The New York Times. October 6, 2007.
- "Lebanon". NOW Lebanon. Retrieved 2009-08-18.
- "Article 11 of the Lebanese Constitution" http://www.servat.unibe.ch/law/icl/le00000_.html#A011_Retrieved 28 June 2008.
- Armenians jump Lebanon's divide. BBC News. April 16, 2009.
- Lebanese Diaspora. Prof. Van Dusenbery. Hamline University.
- The world's successful diasporas. Management Today. April 3, 2007.
- Marina Sarruf (2006). "Brazil Has More Lebanese than Lebanon". Retrieved 30 November 2006.
- Ivory Coast - The Levantine Community. Source: U.S. Library of Congress.
- Lebanese Immigrants Boost West African Commerce, By Naomi Schwarz, voanews.com, July 10, 2007
- Australian Population: Ethnic Origins. (PDF)
- Lebanon, Opinion survey 2009 , by ICRC and Ipsos
- Lebanon Culture. . 18 December 2006.
- Smith, Whitney (2009). "Lebanon, flag of". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2009-08-10.
- Bell, Bethany (2008-08-27). "Threat to Lebanon's symbol of survival". BBC. Retrieved 2009-08-10.
- "Government". Embassy of Lebanon to the Netherlands. Retrieved 2009-08-10.
- The Hindu (5 January 2003). "Called by life";. Retrieved 8 January 2007.
- ^ Carter, Terry (2008-07-15). "Arts". Lonely Planet Syria & Lebanon. Lonely Planet. Thomas Amelia (3 ed.). Lonely Planet. pp. 254–255. ISBN 978-1741046090. Retrieved 2009-09-19.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ World Intellectual Property Organization (2003). "COPYRIGHT INDUSTRIES IN LEBANON". Performance of copyright industries in selected Arab countries: Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Morocco, Tunisia. World Intellectual Property Organization. pp. 148–152. ISBN 978-9280513165. Retrieved 2009-09-19.
- ^ Sheehan, Sean (2007-08-30). "Arts". Lebanon. Cultures of the World (2 ed.). Marshall Cavendish Children's Books. p. 105. ISBN 978-0761420811. Retrieved 2009-09-19.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Kamalipour, Yahya (2001-11-15). "Between Globalization and Localization". Media, sex, violence, and drugs in the global village. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc. p. 265. ISBN 978-0742500617. Retrieved 2009-09-19.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - One source says "cult following", other says "folk hero"
- Karam, Michael (2005-10-27). Wines of Lebanon. Saqi Books. p. 263. ISBN 978-0863565984. Retrieved 2009-09-18.
Further reading
- Fisk, Robert. Pity the Nation: The Abduction of Lebanon. New York: Nation Books, 2002.
- Firzli, Nicola Y. Al-Baath wa-Lubnân ("The Baath and Lebanon"). Beirut: Dar-al-Tali'a Books, 1973
- Glass, Charles, "Tribes with Flags: A Dangerous Passage Through the Chaos of the Middle East", Atlantic Monthly Press (New York) and Picador (London), 1990 ISBN 0436181304
- Hitti Philip K. History of Syria Including Lebanon and Palestine, Vol. 2 (2002) (ISBN 1-931956-61-8)
- Holst, Sanford. Phoenicians: Lebanon's Epic Heritage. Los Angeles: Cambridge and Boston Press, 2005.
- Norton, Augustus R. Amal and the Shi'a: Struggle for the Soul of Lebanon. Austin and London: University of Texas Press, 1987.
- Plonka Arkadiusz, L’idée de langue libanaise d’après Sa‘īd ‘Aql, Paris, Geuthner, 2004 (French) ISBN 2705337393
- Sobelman, Daniel. New Rules of the Game: Israel and Hizbollah After the Withdrawal From Lebanon, Jaffee Center for Strategic Studies, Tel-Aviv University, 2004.
- Riley-Smith, Jonathan. The Oxford Illustrated History of the Crusades. New York: Oxford University Press, 2001.
- Salibi, Kamal. A House of Many Mansions: The History of Lebanon Reconsidered. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1990.
External links
- Presidency of the Republic of Lebanon
- The Lebanese Parliament Template:Ar icon
- The Lebanese Governmental Portal for Information & Forms Template:Ar icon Template:Fr icon Template:En icon
- Central Administration for Statistics
- Ministry of Tourism
- "Lebanon". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Lebanon at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Template:Dmoz
- Lebanon Country Study by the United States Department of State
 Wikimedia Atlas of Lebanon
Wikimedia Atlas of Lebanon- UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Lebanon
- Template:Wikitravel
| Lebanon articles | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| History | |||
| Geography | |||
| Politics | |||
| Economy | |||
| Culture | |||
| International membership | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Template:Member states of the Arab League
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories:- Articles with dead external links from October 2008
- Lebanon
- Southwest Asian countries
- Middle Eastern countries
- Countries of the Mediterranean Sea
- Levant
- Mediterranean
- Fertile Crescent
- Arabic-speaking countries
- Arab League member states
- Member states of La Francophonie
- Near Eastern countries
- Organisation of the Islamic Conference members
- Western Asia
- States and territories established in 1943