This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Nono64 (talk | contribs) at 19:38, 29 March 2011 (natural phenol-stub). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 19:38, 29 March 2011 by Nono64 (talk | contribs) (natural phenol-stub)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)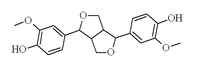
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 4-furan-3-yl]-2-methoxyphenol | |
| Other names (+)-Pinoresinol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C20H22O6 |
| Molar mass | 358.38 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Pinoresinol is a lignan found in Styrax sp. and in Forsythia suspensa. It is also found in the caterpillar of the cabbage butterfly, Pieris rapae where it serves as a defence against ants.
In food, it is found in sesame seed and in Brassica vegetables.
See also
References
- Pastrorova et al. (1997)
- On the stereoselective synthesis of (+)-pinoresinol in Forsythia suspensa from its achiral precursor, coniferyl alcohol. Laurence B. Davin, Diana L. Bedgar, Takeshi Katayama and Norman G. Lewis, Phytochemistry, Volume 31, Issue 11, 1992, Pages 3869-3874, doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)97544-7
- Pinoresinol: A lignol of plant origin serving for defense in a caterpillar. Frank C. Schroeder, Marta L. del Campo, Jacqualine B. Grant, Douglas B. Weibel, Scott R. Smedley, Kelly L. Bolton, Jerrold Meinwald and Thomas Eisner, PNAS October 17, 2006 vol. 103 no. 42 15497-15501, doi:10.1073/pnas.0605921103
- Lignan contents of Dutch plant foods: a database including lariciresinol, pinoresinol, secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol. Ivon E. J. Milder, Ilja C. W. Arts, Betty van de Putte, Dini P. Venema and Peter C. H. Hollman, British Journal of Nutrition (2005), 93: 393-402, doi:10.1079/BJN20051371