This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 16:22, 19 January 2012 (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'CASNo_Ref') per [[WP:CHEMVALID|Chem/Drugbox validat...). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 16:22, 19 January 2012 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'CASNo_Ref') per [[WP:CHEMVALID|Chem/Drugbox validat...)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)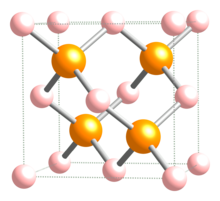
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.039.616 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | BP |
| Molar mass | 41.7855 g/mol |
| Appearance | maroon powder |
| Density | 2.90 g/cm |
| Melting point | 1100 °C (decomposes) |
| Band gap | 2 eV (indirect) |
| Electron mobility | 5400 cm/(V*s) (300 K) |
| Thermal conductivity | 4 W/(cm*K) (300 K) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 3.05 (0.63 µm) |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Zinc Blende |
| Space group | Td-F-43m |
| Coordination geometry | Tetrahedral |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Boron phosphide (BP) (also referred to as boron monophosphide, to distinguish it from boron subphosphide B12P2) is a chemical compound of boron and phosphorus. It is a semiconductor .
History
Crystals of boron phosphide were synthesized by Henri Moissan as early as in 1891 .
Appearance
Pure BP is almost transparent, n-type crystals are orange-red whereas p-type ones are dark red .
Chemical properties
BP is not attacked by acids or boiling aqueous alkali water solutions. It is only attacked by molten alkalis..
Physical properties
- coefficient of thermal expansion ~3x10 /°K
- heat capacity CP ~ 0.8 J/(g*K) (300 K)
- Debye temperature = 1000 K
- relatively high microhardness of 32 GPa (100 g load).
- electron and hole mobilities of few hundred cm/(V*s) (up to 500)
See also
Related materials
References
- refractive index database
- Boron Phosphide, a III–V Compound of Zinc-Blende Structure P. Popper & T. A. Ingles Nature 179, 1075, 1957 doi:10.1038/1791075a0
- Moissan, H., Comp. Rend. 113 (1891) 726
- ^ L. I. Berger "Semiconductor materials" CRC Press, 1996 ISBN 0849389127, 9780849389122 (available on google books), p. 199
- Boron Chemistry at the Millennium, Editor: R.B. King, Elsevier Science & Technology (1999) ISBN 0-444-72006-5
- P-n junction type boron phosphide-based semiconductor light-emitting device and production method thereof, United States Patent 6831304
- Semiconducting Properties of Cubic Boron Phosphide, B. Stone and D. Hill, Phys. Rev. Lett. vol. 4, 282–284 (1960) doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.4.282
External links
| Boron compounds | |
|---|---|
| Boron pnictogenides | |
| Boron halides | |
| Acids | |
| Boranes | |
| Boron oxides and sulfides | |
| Carbides | |
| Organoboron compounds | |
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |