| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
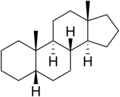
| IUPAC name 5ξ-Androstane | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (3aS,3bS,5aΞ,9aS,9bS,11aS)-9a,11a-Dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopentaphenanthrene | |
| Other names Etioallocholane; 10β,13β-Dimethylgonane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C19H32 |
| Molar mass | 260.465 g·mol |
| Density | 0.95 g/ml |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Androstane is a C19 steroidal hydrocarbon with a gonane core. Androstane can exist as either of two isomers, known as 5α-androstane and 5β-androstane.
Pharmacology
5α-Androstane is reported to be effective as an androgen, in spite of having no oxygen containing functional groups.
Androstanes
Androstanes are steroid derivatives with carbons present at positions 1 through 19.
See also: List of androstanes
See also
References
- Wilson JD (1996). "Role of dihydrotestosterone in androgen action". Prostate Suppl. 6 (S6): 88–92. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0045(1996)6+<88::AID-PROS17>3.0.CO;2-N. PMID 8630237. S2CID 41352599.
- Segaloff A, Gabbard RB (1960). "5α-Androstane—An Androgenic Hydrocarbon". Endocrinology. 67 (6): 887–889. doi:10.1210/endo-67-6-887. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 13749674.
| Steroid classification | |
|---|---|
| C17 | |
| C18 |
|
| C19 | |
| C20 | |
| C21 |
|
| C23 | |
| C24 | |
| C27 | |
| Functional group | |
| Elements removed | |
| Elements replaced | |