| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
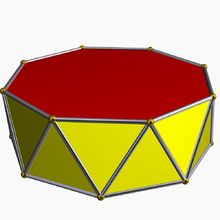
In geometry, an n-gonal antiprism or n-antiprism is a polyhedron composed of two parallel direct copies (not mirror images) of an n-sided polygon, connected by an alternating band of 2n triangles. They are represented by the Conway notation An.
Antiprisms are a subclass of prismatoids, and are a (degenerate) type of snub polyhedron.
Antiprisms are similar to prisms, except that the bases are twisted relatively to each other, and that the side faces (connecting the bases) are 2n triangles, rather than n quadrilaterals.
The dual polyhedron of an n-gonal antiprism is an n-gonal trapezohedron.
History
In his 1619 book Harmonices Mundi, Johannes Kepler observed the existence of the infinite family of antiprisms. This has conventionally been thought of as the first discovery of these shapes, but they may have been known earlier: an unsigned printing block for the net of a hexagonal antiprism has been attributed to Hieronymus Andreae, who died in 1556.
The German form of the word "antiprism" was used for these shapes in the 19th century; Karl Heinze credits its introduction to Theodor Wittstein [de]. Although the English "anti-prism" had been used earlier for an optical prism used to cancel the effects of a primary optimal element, the first use of "antiprism" in English in its geometric sense appears to be in the early 20th century in the works of H. S. M. Coxeter.
Special cases
Right antiprism
For an antiprism with regular n-gon bases, one usually considers the case where these two copies are twisted by an angle of 180/n degrees.
The axis of a regular polygon is the line perpendicular to the polygon plane and lying in the polygon centre.
For an antiprism with congruent regular n-gon bases, twisted by an angle of 180/n degrees, more regularity is obtained if the bases have the same axis: are coaxial; i.e. (for non-coplanar bases): if the line connecting the base centers is perpendicular to the base planes. Then the antiprism is called a right antiprism, and its 2n side faces are isosceles triangles.
Uniform antiprism
A uniform n-antiprism has two congruent regular n-gons as base faces, and 2n equilateral triangles as side faces.
Uniform antiprisms form an infinite class of vertex-transitive polyhedra, as do uniform prisms. For n = 2, we have the digonal antiprism (degenerate antiprism), which is visually identical to the regular tetrahedron; for n = 3, the regular octahedron as a triangular antiprism (non-degenerate antiprism).
| Antiprism name | Digonal antiprism | (Trigonal) Triangular antiprism |
(Tetragonal) Square antiprism |
Pentagonal antiprism | Hexagonal antiprism | Heptagonal antiprism | ... | Apeirogonal antiprism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyhedron image | ... | |||||||
| Spherical tiling image | Plane tiling image | |||||||
| Vertex config. | 2.3.3.3 | 3.3.3.3 | 4.3.3.3 | 5.3.3.3 | 6.3.3.3 | 7.3.3.3 | ... | ∞.3.3.3 |
The Schlegel diagrams of these semiregular antiprisms are as follows:
 A3 |
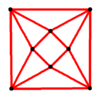 A4 |
 A5 |
 A6 |
 A7 |
 A8 |
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a right n-antiprism (i.e. with regular n-gon bases and 2n isosceles triangle side faces, circumradius of the bases equal to 1) are:
where 0 ≤ k ≤ 2n – 1;
if the n-antiprism is uniform (i.e. if the triangles are equilateral), then:
Volume and surface area
Let a be the edge-length of a uniform n-gonal antiprism; then the volume is:
and the surface area is:
Furthermore, the volume of a regular right n-gonal antiprism with side length of its bases l and height h is given by:
Derivation
The circumradius of the horizontal circumcircle of the regular -gon at the base is
The vertices at the base are at
the vertices at the top are at
Via linear interpolation, points on the outer triangular edges of the antiprism that connect vertices at the bottom with vertices at the top are at
and at
By building the sums of the squares of the and coordinates in one of the previous two vectors, the squared circumradius of this section at altitude is
The horizontal section at altitude above the base is a -gon (truncated -gon) with sides of length alternating with sides of length . (These are derived from the length of the difference of the previous two vectors.) It can be dissected into isoceless triangles of edges and (semiperimeter ) plus isoceless triangles of edges and (semiperimeter ). According to Heron's formula the areas of these triangles are
and
The area of the section is , and the volume is
Note that the volume of a right n-gonal prism with the same l and h is:
which is smaller than that of an antiprism.
Symmetry
The symmetry group of a right n-antiprism (i.e. with regular bases and isosceles side faces) is Dnd = Dnv of order 4n, except in the cases of:
- n = 2: the regular tetrahedron, which has the larger symmetry group Td of order 24 = 3 × (4 × 2), which has three versions of D2d as subgroups;
- n = 3: the regular octahedron, which has the larger symmetry group Oh of order 48 = 4 × (4 × 3), which has four versions of D3d as subgroups.
The symmetry group contains inversion if and only if n is odd.
The rotation group is Dn of order 2n, except in the cases of:
- n = 2: the regular tetrahedron, which has the larger rotation group T of order 12 = 3 × (2 × 2), which has three versions of D2 as subgroups;
- n = 3: the regular octahedron, which has the larger rotation group O of order 24 = 4 × (2 × 3), which has four versions of D3 as subgroups.
Note: The right n-antiprisms have congruent regular n-gon bases and congruent isosceles triangle side faces, thus have the same (dihedral) symmetry group as the uniform n-antiprism, for n ≥ 4.
Generalizations
In higher dimensions
Four-dimensional antiprisms can be defined as having two dual polyhedra as parallel opposite faces, so that each three-dimensional face between them comes from two dual parts of the polyhedra: a vertex and a dual polygon, or two dual edges. Every three-dimensional convex polyhedron is combinatorially equivalent to one of the two opposite faces of a four-dimensional antiprism, constructed from its canonical polyhedron and its polar dual. However, there exist four-dimensional polychora that cannot be combined with their duals to form five-dimensional antiprisms.
Self-crossing polyhedra
 3/2-antiprism nonuniform |
 5/4-antiprism nonuniform |
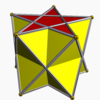 5/2-antiprism |
 5/3-antiprism |
 9/2-antiprism |
 9/4-antiprism |
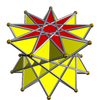 9/5-antiprism |
Uniform star antiprisms are named by their star polygon bases, {p/q}, and exist in prograde and in retrograde (crossed) solutions. Crossed forms have intersecting vertex figures, and are denoted by "inverted" fractions: p/(p – q) instead of p/q; example: 5/3 instead of 5/2.
A right star antiprism has two congruent coaxial regular convex or star polygon base faces, and 2n isosceles triangle side faces.
Any star antiprism with regular convex or star polygon bases can be made a right star antiprism (by translating and/or twisting one of its bases, if necessary).
In the retrograde forms, but not in the prograde forms, the triangles joining the convex or star bases intersect the axis of rotational symmetry. Thus:
- Retrograde star antiprisms with regular convex polygon bases cannot have all equal edge lengths, and so cannot be uniform. "Exception": a retrograde star antiprism with equilateral triangle bases (vertex configuration: 3.3/2.3.3) can be uniform; but then, it has the appearance of an equilateral triangle: it is a degenerate star polyhedron.
- Similarly, some retrograde star antiprisms with regular star polygon bases cannot have all equal edge lengths, and so cannot be uniform. Example: a retrograde star antiprism with regular star 7/5-gon bases (vertex configuration: 3.3.3.7/5) cannot be uniform.
Also, star antiprism compounds with regular star p/q-gon bases can be constructed if p and q have common factors. Example: a star 10/4-antiprism is the compound of two star 5/2-antiprisms.
| Symmetry group | Uniform stars | Right stars | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D4d (2*4) |
 3.3/2.3.4 Crossed square antiprism | ||||
| D5h (*225) |
 3.3.3.5/2 Pentagrammic antiprism |
 3.3/2.3.5 crossed pentagonal antiprism | |||
| D5d (2*5) |
 3.3.3.5/3 Pentagrammic crossed-antiprism | ||||
| D6d (2*6) |
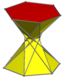 3.3/2.3.6 crossed hexagonal antiprism | ||||
| D7h (*227) |
 3.3.3.7/2 |
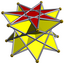 3.3.3.7/4 | |||
| D7d (2*7) |
 3.3.3.7/3 | ||||
| D8d (2*8) |
 3.3.3.8/3 Octagrammic antiprism |
 3.3.3.8/5 Octagrammic crossed-antiprism | |||
| D9h (*229) |
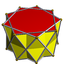 3.3.3.9/2 Enneagrammic antiprism (9/2) |
 3.3.3.9/4 Enneagrammic antiprism (9/4) | |||
| D9d (2*9) |
 3.3.3.9/5 Enneagrammic crossed-antiprism | ||||
| D10d (2*10) |
 3.3.3.10/3 Decagrammic antiprism | ||||
| D11h (*2.2.11) |
 3.3.3.11/2 |
 3.3.3.11/4 |
 3.3.3.11/6 | ||
| D11d (2*11) |
 3.3.3.11/3 |
 3.3.3.11/5 |
 3.3.3.11/7 | ||
| D12d (2*12) |
 3.3.3.12/5 |
 3.3.3.12/7 | |||
| ... | ... | ||||
See also
- Grand antiprism, a four-dimensional polytope
- Skew polygon, a three-dimensional polygon whose convex hull is an antiprism
References
- Kepler, Johannes (1619). "Book II, Definition X". Harmonices Mundi (in Latin). p. 49. See also illustration A, of a heptagonal antiprism.
- Schreiber, Peter; Fischer, Gisela; Sternath, Maria Luise (July 2008). "New light on the rediscovery of the Archimedean solids during the Renaissance". Archive for History of Exact Sciences. 62 (4): 457–467. doi:10.1007/s00407-008-0024-z. JSTOR 41134285.
- Heinze, Karl (1886). Lucke, Franz (ed.). Genetische Stereometrie (in German). B. G. Teubner. p. 14.
- Smyth, Piazzi (1881). "XVII. On the Constitution of the Lines forming the Low-Temperature Spectrum of Oxygen". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 30 (1): 419–425. doi:10.1017/s0080456800029112.
- Coxeter, H. S. M. (January 1928). "The pure Archimedean polytopes in six and seven dimensions". Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. 24 (1): 1–9. Bibcode:1928PCPS...24....1C. doi:10.1017/s0305004100011786.
- Grünbaum, Branko (2005). "Are prisms and antiprisms really boring? (Part 3)" (PDF). Geombinatorics. 15 (2): 69–78. MR 2298896.
- Dobbins, Michael Gene (2017). "Antiprismlessness, or: reducing combinatorial equivalence to projective equivalence in realizability problems for polytopes". Discrete & Computational Geometry. 57 (4): 966–984. doi:10.1007/s00454-017-9874-y. MR 3639611.
Further reading
- Anthony Pugh (1976). Polyhedra: A visual approach. California: University of California Press Berkeley. ISBN 0-520-03056-7. Chapter 2: Archimedean polyhedra, prisms and antiprisms
External links
 Media related to Antiprisms at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Antiprisms at Wikimedia Commons- Weisstein, Eric W. "Antiprism". MathWorld.
- Nonconvex Prisms and Antiprisms
- Paper models of prisms and antiprisms
| Convex polyhedra | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platonic solids (regular) | |||||
| Archimedean solids (semiregular or uniform) | |||||
| Catalan solids (duals of Archimedean) |
| ||||
| Dihedral regular | |||||
| Dihedral uniform |
| ||||
| Dihedral others | |||||
| Degenerate polyhedra are in italics. | |||||





 -gon at the base is
-gon at the base is





 and
and  coordinates in one of the previous two vectors,
the squared circumradius of this section at altitude
coordinates in one of the previous two vectors,
the squared circumradius of this section at altitude  is
is

 above the base is a
above the base is a  -gon (truncated
-gon (truncated  alternating with
alternating with  .
(These are derived from the length of the difference of the previous two vectors.)
It can be dissected into
.
(These are derived from the length of the difference of the previous two vectors.)
It can be dissected into  and
and  (semiperimeter
(semiperimeter  )
plus
)
plus  (semiperimeter
(semiperimeter  ).
According to Heron's formula the areas of these triangles are
).
According to Heron's formula the areas of these triangles are


 , and the volume is
, and the volume is

 which is smaller than that of an antiprism.
which is smaller than that of an antiprism.