

A conic section, conic or a quadratic curve is a curve obtained from a cone's surface intersecting a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though it was sometimes called as a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties.
The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a focus, and some particular line, called a directrix, are in a fixed ratio, called the eccentricity. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curve of degree 2; that is, as the set of points whose coordinates satisfy a quadratic equation in two variables which can be written in the form The geometric properties of the conic can be deduced from its equation.
In the Euclidean plane, the three types of conic sections appear quite different, but share many properties. By extending the Euclidean plane to include a line at infinity, obtaining a projective plane, the apparent difference vanishes: the branches of a hyperbola meet in two points at infinity, making it a single closed curve; and the two ends of a parabola meet to make it a closed curve tangent to the line at infinity. Further extension, by expanding the real coordinates to admit complex coordinates, provides the means to see this unification algebraically.
Euclidean geometry

1: Circle 2: Ellipse
3: Parabola 4: Hyperbola
The conic sections have been studied for thousands of years and have provided a rich source of interesting and beautiful results in Euclidean geometry.
Definition
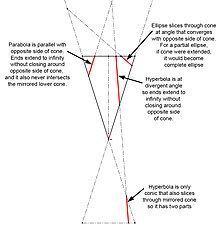
A conic is the curve obtained as the intersection of a plane, called the cutting plane, with the surface of a double cone (a cone with two nappes). It is usually assumed that the cone is a right circular cone for the purpose of easy description, but this is not required; any double cone with some circular cross-section will suffice. Planes that pass through the vertex of the cone will intersect the cone in a point, a line or a pair of intersecting lines. These are called degenerate conics and some authors do not consider them to be conics at all. Unless otherwise stated, "conic" in this article will refer to a non-degenerate conic.
There are three types of conics: the ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. The circle is a special kind of ellipse, although historically Apollonius considered it a fourth type. Ellipses arise when the intersection of the cone and plane is a closed curve. The circle is obtained when the cutting plane is parallel to the plane of the generating circle of the cone; for a right cone, this means the cutting plane is perpendicular to the axis. If the cutting plane is parallel to exactly one generating line of the cone, then the conic is unbounded and is called a parabola. In the remaining case, the figure is a hyperbola: the plane intersects both halves of the cone, producing two separate unbounded curves.
Compare also spheric section (intersection of a plane with a sphere, producing a circle or point), and spherical conic (intersection of an elliptic cone with a concentric sphere).
Eccentricity, focus and directrix

Alternatively, one can define a conic section purely in terms of plane geometry: it is the locus of all points P whose distance to a fixed point F (called the focus) is a constant multiple e (called the eccentricity) of the distance from P to a fixed line L (called the directrix). For 0 < e < 1 we obtain an ellipse, for e = 1 a parabola, and for e > 1 a hyperbola.
A circle is a limiting case and is not defined by a focus and directrix in the Euclidean plane. The eccentricity of a circle is defined to be zero and its focus is the center of the circle, but its directrix can only be taken as the line at infinity in the projective plane.
The eccentricity of an ellipse can be seen as a measure of how far the ellipse deviates from being circular.
If the angle between the surface of the cone and its axis is and the angle between the cutting plane and the axis is the eccentricity is
A proof that the above curves defined by the focus-directrix property are the same as those obtained by planes intersecting a cone is facilitated by the use of Dandelin spheres.
Alternatively, an ellipse can be defined in terms of two focus points, as the locus of points for which the sum of the distances to the two foci is 2a; while a hyperbola is the locus for which the difference of distances is 2a. (Here a is the semi-major axis defined below.) A parabola may also be defined in terms of its focus and latus rectum line (parallel to the directrix and passing through the focus): it is the locus of points whose distance to the focus plus or minus the distance to the line is equal to 2a; plus if the point is between the directrix and the latus rectum, minus otherwise.
Conic parameters

In addition to the eccentricity (e), foci, and directrix, various geometric features and lengths are associated with a conic section.
The principal axis is the line joining the foci of an ellipse or hyperbola, and its midpoint is the curve's center. A parabola has no center.
The linear eccentricity (c) is the distance between the center and a focus.
The latus rectum is the chord parallel to the directrix and passing through a focus; its half-length is the semi-latus rectum (ℓ).
The focal parameter (p) is the distance from a focus to the corresponding directrix.
The major axis is the chord between the two vertices: the longest chord of an ellipse, the shortest chord between the branches of a hyperbola. Its half-length is the semi-major axis (a). When an ellipse or hyperbola are in standard position as in the equations below, with foci on the x-axis and center at the origin, the vertices of the conic have coordinates (−a, 0) and (a, 0), with a non-negative.
The minor axis is the shortest diameter of an ellipse, and its half-length is the semi-minor axis (b), the same value b as in the standard equation below. By analogy, for a hyperbola the parameter b in the standard equation is also called the semi-minor axis.
The following relations hold:
For conics in standard position, these parameters have the following values, taking .
| conic section | equation | eccentricity (e) | linear eccentricity (c) | semi-latus rectum (ℓ) | focal parameter (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circle | |||||
| ellipse | |||||
| parabola | N/A | ||||
| hyperbola |
Standard forms in Cartesian coordinates



After introducing Cartesian coordinates, the focus-directrix property can be used to produce the equations satisfied by the points of the conic section. By means of a change of coordinates (rotation and translation of axes) these equations can be put into standard forms. For ellipses and hyperbolas a standard form has the x-axis as principal axis and the origin (0,0) as center. The vertices are (±a, 0) and the foci (±c, 0). Define b by the equations c = a − b for an ellipse and c = a + b for a hyperbola. For a circle, c = 0 so a = b, with radius r = a = b. For the parabola, the standard form has the focus on the x-axis at the point (a, 0) and the directrix the line with equation x = −a. In standard form the parabola will always pass through the origin.
For a rectangular or equilateral hyperbola, one whose asymptotes are perpendicular, there is an alternative standard form in which the asymptotes are the coordinate axes and the line x = y is the principal axis. The foci then have coordinates (c, c) and (−c, −c).
- Circle:
- Ellipse:
- Parabola:
- Hyperbola:
- Rectangular hyperbola:
The first four of these forms are symmetric about both the x-axis and y-axis (for the circle, ellipse and hyperbola), or about the x-axis only (for the parabola). The rectangular hyperbola, however, is instead symmetric about the lines y = x and y = −x.
These standard forms can be written parametrically as,
General Cartesian form
In the Cartesian coordinate system, the graph of a quadratic equation in two variables is always a conic section (though it may be degenerate), and all conic sections arise in this way. The most general equation is of the form
with all coefficients real numbers and A, B, C not all zero.
Matrix notation
Main article: Matrix representation of conic sectionsThe above equation can be written in matrix notation as
The general equation can also be written as
This form is a specialization of the homogeneous form used in the more general setting of projective geometry (see below).
Discriminant
The conic sections described by this equation can be classified in terms of the value , called the discriminant of the equation. Thus, the discriminant is − 4Δ where Δ is the matrix determinant
If the conic is non-degenerate, then:
- if B − 4AC < 0, the equation represents an ellipse;
- if A = C and B = 0, the equation represents a circle, which is a special case of an ellipse;
- if B − 4AC = 0, the equation represents a parabola;
- if B − 4AC > 0, the equation represents a hyperbola;
- if A + C = 0, the equation represents a rectangular hyperbola.
In the notation used here, A and B are polynomial coefficients, in contrast to some sources that denote the semimajor and semiminor axes as A and B.
Invariants
The discriminant B – 4AC of the conic section's quadratic equation (or equivalently the determinant AC – B/4 of the 2 × 2 matrix) and the quantity A + C (the trace of the 2 × 2 matrix) are invariant under arbitrary rotations and translations of the coordinate axes, as is the determinant of the 3 × 3 matrix above. The constant term F and the sum D + E are invariant under rotation only.
Eccentricity in terms of coefficients
When the conic section is written algebraically as
the eccentricity can be written as a function of the coefficients of the quadratic equation. If 4AC = B the conic is a parabola and its eccentricity equals 1 (provided it is non-degenerate). Otherwise, assuming the equation represents either a non-degenerate hyperbola or ellipse, the eccentricity is given by
where η = 1 if the determinant of the 3 × 3 matrix above is negative and η = −1 if that determinant is positive.
It can also be shown that the eccentricity is a positive solution of the equation
where again This has precisely one positive solution—the eccentricity— in the case of a parabola or ellipse, while in the case of a hyperbola it has two positive solutions, one of which is the eccentricity.
Conversion to canonical form
See also: Ellipse § Canonical formIn the case of an ellipse or hyperbola, the equation
can be converted to canonical form in transformed variables as
or equivalently
where and are the eigenvalues of the matrix — that is, the solutions of the equation
— and is the determinant of the 3 × 3 matrix above, and is again the determinant of the 2 × 2 matrix. In the case of an ellipse the squares of the two semi-axes are given by the denominators in the canonical form.
Polar coordinates
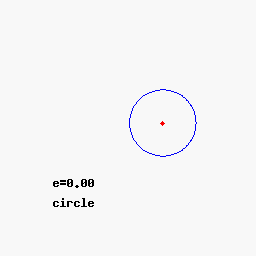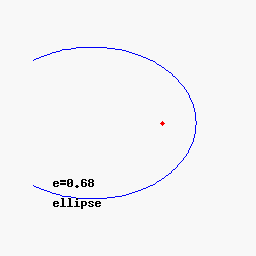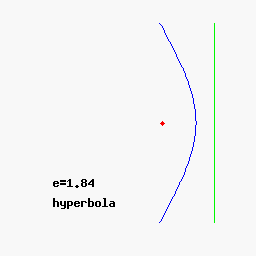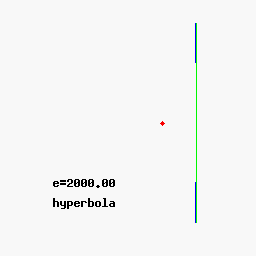
In polar coordinates, a conic section with one focus at the origin and, if any, the other at a negative value (for an ellipse) or a positive value (for a hyperbola) on the x-axis, is given by the equation
where e is the eccentricity and l is the semi-latus rectum.
As above, for e = 0, the graph is a circle, for 0 < e < 1 the graph is an ellipse, for e = 1 a parabola, and for e > 1 a hyperbola.
The polar form of the equation of a conic is often used in dynamics; for instance, determining the orbits of objects revolving about the Sun.
Properties
Just as two (distinct) points determine a line, five points determine a conic. Formally, given any five points in the plane in general linear position, meaning no three collinear, there is a unique conic passing through them, which will be non-degenerate; this is true in both the Euclidean plane and its extension, the real projective plane. Indeed, given any five points there is a conic passing through them, but if three of the points are collinear the conic will be degenerate (reducible, because it contains a line), and may not be unique; see further discussion.
Four points in the plane in general linear position determine a unique conic passing through the first three points and having the fourth point as its center. Thus knowing the center is equivalent to knowing two points on the conic for the purpose of determining the curve.
Furthermore, a conic is determined by any combination of k points in general position that it passes through and 5 – k lines that are tangent to it, for 0≤k≤5.
Any point in the plane is on either zero, one or two tangent lines of a conic. A point on just one tangent line is on the conic. A point on no tangent line is said to be an interior point (or inner point) of the conic, while a point on two tangent lines is an exterior point (or outer point).
All the conic sections share a reflection property that can be stated as: All mirrors in the shape of a non-degenerate conic section reflect light coming from or going toward one focus toward or away from the other focus. In the case of the parabola, the second focus needs to be thought of as infinitely far away, so that the light rays going toward or coming from the second focus are parallel.
Pascal's theorem concerns the collinearity of three points that are constructed from a set of six points on any non-degenerate conic. The theorem also holds for degenerate conics consisting of two lines, but in that case it is known as Pappus's theorem.
Non-degenerate conic sections are always "smooth". This is important for many applications, such as aerodynamics, where a smooth surface is required to ensure laminar flow and to prevent turbulence.
History
Menaechmus and early works
It is believed that the first definition of a conic section was given by Menaechmus (died 320 BC) as part of his solution of the Delian problem (Duplicating the cube). His work did not survive, not even the names he used for these curves, and is only known through secondary accounts. The definition used at that time differs from the one commonly used today. Cones were constructed by rotating a right triangle about one of its legs so the hypotenuse generates the surface of the cone (such a line is called a generatrix). Three types of cones were determined by their vertex angles (measured by twice the angle formed by the hypotenuse and the leg being rotated about in the right triangle). The conic section was then determined by intersecting one of these cones with a plane drawn perpendicular to a generatrix. The type of the conic is determined by the type of cone, that is, by the angle formed at the vertex of the cone: If the angle is acute then the conic is an ellipse; if the angle is right then the conic is a parabola; and if the angle is obtuse then the conic is a hyperbola (but only one branch of the curve).
Euclid (fl. 300 BC) is said to have written four books on conics but these were lost as well. Archimedes (died c. 212 BC) is known to have studied conics, having determined the area bounded by a parabola and a chord in Quadrature of the Parabola. His main interest was in terms of measuring areas and volumes of figures related to the conics and part of this work survives in his book on the solids of revolution of conics, On Conoids and Spheroids.
Apollonius of Perga
The greatest progress in the study of conics by the ancient Greeks is due to Apollonius of Perga (died c. 190 BC), whose eight-volume Conic Sections or Conics summarized and greatly extended existing knowledge. Apollonius's study of the properties of these curves made it possible to show that any plane cutting a fixed double cone (two napped), regardless of its angle, will produce a conic according to the earlier definition, leading to the definition commonly used today. Circles, not constructible by the earlier method, are also obtainable in this way. This may account for why Apollonius considered circles a fourth type of conic section, a distinction that is no longer made. Apollonius used the names 'ellipse', 'parabola' and 'hyperbola' for these curves, borrowing the terminology from earlier Pythagorean work on areas.
Pappus of Alexandria (died c. 350 AD) is credited with expounding on the importance of the concept of a conic's focus, and detailing the related concept of a directrix, including the case of the parabola (which is lacking in Apollonius's known works).
Islamic world
Apollonius's work was translated into Arabic, and much of his work only survives through the Arabic version. Islamic mathematicians found applications of the theory, most notably the Persian mathematician and poet Omar Khayyám, who found a geometrical method of solving cubic equations using conic sections.
A century before the more famous work of Khayyam, Abu al-Jud used conics to solve quartic and cubic equations, although his solution did not deal with all the cases.
An instrument for drawing conic sections was first described in 1000 AD by Al-Kuhi.
Europe

Johannes Kepler extended the theory of conics through the "principle of continuity", a precursor to the concept of limits. Kepler first used the term 'foci' in 1604.
Girard Desargues and Blaise Pascal developed a theory of conics using an early form of projective geometry and this helped to provide impetus for the study of this new field. In particular, Pascal discovered a theorem known as the hexagrammum mysticum from which many other properties of conics can be deduced.
René Descartes and Pierre Fermat both applied their newly discovered analytic geometry to the study of conics. This had the effect of reducing the geometrical problems of conics to problems in algebra. However, it was John Wallis in his 1655 treatise Tractatus de sectionibus conicis who first defined the conic sections as instances of equations of second degree. Written earlier, but published later, Jan de Witt's Elementa Curvarum Linearum starts with Kepler's kinematic construction of the conics and then develops the algebraic equations. This work, which uses Fermat's methodology and Descartes' notation has been described as the first textbook on the subject. De Witt invented the term 'directrix'.
Applications
For specific applications of each type of conic section, see Circle, Ellipse, Parabola, and Hyperbola.Conic sections are important in astronomy: the orbits of two massive objects that interact according to Newton's law of universal gravitation are conic sections if their common center of mass is considered to be at rest. If they are bound together, they will both trace out ellipses; if they are moving apart, they will both follow parabolas or hyperbolas. See two-body problem.
The reflective properties of the conic sections are used in the design of searchlights, radio-telescopes and some optical telescopes. A searchlight uses a parabolic mirror as the reflector, with a bulb at the focus; and a similar construction is used for a parabolic microphone. The 4.2 meter Herschel optical telescope on La Palma, in the Canary islands, uses a primary parabolic mirror to reflect light towards a secondary hyperbolic mirror, which reflects it again to a focus behind the first mirror.
In the real projective plane
The conic sections have some very similar properties in the Euclidean plane and the reasons for this become clearer when the conics are viewed from the perspective of a larger geometry. The Euclidean plane may be embedded in the real projective plane and the conics may be considered as objects in this projective geometry. One way to do this is to introduce homogeneous coordinates and define a conic to be the set of points whose coordinates satisfy an irreducible quadratic equation in three variables (or equivalently, the zeros of an irreducible quadratic form). More technically, the set of points that are zeros of a quadratic form (in any number of variables) is called a quadric, and the irreducible quadrics in a two dimensional projective space (that is, having three variables) are traditionally called conics.
The Euclidean plane R is embedded in the real projective plane by adjoining a line at infinity (and its corresponding points at infinity) so that all the lines of a parallel class meet on this line. On the other hand, starting with the real projective plane, a Euclidean plane is obtained by distinguishing some line as the line at infinity and removing it and all its points.
Intersection at infinity
In a projective space over any division ring, but in particular over either the real or complex numbers, all non-degenerate conics are equivalent, and thus in projective geometry one speaks of "a conic" without specifying a type. That is, there is a projective transformation that will map any non-degenerate conic to any other non-degenerate conic.
The three types of conic sections will reappear in the affine plane obtained by choosing a line of the projective space to be the line at infinity. The three types are then determined by how this line at infinity intersects the conic in the projective space. In the corresponding affine space, one obtains an ellipse if the conic does not intersect the line at infinity, a parabola if the conic intersects the line at infinity in one double point corresponding to the axis, and a hyperbola if the conic intersects the line at infinity in two points corresponding to the asymptotes.
Homogeneous coordinates
In homogeneous coordinates a conic section can be represented as:
Or in matrix notation
The 3 × 3 matrix above is called the matrix of the conic section.
Some authors prefer to write the general homogeneous equation as
(or some variation of this) so that the matrix of the conic section has the simpler form,
but this notation is not used in this article.
If the determinant of the matrix of the conic section is zero, the conic section is degenerate.
As multiplying all six coefficients by the same non-zero scalar yields an equation with the same set of zeros, one can consider conics, represented by (A, B, C, D, E, F) as points in the five-dimensional projective space
Projective definition of a circle
Metrical concepts of Euclidean geometry (concepts concerned with measuring lengths and angles) can not be immediately extended to the real projective plane. They must be redefined (and generalized) in this new geometry. This can be done for arbitrary projective planes, but to obtain the real projective plane as the extended Euclidean plane, some specific choices have to be made.
Fix an arbitrary line in a projective plane that shall be referred to as the absolute line. Select two distinct points on the absolute line and refer to them as absolute points. Several metrical concepts can be defined with reference to these choices. For instance, given a line containing the points A and B, the midpoint of line segment AB is defined as the point C which is the projective harmonic conjugate of the point of intersection of AB and the absolute line, with respect to A and B.
A conic in a projective plane that contains the two absolute points is called a circle. Since five points determine a conic, a circle (which may be degenerate) is determined by three points. To obtain the extended Euclidean plane, the absolute line is chosen to be the line at infinity of the Euclidean plane and the absolute points are two special points on that line called the circular points at infinity. Lines containing two points with real coordinates do not pass through the circular points at infinity, so in the Euclidean plane a circle, under this definition, is determined by three points that are not collinear.
It has been mentioned that circles in the Euclidean plane can not be defined by the focus-directrix property. However, if one were to consider the line at infinity as the directrix, then by taking the eccentricity to be e = 0 a circle will have the focus-directrix property, but it is still not defined by that property. One must be careful in this situation to correctly use the definition of eccentricity as the ratio of the distance of a point on the circle to the focus (length of a radius) to the distance of that point to the directrix (this distance is infinite) which gives the limiting value of zero.
Steiner's projective conic definition
Main article: Steiner conic
A synthetic (coordinate-free) approach to defining the conic sections in a projective plane was given by Jakob Steiner in 1867.
- Given two pencils of lines at two points (all lines containing and resp.) and a projective but not perspective mapping of onto . Then the intersection points of corresponding lines form a non-degenerate projective conic section.
A perspective mapping of a pencil onto a pencil is a bijection (1-1 correspondence) such that corresponding lines intersect on a fixed line , which is called the axis of the perspectivity .
A projective mapping is a finite sequence of perspective mappings.
As a projective mapping in a projective plane over a field (pappian plane) is uniquely determined by prescribing the images of three lines, for the Steiner generation of a conic section, besides two points only the images of 3 lines have to be given. These 5 items (2 points, 3 lines) uniquely determine the conic section.
Line conics
By the Principle of Duality in a projective plane, the dual of each point is a line, and the dual of a locus of points (a set of points satisfying some condition) is called an envelope of lines. Using Steiner's definition of a conic (this locus of points will now be referred to as a point conic) as the meet of corresponding rays of two related pencils, it is easy to dualize and obtain the corresponding envelope consisting of the joins of corresponding points of two related ranges (points on a line) on different bases (the lines the points are on). Such an envelope is called a line conic (or dual conic).
In the real projective plane, a point conic has the property that every line meets it in two points (which may coincide, or may be complex) and any set of points with this property is a point conic. It follows dually that a line conic has two of its lines through every point and any envelope of lines with this property is a line conic. At every point of a point conic there is a unique tangent line, and dually, on every line of a line conic there is a unique point called a point of contact. An important theorem states that the tangent lines of a point conic form a line conic, and dually, the points of contact of a line conic form a point conic.
Von Staudt's definition
Main article: Von Staudt conicKarl Georg Christian von Staudt defined a conic as the point set given by all the absolute points of a polarity that has absolute points. Von Staudt introduced this definition in Geometrie der Lage (1847) as part of his attempt to remove all metrical concepts from projective geometry.
A polarity, π, of a projective plane P is an involutory bijection between the points and the lines of P that preserves the incidence relation. Thus, a polarity associates a point Q with a line q by π(Q) = q and π(q) = Q. Following Gergonne, q is called the polar of Q and Q the pole of q. An absolute point (or line) of a polarity is one which is incident with its polar (pole).
A von Staudt conic in the real projective plane is equivalent to a Steiner conic.
Constructions
No continuous arc of a conic can be constructed with straightedge and compass. However, there are several straightedge-and-compass constructions for any number of individual points on an arc.
One of them is based on the converse of Pascal's theorem, namely, if the points of intersection of opposite sides of a hexagon are collinear, then the six vertices lie on a conic. Specifically, given five points, A, B, C, D, E and a line passing through E, say EG, a point F that lies on this line and is on the conic determined by the five points can be constructed. Let AB meet DE in L, BC meet EG in M and let CD meet LM at N. Then AN meets EG at the required point F. By varying the line through E, as many additional points on the conic as desired can be constructed.
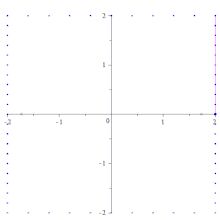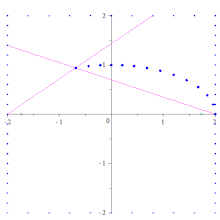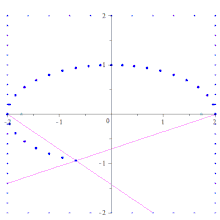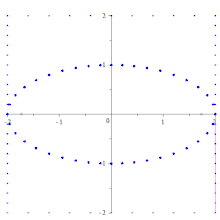
Another method, based on Steiner's construction and which is useful in engineering applications, is the parallelogram method, where a conic is constructed point by point by means of connecting certain equally spaced points on a horizontal line and a vertical line. Specifically, to construct the ellipse with equation x/a + y/b = 1, first construct the rectangle ABCD with vertices A(a, 0), B(a, 2b), C(−a, 2b) and D(−a, 0). Divide the side BC into n equal segments and use parallel projection, with respect to the diagonal AC, to form equal segments on side AB (the lengths of these segments will be b/a times the length of the segments on BC). On the side BC label the left-hand endpoints of the segments with A1 to An starting at B and going towards C. On the side AB label the upper endpoints D1 to Dn starting at A and going towards B. The points of intersection, AAi ∩ DDi for 1 ≤ i ≤ n will be points of the ellipse between A and P(0, b). The labeling associates the lines of the pencil through A with the lines of the pencil through D projectively but not perspectively. The sought for conic is obtained by this construction since three points A, D and P and two tangents (the vertical lines at A and D) uniquely determine the conic. If another diameter (and its conjugate diameter) are used instead of the major and minor axes of the ellipse, a parallelogram that is not a rectangle is used in the construction, giving the name of the method. The association of lines of the pencils can be extended to obtain other points on the ellipse. The constructions for hyperbolas and parabolas are similar.
Yet another general method uses the polarity property to construct the tangent envelope of a conic (a line conic).
In the complex geometry
In the complex coordinate plane C, ellipses and hyperbolas are not distinct: one may consider a hyperbola as an ellipse with an imaginary axis length. For example, the ellipse becomes a hyperbola under the substitution geometrically a complex rotation, yielding . Thus there is a 2-way classification: ellipse/hyperbola and parabola. Extending the curves to the complex projective plane, this corresponds to intersecting the line at infinity in either 2 distinct points (corresponding to two asymptotes) or in 1 double point (corresponding to the axis of a parabola); thus the real hyperbola is a more suggestive real image for the complex ellipse/hyperbola, as it also has 2 (real) intersections with the line at infinity.
Further unification occurs in the complex projective plane CP: the non-degenerate conics cannot be distinguished from one another, since any can be taken to any other by a projective linear transformation.
It can be proven that in CP, two conic sections have four points in common (if one accounts for multiplicity), so there are between 1 and 4 intersection points. The intersection possibilities are: four distinct points, two singular points and one double point, two double points, one singular point and one with multiplicity 3, one point with multiplicity 4. If any intersection point has multiplicity > 1, the two curves are said to be tangent. If there is an intersection point of multiplicity at least 3, the two curves are said to be osculating. If there is only one intersection point, which has multiplicity 4, the two curves are said to be superosculating.
Furthermore, each straight line intersects each conic section twice. If the intersection point is double, the line is a tangent line. Intersecting with the line at infinity, each conic section has two points at infinity. If these points are real, the curve is a hyperbola; if they are imaginary conjugates, it is an ellipse; if there is only one double point, it is a parabola. If the points at infinity are the cyclic points and , the conic section is a circle. If the coefficients of a conic section are real, the points at infinity are either real or complex conjugate.
Degenerate cases
Further information: Degenerate conicWhat should be considered as a degenerate case of a conic depends on the definition being used and the geometric setting for the conic section. There are some authors who define a conic as a two-dimensional nondegenerate quadric. With this terminology there are no degenerate conics (only degenerate quadrics), but we shall use the more traditional terminology and avoid that definition.
In the Euclidean plane, using the geometric definition, a degenerate case arises when the cutting plane passes through the apex of the cone. The degenerate conic is either: a point, when the plane intersects the cone only at the apex; a straight line, when the plane is tangent to the cone (it contains exactly one generator of the cone); or a pair of intersecting lines (two generators of the cone). These correspond respectively to the limiting forms of an ellipse, parabola, and a hyperbola.
If a conic in the Euclidean plane is being defined by the zeros of a quadratic equation (that is, as a quadric), then the degenerate conics are: the empty set, a point, or a pair of lines which may be parallel, intersect at a point, or coincide. The empty set case may correspond either to a pair of complex conjugate parallel lines such as with the equation or to an imaginary ellipse, such as with the equation An imaginary ellipse does not satisfy the general definition of a degeneracy, and is thus not normally considered as degenerated. The two lines case occurs when the quadratic expression factors into two linear factors, the zeros of each giving a line. In the case that the factors are the same, the corresponding lines coincide and we refer to the line as a double line (a line with multiplicity 2) and this is the previous case of a tangent cutting plane.
In the real projective plane, since parallel lines meet at a point on the line at infinity, the parallel line case of the Euclidean plane can be viewed as intersecting lines. However, as the point of intersection is the apex of the cone, the cone itself degenerates to a cylinder, i.e. with the apex at infinity. Other sections in this case are called cylindric sections. The non-degenerate cylindrical sections are ellipses (or circles).
When viewed from the perspective of the complex projective plane, the degenerate cases of a real quadric (i.e., the quadratic equation has real coefficients) can all be considered as a pair of lines, possibly coinciding. The empty set may be the line at infinity considered as a double line, a (real) point is the intersection of two complex conjugate lines and the other cases as previously mentioned.
To distinguish the degenerate cases from the non-degenerate cases (including the empty set with the latter) using matrix notation, let β be the determinant of the 3 × 3 matrix of the conic section—that is, β = (AC − B/4)F + BED − CD − AE/4; and let α = B − 4AC be the discriminant. Then the conic section is non-degenerate if and only if β ≠ 0. If β = 0 we have a point when α < 0, two parallel lines (possibly coinciding) when α = 0, or two intersecting lines when α > 0.
Pencil of conics
Main article: Pencil (mathematics) § Pencil of conicsA (non-degenerate) conic is completely determined by five points in general position (no three collinear) in a plane and the system of conics which pass through a fixed set of four points (again in a plane and no three collinear) is called a pencil of conics. The four common points are called the base points of the pencil. Through any point other than a base point, there passes a single conic of the pencil. This concept generalizes a pencil of circles.
Intersecting two conics
The solutions to a system of two second degree equations in two variables may be viewed as the coordinates of the points of intersection of two generic conic sections. In particular two conics may possess none, two or four possibly coincident intersection points. An efficient method of locating these solutions exploits the homogeneous matrix representation of conic sections, i.e. a 3 × 3 symmetric matrix which depends on six parameters.
The procedure to locate the intersection points follows these steps, where the conics are represented by matrices:
- given the two conics and , consider the pencil of conics given by their linear combination
- identify the homogeneous parameters which correspond to the degenerate conic of the pencil. This can be done by imposing the condition that and solving for and . These turn out to be the solutions of a third degree equation.
- given the degenerate conic , identify the two, possibly coincident, lines constituting it.
- intersect each identified line with either one of the two original conics.
- the points of intersection will represent the solutions to the initial equation system.
Generalizations
Conics may be defined over other fields (that is, in other pappian geometries). However, some care must be used when the field has characteristic 2, as some formulas can not be used. For example, the matrix representations used above require division by 2.
A generalization of a non-degenerate conic in a projective plane is an oval. An oval is a point set that has the following properties, which are held by conics: 1) any line intersects an oval in none, one or two points, 2) at any point of the oval there exists a unique tangent line.
Generalizing the focus properties of conics to the case where there are more than two foci produces sets called generalized conics.
The intersection of an elliptic cone with a sphere is a spherical conic, which shares many properties with planar conics.
In other areas of mathematics
The classification into elliptic, parabolic, and hyperbolic is pervasive in mathematics, and often divides a field into sharply distinct subfields. The classification mostly arises due to the presence of a quadratic form (in two variables this corresponds to the associated discriminant), but can also correspond to eccentricity.
Quadratic form classifications:
- Quadratic forms
- Quadratic forms over the reals are classified by Sylvester's law of inertia, namely by their positive index, zero index, and negative index: a quadratic form in variables can be converted to a diagonal form, as where the number of +1 coefficients, is the positive index, the number of −1 coefficients, is the negative index, and the remaining variables are the zero index so In two variables the non-zero quadratic forms are classified as:
- — positive-definite (the negative is also included), corresponding to ellipses,
- — degenerate, corresponding to parabolas, and
- — indefinite, corresponding to hyperbolas.
- In two variables quadratic forms are classified by discriminant, analogously to conics, but in higher dimensions the more useful classification is as definite, (all positive or all negative), degenerate, (some zeros), or indefinite (mix of positive and negative but no zeros). This classification underlies many that follow.
- Curvature
- The Gaussian curvature of a surface describes the infinitesimal geometry, and may at each point be either positive – elliptic geometry, zero – Euclidean geometry (flat, parabola), or negative – hyperbolic geometry; infinitesimally, to second order the surface looks like the graph of (or 0), or . Indeed, by the uniformization theorem every surface can be taken to be globally (at every point) positively curved, flat, or negatively curved. In higher dimensions the Riemann curvature tensor is a more complicated object, but manifolds with constant sectional curvature are interesting objects of study, and have strikingly different properties, as discussed at sectional curvature.
- Second order PDEs
- Partial differential equations (PDEs) of second order are classified at each point as elliptic, parabolic, or hyperbolic, accordingly as their second order terms correspond to an elliptic, parabolic, or hyperbolic quadratic form. The behavior and theory of these different types of PDEs are strikingly different – representative examples is that the Poisson equation is elliptic, the heat equation is parabolic, and the wave equation is hyperbolic.
Eccentricity classifications include:
- Möbius transformations
- Real Möbius transformations (elements of PSL2(R) or its 2-fold cover, SL2(R)) are classified as elliptic, parabolic, or hyperbolic accordingly as their half-trace is or mirroring the classification by eccentricity.
- Variance-to-mean ratio
- The variance-to-mean ratio classifies several important families of discrete probability distributions: the constant distribution as circular (eccentricity 0), binomial distributions as elliptical, Poisson distributions as parabolic, and negative binomial distributions as hyperbolic. This is elaborated at cumulants of some discrete probability distributions.

See also
- Confocal conic sections
- Circumconic and inconic
- Director circle
- Elliptic coordinate system
- Equidistant set
- Parabolic coordinates
- Quadratic function
- Spherical conic
Notes
- The empty set is included as a degenerate conic, since it may arise as a solution of this equation.
- According to Plutarch, this solution was rejected by Plato on the grounds that it could not be achieved using only straightedge and compass, however this interpretation of Plutarch's statement has come under criticism. Boyer 2004, p.14, footnote 14.
- This form of the equation does not generalize to fields of characteristic two.
- Consider finding the midpoint of a line segment with one endpoint on the line at infinity.
- Coxeter and several other authors use the term 'self-conjugate' instead of 'absolute'.
References
- Eves 1963, p. 319
- Brannan, Esplen & Gray 1999, p. 13
- Cohen, D., Precalculus: With Unit Circle Trigonometry (Stamford: Thomson Brooks/Cole, 2006), p. 844.
- Thomas & Finney 1979, p. 434
- Brannan, Esplen & Gray 1999, p. 19; Kendig 2005, pp. 86, 141
- Brannan, Esplen & Gray 1999, pp. 13–16
- Brannan, Esplen & Gray 1999, pp. 11–16
- Protter & Morrey 1970, pp. 314–328, 585–589
- Protter & Morrey 1970, pp. 290–314
- Wilson & Tracey 1925, p. 130
- Protter & Morrey 1970, p. 316
- Brannan, Esplen & Gray 1999, p. 30
- Fanchi, John R. (2006), Math refresher for scientists and engineers, John Wiley and Sons, pp. 44–45, ISBN 0-471-75715-2, Section 3.2, page 45
- ^ Protter & Morrey 1970, p. 326
- Wilson & Tracey 1925, p. 153
- Pettofrezzo, Anthony, Matrices and Transformations, Dover Publ., 1966, p. 110.
- ^ Spain, B., Analytical Conics (Mineola, NY: Dover, 2007). Originally published in 1957 by Pergamon.
- Ayoub, Ayoub B., "The eccentricity of a conic section", The College Mathematics Journal 34(2), March 2003, 116–121.
- Ayoub, A. B., "The central conic sections revisited", Mathematics Magazine 66(5), 1993, 322–325.
- Brannan, Esplen & Gray 1999, p. 17
- Whitworth, William Allen. Trilinear Coordinates and Other Methods of Modern Analytical Geometry of Two Dimensions, Forgotten Books, 2012 (orig. Deighton, Bell, and Co., 1866), p. 203.
- Pamfilos, Paris (2014). "A gallery of conics by five elements" (PDF). Forum Geometricorum. 14: 295–348.
- Brannan, Esplen & Gray 1999, p. 28
- Downs 2003, pp. 36ff.
- Boyer 2004, pp. 17–18
- Boyer 2004, p. 18
- Katz 1998, p. 117
- Heath, T.L., The Thirteen Books of Euclid's Elements, Vol. I, Dover, 1956, pg.16
- Eves 1963, p. 28
- Apollonius of Perga, Treatise on Conic Sections, edited by T. L. Heath (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013).
- Eves 1963, p. 30.
- Boyer 2004, p. 36.
- Turner, Howard R. (1997). Science in Medieval Islam: An Illustrated Introduction. University of Texas Press. p. 53. ISBN 0-292-78149-0.
- Boyer, C. B., & Merzbach, U. C., A History of Mathematics (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1968), p. 219.
- Van der Waerden, B. L., Geometry and Algebra in Ancient Civilizations (Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer Verlag, 1983), p. 73.
- Sidoli, Nathan; Brummelen, Glen Van (2013-10-30). From Alexandria, Through Baghdad: Surveys and Studies in the Ancient Greek and Medieval Islamic Mathematical Sciences in Honor of J.L. Berggren. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 110. ISBN 978-3-642-36736-6.
- Waerden, Bartel L. van der (2013-06-29). A History of Algebra: From al-Khwārizmī to Emmy Noether. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 29. ISBN 978-3-642-51599-6.
- Stillwell, John (2010). Mathematics and its history (3rd ed.). New York: Springer. p. 30. ISBN 978-1-4419-6052-8.
- "Apollonius of Perga Conics Books One to Seven" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 May 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- Katz 1998, p. 126.
- Boyer 2004, p. 110.
- ^ Boyer 2004, p. 114.
- Brannan, Esplen & Gray 1999, p. 27
- Artzy 2008, p. 158, Thm 3-5.1
- Artzy 2008, p. 159
- Faulkner 1952, p. 71
- Faulkner 1952, p. 72
- Eves 1963, p. 320
- Coxeter 1993, p. 80
- Hartmann, p. 38
- Merserve 1983, p. 65
- Jacob Steiner's Vorlesungen über synthetische Geometrie, B. G. Teubner, Leipzig 1867 (from Google Books: (German) Part II follows Part I) Part II, pg. 96
- Hartmann, p. 19
- Faulkner 1952, pp. 48–49.
- Coxeter 1964, p. 60
- Coxeter 1964, p. 80
- Faulkner 1952, pp. 52–53
- Downs 2003, p. 5
- Downs 2003, p. 14
- Downs 2003, p. 19
- Akopyan & Zaslavsky 2007, p. 70
- Wilczynski, E. J. (1916), "Some remarks on the historical development and the future prospects of the differential geometry of plane curves", Bull. Amer. Math. Soc., 22 (7): 317–329, doi:10.1090/s0002-9904-1916-02785-6.
- Brannan, Esplen & Gray 1999, p. 6
- Korn, G. A., & Korn, T. M., Mathematical Handbook for Scientists and Engineers: Definitions, Theorems, and Formulas for Reference and Review (Mineola, NY: Dover Publications, 1961), p. 42.
- "MathWorld: Cylindric section".
- Lawrence, J. Dennis (1972), A Catalog of Special Plane Curves, Dover, p. 63, ISBN 0-486-60288-5
- Faulkner 1952, pg. 64.
- Berger, M., Geometry Revealed: A Jacob's Ladder to Modern Higher Geometry (Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer, 2010), p. 127.
- Richter-Gebert 2011, p. 196
Bibliography
- Akopyan, A.V.; Zaslavsky, A.A. (2007). Geometry of Conics. American Mathematical Society. ISBN 978-0-8218-4323-9.
- Artzy, Rafael (2008) , Linear Geometry, Dover, ISBN 978-0-486-46627-9
- Boyer, Carl B. (2004) , History of Analytic Geometry, Dover, ISBN 978-0-486-43832-0
- Brannan, David A.; Esplen, Matthew F.; Gray, Jeremy J. (1999), Geometry, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-59787-6
- Coxeter, H.S.M. (1964), Projective Geometry, Blaisdell, ISBN 9780387406237
- Coxeter, H.S.M. (1993), The Real Projective Plane, Springer Science & Business Media
- Downs, J.W. (2003) , Practical Conic Sections: The geometric properties of ellipses, parabolas and hyperbolas, Dover, ISBN 0-486-42876-1
- Eves, Howard (1963), A Survey of Geometry (Volume One), Boston: Allyn and Bacon
- Glaeser, Georg; Stachel, Hellmuth; Odehnal, Boris (2016), The Universe of Conics: From the ancient Greeks to 21st century developments, Berlin: Springer
- Hartmann, Erich, Planar Circle Geometries, an Introduction to Moebius-, Laguerre- and Minkowski Planes (PDF), retrieved 20 September 2014 (PDF; 891 kB).
- Katz, Victor J. (1998), A History of Mathematics / An Introduction (2nd ed.), Addison Wesley Longman, ISBN 978-0-321-01618-8
- Kendig, Keith (2005), Conics, The Mathematical Association of America, ISBN 978-0-88385-335-1
- Faulkner, T. E. (1952), Projective Geometry (2nd ed.), Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd, ISBN 9780486154893
- Merserve, Bruce E. (1983) , Fundamental Concepts of Geometry, Dover, ISBN 0-486-63415-9
- Protter, Murray H.; Morrey, Charles B. Jr. (1970), College Calculus with Analytic Geometry (2nd ed.), Reading: Addison-Wesley, LCCN 76087042
- Richter-Gebert, Jürgen (2011). Perspectives on Projective Geometry: A Guided Tour Through Real and Complex Geometry. Springer. ISBN 9783642172854.
- Samuel, Pierre (1988), Projective Geometry, Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics (Readings in Mathematics), New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 0-387-96752-4
- Thomas, George B.; Finney, Ross L. (1979), Calculus and Analytic Geometry (fifth ed.), Addison-Wesley, p. 434, ISBN 0-201-07540-7
- Wilson, W.A.; Tracey, J.I. (1925), Analytic Geometry (Revised ed.), D.C. Heath and Company
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Conic Section". MathWorld.
- Occurrence of the conics. Conics in nature and elsewhere.
| Topics in algebraic curves | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rational curves | |||||||||||
| Elliptic curves |
| ||||||||||
| Higher genus | |||||||||||
| Plane curves | |||||||||||
| Riemann surfaces | |||||||||||
| Constructions | |||||||||||
| Structure of curves |
| ||||||||||
 The geometric properties of the conic can be deduced from its equation.
The geometric properties of the conic can be deduced from its equation.
 and the angle between the cutting plane and the axis is
and the angle between the cutting plane and the axis is  the eccentricity is
the eccentricity is 



 .
.
























 ,
,



 , called the
, called the 



 This has precisely one positive solution—the eccentricity— in the case of a parabola or ellipse, while in the case of a hyperbola it has two positive solutions, one of which is the eccentricity.
This has precisely one positive solution—the eccentricity— in the case of a parabola or ellipse, while in the case of a hyperbola it has two positive solutions, one of which is the eccentricity.

 as
as


 and
and  are the
are the  — that is, the solutions of the equation
— that is, the solutions of the equation

 is the determinant of the
is the determinant of the  is again the determinant of the 2 × 2 matrix. In the case of an ellipse the squares of the two semi-axes are given by the denominators in the canonical form.
is again the determinant of the 2 × 2 matrix. In the case of an ellipse the squares of the two semi-axes are given by the denominators in the canonical form.






 of lines at two points
of lines at two points  (all lines containing
(all lines containing  and
and  resp.) and a
resp.) and a  of
of  onto
onto  . Then the intersection points of corresponding lines form a non-degenerate projective conic section.
. Then the intersection points of corresponding lines form a non-degenerate projective conic section. , which is called the axis of the perspectivity
, which is called the axis of the perspectivity  becomes a hyperbola under the substitution
becomes a hyperbola under the substitution  geometrically a complex rotation, yielding
geometrically a complex rotation, yielding  . Thus there is a 2-way classification: ellipse/hyperbola and parabola. Extending the curves to the
. Thus there is a 2-way classification: ellipse/hyperbola and parabola. Extending the curves to the  or to an imaginary ellipse, such as with the equation
or to an imaginary ellipse, such as with the equation  An imaginary ellipse does not satisfy the general definition of a
An imaginary ellipse does not satisfy the general definition of a  and
and  , consider the pencil of conics given by their linear combination
, consider the pencil of conics given by their linear combination 
 which correspond to the degenerate conic of the pencil. This can be done by imposing the condition that
which correspond to the degenerate conic of the pencil. This can be done by imposing the condition that  and solving for
and solving for  and
and  . These turn out to be the solutions of a third degree equation.
. These turn out to be the solutions of a third degree equation. , identify the two, possibly coincident, lines constituting it.
, identify the two, possibly coincident, lines constituting it. variables can be converted to a
variables can be converted to a  where the number of +1 coefficients,
where the number of +1 coefficients,  is the positive index, the number of −1 coefficients,
is the positive index, the number of −1 coefficients,  is the negative index, and the remaining variables are the zero index
is the negative index, and the remaining variables are the zero index  so
so  In two variables the non-zero quadratic forms are classified as:
In two variables the non-zero quadratic forms are classified as:
 — positive-definite (the negative is also included), corresponding to ellipses,
— positive-definite (the negative is also included), corresponding to ellipses, — degenerate, corresponding to parabolas, and
— degenerate, corresponding to parabolas, and — indefinite, corresponding to hyperbolas.
— indefinite, corresponding to hyperbolas.

 or
or  mirroring the classification by eccentricity.
mirroring the classification by eccentricity.