| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Cytidine 5′-(tetrahydrogen triphosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name O-{methyl} tetrahydrogen triphosphate | |
| Other names CTP; Cytidine-5'-triphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.556 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| MeSH | Cytidine+triphosphate |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C9H16N3O14P3 |
| Molar mass | 483.156 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
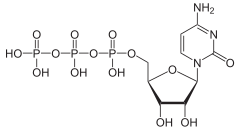
Cytidine triphosphate (CTP) is a pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate. CTP, much like ATP, consists of a ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups. The major difference between the two molecules is the base used, which in CTP is cytosine.
CTP is a substrate in the synthesis of RNA.
CTP is a high-energy molecule similar to ATP, but its role as an energy coupler is limited to a much smaller subset of metabolic reactions. CTP is a coenzyme in metabolic reactions like the synthesis of glycerophospholipids, where it is used for activation and transfer of diacylglycerol and lipid head groups, and glycosylation of proteins.
CTP acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme aspartate carbamoyltransferase, which is used in pyrimidine biosynthesis.
See also
References
- Buchanan BB, Gruissem W, Jones RL (2000). Biochemistry & molecular biology of plants (1st ed.). American society of plant physiology. ISBN 978-0-943088-39-6.
- Blackburn, G. Michael. Nucleic Acids in Chemistry and Biology. The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2006, p. 119-120.
| Nucleic acid constituents | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleobase | |||||||
| Nucleoside |
| ||||||
| Nucleotide (Nucleoside monophosphate) |
| ||||||
| Nucleoside diphosphate | |||||||
| Nucleoside triphosphate | |||||||