The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the paleohispanic scripts that present signs with syllabic value, for the occlusives and signs with monophonemic value for the rest of consonants and vowels.
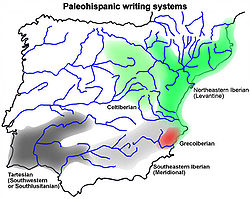
Location of findings

The inscriptions that use the Greco-Iberian alphabet had been found mainly in Alicante and Murcia and the direction of the writing is left to right, or sinistroverse. The number of known Greco-Iberian inscriptions is small: fewer than two dozen ceramic inscriptions and a dozen lead plaques, among them the lead plaque from La Serreta (Alcoy, Alicante) and the lead plaque from El Cigarralejo (Mula, Murcia). The archaeological context of the Greco-Iberian inscriptions seems to concentrate in the 4th century BC, but the paleographic characteristics of the model indicate that the adaptation may date from the 5th century BC.
Typology

The Greco-Iberian alphabet contains 16 signs identical to Greek signs, except for the sign corresponding to the second rhotic consonant: five vowels, three voiced occlusives (labial, dental and velar), but only two voiceless occlusives (dental and velar), two sibilants, two rhotics, one lateral, and only one nasal sign. To represent the second rhotic , rho gets an additional stroke. Eta is used instead of epsilon to represent /e/. The only letter not found in the modern variant of the Greek alphabet is sampi.
The letter forms are petroglyphic since the writing surface (ceramic, stone, lead) affords angular glyphs with straight lines.
| Vowels | Occlusives | Sibilant, Rhotic, Lateral | Nasal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha | Α | Gamma | Γ | Sampi | Ͳ | Nu | Ν |
| Eta | Η | Kappa | Κ | Sigma | Σ | ||
| Iota | Ι | Tau | Τ | Rho’ | Ρ̓ | ||
| Omicron | Ο | Delta | Δ | Rho | Ρ | ||
| Upsilon | Υ | Beta | Β | Lambda | Λ | ||
See also
- Celtiberian script
- Iberian languages
- Iberian scripts
- Northeastern Iberian script
- Southeastern Iberian script
- Tartessian script
- Paleohispanic languages
- Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula
Notes
Bibliography
- Gómez-Moreno, Manuel (1922): «De Epigrafia ibérica: el plomo de Alcoy», Revista de filología española 9, pp. 341–366.
- Hoz, Javier de (1987): «La escritura greco-ibérica», Veleia 2–3, pp. 285–298.
- Hoz, Javier de (1998): «Epigrafía griega de occidente y escritura greco-ibérica», Los griegos en España, pp. 180–196.
- Rodríguez Ramos, Jesús (2005): «Introducció a l’estudi de les inscripcions ibèriques», Revista de la Fundació Privada Catalana per l’Arqueologia ibèrica, 1, pp. 13–144.
- Untermann, Jürgen (1990): Monumenta Linguarum Hispanicarum. III Die iberischen Inschriften aus Spanien, Wiesbaden.
- Velaza, Javier (1996): Epigrafía y lengua ibéricas, Barcelona.
External links
- The Greek-Iberian writing- Jesús Rodríguez Ramos
- Detailed map of the Pre-Roman Peoples of Iberia (around 200 BC)