| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Hafnium triiodide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| PubChem CID |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | HfI3 |
| Molar mass | 559.20 g·mol |
| Appearance | black crystals |
| Melting point | decomposes |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Hafnium(III) chloride Hafnium(III) bromide |
| Other cations | Titanium(III) iodide Zirconium(III) iodide |
| Related compounds | Hafnium(IV) iodide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Hafnium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound of hafnium and iodine with the formula Hf I3. It is a black solid.
Preparation
Like other group 4 trihalides, hafnium(III) iodide can be prepared from hafnium(IV) iodide by high-temperature reduction with hafnium metal, although incomplete reaction and contamination of the product with excess metal often occurs.
- 3 Hf I4 + Hf → 4 Hf I3
Other metals can be used as the reducing agent, for example aluminium. The product is often nonstoichiometric, with the compositions Hf I3.2–3.3 and Hf I3.0–3.5 reported.
Structure and bonding
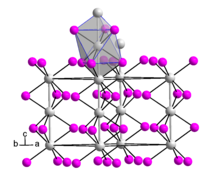
Hafnium(III) iodide adopts the same crystal structure as zirconium(III) iodide. This is very similar to the β-TiCl3 structure. The structure is based on hexagonal close packing of iodide ions with one third of the octahedral interstices occupied by Hf ions. It consists of parallel chains of face-sharing {HfI6} octahedra.
Hafnium(III) iodide has a lower magnetic moment than is expected for the d metal ion Hf, indicating non-negligible Hf–Hf bonding. The Hf–Hf separation was originally reported to be 3.295 Å, but a subsequent study of nonstoichiometric hafnium(III) iodide indicated a lower symmetry structure.
Reactivity
Like the chloride and bromide, hafnium(III) iodide is a powerful enough reducing agent to reduce water and therefore does not have any aqueous chemistry.
References
- William M. Haynes, ed. (2013). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (93rd ed.). CRC Press. p. 4–66. ISBN 978-1466571143.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 965. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Struss, Arthur W.; Corbett, John D. (1969). "Lower halides of hafnium. Nonstoichiometric hafnium triiodide phase". Inorg. Chem. 8 (2): 227–232. doi:10.1021/ic50072a009.
- Clark, R. J. H.; Bradley, D. C.; Thornton, P. (2013). The Chemistry of Titanium, Zirconium and Hafnium Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 432. ISBN 978-1-4831-5921-8.
- ^ Wells, A. F. (1984). Structural Inorganic Chemistry (5th ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 418–419. ISBN 978-0-19-965763-6.
- Dahl, Lawrence F.; Chiang, Tao-I; Seabaugh, Pyrtle W.; Larsen, Edwin M. (1964). "Structural Studies of Zirconium Trihalides and Hafnium Triiodide". Inorg. Chem. 3 (9): 1236–1242. doi:10.1021/ic50019a008.
| Hafnium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Hf(II) | |
| Hf(III) | |
| Hf(IV) | |
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the iodide ion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||