| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Acute interstitial pneumonitis" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| HR syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Acute interstitial pneumonia or Hamman–Rich syndrome |
 | |
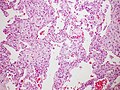
| Micrograph of diffuse alveolar damage, the histologic correlate of acute interstitial pneumonitis. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Pulmonology |
Acute interstitial pneumonitis (also known as acute interstitial pneumonia) is a rare, severe lung disease that usually affects otherwise healthy individuals. There is no known cause or cure.
Acute interstitial pneumonitis is often categorized as both an interstitial lung disease and a form of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). In uncommon instances, if ARDS appears acutely, in the absence of known triggers, and follows a rapidly progressing clinical course, the term "Acute interstitial pneumonia" is used. ARDS is distinguished from the chronic forms of interstitial pneumonia such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Symptoms and signs
The most common symptoms of acute interstitial pneumonitis are highly productive cough with expectoration of thick mucus, fever, and difficulties breathing. These often occur over a period of one to two weeks before medical attention is sought. The presence of fluid means the person experiences a feeling similar to 'drowning'. Difficulties breathing can quickly progress to an inability to breathe without support (respiratory failure).
Acute interstitial pneumonitis typically progresses rapidly, with hospitalization and mechanical ventilation often required only days to weeks after initial symptoms of cough, fever, and difficulties breathing develop.
Diagnosis
Rapid progression from initial symptoms to respiratory failure is a key feature. An X-ray that shows ARDS is necessary for diagnosis (fluid in the small air sacs (alveoli) in both lungs). In addition, a biopsy of the lung that shows organizing diffuse alveolar damage is required for diagnosis. This type of alveolar damage can be attributed to nonconcentrated and nonlocalized alveoli damage, marked alveolar septal edema with inflammatory cell infiltration, fibroblast proliferation, occasional hyaline membranes, and thickening of the alveolar walls. The septa are lined with atypical, hyperplastic type II pneumocytes, thus leading to the collapse of airspaces. Other diagnostic tests are useful in excluding other similar conditions, but history, X-ray, and biopsy are essential. These other tests may include basic blood work, blood cultures, and bronchoalveolar lavage.
The clinical picture is similar to ARDS, but AIP differs from ARDS in that the cause for AIP is not known.
Treatment
Treatment is primarily supportive. Management in an intensive care unit is required and the need for mechanical ventilation is common. Therapy with corticosteroids is generally attempted, though their usefulness has not been established. The only treatment that has met with success to date is a lung transplant.
Prognosis
Sixty percent of people with acute interstitial pneumonitis will die in the first six months of illness. The median survival is 1+1⁄2 months. However, most people who have one episode do not have a second. People who survive often recover lung function completely.
Epidemiology
Acute interstitial pneumonitis occurs most frequently among people older than forty years old. It affects men and women equally. There are no known risk factors; in particular, smoking is not associated with increased risk.
History
Acute interstitial pneumonitis was first described in 1935 by Louis Hamman and Arnold Rich, and given the name Hamman–Rich syndrome.
References
- Robbin's Pathological Basis of Disease.
- Hamman L.; Rich A.R. (1944). "Acute diffuse interstitial fibrosis of the lungs". Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 74: 177–212.
- Bouros, D; Nicholson AC; Polychronopoulos V; du Bois RM (2000). "Acute interstitial pneumonia". Eur. Respir. J. 15 (2): 412–8. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.15b31.x. PMID 10706513.
- Hamman, L; Rich AR (1935). "Fulminating diffuse interstitial fibrosis of the lungs". Transactions of the American Clinical and Climatological Association. 51. European Respiratory Society: 154–163. PMC 2242096. PMID 21407504.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|
- synd/3010 at Who Named It?
- 00181 at CHORUS
| Diseases of the respiratory system | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper RT (including URTIs, common cold) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lower RT/ lung disease (including LRTIs) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pleural cavity/ mediastinum |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other/general | |||||||||||||||||||||||