| Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Noninfectious pneumonia |
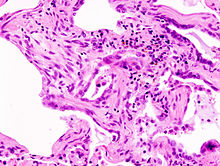 | |
| Micrograph of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). UIP is the most common pattern of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and usually represents idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. H&E stain. Autopsy specimen. | |
| Specialty | Respirology |
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), or noninfectious pneumonia are a class of diffuse lung diseases. These diseases typically affect the pulmonary interstitium, although some also have a component affecting the airways (for instance, cryptogenic organizing pneumonitis). There are seven recognized distinct subtypes of IIP.
Diagnosis
Classification can be complex, and the combined efforts of clinicians, radiologists, and pathologists can help in the generation of a more specific diagnosis.
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia can be subclassified based on histologic appearance into the following patterns:
| Histology | Clinical Correlates |
|---|---|
| Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) | DIP |
| Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) | ARDS, AIP, TRALI |
| Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) | NSIP |
| Respiratory bronchiolitis | RB-ILD |
| Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) | CVD, IPF, drug toxicity, pneumoconiosis |
| Organizing pneumonia | Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia |
| Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP) | LIP |
Usual interstitial pneumonia is the most common type.
Development
Table 1: Development of the (histologic) idiopathic interstitial pneumonia classification
| Leibow et al. (1969) | Katzenstein (1998) | ATS/ERS (2002) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UIP | UIP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UIP | DAD | DAD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NSIP | NSIP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DIP | DIP/RB | DIP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BIP | OP | OP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LIP | (LPD) | LIP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GIP | (HMF) | (HMF) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UIP=usual interstitial pneumonia; DAD=diffuse alveolar damage; NSIP=non-specific interstitial pneumonia; DIP=desquamative interstitial pneumonia; RB=respiratory bronchiolitis; BIP=bronchiolitis obliterans interstitial pneumonia; OP=organizing pneumonia; LIP=lymphoid interstitial pneumonia; LPD=lymphoproliferative disease (not considered a diffuse lung disease); GIP=giant cell interstitial pneumonia; HMF=heavy metal fibrosis, no longer grouped with diffuse lung disease
Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia was originally included in this category, then excluded, then included again.
References
- Richard K. Root (1999). Clinical Infectious Diseases: A Practical Approach. Oxford University Press. pp. 833–. ISBN 978-0-19-508103-9.
- Mehrjardi, Mohammad Zare (2017). "Classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIPs): radiology in focus (PDF Download Available)". ResearchGate. doi:10.13140/rg.2.2.23985.99687/1.
- Nicholson AG (November 2002). "Classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: making sense of the alphabet soup". Histopathology. 41 (5): 381–91. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2559.2002.01421.x. PMID 12405906. S2CID 38141081.
- Flaherty KR, King TE, Raghu G, et al. (October 2004). "Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: what is the effect of a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis?". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 170 (8): 904–10. doi:10.1164/rccm.200402-147OC. PMID 15256390.
- Kim DS, Collard HR, King TE (June 2006). "Classification and natural history of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias". Proc Am Thorac Soc. 3 (4): 285–92. doi:10.1513/pats.200601-005TK. PMC 2658683. PMID 16738191.
- Leslie KO, Wick MR. Practical Pulmonary Pathology: A Diagnostic Approach. Elsevier Inc. 2005. ISBN 978-0-443-06631-3.
- ^ American Thoracic, Society; European Respiratory, Society (January 2002). "American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 165 (2): 277–304. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.ats01. PMID 11790668.
- Visscher DW, Myers JL (June 2006). "Histologic spectrum of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias". Proc Am Thorac Soc. 3 (4): 322–9. doi:10.1513/pats.200602-019TK. PMID 16738196.
- Katzenstein AL, Myers JL (1998). "Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical relevance of pathologic classification". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 157 (4 Pt 1): 1301–15. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.157.4.9707039. PMID 9563754.
- Swigris JJ, Berry GJ, Raffin TA, Kuschner WG (December 2002). "Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia: a narrative review". Chest. 122 (6): 2150–64. doi:10.1378/chest.122.6.2150. PMID 12475860.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Diseases of the respiratory system | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper RT (including URTIs, common cold) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lower RT/ lung disease (including LRTIs) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pleural cavity/ mediastinum |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other/general | |||||||||||||||||||||||