In pharmacology, clearance () is a pharmacokinetic parameter representing the efficiency of drug elimination. This is the rate of elimination of a substance divided by its concentration. The parameter also indicates the theoretical volume of plasma from which a substance would be completely removed per unit time. Usually, clearance is measured in L/h or mL/min. Excretion, on the other hand, is a measurement of the amount of a substance removed from the body per unit time (e.g., mg/min, μg/min, etc.). While clearance and excretion of a substance are related, they are not the same thing. The concept of clearance was described by Thomas Addis, a graduate of the University of Edinburgh Medical School.
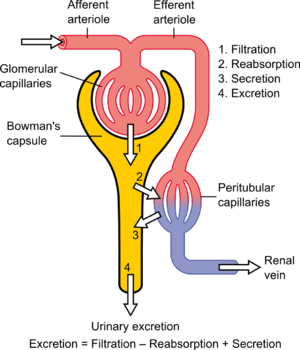
Substances in the body can be cleared by various organs, including the kidneys, liver, lungs, etc. Thus, total body clearance is equal to the sum clearance of the substance by each organ (e.g., renal clearance + hepatic clearance + pulmonary clearance = total body clearance). For many drugs, however, clearance is solely a function of renal excretion. In these cases, clearance is almost synonymous with renal clearance or renal plasma clearance. Each substance has a specific clearance that depends on how the substance is handled by the nephron. Clearance is a function of 1) glomerular filtration, 2) secretion from the peritubular capillaries to the nephron, and 3) reabsorption from the nephron back to the peritubular capillaries. Clearance is variable in zero-order kinetics because a constant amount of the drug is eliminated per unit time, but it is constant in first-order kinetics, because the amount of drug eliminated per unit time changes with the concentration of drug in the blood.
Clearance can refer to the volume of plasma from which the substance is removed (i.e., cleared) per unit time or, in some cases, inter-compartmental clearances can be discussed when referring to redistribution between body compartments such as plasma, muscle, and fat.
Definition
The clearance of a substance is the volume of plasma that contains the same amount of the substance as has been removed from the plasma per unit time.
When referring to the function of the kidney, clearance is considered to be the amount of liquid filtered out of the blood that gets processed by the kidneys or the amount of blood cleaned per time because it has the units of a volumetric flow rate . However, it does not refer to a real value; "the kidney does not completely remove a substance from the total renal plasma flow." From a mass transfer perspective and physiologically, volumetric blood flow (to the dialysis machine and/or kidney) is only one of several factors that determine blood concentration and removal of a substance from the body. Other factors include the mass transfer coefficient, dialysate flow and dialysate recirculation flow for hemodialysis, and the glomerular filtration rate and the tubular reabsorption rate, for the kidney. A physiologic interpretation of clearance (at steady-state) is that clearance is a ratio of the mass generation and blood (or plasma) concentration.
Its definition follows from the differential equation that describes exponential decay and is used to model kidney function and hemodialysis machine function:
| 1 |
Where:
- is the mass generation rate of the substance - assumed to be a constant, i.e. not a function of time (equal to zero for exogenous (foreign) substances/drugs) or
- t is dialysis time or time since injection of the substance/drug or
- V is the volume of distribution or total body water or
- K is the clearance or
- C is the concentration or (in the United States often )
From the above definitions it follows that is the first derivative of concentration with respect to time, i.e. the change in concentration with time.
It is derived from a mass balance.
Clearance of a substance is sometimes expressed as the inverse of the time constant that describes its removal rate from the body divided by its volume of distribution (or total body water).
In steady-state, it is defined as the mass generation rate of a substance (which equals the mass removal rate) divided by its concentration in the blood.
Clearance, half-life and volume of distribution
There is an important relationship between clearance, elimination half-life and distribution volume. The elimination rate constant of a drug is equivalent to total clearance divided by the distribution volume
(note the usage of Cl and not Κ, not to confuse with ). But is also equivalent to divided by elimination rate half-life , . Thus, . This means, for example, that an increase in total clearance results in a decrease in elimination rate half-life, provided distribution volume is constant.
Effect of plasma protein binding
For substances that exhibit substantial plasma protein binding, clearance is generally dependent on the total concentration (free + protein-bound) and not the free concentration.
Most plasma substances have primarily their free concentrations regulated, which thus remains the same, so extensive protein binding increases total plasma concentration (free + protein-bound). This decreases clearance compared to what would have been the case if the substance did not bind to protein. However, the mass removal rate is the same, because it depends only on concentration of free substance, and is independent on plasma protein binding, even with the fact that plasma proteins increase in concentration in the distal renal glomerulus as plasma is filtered into Bowman's capsule, because the relative increases in concentrations of substance-protein and non-occupied protein are equal and therefore give no net binding or dissociation of substances from plasma proteins, thus giving a constant plasma concentration of free substance throughout the glomerulus, which also would have been the case without any plasma protein binding.
In other sites than the kidneys, however, where clearance is made by membrane transport proteins rather than filtration, extensive plasma protein binding may increase clearance by keeping concentration of free substance fairly constant throughout the capillary bed, inhibiting a decrease in clearance caused by decreased concentration of free substance through the capillary.
Derivation of equation
Equation 1 is derived from a mass balance:
| 2 |
where:
- is a period of time
- the change in mass of the toxin in the body during
- is the toxin intake rate
- is the toxin removal rate
- is the toxin generation rate
In words, the above equation states:
- The change in the mass of a toxin within the body () during some time is equal to the toxin intake plus the toxin generation minus the toxin removal.
Since
| 3 |
and
| 4 |
Equation A1 can be rewritten as:
| 5 |
If one lumps the in and gen. terms together, i.e. and divides by the result is a difference equation:
| 6 |
If one applies the limit one obtains a differential equation:
| 7 |
Using the product rule this can be rewritten as:
| 8 |
If one assumes that the volume change is not significant, i.e. , the result is Equation 1:
Solution to the differential equation
The general solution of the above differential equation (1) is:
| 9 |
Where:
- Co is the concentration at the beginning of dialysis or the initial concentration of the substance/drug (after it has distributed) or
- e is the base of the natural logarithm
Steady-state solution
The solution to the above differential equation (9) at time infinity (steady state) is:
| 10a |
The above equation (10a) can be rewritten as:
| 10b |
The above equation (10b) makes clear the relationship between mass removal and clearance. It states that (with a constant mass generation) the concentration and clearance vary inversely with one another. If applied to creatinine (i.e. creatinine clearance), it follows from the equation that if the serum creatinine doubles the clearance halves and that if the serum creatinine quadruples the clearance is quartered.
Measurement of renal clearance
Renal clearance can be measured with a timed collection of urine and an analysis of its composition with the aid of the following equation (which follows directly from the derivation of (10b)):
| 11 |
Where:
- K is the clearance
- CU is the urine concentration (in the USA often )
- Q is the urine flow (volume/time) (often )
- CB is the plasma concentration (in the USA often )
When the substance "C" is creatinine, an endogenous chemical that is excreted only by filtration, the clearance is an approximation of the glomerular filtration rate. Inulin clearance is less commonly used to precisely determine glomerular filtration rate.
Note - the above equation (11) is valid only for the steady-state condition. If the substance being cleared is not at a constant plasma concentration (i.e. not at steady-state) K must be obtained from the (full) solution of the differential equation (9).
See also
- Augmented renal clearance
- Creatinine clearance
- Kt/V
- Pharmacokinetics
- Renal clearance ratio
- Sieving coefficient
- Standardized Kt/V
- Table of medication secreted in kidney
- Urea reduction ratio
References
- Ma, Guangda (2020). "Non-Linear Elimination" (PDF). clinpharmacol.fmhs.auckland.ac.nz. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ^ Rowland M, Tozer TM (2011). Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, Concepts and Applications (4th ed.). Baltimore MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- "Pharmacokinetics objectives". Pharmacology2000.com. 2006-12-27. Retrieved 2013-05-06.
- Kaplan Step1 Pharmacology 2010, page 14
- Wright, Samson (1972). Samson Wright's applied physiology. Cyril Arthur Keele, Neil Eric (12th ed.). London: English Language Book Society, and Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-263321-X. OCLC 396722036.
- Seldin DW (2004). "The development of the clearance concept". Journal of Nephrology. 17 (1): 166–71. PMID 15151274.
- Babb AL, Popovich RP, Christopher TG, Scribner BH (1971). "The genesis of the square meter-hour hypothesis". Transactions of the American Society for Artificial Internal Organs. 17: 81–91. PMID 5158139.
- Ritter J, Flower R, Henderson G, Rang H. Rang & Dale's Pharmacology. 8th ed. London. Churchill Livingstone; 2015
- ^ Winter ME (2003). "Plasma protein binding". Basic clinical pharmacokinetics (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-7817-4147-7.
- Gotch FA (1998). "The current place of urea kinetic modelling with respect to different dialysis modalities". Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation. 13 (Suppl 6): 10–4. doi:10.1093/ndt/13.suppl_6.10. PMID 9719197. Full Text
- Gotch FA, Sargent JA, Keen ML (August 2000). "Whither goest Kt/V?". Kidney International. 76 (Suppl 76): S3-18. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.07602.x. PMID 10936795.
Further reading
- Sharifi M, Ghafourian T (January 2014). "Estimation of biliary excretion of foreign compounds using properties of molecular structure". The AAPS Journal. 16 (1): 65–78. doi:10.1208/s12248-013-9541-z. PMC 3889537. PMID 24202722.
| Physiology of the kidneys and acid–base physiology | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creating urine |
| ||||||
| Other functions |
| ||||||
| Assessment and measurement | |||||||
| Other | |||||||
| Pharmacology | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand (biochemistry) |
| ||||||||||
| Pharmacodynamics |
| ||||||||||
| Pharmacokinetics |
| ||||||||||
| Related fields |
| ||||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||||
 ) is a
) is a 
 is the mass generation rate of the substance - assumed to be a constant, i.e. not a function of time (equal to zero for exogenous (foreign) substances/drugs) or
is the mass generation rate of the substance - assumed to be a constant, i.e. not a function of time (equal to zero for exogenous (foreign) substances/drugs) or  is the first
is the first  is equivalent to total clearance divided by the distribution volume
is equivalent to total clearance divided by the distribution volume

 divided by elimination rate half-life
divided by elimination rate half-life  ,
,  . Thus,
. Thus,  . This means, for example, that an increase in total clearance results in a decrease in elimination rate half-life, provided distribution volume is constant.
. This means, for example, that an increase in total clearance results in a decrease in elimination rate half-life, provided distribution volume is constant.

 is a period of time
is a period of time the change in mass of the toxin in the body during
the change in mass of the toxin in the body during  is the toxin intake rate
is the toxin intake rate is the toxin removal rate
is the toxin removal rate is the toxin generation rate
is the toxin generation rate ) during some time
) during some time 


 and divides by
and divides by 
 one obtains a differential equation:
one obtains a differential equation:


 , the result is Equation
, the result is Equation 


