| Timótean | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Venezuela |
| Linguistic classification | Timotean |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | (not evaluated) |
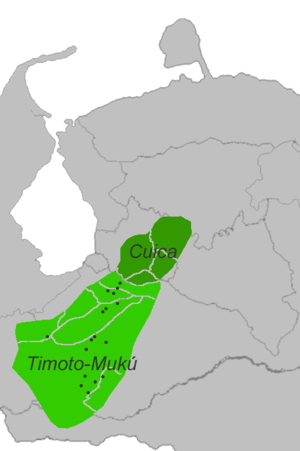 Timote and Cuica toponyms Timote and Cuica toponyms | |
The Timotean languages were spoken in the Venezuelan Andes around what is now Mérida. It is assumed that they are extinct. However, Timote may survive in the so-far unattested Mutú (Loco) language, as this occupies a mountain village (Mutús) within the old Timote state.
Genetic relations
There is no apparent connection to the Chibchan, Arawakan, or Cariban families, apart from sporadic resemblances with Paez and some divergent Chibchan languages, so Timotean appears to be an independent family.
Jolkesky (2016) also notes that there are lexical similarities with the Jirajaran languages.
Languages
There were two closely related languages, each a pair of dialects:
- Timote–Cuica (Miguri, Cuica, "Cicua", spoken by the Timoto–Cuica people)
- Mucuchí–Maripú (Mocochí, Mirripú)
Traditionally, Mucuchí and Mirripú have been classified as dialects of Timote, with Cuica as a distinct language, but the data in Loukotka (1968) indicates that Cuica is a dialect of Timote, and that Mucuchí–Mirripú are a separate language (Kaufman 2007; Campbell 1997, 2012).
Vocabulary
Loukotka (1968) lists the following basic vocabulary items for Timotean languages.
gloss Timote Cuica Mocochi Mirripú one kári karí karí karí two gem xem xem xem three shuént shuent shut sut head ki-kushám ki-kushan kisham ear ki-kumeu ki-kumeu ti-subú tooth ki-kunñuch chi-runch man kiukiai kiukiai kaʔak kage water shömpú shombuch shimpué shimpú fire shirup shnopa churup chirup sun nareúpa nareupa umpú maize chxá chxa chixsak chipxak bird kiukchú kchu house kurakata kfok shimanakot sharakot
References
- Lyle Campbell, 2000. American Indian Languages: The Historical Linguistics of Native America.
- Willem Adelaar with Pieter Muysken, The Languages of the Andes, CUP, 2004:124–125
- Jolkesky, Marcelo Pinho de Valhery (2016). Estudo arqueo-ecolinguístico das terras tropicais sul-americanas (Ph.D. dissertation) (2 ed.). Brasília: University of Brasília.
- ^ Loukotka, Čestmír (1968). Classification of South American Indian languages. Los Angeles: UCLA Latin American Center.
External links
- Fabre: Mutús
| Indigenous language families and isolates of South America (based on Campbell 2012 classification) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language families and isolates |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proposed groupings |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Linguistic areas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Countries | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||