| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Chukotko-Kamchatkan | |
|---|---|
| Chukchi–Kamchatkan, Luorawetlan | |
| Geographic distribution | Russian Far East |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Chukotko-Kamchatkan |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | chuk1271 |
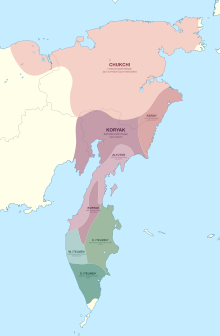
 The distribution of Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages (red) in the 17th century (hatching, approximate) and at the end of the 20th century (solid). The distribution of Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages (red) in the 17th century (hatching, approximate) and at the end of the 20th century (solid). | |
The Chukotko-Kamchatkan or Chukchi–Kamchatkan languages are a language family of extreme northeastern Siberia. Its speakers traditionally were indigenous hunter-gatherers and reindeer-herders. Chukotko-Kamchatkan is endangered. The Kamchatkan branch is moribund, represented only by Western Itelmen, with less than a hundred speakers left. The Chukotkan branch had close to 7,000 speakers left (as of 2010, the majority being speakers of Chukchi), with a reported total ethnic population of 25,000.
While the family is sometimes grouped typologically and geographically as Paleosiberian, no external genetic relationship has been widely accepted as proven. The most popular such proposals have been for links with Eskimo–Aleut, either alone or in the context of a wider grouping.
Alternative names
Less commonly encountered names for the family are Chukchian, Chukotian, Chukotan, Kamchukchee and Kamchukotic. Of these, Chukchian, Chukotian and Chukotan are ambiguous, since the three terms are sometimes used to refer specifically to the family's northern branch; the last two names are portmanteau words referring to both branches.
In addition, Luorawetlan (also spelled Luoravetlan) has been in wide use since 1775 as a name for the family, although it is properly the self-designation of one of its constituent languages, Chukchi.
Languages
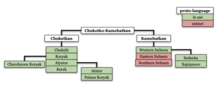
The Chukotko-Kamchatkan family consists of two distantly related dialect clusters, Chukotkan and Kamchatkan. Chukotkan is considered anywhere from three to five languages, whereas there is only one surviving Kamchatkan language, Itelmen.
The relationship of the Chukotkan languages to Itelmen is at best distant, and has been met with only partial acceptance by scholars.
All the Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages are under pressure from Russian. Almost all speakers are bilingual in Russian, and few members of the ethnic groups associated with the languages born after 1970 speak any language but Russian.
The accepted classification is this:
- Chukotko-Kamchatkan
- Kamchatkan
- Southern Kamchadal †
- Eastern Kamchadal †
- Itelmen (Western Kamchadal)
- Chukotkan
- Kamchatkan
Relation to other language families
The Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages have no generally accepted relation to any other language family. There are several theories about possible relationships to existing or hypothetical language families.
Paleosiberian
The Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages are sometimes classified among the Paleosiberian languages, a catch-all term for language groups with no identified relationship to one another that are believed to represent remnants of the language map of Siberia prior to the advances of Turkic and Tungusic.
Eurasiatic
Joseph Greenberg identifies Chukotko-Kamchatkan (which he names Chukotian) as a member of Eurasiatic, a proposed macrofamily that includes Indo-European, Altaic, and Eskimo–Aleut, among others. Greenberg also assigns Nivkh and Yukaghir, sometimes classed as "Paleosiberian" languages, to the Eurasiatic family.
While the Eurasiatic hypothesis has been well received by Nostraticists and some Indo-Europeanists, it remains very controversial. Part of the reason is that the Eurasiatic hypothesis rests on mass comparison of lexemes, grammatical formatives, and vowel systems (see Greenberg 2000–2002), rather than on the prevailing view that regular sound correspondences that are linked to a wide array of lexemes and grammatical formatives are the only valid means to establish genetic relationship (see for instance Baldi 2002:2–19).
Murray Gell-Mann, Ilia Peiros, and Georgiy Starostin group Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages and Nivkh with Almosan instead of Eurasiatic.
Uralo-Siberian
In 1998, Michael Fortescue, a specialist in Eskimo–Aleut as well as in Chukotko-Kamchatkan, argued for a link between Uralic, Yukaghir, Chukotko-Kamchatkan, and Eskimo–Aleut calling this proposed grouping Uralo-Siberian.
Chukotko-Kamchatkan–Amuric
See also: Chukotko-Kamchatkan–Amuric languagesIn 2011, Fortescue instead suggested that Nivkh (Gilyak, Amuric), another Paleo-Siberian language, is related to Chukotko-Kamchatkan on the basis of morphological, typological, and lexical evidence as the closest relative of Chukotko-Kamchatkan and came to prefer an interpretation of the similarities to Uralo-Siberian through language contact. Together, Chukotko-Kamchatkan and Nivkh could form a larger Chukotko-Kamchatkan-Amuric language family, and their common ancestor might have been spoken 4000 years ago.
See also
References
- "Russian National Census". Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 27 August 2024.
- Russian Census (2010); see also Demographics of Siberia.
- Gell-Mann et al., pp. 13–30
- Fortescue, M. (1998). Language Relations Across Bering Strait
- Fortescue, Michael (June 2011). "The relationship of Nivkh to Chukotko-Kamchatkan revisited". Lingua. 121 (8): 1359–1376. doi:10.1016/j.lingua.2011.03.001.
- Fortescue 2011, p. 1361: "I would no longer wish to relate CK directly to , although I believe that some of the lexical evidence will hold up in terms of borrowing/diffusion."
- Baldi, Philip (2002). The Foundations of Latin. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
- Fortescue, Michael (1998). Language Relations Across Bering Strait. London: Cassell & Co.
- Fortescue, Michael (2005). Comparative Chukotko–Kamchatkan Dictionary. Trends in Linguistics 23. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
- Fortescue, Michael (2011). "The relationship of Nivkh to Chukotko-Kamchatkan revisited". Lingua. 121 (8): 1359–1376. doi:10.1016/j.lingua.2011.03.001.
- Gell-Mann, Murray; Ilia Peiros; George Starostin (2009). "Distant Language Relationship: The Current Perspective" (PDF). Journal of Language Relationship (1).
- Greenberg, Joseph H. (2000). Indo-European and Its Closest Relatives: The Eurasiatic Language Family. Volume 1, Grammar. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
- Greenberg, Joseph H. (2002). Indo-European and Its Closest Relatives: The Eurasiatic Language Family. Volume 2, Lexicon. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
External links
 The dictionary definition of Appendix:Proto-Chukotko-Kamchatkan reconstructions at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of Appendix:Proto-Chukotko-Kamchatkan reconstructions at Wiktionary
| Paleo-Siberian languages | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chukotko-Kamchatkan |
|  | ||||
| Yeniseian |
| |||||
| Yukaghir | ||||||
| Nivkh | ||||||
| Others | ||||||
| Italics indicate extinct languages | ||||||
| Language families of Eurasia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | |||||||
| West Asia | |||||||
| Caucasus | |||||||
| South Asia | |||||||
| East Asia | |||||||
| Indian Ocean rim | |||||||
| North Asia |
| ||||||
| Proposed groupings |
| ||||||
| Substrata | |||||||
| |||||||