| Revision as of 09:38, 9 August 2006 editChris 73 (talk | contribs)25,597 editsm Reverted edits by Guru Nanak (talk) to last version by Chris 73← Previous edit | Revision as of 07:57, 30 December 2024 edit undoOAbot (talk | contribs)Bots441,761 editsm Open access bot: hdl, pmc updated in citation with #oabot.Next edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Progressive neurodegenerative disease}} | |||
| {{sprotect-banneduser}} | |||
| {{Redirect|Parkinson's|the medical journal|Parkinson's Disease (journal)|other uses}} | |||
| {{Infobox_Disease | | |||
| {{Cs1 config|name-list-style=vanc|display-authors=6}} | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=July 2024}} | |||
| DiseasesDB = 9651 | | |||
| {{Infobox medical condition | |||
| ICD10 = G10 | | |||
| | name = Parkinson's disease | |||
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|332}} | | |||
| | synonyms = Idiopathic or primary parkinsonism, hypokinetic rigid syndrome, paralysis agitans, shaking palsy | |||
| ICDO = | | |||
| | image = {{Multiple image|perrow = 2|total_width=300|align=center|image_gap=10 | |||
| OMIM = | | |||
| | border = infobox | |||
| MedlinePlus = 000755 | | |||
| | image_style = border:none; | |||
| eMedicineSubj = neuro | | |||
| | image1 = Parkinson’s disease 1880s.jpg | |||
| eMedicineTopic = 304 | | |||
| | caption1 = A. 1880s illustration of Parkinson's disease (PD) | |||
| eMedicine_mult = {{eMedicine2|neuro|635}} in young<br>{{eMedicine2|pmr|99}} rehab | | |||
| | image2 = Mild motor-predominant PD.jpg | |||
| Image = Sir William Richard Gowers Parkinson Disease sketch 1886.jpg | | |||
| | caption2 = B. Mild motor-predominant PD | |||
| Caption = Illustration of the Parkinson disease by Sir William Richard Gowers from ''A Manual of Diseases of the Nervous System''in 1886 | | |||
| | image3 = Intermediate PD.jpg | |||
| }}'''Parkinson's disease''' (also known as '''Parkinson disease''' or '''PD''') is a degenerative disorder of the ], that affects the control of muscles, and so may affect movement, speech and posture. Parkinson's disease belongs to a group of conditions called movement disorders. It is often characterized by muscle rigidity, tremor, a slowing of physical movement (]), and in extreme cases, a loss of physical movement (]). The primary symptoms are due to excessive muscle contraction, normally caused by the insufficient formation and action of ], which is produced in the dopaminergic neurons of the brain. PD is both chronic, meaning it persists over a long period of time, and progressive. | |||
| | caption3 = C. Intermediate PD | |||
| | image4 = Diffuse malignant PD.jpg | |||
| | caption4 = D. Diffuse malignant PD | |||
| | footer = | |||
| }} | |||
| | symptoms = {{Unbulleted list|Main: ], ], ], ] (collectively known as ])|Other: ], ], ], ]}} | |||
| | complications = ], ], ] | |||
| | onset = Age over 60{{sfn|National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke}} | |||
| | duration = Long-term | |||
| | causes = | |||
| | risks = Family history, ], ], ] exposure, ] | |||
| | diagnosis = Symptomatic, ] | |||
| | differential = ], ], ], ] use,{{Sfn|Ferri|2010|loc= Chapter P}} ], ], ], ]{{sfn|Koh|Ito|2017}} | |||
| | prevention = Physical activity, ], ] | |||
| | treatment = ], ] | |||
| | medication = ], ]s, ], ]s, ]s | |||
| | prognosis = Near-normal life expectancy | |||
| | frequency = 8.5 million (2019){{sfn|Ou|Pan|Tang|Duan|2021}} | |||
| | named after = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| <!-- Definition and symptoms --> | |||
| PD is the most common cause of ], a group of similar symptoms. PD is also called "primary parkinsonism" or "idiopathic PD" ("idiopathic" meaning of no known cause). While most forms of parkinsonism are idiopathic, there are some cases where the symptoms may result from toxicity, drugs, genetic mutation, head trauma, or other medical disorders. | |||
| '''Parkinson's disease''' ('''PD'''), or simply '''Parkinson's''', is a ] primarily of the ], affecting both ] and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually, with non-motor issues becoming more prevalent as the disease progresses. Common motor symptoms include ]s, ] (slowness of movement), ], and ], collectively termed ]. In later stages, ], ], and ] such as ], ], ]s, or ] may arise. | |||
| <!-- Causes and pathophysiology --> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| Most cases of Parkinson's disease are ], though contributing factors have been identified. Pathophysiology involves progressive ] in the ], a ] region that provides ] to the ], a system involved in voluntary ]. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood but involves the aggregation of ] into ] within ]s. Other potential factors involve ] and environmental influences, medications, lifestyle, and prior health conditions. | |||
| Symptoms of Parkinson's disease have been known and treated since ancient times.{{fact}} However, it was not formally recognised and its symptoms documented until ] in ''An Essay on the Shaking Palsy''<ref>{{cite journal | author = Parkinson J | title = An essay on the shaking palsy. 1817. | journal = J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci | volume = 14 | issue = 2 | pages = 223-36; discussion 222 | year = 2002 | id = PMID 11983801 | url=http://neuro.psychiatryonline.org/cgi/content/full/14/2/223 | format=Reproduced }}</ref> by the British physician Dr. ]. Parkinson's disease was then known as paralysis agitans. The underlying ] changes in the ] were identified in the ], due largely to the work of Swedish scientist ] who later went on to win a ]. ] entered clinical practice in 1967, and the first study reporting improvements in patients with Parkinson's disease resulting from treatment with L-dopa was published in 1968.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Cotzias G | title = L-Dopa for Parkinsonism. | journal = N Engl J Med | volume = 278 | issue = 11 | pages = 630 | year = 1968 | id = PMID 5637779}}</ref> | |||
| <!-- Diagnosis and epidemiology --> | |||
| ==Symptoms== | |||
| Diagnosis is primarily based on ], typically motor-related, identified through ]. ] like ] can support the diagnosis. Parkinson's typically manifests in individuals over 60, with about one percent affected. In those younger than 50, it is termed "early-onset PD". | |||
| Parkinson disease affects movement (motor symptoms). Typical other symptoms include disorders of mood, behavior, thinking, and sensation (non-motor symptoms). Individual patients' symptoms may be quite dissimilar; progression is also distinctly individual. | |||
| <!-- Treatment and prognosis --> | |||
| There are four major dopamine pathways in the brain; the nigrostriatal pathway, referred to above, mediates movement and is the most conspicuously affected in early Parkinson's disease. The other pathways are the mesocortical, the mesolimbic, and the tuberoinfundibular. These pathways are associated with, respectively: volition and emotional responsiveness; desire, initiative, and reward; and sensory processes and maternal behavior. Reduction in dopamine along the non-striatal pathways is the likely explanation for much of the neuropsychiatric pathology associated with Parkinson's disease. | |||
| No cure for Parkinson's is known, and treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms. Initial treatment typically includes ], ]s, or ]s. As the disease progresses, these medications become less effective and may cause ]. Diet and rehabilitation therapies can help improve symptoms. ] is used to manage severe motor symptoms when drugs are ineffective. There is little evidence for treatments addressing non-motor symptoms, such as sleep disturbances and mood instability. Life expectancy for those with PD is near-normal but is decreased for early-onset. | |||
| {{TOC limit}} | |||
| ===Motor symptoms=== | |||
| The ]s are: | |||
| *'']'': normally 4-7] tremor, maximal when the limb is at rest, and decreased with voluntary movement. It is typically unilateral at onset. This is the most apparent and well-known symptom. However, an estimated 30% of patients have little perceptible tremor; these are classified as akinetic-rigid. | |||
| *'']'': stiffness; increased muscle tone. In combination with a resting tremor, this produces a ratchety, "]" rigidity when the limb is passively moved. | |||
| *'']/]'': respectively, slowness or absence of movement. Rapid, repetitive movements produce a ] and decremental loss of ]. | |||
| *'']'': failure of postural ], which leads to impaired balance and falls. | |||
| ==Classification and terminology== | |||
| Other motor symptoms include: | |||
| {{See also|Parkinsonism|Parkinson-plus syndrome}} | |||
| *] and posture disturbances: | |||
| Parkinson's disease (PD) is a ] affecting both the ] and ], characterized by the ] of ]-producing ] in the ] region of the brain.{{Sfn|Ramesh|Arachchige|2023|pp=200–201, 203}} It is classified as a ] due to the abnormal accumulation of the protein ], which aggregates into ] within affected neurons.{{Sfn|Calabresi|Mechelli|Natale|Volpicelli-Daley|2023|pp=1,5}} | |||
| **Shuffling: gait is characterized by short steps, with feet barely leaving the ground, producing an audible shuffling noise. Small obstacles tend to trip the patient | |||
| **Decreased arm swing: a form of bradykinesia | |||
| **Turning "en bloc": rather than the usual twisting of the neck and trunk and pivoting on the toes, PD patients keep their neck and trunk rigid, requiring multiple small steps to accomplish a turn. | |||
| **Stooped, forward-flexed posture. In severe forms, the head and upper shoulders may be bent at a ] relative to the trunk (]). | |||
| **Festination: a combination of stooped posture, imbalance, and short steps. It leads to a gait that gets progressively faster and faster, often ending in a fall. | |||
| **Gait freezing: "freezing" is another word for akinesia, the inability to move. Gait freezing is characterized by inability to move the feet, especially in tight, cluttered spaces or when initiating gait. | |||
| **]: abnormal, sustained, painful twisting muscle contractions, usually affecting the foot and ankle in PD patients. This causes toe flexion and foot inversion, interfering with gait. | |||
| *Speech and swallowing disturbances | |||
| **Hypophonia: soft speech. Speech quality tends to be soft, hoarse, and monotonous. | |||
| **Festinating speech: excessively rapid, soft, poorly-intelligible speech. | |||
| **]: most likely caused by a weak, infrequent swallow and stooped posture. | |||
| **(Non-motor causes of speech/language disturbance in both expressive and receptive language: these include decreased verbal fluency and cognitive disturbance especially related to comprehension of emotional content of speech and of facial expression<ref>{{cite journal | author = Pell M | title = On the receptive prosodic loss in Parkinson's disease. | journal = Cortex | volume = 32 | issue = 4 | pages = 693-704 | year = 1996 | id = PMID 8954247}}</ref> | |||
| **]: impaired ability to swallow. Can lead to ], ], and ultimately death. | |||
| *Other motor symptoms: | |||
| **] (up to 50% of cases); | |||
| **masked facies (a mask-like face also known as ]), with infrequent ];<ref>{{cite journal |author=Günther Deuschl, Christof Goddemeier | title=Spontaneous and reflex activity of facial muscles in dystonia, Parkinson's disease, and in normal subjects | journal=] | year=1998 | volume=64 | issue=March | pages= 320–324 | url=http://jnnp.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/64/3/320}}</ref> | |||
| **difficulty rolling in bed or rising from a seated position; | |||
| **] (small, cramped handwriting); | |||
| **impaired fine motor dexterity and coordination; | |||
| **impaired gross motor coordination; | |||
| **Poverty of movement: overall loss of accessory movements, such as decreased arm swing when walking, as well as spontaneous movement. | |||
| The loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra initially presents as movement abnormalities, leading to Parkinson's further categorization as a ].{{Sfn|National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke}} In 30% of cases, disease progression leads to the cognitive decline known as ] (PDD).{{Sfn|Wallace|Segerstrom|van Horne|Schmitt|2022|p=149}} Alongside ], PDD is one of the two subtypes of ].{{Sfn|Hansen|Ling|Lashley|Holton|2019|p=635}} | |||
| ===Non-motor symptoms=== | |||
| ====Mood disturbances==== | |||
| *Estimated prevalence rates of depression vary widely according to the population sampled and methodology used. Reviews of ] estimate its occurrence in anywhere from 20-80% of cases.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Lieberman A | title = Depression in Parkinson's disease -- a review. | journal = Acta Neurol Scand | volume = 113 | issue = 1 | pages = 1-8 | year = 2006 | id = PMID 16367891}}</ref> Estimates from community samples tend to find lower rates than from specialist centres. Most studies use self-report questionnaires such as the ] which may overinflate scores due to physical symptoms. Studies using diagnostic interviews by trained psychiatrists also report lower rates of depression. | |||
| The four cardinal motor symptoms of Parkinson's—] (slowed movements), ], ], and ]—are called ].{{Sfn|Bhattacharyya|2017|p=7}}{{Sfn|Stanford University School Medicine}} These four symptoms are not exclusive to Parkinson's and can occur in many other conditions,{{Sfn|Bologna|Truong|Jankovic|2022|pp=1–6}}{{Sfn|Limphaibool|Iwanowski|Holstad|Kobylarek|2019|pp=1–2}} including ] and ].{{Sfn|Leta|Urso|Batzu|Lau|2022|p=1122}}{{Sfn|Langston|2017|p=S11}} Neurodegenerative diseases that feature parkinsonism but have distinct differences are grouped under the umbrella of ] or, alternatively, atypical parkinsonian disorders.{{Sfn|Prajjwal|Kolanu|Reddy|Ahmed|2024|pp=1–3}}{{Sfn|Olfatia|Shoeibia|Litvanb|2019|p=101}} Parkinson's disease can be attributed to ] or be ], in which there is no clearly identifiable cause. The latter, also called ] Parkinson's, makes up some 85–90% of cases.{{Sfn|Dolgacheva|Zinchenko|Goncharov|2022|p=2}} | |||
| *More generally, there is an increased risk for any individual with depression to go on to develop Parkinson's disease at a later date.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Ishihara L, Brayne C | title = A systematic review of depression and mental illness preceding Parkinson's disease. | journal = Acta Neurol Scand | volume = 113 | issue = 4 | pages = 211-20 | year = 2006 | id = PMID 16542159}}</ref> | |||
| *Seventy percent of individuals with Parkinson's disease diagnosed with pre-existing depression go on to develop anxiety. Ninety percent of Parkinson's disease patients with pre-existing anxiety subsequently develop depression); ] or ]. | |||
| ==Signs and symptoms== | |||
| ====] disturbances==== | |||
| {{Main|Signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| *]; both voluntary and involuntary motor responses are significantly slowed. | |||
| ===Motor=== | |||
| *], characterized by difficulties in: differential allocation of attention, impulse control, set shifting, prioritizing, evaluating the salience of ambient data, interpreting social cues, and subjective time awareness. This complex is present to some degree in most Parkinson's patients; it may progress to: | |||
| {{See also|Parkinsonism}} | |||
| *]: a later development in approximately 20-40% of all patients, typically starting with slowing of thought and progressing to difficulties with abstract thought, memory, and behavioral regulation. | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| *]; ] is more impaired than ]. Prompting elicits improved recall. | |||
| | align = right | |||
| *medication effects: some of the above cognitive disturbances are improved by dopaminergic medications, while others are actually worsened <ref>{{cite journal | author=Michael J Frank | title= Dynamic Dopamine Modulation in the Basal Ganglia: A Neurocomputational Account of Cognitive Deficits in Medicated and Non-mediacated Parkinsonism | journal=] | year=2005 | volume=17 | pages= 51–73 | url=http://www.u.arizona.edu/~mfrank/pubs-abstr.html#Frank05}}</ref> | |||
| | direction = vertical | |||
| | total_width = 220 | |||
| | image1 = Paralysis agitans-Male Parkinson's victim-1892 cropped.png | |||
| | image2 = Writing by a Parkinson's disease patient.png | |||
| | footer = Motor symptoms include a stooping posture, the "]", and ]—jagged, diminutive handwriting. | |||
| }} | |||
| Although a wide spectrum of motor and non-motor symptoms appear in Parkinson's, the cardinal features remain tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability, collectively termed parkinsonism.{{sfn|Abusrair|Elsekaily|Bohlega|2022|p=2}} Appearing in 70–75 percent of PD patients,{{sfn|Abusrair|Elsekaily|Bohlega|2022|p=2}}{{sfn|Moustafa|Chakravarthy|Phillips|Gupta|2016|p=730}} tremor is often the predominant motor symptom.{{sfn|Abusrair|Elsekaily|Bohlega|2022|p=2}} Resting tremor is the most common, but kinetic tremors—occurring during voluntary movements—and postural tremor—preventing upright, stable posture—also occur.{{sfn|Moustafa|Chakravarthy|Phillips|Gupta|2016|p=730}} Tremor largely affects the hands and feet:{{sfn|Moustafa|Chakravarthy|Phillips|Gupta|2016|p=730}} a classic parkinsonian tremor is "]", a resting tremor in which the thumb and index finger make contact in a circular motion at 4–6 Hz frequency.{{sfn|Abusrair|Elsekaily|Bohlega|2022|p=4}}{{sfn|Sveinbjornsdottir|2016|p=319}} | |||
| ====]==== | |||
| *Excessive daytime ]; | |||
| *Initial, intermediate, and terminal insomnia; | |||
| *Disturbances in REM sleep: disturbingly vivid dreams, and REM Sleep Disorder, characterized by acting out of dream content; | |||
| ====] disturbances==== | |||
| *impaired visual ], spatial reasoning, ] discrimination, convergence insufficiency (characterized by ]) and ] | |||
| *] and fainting; usually attributable orthostatic hypotension, a failure of the autonomous nervous system to adjust blood pressure in response to changes in body position | |||
| *impaired ] (the awareness of bodily position in three-dimensional space) | |||
| *reduction or loss of sense of ] (]), | |||
| *]: neuropathic, muscle, joints, and tendons, attributable to tension, dystonia, rigidity, joint stiffness, and injuries associated with attempts at accommodation | |||
| Bradykinesia describes difficulties in ], beginning, and executing, resulting in overall slowed movement with reduced amplitude that affects sequential and simultaneous tasks.{{sfn|Bologna|Paparella|Fasano|Hallett|2019|pp=727-729}} Bradykinesia can also lead to ], reduced facial expressions.{{sfn|Sveinbjornsdottir|2016|p=319}} ], also called rigor, refers to a feeling of stiffness and resistance to passive stretching of muscles that occurs in up to 89 percent of cases.{{sfn|Ferreira-Sánchez|Moreno-Verdú|Cano-de-la-Cuerda|2020|p=1}}{{sfn|Moustafa|Chakravarthy|Phillips|Gupta|2016|p=728}} ] typically appears in later stages, leading to ] and ].{{sfn|Palakurthi|Burugupally|2019|pp=1-2}} Postural instability also leads to a forward stooping posture.{{sfn|Palakurthi|Burugupally|2019|pp=1,4}} | |||
| ====] disturbances==== | |||
| *] and ]; | |||
| *], typically in later disease progression | |||
| *] and ]dysmotility, severe enough to endanger comfort and even health | |||
| *]: characterized by profound impairment of sexual arousal, behavior, orgasm, and drive is found in mid and late Parkinson disease. Current data addresses male sexual function almost exclusively. | |||
| Beyond the cardinal four, other motor deficits, termed secondary motor symptoms, commonly occur.{{sfn|Moustafa|Chakravarthy|Phillips|Gupta|2016|pp=727-728}} Notably, gait disturbances result in the ], which includes shuffling and ], where a normal gait is interrupted by rapid footsteps—known as festination—or sudden stops, impairing balance and causing falls.{{sfn|Moustafa|Chakravarthy|Phillips|Gupta|2016|p=731}} {{sfn|Mirelman|Bonato|Camicioli|Ellis|2019|p=1}} Most PD patients experience speech problems, including ], ], ], and festinating speech (rapid and poorly intelligible).{{sfn|Moustafa|Chakravarthy|Phillips|Gupta|2016|p=734}} Handwriting is commonly altered in Parkinson's, decreasing in size—known as ]—and becoming jagged and sharply fluctuating.{{sfn|Moustafa|Chakravarthy|Phillips|Gupta|2016|p=732}} Grip and dexterity are also impaired.{{sfn|Moustafa|Chakravarthy|Phillips|Gupta|2016|p=733}} | |||
| == Diagnosis == | |||
| ], a pattern which aids in diagnosing Parkinson's disease.]] | |||
| There are currently no blood or laboratory tests that have been proven to help in diagnosing sporadic PD. Therefore the diagnosis is based on medical history and a neurological examination. The disease can be difficult to diagnose accurately. Indeed, only 75% of clinical diagnoses of PD are confirmed at autopsy<ref>{{cite journal | author = Gelb D, Oliver E, Gilman S | title = Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. | journal = Arch Neurol | volume = 56 | issue = 1 | pages = 33-9 | year = 1999 | id = PMID 9923759}}</ref>. Early signs and symptoms of PD may sometimes be dismissed as the effects of normal aging. The physician may need to observe the person for some time until it is apparent that the symptoms are consistently present. Doctors may sometimes request brain scans or laboratory tests in order to rule out other diseases. However, CT and MRI brain scans of people with PD usually appear normal. | |||
| ===Non-motor=== | |||
| == Descriptive epidemiology== | |||
| ====Neuropsychiatric and cognitive==== | |||
| The worldwide ] of Parkinson's disease is 4 to 6 million people. There are over 1.5 million in ] alone. The disease usually has a long, subtle onset, so diagnosis occurs most often after many years of subclinical disease {{fact}}. Prevalence estimates range from a low of 7 per 100,000 in ] to a high of 329.3 per 100,000 in ], U.S.A. (although that figure was arrived at using capture-recapture estimates), and 328.3 cases per 100,000 in the ] community in ]. The greatest prevalence of any country is the ], with between 100 and 250 cases per 100,000.{{fact}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="float:right; margin-left:1em; font-size:90%; line-height:1.4em; width:280px;" | |||
| |+ Neuropsychiatric symptom prevalence in Parkinson's disease{{sfn|Aarslanda|Krambergera|2015|pp=660, 662}} | |||
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#33D2FD;color:black;text-align:center;" |Symptom | |||
| |- | |||
| ! style="background:#33D2FD;color:black;" |Prevalence (%) | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 40–50 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 40 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 20–40 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 36–60 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 15–30 | |||
| |- | |||
| |} | |||
| ] symptoms like ], ], ], hallucinations, and ] occur in up to 60% of those with Parkinson's. They often precede motor symptoms and vary with disease progression.{{sfn|Aarslanda|Krambergera|2015|pp=659-660}} Non-motor fluctuations, including ], ], and slowness of thought, are also common.{{sfn|Weintraub|Mamikonyan|2019|p=661}} Some neuropsychiatric symptoms are not directly caused by neurodegeneration but rather by its pharmacological management.{{sfn|Aarslanda|Krambergera|2015|p=660}} | |||
| Cognitive impairments rank among the most prevalent and debilitating non-motor symptoms.{{Sfn|Biundo|Weis|Antonini|2016|p=1}} These deficits may emerge in the early stages or before diagnosis,{{Sfn|Biundo|Weis|Antonini|2016|p=1}}{{Sfn|Gonzalez-Latapi|Bayram|Litvan|Marras|2021|p=74}} and their prevalence and severity tend to increase with disease progression. Ranging from ] to severe ], these impairments include ], ], and disruptions in time perception and estimation.{{Sfn|Gonzalez-Latapi|Bayram|Litvan|Marras|2021|p=74}} | |||
| The average age at which symptoms begin is 55-60, and although cases at ages as low as 11 have been reported it is highly unusual for people under 30 to develop Parkinson's. It occurs in all parts of the world, but appears to be more common in people of European ancestry than in those of African ancestry. Those of East Asian ancestry have an intermediate risk. It is more common in rural than urban areas in developed countries, but the converse is true in poorer countries, leading Tanner to speculate about environmental causes {{fact}}. Men are affected at a rate about double that of women, especially in the older age groups. There is a suggestion of increased prevalence in the California Hispanic population.<ref name="VanDenEeden2003">{{cite journal | author = Van Den Eeden S, Tanner C, Bernstein A, Fross R, Leimpeter A, Bloch D, Nelson L | title = Incidence of Parkinson's disease: variation by age, gender, and race/ethnicity. | journal = Am J Epidemiol | volume = 157 | issue = 11 | pages = 1015-22 | year = 2003 | id = PMID 12777365}}</ref> About 2% of the population develops the disease some time during life {{fact}}. | |||
| ====Autonomic==== | |||
| Incidence has been estimated by several groups, starting with northern California.<ref name="VanDenEeden2003">{{cite journal | author = Van Den Eeden S, Tanner C, Bernstein A, Fross R, Leimpeter A, Bloch D, Nelson L | title = Incidence of Parkinson's disease: variation by age, gender, and race/ethnicity. | journal = Am J Epidemiol | volume = 157 | issue = 11 | pages = 1015-22 | year = 2003 | id = PMID 12777365}}</ref> They observed age and sex corrected incidence of 13.4 per 100,000/year. They note a rapid increase in incidence with age, male rates nearly double female rates, and an elevated rate amongst Hispanics. This study was followed by a group in Spain <ref>{{cite journal | author = Benito-León J, Bermejo-Pareja F, Morales-González J, Porta-Etessam J, Trincado R, Vega S, Louis E | title = Incidence of Parkinson disease and parkinsonism in three elderly populations of central Spain. | journal = Neurology | volume = 62 | issue = 5 | pages = 734-41 | year = 2004 | id = PMID 15007123}}</ref> who used the two-stage survey technique pioneered in the Copiah County study {{fact}} to survey a cohort age 65 to 85. Within that group, incidence adjusted for age and sex was 186.8/100,000 per year, with men's rates being 2.55 times that of women. For the same age group, Van den Eeden and colleagues observed an incidence of roughly 120/100,000/year. Soon thereafter the Rotterdam sudy was published <ref>{{cite journal | author = de Lau L, Giesbergen P, de Rijk M, Hofman A, Koudstaal P, Breteler M | title = Incidence of parkinsonism and Parkinson disease in a general population: the Rotterdam Study. | journal = Neurology | volume = 63 | issue = 7 | pages = 1240-4 | year = 2004 | id = PMID 15477545}}</ref> using techniques similar to the Spanish group and Copiah County. They note age-specific incidence rates from 0.3 per 1000 person-years in subjects aged 55 to 65 years, to 4.4 per 1000 person-years for those aged ≥85 year, and a sex ratio of 1.55 for male incidence. | |||
| ]—an autonomic failure—can lead to ] (pictured).]] | |||
| ] failures, known as ], can appear at any stage of Parkinson's.{{sfn|Palma|Kaufmann|2018|pp=372-373}}{{sfn|Pfeiffer|2020|p=1464}} They are among the most debilitating symptoms and greatly reduce quality of life.{{sfn|Palma|Kaufmann|2018|p=373}} Although almost all PD patients suffer cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction, only some are symptomatic.{{sfn|Palma|Kaufmann|2018|p=373}} Chiefly, ]—a sustained ] drop of at least 20 mmHg ] or 10 mmHg ] after standing—occurs in 30–50 percent of cases. This can result in ] or ]: subsequent falls are associated with higher morbidity and mortality.{{sfn|Palma|Kaufmann|2018|p=373}}{{sfn|Palma|Kaufmann|2020|pp=1465-1466}} | |||
| Other autonomic failures include ] like chronic constipation, ] and subsequent ], ], and ] (difficulty swallowing): all greatly reduce quality of life.{{sfn|Pfeiffer|2020|p=1467}}{{sfn|Han|Finkelstein|McQuade|Diwakarla|2022|p=2}} Dysphagia, for instance, can prevent pill swallowing and lead to ].{{sfn|Pfeiffer|2020|p=1468}} ], ], and ]—including heat and cold intolerance and excessive sweating—also frequently occur.{{sfn|Pfeiffer|2020|pp=1471-1473}} | |||
| ==Related diseases== | |||
| ====Other non-motor symptoms==== | |||
| There are other disorders that are called '']''. These include: | |||
| Sensory deficits appear in up to 90 percent of patients and are usually present at early stages.{{Sfn|Zhu|Li|Ye|Jiang|2016|p=685}} ] and ] are common,{{Sfn|Zhu|Li|Ye|Jiang|2016|p=685}} with ] affecting up to 55 percent of individuals.{{Sfn|Corrà|Vila-Chã|Sardoeira|Hansen|2023|pp=225-226}} ] are also frequently observed, including deficits in ], ], ], and ].{{Sfn|Zhu|Li|Ye|Jiang|2016|p=688}} An ] is also prevalent.{{Sfn|Zhu|Li|Ye|Jiang|2016|p=687}} PD patients often struggle with spatial awareness, recognizing faces and emotions, and may experience challenges with reading and double vision.{{Sfn|Weil|Schrag|Warren|Crutch|2016|pp=2828, 2831-2832}} | |||
| ]s are highly prevalent in PD, affecting up to 98%.{{Sfn|Stefani|Högl|2020|p=121}} These disorders include ], ], ], ] (RBD), and ], many of which can be worsened by medication. RBD may begin years before the initial motor symptoms. Individual presentation of symptoms varies, although most people affected by PD show an altered ] at some point of disease progression.{{sfn|Dodet|Houot|Leu-Semenescu|Corvol|2024|p=1}}{{sfn|Bollu|Sahota|2017|pp=381-382}} | |||
| * ] (MSA) | |||
| ** ] (SDS) | |||
| ** Striatonigral degeneration (SND) | |||
| ** Olivopontocerebellar atrophy (OPCA) | |||
| * Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) | |||
| * Corticobasal degeneration (CBD) | |||
| PD is also associated with a variety of ]s that include ], ], ], and ].{{sfn|Niemann|Billnitzer|Jankovic|2021|p=61}} Seborrheic dermatitis is recognized as a premotor feature that indicates dysautonomia and demonstrates that PD can be detected not only by changes of ], but tissue abnormalities outside the nervous system as well.{{sfn|Almikhlafi|2024|p=7}} | |||
| Some people include dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) as one of the 'Parkinson-plus' syndromes. Although idiopathic Parkinson's disease patients also have Lewy bodies in their brain tissue, the distribution is denser and more widespread in DLB. Even so, the relationship between Parkinson disease, Parkinson disease with dementia (PDD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) might be most accurately conceptualized as a spectrum, with a discrete area of overlap between each of the three disorders. The natural history and role of Lewy bodies is very little understood. | |||
| ==Causes== | |||
| Patients often begin with typical Parkinson's disease symptoms which persist for some years; these Parkinson-plus diseases can only be diagnosed when other symptoms become apparent with the passage of time. These Parkinson-plus diseases usually progress more quickly than typical ideopathic Parkinson disease. The usual anti-Parkinson's medications are typically either less effective or not effective at all in controlling symptoms; patients may be exquisitely sensitive to neuroleptic medications like ]. Additionally, the cholinesterase inhibiting medications have shown preliminary efficacy in treating the cognitive, psychiatric, and behavioral aspects of the disease, so correct differential diagnosis is important. | |||
| {{Main|Causes of Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | total_width = 320 | |||
| | image1 = Alpha-synuclein 2005.png | |||
| | alt1 = | |||
| | caption1 = | |||
| | image2 = Lewy bodies (alpha synuclein inclusions) 1.jpg | |||
| | alt2 = | |||
| | footer = The protein ] aggregates into ]. Structural model of alpha-synuclein (left), photomicrograph of Lewy bodies (right). | |||
| }} | |||
| As of 2024, the cause of neurodegeneration in Parkinson's remains unclear,{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}} though it is believed to result from the interplay of ] and ] factors.{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}} The majority of cases are ] with no clearly identifiable cause, while approximately 5–10 percent are familial.{{sfn|Toffoli|Vieira|Schapira|2020|p=1}} Around a third of familial cases can be attributed to a single monogenic cause.{{sfn|Toffoli|Vieira|Schapira|2020|p=1}} | |||
| Molecularly, abnormal aggregation of alpha-synuclein is considered a key contributor to PD ],{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}} although the trigger for this aggregation remains debated.{{sfn|Brundin|Melki|2017|p=9808}} ] disruption and the dysfunction of cell ], including ], ], and ], are implicated in pathogenesis.{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}}{{sfn|Ho|Wing|2024|pp=1-2}} Additionally, maladaptive immune and inflammatory responses are potential contributors.{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}} The substantial heterogeneity in PD presentation and progression suggests the involvement of multiple interacting triggers and pathogenic pathways.{{sfn|Brundin|Melki|2017|p=9808}} | |||
| ] (hereditary copper accumulation) may present with parkinsonistic features; young patients presenting with parkinsonism may be screened for this (rare) condition. ] is often mistaken for Parkinson's disease but usually lacks all features besides tremor. | |||
| == |
=== Genetic === | ||
| ] of ]]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Parkinson's can be narrowly defined as a genetic disease, as rare inherited gene variants have been firmly linked to monogenic PD, and the majority of sporadic cases carry variants that increase PD risk.{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}}{{sfn|Toffoli|Vieira|Schapira|2020|p=2}}{{sfn|Salles|Tirapegui|Chaná-Cuevas|2024|p=2}} PD ] is estimated to range from 22 to 40 percent.{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}} Around 15 percent of diagnosed individuals have a ], of which 5–10 percent can be attributed to a causative risk gene ]. However, carrying one of these mutations may not lead to disease. Rates of familial PD vary by ethnicity: monogenic PD occurs in up to 40% of ] patients and 20% of ] patients.{{sfn|Salles|Tirapegui|Chaná-Cuevas|2024|p=2}} | |||
| The symptoms of Parkinson's disease result from the loss of ]-secreting (dopaminergic) cells and subsequent loss of ], secreted by the same cells, in the ] region of the ] (literally "black substance"). These neurons project to the ] and their loss leads to alterations in the activity of the neural circuits within the basal ganglia that regulate movement, in essence an inhibition of the ] and excitation of the ]. | |||
| As of 2024, around 90 genetic risk variants across 78 genomic loci have been identified.{{sfn|Farrow|Gokuladhas|Schierding|Pudjihartono|2024|p=1}} Notable risk variants include ''SNCA'' (which encodes alpha-synuclein), ''LRRK2'', and ''VPS35'' for ] inheritance, and ''PRKN'', ''PINK1'', and ''DJ1'' for ] inheritance.{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}}{{sfn|Bandres-Ciga|Diez-Fairen|Kim|Singleton|2020|p=2}} ''LRRK2'' is the most common autosomal dominant variant, responsible for 1–2 percent of all PD cases and 40 percent of familial cases.{{sfn|Tanner|Ostrem|2024}} {{sfn|Toffoli|Vieira|Schapira|2020|p=1}} ] variants are associated with nearly half of recessive, early-onset monogenic PD.{{sfn|Toffoli|Vieira|Schapira|2020|pp=1-2}} Mutations in the ''GBA1'' gene, linked to ], are found in 5–15 percent of PD cases.{{sfn|Smith|Schapira|2022|pp=1-15}} The ''GBA1'' variant frequently leads to cognitive decline.{{sfn|Tanner|Ostrem|2024}} | |||
| The direct pathway facilitates movement and the indirect pathway inhibits movement, thus the loss of these cells leads to a hypokinetic movement disorder. The lack of ] results in increased inhibition of the ventral lateral nucleus of the thalamus, which sends excitatory projections to the motor cortex, thus leading to ]. | |||
| ===Environmental=== | |||
| There are four major dopamine pathways in the brain; the nigrostriatal pathway, referred to above, mediates movement and is the most conspicuously affected in early Parkinson's disease. The other pathways are the mesocortical, the mesolimbic, and the tuberoinfundibular. These pathways are associated with, respectively: volition and emotional responsiveness; desire, initiative, and reward; and sensory processes and maternal behavior. Disruption of dopamine along the non-striatal pathways is the likely explantion for much of the neuropsychiatric pathology associated with Parkinson's disease. | |||
| {{See also|Environmental health|Exposome}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The limited heritability of Parkinson's strongly suggests environmental factors are involved, though identifying these risk factors and establishing ] is challenging due to PD's decade-long prodromal period.{{sfn|De Mirandaa|Goldmanb|Millerc|Greenamyred|2024|p=46}} However, environmental toxicants such as air pollution, pesticides, and industrial solvents like ] are strongly linked to Parkinson's.{{sfn|Dorsey|Bloem|2024|pp=453-454}} | |||
| Certain pesticides—like ], ], and ]—are the most established environmental toxicants for Parkinson's and are likely causal.{{sfn|Dorsey|Bloem|2024|p=454}}{{sfn|Bloem|Boonstra|2023|p=e948–e949}}{{sfn|Rietdijk|Perez-Pardo|Garssen|van Wezel|2017|p=1}} PD prevalence is strongly associated with local pesticide use, and many pesticides are mitochondrial toxins.{{sfn|Dorsey|Bloem|2024|pp=453-455}} Paraquat, for instance, structurally resembles metabolized ],{{sfn|Dorsey|Bloem|2024|p=454}} which selectively kills dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting ] and is widely used to ] PD.{{sfn|Langston|2017|p=S14}}{{sfn|Dorsey|Bloem|2024|p=454}} Pesticide exposure after diagnosis may also accelerate disease progression.{{sfn|Dorsey|Bloem|2024|p=454}} Without pesticide exposure, an estimated 20 percent of all PD cases would be prevented.{{sfn|Santos-Lobato|2024|p=1}} | |||
| Brain cells producing other brain chemicals such as ], ], ] and ] exhibit damage in Parkinson's disease, accounting for some of the wide array of symptoms. It is not known whether this damage is a primary disease process, or secondary to loss of normal dopaminergic stimulation. | |||
| ===Hypotheses=== | |||
| The mechanism by which the brain cells in Parkinson's are lost appears to center on an abnormal accumulation of the protein ] bound to ubiquitin in the damaged cells.]-ubiquitin complex cannot be directed to the proteosome. This protein accumulation forms proteinaceous cytoplasmic inclusions called ]. Excessive accumulations of iron, which are toxic to nerve cells, are also typically observed in conjunction with the protein inclusions. | |||
| ====Prionic hypothesis==== | |||
| {{See also|Prion}} | |||
| The hallmark of Parkinson's is the formation of protein aggregates, beginning with alpha-synuclein fibrils and followed by Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites.{{sfn|Wu|Schekman|2024|p=1}} The prion hypothesis suggests that alpha-synuclein aggregates are pathogenic and can spread to neighboring, healthy neurons and seed new aggregates. Some propose that the heterogeneity of PD may stem from different "strains" of alpha-synuclein aggregates and varying anatomical sites of origin.{{sfn|Brundin|Melki|2017|p=9809}}{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|p=96}} Alpha-synuclein propagation has been demonstrated in cell and animal models and is the most popular explanation for the progressive spread through specific neuronal systems.{{sfn|Dickson|2018|p=S31}} However, therapeutic efforts to clear alpha-synuclein have failed.{{sfn|Wu|Schekman|2024|pp=1-2}} Additionally, postmortem brain tissue analysis shows that alpha-synuclein pathology does not clearly progress through the nearest neural connections.{{sfn|Brundin|Melki|2017|p=9812}} | |||
| ====Braak's hypothesis==== | |||
| The precise mechanism whereby aggregates of alpha-synuclein damage the cells is not known. The aggregates may be merely a normal reaction by the cells as part of their effort to correct a different, as-yet unknown, insult. It does appear that alpha-synuclein aggregation is enhanced by the presence of dopamine and the byproducts of dopamine production. Based on this mechanistic hypothesis, a ] of Parkinson's has been generated by introduction of human wild-type α-synuclein into the mouse genome under control of the ]-β promoter. | |||
| {{Main|Parkinson's disease and gut-brain axis#Braak's hypothesis}} | |||
| <ref>{{cite journal | |||
| In 2002, ] and colleagues proposed that Parkinson's disease begins outside the brain and is triggered by a "neuroinvasion" of some unknown pathogen.{{sfn|Dorsey|De Mirandab|Horsager|Borghammer|2024|p=363}}{{sfn|Rietdijk|Perez-Pardo|Garssen|van Wezel|2017|p=2}} The pathogen enters through the nasal cavity and is swallowed into the digestive tract, initiating Lewy pathology in both areas.{{sfn|Rietdijk|Perez-Pardo|Garssen|van Wezel|2017|p=1}}{{sfn|Dorsey|De Mirandab|Horsager|Borghammer|2024|p=363}} This alpha-synuclein pathology may then travel from the gut to the central nervous system through the ].{{sfn|Rietdijk|Perez-Pardo|Garssen|van Wezel|2017|p=3}} This theory could explain the presence of Lewy pathology in both the enteric nervous system and olfactory tract neurons, as well as clinical symptoms like loss of small and gastrointestinal problems.{{sfn|Rietdijk|Perez-Pardo|Garssen|van Wezel|2017|p=2}} It has also been suggested that environmental toxicants might be ingested in a similar manner to trigger PD.{{sfn|Dorsey|De Mirandab|Horsager|Borghammer|2024|pp=363-364, 371-372}} | |||
| | author=Eliezer Masliah, Edward Rockenstein, Isaac Veinbergs, Margaret Mallory, Makoto Hashimoto, Ayako Takeda, Yutaka Sagara, Abbyann Sisk, Lennart Mucke | |||
| | title= Dopaminergic Loss and Inclusion Body Formation in alpha-Synuclein Mice: Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders | |||
| | journal=Science | |||
| | volume=287 | issue=5456 | year=2000 | pages= 1265–1269 | |||
| | id=PMID 10678833 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| ====Catecholaldehyde hypothesis==== | |||
| ==Causes of Parkinson's disease== | |||
| {{Main|Catecholaldehyde hypothesis}} | |||
| ] argues that the ] metabolite ] (pictured) triggers ] aggregation.]] | |||
| The enzyme ] (MAO) plays a central role in the metabolism of the neurotransmitter ] and other ]. The ] argues that the oxidation of dopamine by MAO into ] (DOPAL) and ] and the subsequent abnormal accumulation thereof leads to neurodegeneration. The theory posits that DOPAL interacts with alpha-synuclein and causes it to aggregate.{{sfn|Goldstein|2020|p=169}}{{sfn|Goldstein|2021|pp=1-3}} | |||
| ====Mitochondrial dysfunction==== | |||
| Most people with Parkinson's disease are described as having idiopathic Parkinson's disease (having no specific cause). There are far less common causes of Parkinson's disease including genetic, toxins, head trauma, and drug induced Parkinson's disease. | |||
| Whether mitochondrial dysfunction is a cause or consequence of PD pathology remains unclear.{{sfn|Chen|Turnbull|Reeve|2019|pp=1, 15}} Impaired ], increased ], and reduced ] may contribute to neurodegeneration.{{sfn|Chen|Turnbull|Reeve|2019|pp=1, 4-5, 15}} The finding that ]—a ] inhibitor and MPTP metabolite—caused parkinsonian symptoms strongly implied that mitochondria contributed to PD pathogenesis.{{sfn|Chen|Turnbull|Reeve|2019|p=2}}{{sfn|Borsche|Pereira|Klein|Grünewald|2021|p=45}} Alpha-synuclein and toxicants like ] similarly disrupt respiratory complex I.{{sfn|Chen|Turnbull|Reeve|2019|p=2, 13}} Additionally, faulty gene variants involved in familial Parkinson's—including ''PINK1'' and ''Parkin''—prevent the elimination of dysfunctional mitochondria through ].{{sfn|Chen|Turnbull|Reeve|2019|pp=6-7, 8, 15}}{{sfn|Borsche|Pereira|Klein|Grünewald|2021|pp=47-49}} | |||
| === |
====Neuroinflammation==== | ||
| Some hypothesize that neurodegeneration arises from a chronic ] created by local activated ] and infiltrating immune cells.{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}} Mitochondrial dysfunction may also drive immune activation, particularly in monogenic PD.{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}} Some ] increase the risk of developing PD, supporting an autoimmune contribution.{{sfn|Tan|Chao|West|Chan|2020|p=303}} Additionally, ] and ] infections increase the risk of PD, possibly due to a ] alpha-synuclein.{{sfn|Tan|Chao|West|Chan|2020|p=304}} Parkinson's risk is also decreased with ].{{sfn|Morris|Spillantini|Sue|Williams-Gray|2024}} | |||
| In recent years, a number of specific genetic mutations causing Parkinson's disease have been discovered, including in certain populations (]). These account for a small minority of cases of Parkinson's disease. Somebody who has Parkinson's disease is more likely to have relatives that also have Parkinson's disease. However, this does not mean that the disorder has been passed on genetically. | |||
| == Pathophysiology == | |||
| Genetic forms that have been identified include: | |||
| {{Main|Pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| :''external links in this section are to ]'' | |||
| ]-releasing ]s in the ], seen by the loss of dark ] in the lower inset.]] | |||
| * '']'' (), caused by mutations in the '']'' gene, which codes for the ] ]. PARK1 causes ] Parkinson disease. So-called '']'' is probably caused by triplication of ''SNCA''.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Singleton A, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, Lincoln S, Crawley A, Hanson M, Maraganore D, Adler C, Cookson M, Muenter M, Baptista M, Miller D, Blancato J, Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K | title = alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. | journal = Science | volume = 302 | issue = 5646 | pages = 841 | year = 2003 | id = PMID 14593171}}</ref> | |||
| Parkinson's disease has two hallmark pathophysiological processes: the abnormal aggregation of alpha-synuclein that leads to Lewy pathology, and the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the ].{{sfn|Pardo-Moreno|García-Morales|Suleiman-Martos|Rivas-Domínguez|2023|p=3}}{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|p=88}} The death of these neurons reduces available dopamine in the ], which in turn affects circuits controlling movement in the ].{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|p=88}} By the time motor symptoms appear, 50–80 percent of all dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra have degenerated.{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|p=88}} | |||
| * '']'' (), caused by mutations in protein ]. Parkin mutations may be one of the most common known genetic causes of early-onset Parkinson disease. In one study, of patients with onset of Parkinson disease prior to age 40 (10% of all PD patients), 18% had parkin mutations, with 5% ] mutations.<ref>{{cite journal | author=P Poorkaj ''et al.'' | title=parkin mutation analysis in clinic patients with early-onset Parkinson's disease | journal=] | year=2004 | volume=129A | issue=1 | pages= 44–50 | url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/109062750/ABSTRACT?CRETRY=1&SRETRY=0}}</ref> Patients with an ] family history of parkinsonism are much more likely to carry parkin mutations if age at onset is less than 20 (80% vs. 28% with onset over age 40).<ref>{{cite journal | author=Ebba Lohmann ''et al.'' | title=How much phenotypic variation can be attributed to parkin genotype? | journal=] | year=2003 | volume=54 | issue=2 | pages= 176–185 | url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/104536414/ABSTRACT}}</ref>Patients with ] mutations (PARK2) do not have Lewy bodies. Such patients develop a syndrome that closely resembles the sporadic form of PD; however, they tend to develop symptoms at a much younger age. | |||
| However, cell death and Lewy pathology are not limited to the substantia nigra.{{sfn|Dickson|2018|p=S32}} The ] holds that alpha-synuclein pathology begins in the ] or outside the central nervous system in the ] before ascending the brain stem.{{sfn|Ye|Robak|Yu|Cykowski|2023|p=98}} In the third Braak stage, Lewy body pathology appears in the substantia nigra,{{sfn|Ye|Robak|Yu|Cykowski|2023|p=98}} and, by the sixth step, Lewy pathology has spread to the limbic and neocortical regions.{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|p=93}} Although Braak staging offers a strong basis for PD progression, the Lewy pathology around 50 percent patients do not adhere to the predicted model.{{sfn|Henderson|Trojanowski|Lee|2019|p=2}} Indeed, Lewy pathology is highly variable and may be entirely absent in some PD patients.{{sfn|Dickson|2018|p=S32}}{{sfn|Ye|Robak|Yu|Cykowski|2023|p=96}} | |||
| * '']'' (), mapped to 2p, autosomal dominant, only described in a few kindreds. | |||
| * '']'', caused by mutations in the ''UCHL1'' gene () which codes for the protein ] | |||
| * '']'' (), caused by mutations in ''PINK1'' () which codes for the protein ]. | |||
| * '']'' (), caused by mutations in ] () | |||
| * '']'' (), caused by mutations in ] which codes for the protein ]. ''In vitro'', mutant LRRK2 causes protein aggregation and cell death, possibly through an interaction with parkin.<ref>{{cite journal | author=Wanli W. Smith ''et al.'' | title=Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) interacts with parkin, and mutant LRRK2 induces neuronal degeneration | journal=] | year=2005 | volume=102 | issue=51 | pages= 18676–18681 | url=http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/abstract/102/51/18676}}</ref> LRRK2 mutations, of which the most common is G2019S, cause autosomal dominant Parkinson disease, with a ] of nearly 100% by age 80.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Kachergus J, Mata I, Hulihan M, Taylor J, Lincoln S, Aasly J, Gibson J, Ross O, Lynch T, Wiley J, Payami H, Nutt J, Maraganore D, Czyzewski K, Styczynska M, Wszolek Z, Farrer M, Toft M | title = Identification of a novel LRRK2 mutation linked to autosomal dominant parkinsonism: evidence of a common founder across European populations. | journal = Am J Hum Genet | volume = 76 | issue = 4 | pages = 672-80 | year = 2005 | id = PMID 15726496}}</ref> G2019S is the most common known genetic cause of Parkinson disease, found in 1-6% of U.S. and European PD patients.<ref>{{cite journal | author=A Brice | title=Genetics of Parkinson's disease: LRRK2 on the rise (Scientific Commentary) | journal=] | year=2005 | volume=128 | issue=12 | pages= 2760–2762 | url=http://brain.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/extract/128/12/2760}}</ref> It is especially common in Ashkenazi Jewish patients, with a prevalence of 29.7% in familial cases and 13.3% in sporadic.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Ozelius L, Senthil G, Saunders-Pullman R, Ohmann E, Deligtisch A, Tagliati M, Hunt A, Klein C, Henick B, Hailpern S, Lipton R, Soto-Valencia J, Risch N, Bressman S | title = LRRK2 G2019S as a cause of Parkinson's disease in Ashkenazi Jews. | journal = N Engl J Med | volume = 354 | issue = 4 | pages = 424-5 | year = 2006 | id = PMID 16436782}}</ref> | |||
| * '']'' (), maps to the X chromosome | |||
| ===Alpha-synuclein pathology=== | |||
| ===Toxins=== | |||
| {{Further|Protein aggregation|Lewy body}} | |||
| One theory holds that the disease may result in many or even most cases from the combination of a genetically determined vulnerability to environmental ]s along with exposure to those toxins.<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| ] stained brown in PD brain tissue]] | |||
| |author=DA Di Monte, M Lavasani, AB Manning-Bog | |||
| Alpha-synuclein is an intracellular protein typically localized to ] and involved in ], ], and ].{{sfn|Henderson|Trojanowski|Lee|2019|p=2}}{{sfn|Chen|Gu|Wang|2022}} When ], it can aggregate into oligomers and proto-fibrils that in turn lead to Lewy body formation.{{sfn|Chen|Gu|Wang|2022}}{{sfn|Menšíková|Matěj|Colosimo|Rosales|2022|p=8}}{{sfn|Borghammer|2018|p=5}} Due to their lower ], oligomers and proto-fibrils may disseminate and be transmitted to other cells more rapidly.{{sfn|Borghammer|2018|p=5}} | |||
| |title=Environmental factors in Parkinson's disease | |||
| |journal=] | year=2002 | volume=23 | issue=4–5 | pages=487–502 | |||
| |url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=12428721 | |||
| }}</ref> This hypothesis is consistent with the fact that Parkinson's disease is not distributed homogenously throughout the population: rather, its incidence varies geographically. It would appear that incidence varies by time as well, for although the later stages of untreated PD are distinct and readily recognizable, the disease was not remarked upon until the beginnings of the Industrial Revolution, and not long thereafter become a common observation in clinical practice. The toxins most strongly suspected at present are certain ]s and industrial metals. ] is used as a model for Parkinson's as it can rapidly induce parkinsonian symptoms in human beings and other animals, of any age. MPTP was notorious for a string of Parkinson's disease cases in California in 1982 when it contaminated the illicit production of the synthetic opiate ]. | |||
| Lewy bodies consist of a fibrillar exterior and granular core. Although alpha-synuclein is the dominant ] component, the core contains mitochondrial and autophagosomal membrane components, suggesting a link with organelle dysfunction.{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|p=95}}{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|p=89}} It is unclear whether Lewy bodies themselves contribute to or are simply the result of PD pathogenesis: alpha-synuclein oligomers can independently mediate cell damage, and neurodegeneration can precede Lewy body formation.{{sfn|Menšíková|Matěj|Colosimo|Rosales|2022|p=6}} | |||
| Other toxin-based models employ PCBs,<ref>{{cite news | |||
| |first=Leslie | |||
| |last=Orr | |||
| |title=PCBs, fungicide open brain cells to Parkinson's assault | |||
| |date=February 10, 2005 | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| |url=http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/medicalnews.php?newsid=19791 | |||
| }}</ref> ]<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| |author=Amy B. Manning-Bog ''et al.'' | |||
| |title= The Herbicide Paraquat Causes Up-regulation and Aggregation of α-Synuclein in Mice | |||
| |journal=] | year=2002 | volume=277 | issue=3 | pages=1641–1644 | |||
| |url=http://www.jbc.org/cgi/content/full/277/3/1641 | |||
| }}</ref> (a herbicide) in combination with maneb, a fungicide<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| |author=Mona Thiruchelvam ''et al.'' | |||
| |title=The Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic System as a Preferential Target of Repeated Exposures to Combined Paraquat and Maneb: Implications for Parkinson's Disease | |||
| |journal=] | year=2000 | volume=20 | issue=24 | pages=9207–9214 | |||
| |url=http://www.jneurosci.org/cgi/content/full/20/24/9207 | |||
| }}</ref> ]<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| |author=Ranjita Betarbet ''et al.'' | |||
| |title=Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson's disease | |||
| |journal=] | year=2000 | volume=3 | pages=1301–1306 | |||
| |url=http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v3/n12/abs/nn1200_1301.html | |||
| }}</ref> (an insecticide), and specific organochlorine pesticides including dieldrin<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| |author=Masashi Kitazawaa, Vellareddy Anantharama and Anumantha G. Kanthasamy | |||
| |title=Dieldrin-induced oxidative stress and neurochemical changes contribute to apoptopic cell death in dopaminergic cells | |||
| |journal=] | year=2001 | volume=31 | issue=11 | pages=1473–1485 | |||
| |url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T38-44HSN76-P&_coverDate=12%2F01%2F2001&_alid=373422978&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_qd=1&_cdi=4940&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=5a104ac89bd7948e14863371142a639a | |||
| }}</ref> and lindane.<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| |author=F.M. Corrigan, C.L. Wienburg, R.F. Shore, S.E. Daniel, D. Mann | |||
| |title=Organochlorine Insecticides in Substandia Nigra in Parkinson's Disease | |||
| |journal=] | year=2000 | volume=59 | issue=4 | pages=229–234 | |||
| |url=http://journalsonline.tandf.co.uk/openurl.asp?genre=article&eissn=1087-2620&volume=59&issue=4&spage=229 | |||
| }}</ref> Numerous studies have found an increase in Parkinson disease in persons who consume rural well water; researchers theorize that water consumption is a proxy measure of pesticide exposure. In agreement with this hypothesis are studies which have found a dose-dependent an increase in PD in persons exposed to agricultural chemicals. | |||
| ===Pathways involved in neurodegeneration=== | |||
| Almost all of the PD-causing toxins act on the ] ] of the ], and sporadic PD cases have been found to have a partial loss of activity of this enzyme complex. Studies in ] have found that ], rather than nuclear DNA, is responsible for the dysfunction. Most recently, ] mutations in one of the mitochondrial complex I genes, ND5, were found to be sufficient to diagnose sporadic PD correctly in 27 out of 28 cases. While additional studies are needed, mitochondrial microheteroplasmic mutations may be the cause of the majority of PD cases. | |||
| {{See also|Neurodegeneration#Mechanisms}} | |||
| Three major pathways—], ], and mitochondrial maintenance—are known to be affected by and contribute to Parkinson's pathogenesis, with all three linked to alpha-synuclein.{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|pp=96-99}} High risk gene variants also impair all three of these processes.{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|pp=96-99}} All steps of vesicular trafficking are impaired by alpha-synuclein. It blocks ] (ER) vesicles from reaching the ]—leading to ]—and Golgi vesicles from reaching the ], preventing alpha-synuclein degradation and leading to its build-up.{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|pp=96-97}} Risky gene variants, chiefly ''GBA'', further compromise lysosomal function.{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|pp=98-99}} Although the mechanism is not well established, alpha-synuclein can impair mitochondrial function and cause subsequent ]. Mitochondrial dysfunction can in turn lead to further alpha-synuclein accumulation in a ].{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|p=99}} Microglial activation, possibly caused by alpha-synuclein, is also strongly indicated.{{sfn|Vázquez-Vélez|Zoghbi|2021|p=100}}{{sfn|Ye|Robak|Yu|Cykowski|2023|p=112}} | |||
| ==Risk factors== | |||
| However, the ubiquity of agricultural chemical exposures makes it difficult to gauge the true extent of the problem. In the current state of knowledge about the origins of the disease, it appears that family history of the disease and (especially) multiple episodes of head-trauma-induced unconsciousness increase individual risk more than does pesticide exposure, but research is continuing. | |||
| ===Positive risk factors=== | |||
| As 90 percent of Parkinson's cases are sporadic, the identification of the risk factors that may influence disease progression or severity is critical.{{sfn|Ascherio |Schwarzschild|2016|p=1257}}{{sfn|De Mirandaa|Goldmanb|Millerc|Greenamyred|2024|p=46}} The most significant risk factor in developing PD is age, with a prevalence of 1 percent in those aged over 65 and approximately 4.3 percent in age over 85.{{sfn|Coleman|Martin|2022|pp=2321-2322}} ] significant increases PD risk, especially if recent.{{sfn|Ascherio|Schwarzschild|2016|p=1260}}{{sfn|Delic|Beck|Pang|Citron|2020|pp=1-2}} Dairy consumption correlates with a higher risk, possibly due to contaminants like ].{{sfn|Ascherio |Schwarzschild|2016|p=1259}} Although the connection is unclear, ] diagnosis is associated with an approximately 45 percent risk increase.{{sfn|Ascherio |Schwarzschild|2016|p=1259}} There is also an association between ] use and PD risk.{{sfn|Ascherio|Schwarzschild|2016|p=1259}} | |||
| === |
===Protective factors=== | ||
| ]—a potent antioxidant—are associated with a lower risk of Parkinson's.]] | |||
| Past episodes of head trauma are reported more frequently by sufferers than by others in the population.<ref name=Bower>{{cite journal | author=J. H. Bower ''et al.'' | title=Head trauma preceding PD | journal=] | year=2003 | volume=60 | issue= | pages= 1610–1615 | url=http://www.neurology.org/cgi/content/abstract/60/10/1610}}</ref> | |||
| Although no compounds or activities have been mechanistically established as ] for Parkinson's,{{Sfn|Crotty|Schwarzschild|2020|p=1}}{{Sfn|Fabbri|Rascol|Foltynie|Carroll|2024|p=2}} several factors have been found to be associated with a decreased risk.{{Sfn|Crotty|Schwarzschild|2020|p=1}} ] and ] is strongly associated with a decreased risk, reducing the chance of developing PD by up to 70%.{{Sfn|Ascherio|Schwarzschild|2016|p=1262}}{{Sfn|Grotewolda|Albina|2024|pp=1–2}}{{sfn|Ascherio |Schwarzschild|2016|p=1259}} Various tobacco and smoke components have been hypothesized to be neuroprotective, including ], ], and ].{{Sfn|Grotewolda|Albina|2024|p=2}}{{Sfn|Rose|Schwarzschild|Gomperts|2024|pp=268—269}} Consumption of ], ], or ] is also strongly associated with neuroprotection.{{Sfn|Grotewolda|Albina|2024|p=3}}{{Sfn|Ren|Chen|2020|p=1}} Prescribed ] like ] may reduce risk.{{Sfn|Grotewolda|Albina|2024|p=3}} | |||
| <ref>{{cite journal | author=M. Stern ''et al.'' | title=The epidemiology of Parkinson's disease | journal=] | year=1991 | volume=48 | issue=9 | pages= 903–907 | url=http://archneur.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/abstract/48/9/903}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="Uryu2003">{{cite journal | author = Uryu K, Giasson B, Longhi L, Martinez D, Murray I, Conte V, Nakamura M, Saatman K, Talbot K, Horiguchi T, McIntosh T, Lee V, Trojanowski J | title = Age-dependent synuclein pathology following traumatic brain injury in mice. | journal = Exp Neurol | volume = 184 | issue = 1 | pages = 214-24 | year = 2003 | id = PMID 14637093}}</ref> | |||
| A methodologically strong recent study<ref name=Bower/> found that those who have experienced a head injury are four times more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease than those who have never suffered a head injury. The risk of developing Parkinson’s increases eightfold for patients who have had head trauma requiring hospitalization, and it increases 11-fold for patients who have experienced severe head injury. The authors comment that since head trauma is a rare event, the contribution to PD incidence is slight. They express further concern that their results may be biased by recall, i.e., the PD patients because they reflect upon the causes of their illness, may remember head trauma better than the non-ill control subjects. | |||
| Although findings have varied, usage of ] (NSAIDs) like ] may be neuroprotective.{{Sfn|Singh|Tripathi|Singh|2021|p=10}}{{Sfn|Ascherio|Schwarzschild|2016|pp=1265–1266}} ] may also have a protective effect, with a 22% risk reduction reported.{{Sfn|Lin|Pang|Li|Ou|2024|p=1}} Higher blood concentrations of ]—a potent ]—have been proposed to be neuroprotective.{{Sfn|Grotewolda|Albina|2024|p=2}}{{Sfn|Ascherio|Schwarzschild|2016|p=1263}} Although longitudinal studies observe a slight decrease in PD risk among those who consume ]—possibly due to alcohol's urate-increasing effect—alcohol abuse may increase risk.{{Sfn|Ascherio|Schwarzschild|2016|p=1261}}{{Sfn|Kamal|Tan|Ibrahim|Shaikh|2020|p=8}} | |||
| ===Drug-induced=== | |||
| Antipsychotics, which are used to treat ] and psychosis, can induce the symptoms of Parkinson's disease (or parkinsonism) by lowering dopaminergic activity. Due to feedback inhibition, L-dopa can eventually cause the symptoms of Parkinson's disease that it initially relieves. Dopamine receptors can also eventually contribute to Parkinson's disease symptoms by increasing the sensitivity of dopamine receptors. | |||
| == |
==Diagnosis== | ||
| Diagnosis of Parkinson's disease is largely clinical, relying on ] and examination of symptoms, with an emphasis on symptoms that appear in later stages.{{sfn|Armstrong|Okun|2020|p=548}}{{sfn|Rizzo|Copetti|Arcuti|Martino|2016|p=1}} Although early stage diagnosis is not reliable,{{sfn|Rizzo|Copetti|Arcuti|Martino|2016|p=1}}{{sfn|Ugrumov|2020|p=997}} prodromal diagnosis may consider previous family history of Parkinson's and possible early symptoms like ] (RBD), reduced sense of smell, and gastrointestinal issues.{{sfn|Armstrong|Okun|2020|p=551}} Isolated RBD is a particularly significant sign as 90% of those affected will develop some form of neurodegenerative parkinsonism.{{sfn|Tolosa|Garrido|Scholz|Poewe|2021|p=391}} Diagnosis in later stages requires the manifestation of parkinsonism, specifically bradykinesia and rigidity or tremor. Further support includes other motor and non-motor symptoms and genetic profiling.{{sfn|Armstrong|Okun|2020|pp=551-552}} | |||
| Parkinson's disease is a chronic disorder that requires broad-based management including patient and family education, support group services, general wellness maintenance, exercise, and nutrition. At present, there is no cure for PD, but medications or surgery can provide relief from the symptoms. | |||
| A PD diagnosis is typically confirmed by two of the following criteria: responsiveness to levodopa, resting tremor, levodopa-induced dyskinesia, or with ].{{sfn|Armstrong|Okun|2020|pp=551-552}} If these criteria are not met, atypical parkinsonism is considered.{{sfn|Armstrong|Okun|2020|p=551}} However, definitive diagnoses can only be made post-mortem through pathological analysis.{{sfn|Rizzo|Copetti|Arcuti|Martino|2016|p=1}} Misdiagnosis is common, with a reported error rate of near 25 percent, and diagnoses often change during follow-ups.{{sfn|Rizzo|Copetti|Arcuti|Martino|2016|p=1}}{{sfn|Heim|Krismer|De Marzi|Seppi|2017|p=916}} Diagnosis can be further complicated by multiple overlapping conditions.{{sfn|Rizzo|Copetti|Arcuti|Martino|2016|p=1}} | |||
| ==== Levodopa ==== | |||
| ] | |||
| The most widely used form of treatment is ] in various forms. L-dopa is transfomed into dopamine in the dopaminergic neurons by L-aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (often known by its former name dopa-decarboxylase). However, only 1-5% of L-DOPA enters the dopaminergic neurons. The remaining L-DOPA is often metabolised to dopamine elsewhere, causing a wide variety of side effects. Due to feedback inhibition, L-dopa results in a reduction in the endogenous formation of L-dopa, and so eventually becomes counterproductive. | |||
| ===Imaging=== | |||
| ] and ] are dopa decarboxylase inhibitors. They help to prevent the metabolism of L-dopa before it reaches the dopaminergic neurons and are general given as combination preparations of ] (co-careldopa ]) co-careldopa combined L-dopa and ] in fixed ratios in such branded products of and Parcopa and ] (co-beneldopa ]) as Madopar. There are also controlled release versions of Sinemet and Madopar that spread out the effect of the L-dopa. Duodopa is a combination of levodopa and carbidopa, dispersed as a viscous gel. Using a patient-operated portable pump, the drug is continuously delivered via a tube directly into the upper small intestine, where it is rapidly absorbed. | |||
| ] ] uptake in the ] of a Parkinson's patient, captured through ]]] | |||
| Diagnosis can be aided by molecular imaging techniques such as ] (MRI), ] (PET), and ] (SPECT).{{sfn|Bidesi|Andersen|Windhorst|Shalgunov|2021|p=660}} As both conventional MRI and ] (CT) scans are usually normal in patients with early PD, they can be used to exclude other pathologies that cause parkinsonism.{{sfn|Heim|Krismer|De Marzi|Seppi|2017|p=916}}{{sfn|Brooks|2010|p=597}} ] can differentiate PD from ] (MSA).{{sfn|Tolosa|Garrido|Scholz|Poewe|2021|p=392}} Emerging MRI techniques of at least 3.0 T ]—including ], ], and ]—may detect abnormalities in the substantia nigra, nigrostriatal pathway, and elsewhere.{{sfn|Heim|Krismer|De Marzi|Seppi|2017|p=916}} | |||
| Unlike MRI, PET and SPECT use ] for imaging.{{sfn|Bidesi|Andersen|Windhorst|Shalgunov|2021|p=665}} Both techniques can aid diagnosis by characterizing PD-associated alterations in the metabolism and ] of dopamine in the basal ganglia.{{sfn|Suwijn|van Boheemen|de Haan|Tissingh|2015}}{{sfn|Bidesi|Andersen|Windhorst|Shalgunov|2021|pp=664-672}} Largely used outside the United States, iodine-123-meta-iodobenzylguanidine ] ] can assess heart muscle denervation to support a PD diagnosis.{{sfn|Armstrong|Okun|2020|p=552}} | |||
| ] inhibits the COMT enzyme, thereby prolonging the effects of L-dopa, and so has been used to complement L-dopa. However, due to its side effects, such as possible liver failure is limited in its availability. A similar drug, ], has similar efficacy and has not been shown to cause significant alterations of liver function. Stalevo<ref>{{cite web | title=Stalevo | url=http://www.stalevo.com/index.jsp | publisher=Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation}}</ref> contains Levodopa, Carbidopa and Entacopone. | |||
| ===Differential diagnosis=== | |||
| '']'', is a natural source of therapeutic quantities of L-dopa. | |||
| ] with MRI]] | |||
| {{See also|Parkinson-plus syndrome}} | |||
| ] of Parkinson's is among the most difficult in ].{{sfn|Heim|Krismer|De Marzi|Seppi|2017|p=915}} Differentiating early PD from atypical parkinsonian disorders is a major difficulty. In their initial stages, PD can be difficult to distinguish from the atypical neurodegenerative parkinsonisms, including MSA, dementia with Lewy bodies, and the ] ] and ].{{sfn|Tolosa|Garrido|Scholz|Poewe|2021|p=389}}{{sfn|Caproni|Colosimo|2020|p=21}} Other conditions that may present similarly to PD include vascular parkinsonism, ], and ].{{sfn|Tolosa|Garrido|Scholz|Poewe|2021|p=390}}{{sfn|Caproni|Colosimo|2020|pp=15, 21}} | |||
| The International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society has proposed a set of criteria that, unlike the standard Queen's Square Brain Bank Criteria, includes non-exclusionary "red-flag" clinical features that may not suggest Parkinson's.{{sfn|Tolosa|Garrido|Scholz|Poewe|2021|pp=390-391}} A large number of "red flags" have been proposed and adopted for various conditions that might mimic the symptoms of PD.{{sfn|Caproni|Colosimo|2020|p=14}} Diagnostic tests, including gene sequencing, molecular imaging techniques, and assessment of smell may also distinguish PD.{{sfn|Tolosa|Garrido|Scholz|Poewe|2021|p=392}} MRI is particularly powerful due to several unique features for atypical parkinsonisms.{{sfn|Tolosa|Garrido|Scholz|Poewe|2021|p=392}} Key distinguishing symptoms and features include:{{sfn|Tolosa|Garrido|Scholz|Poewe|2021|p=391}}{{Sfn|Simon|Greenberg|Aminoff|2017}}{{Sfn|Greenland|Barker|2018}} | |||
| ==== Dopamine agonists ==== | |||
| The dopamine-agonists ] (Parlodel), ] (Permax), ] (Mirapex), ] (Requip), ] (Cabaser), ] (Apokyn), and ] (Revanil), are moderately effective. These have their own side effects including those listed above in addition to somnolence, hallucinations and /or insomnia. Dopamine agonists initially act by stimulating some of the dopamine receptors. However, they cause the dopamine receptors to become progressively less sensitive, thereby eventually increasing the symptoms. | |||
| {| class="wikitable plainrowheaders" | |||
| Dopamine agonists can be useful for patients experiencing on-off fluctuations and dyskinesias as a result of high doses of L-dopa. Apomorphine can be administered via subcutaneous injection using a small pump which is carried by the patient. A low dose is automatically administered throughout the day, reducing the fluctuations of motor symptoms by providing a steady dose of dopaminergic stimulation. After an initial "apomorphine challenge" in hospital to test its effectiveness and brief patient and caregiver, the primary caregiver (often a spouse or partner) takes over maintenance of the pump. The injection site must be changed daily and rotated around the body to avoid the formation of nodules. Apomorphine is also available in a more acute dose as an ] pen for emergency doses such as after a fall or first thing in the morning. | |||
| |- | |||
| !scope="col" | Disorder | |||
| !scope="col" | Distinguishing symptoms and features | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| | Levodopa resistance, ], ], corticosensory loss, ], ], and ] | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| | Levodopa resistance, cognitive predominance before motor symptoms, and fluctuating cognitive symptoms | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| | Tremor that worsens with action, normal SPECT scan | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| | Levodopa resistance, rapidly progressive, autonomic failure, stridor, present ], cerebellar ataxia, and specific MRI findings like the "Hot Cross Bun" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| | Levodopa resistance, restrictive vertical gaze, ], ], specific MRI findings, and early and different postural difficulties | |||
| |- | |||
| |} | |||
| ==Management== | |||
| ==== MAO-B inhibitors ==== | |||
| {{Main|Management of Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| ] (Eldepryl) and rasagiline (Azilect) reduce the symptoms by inhibiting monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B), which inhibits the breakdown of dopamine secreted by the dopaminergic neurons. By-products of selegiline include amphetamine and methamphetamine, which can cause side effects such as insomnia. Use of L-dopa in conjunction with selegiline has increased mortality rates that have not been effectively explained. Another side effect of the combination can be stomatitis. One report raised concern about increased mortality when MAO-B inhibitors were combined with L-dopa <ref>{{cite journal | author = Thorogood M, Armstrong B, Nichols T, Hollowell J | title = Mortality in people taking selegiline: observational study. | journal = BMJ | volume = 317 | issue = 7153 | pages = 252-4 | year = 1998 | id = PMID 9677215}}</ref>; however subsequent studies have not confirmed this finding<ref>{{cite journal | author = Marras C, McDermott M, Rochon P, Tanner C, Naglie G, Rudolph A, Lang A | title = Survival in Parkinson disease: thirteen-year follow-up of the DATATOP cohort. | journal = Neurology | volume = 64 | issue = 1 | pages = 87-93 | year = 2005 | id = PMID 15642909}}</ref>. Unlike other non selective ], tyramine-containing foods do not cause a hypertensive crisis. | |||
| As of 2024, no disease-modifying therapies exist that reverse or slow neurodegeneration, processes respectively termed neurorestoration and neuroprotection.{{Sfn|Crotty|Schwarzschild|2020|p=1}}{{Sfn|Fabbri|Rascol|Foltynie|Carroll|2024|p=2}} Patients are typically managed with a holistic approach that combines lifestyle modifications with ].{{sfn|Connolly|Lang|2014}} Current pharmacological interventions purely target symptoms, by either increasing endogenous ] levels or directly mimicking dopamine's effect on the patient's brain.{{sfn|de Bie|Clarke|Espay|Fox|2020|p=3}}{{sfn|Connolly|Lang|2014}} These include dopamine agonists, MAO-B inhibitors, and levodopa: the most widely used and effective drug.{{sfn|de Bie|Clarke|Espay|Fox|2020|pp=1, 3}}{{sfn|Connolly|Lang|2014}} The optimal time to initiate pharmacological treatment is debated,{{sfn|Kobylecki|2020|p=395}} but initial dopamine agonist and MAO-B inhibitor treatment and later levodopa therapy is common.{{sfn|de Bie|Clarke|Espay|Fox|2020|p=4}} Invasive procedures such as ] may be used for patients that do not respond to medication.{{sfn|Limousin|Foltynie|2019|p=234}}{{sfn|Bronstein|Tagliati|Alterman|Lozano|2011|p=169}} | |||
| ===Medications=== | |||
| === Surgical interventions === | |||
| ====Levodopa==== | |||
| ] | |||
| ]/]/]) pills contain a cocktail of the dopamine precursor <small>L</small>-DOPA and COMT and AAAD inhibitors.]] | |||
| Treating PD with surgery was once a common practice. But after the discovery of levodopa, surgery was restricted to only a few cases. Studies in the past few decades have led to great improvements in surgical techniques, and surgery is again being used in people with advanced PD for whom drug therapy is no longer sufficient. ] is presently the most used surgical means of treatment. | |||
| ] (<small>L</small>-DOPA) is the most widely used and the most effective therapy—the ]—for Parkinson's treatment.{{sfn|de Bie|Clarke|Espay|Fox|2020|pp=1, 3}} The compound occurs naturally and is the immediate precursor for dopamine synthesis in the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra.{{sfn|Tambasco|Romoli|Calabresi|2018|p=1239}} Levodopa administration reduces the dopamine deficiency, alleviating parkinsonian symptoms.{{sfn|LeWitt|Fahn|2016|p=S5-S6}}{{sfn|Tambasco|Romoli|Calabresi|2018|pp=1239-1240}} | |||
| Despite its efficacy, levodopa poses several challenges and has been called the "pharmacologist's nightmare".{{sfn|Tambasco|Romoli|Calabresi|2018|p=1240}}{{sfn|Leta|Klingelhoefer|Longardner|Campagnolo|2023|p=1466}} Its metabolism outside the brain by ] (AAAD) and ] (COMT) can cause nausea and vomiting; inhibitors like ], ], and ] are usually taken with levodopa to mitigate these effects.{{sfn|Leta|Klingelhoefer|Longardner|Campagnolo|2023|pp=1466-1468}}{{sfn|Tambasco|Romoli|Calabresi|2018|p=1241}}{{efn|group=note|These inhibitors do not cross the ] and thus do not prevent levodopa metabolism there.{{sfn|Leta|Klingelhoefer|Longardner|Campagnolo|2023|p=1468}}}} Symptoms may become unresponsive to levodopa, with sudden changes between a state of mobility ("ON time") and immobility ("OFF time").{{sfn|Jing|Yang|Taximaimaiti|Wang|2023|p=1224}} Long-term levodopa use may also ] and motor fluctuations. Although this often causes levodopa use to be delayed to later stages, earlier administration leads to improved motor function and quality of life.{{sfn|de Bie|Clarke|Espay|Fox|2020|pp=1, 3-4}} | |||
| Currently under investigation is gene therapy. This involves using a harmless virus to shuttle a gene into a part of the brain called the subthalamic nucleus (STN). The gene used leads to the production of an enzyme called glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), which catalyses the production of a neurotransmitter called GABA. GABA acts as a direct inhibitor on the overactive cells in the STN. | |||
| ====Dopamine agonists==== | |||
| ] infusion involves, by surgical means, the infusion of GDNF (glial-derived neurotrophic factor) into the basal ganglia using implanted catheters. Via a series of biochemical reactions, GDNF stimulates the formation of L-dopa. GDNF therapy is still in development. | |||
| ] are an alternative or complement for levodopa therapy. They activate dopamine receptors in the striatum, with reduced risk of motor fluctuations and dyskinesia.{{sfn|Jing|Yang|Taximaimaiti|Wang|2023|p=1225}} ] dopamine agonists were commonly used, but have been largely replaced with non-ergot compounds due to severe adverse effects like ] and cardiovascular issues.{{sfn|Jing|Yang|Taximaimaiti|Wang|2023|p=1225}} Non-ergot agonists are efficacious in both early and late stage Parkinson's,{{sfn|Jing|Yang|Taximaimaiti|Wang|2023|p=1226}} The agonist ] is often used for drug-resistant OFF time in later-stage PD.{{sfn|Jing|Yang|Taximaimaiti|Wang|2023|p=1226}}{{sfn|Kobylecki|2020|p=396}} However, after five years of use, impulse control disorders may occur in over 40 percent of PD patients taking dopamine agonists.{{sfn|Kobylecki|2020|p=395}} A problematic, narcotic-like withdrawal effect may occur when agonist use is reduced or stopped.{{sfn|Kobylecki|2020|p=395}}{{sfn|de Bie|Clarke|Espay|Fox|2020|p=1}} Compared to levodopa, dopamine agonists are more likely to cause fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and hallucinations.{{sfn|de Bie|Clarke|Espay|Fox|2020|p=1}} | |||
| ====MAO-B inhibitors==== | |||
| In the future, implantation of cells genetically engineered to produce dopamine or stem cells that transform into dopamine-producing cells may become available. Even these, however, will not constitute cures because they do not address the considerable loss of activity of the dopaminergic neurons. | |||
| MAO-B inhibitors—such as ], ] and ]—increase the amount of dopamine in the basal ganglia by inhibiting the activity of ], an enzyme that breaks down dopamine.{{sfn|Robakis|Fahn|2015|pp=433-434}} These compounds mildly alleviate motor symptoms when used as monotherapy but can also be used with levodopa and can be used at any disease stage.{{sfn|Robakis|Fahn|2015|p=433}} When used with levodopa, time spent in the off phase is reduced.{{Sfn|Binde|Tvete|Gåsemyr|Natvig|2018|p=1924}}{{sfn|Tan|Jenner|Chen|2022|p=477}} Selegiline has been shown to delay the need for initial levodopa, suggesting that it might be neuroprotective and slow the progression of the disease.{{sfn|Alborghetti|Nicoletti|2019}} Common side effects are nausea, dizziness, insomnia, sleepiness, and (in selegiline and rasagiline) orthostatic hypotension.{{sfn|Alborghetti|Nicoletti|2019}}{{sfn|Armstrong|Okun|2020}} MAO-Bs are known to increase serotonin and cause a potentially dangerous condition known as ].{{sfn|Alborghetti|Nicoletti|2019}}{{sfn|Robakis|Fahn|2015|p=435}} | |||
| === |
====Other drugs==== | ||
| Treatments for non-motor symptoms of PD have not been well studied and many medications are used ].{{sfn|Tanner|Ostrem|2024}} A diverse range of symptoms beyond those related to motor function can be treated pharmaceutically.{{sfn|The National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions}} Examples include ] for cognitive impairment and ] for ].{{sfn|Seppi|Ray Chaudhuri|Coelho|Fox|2019|pp=183, 185, 188}} ], ] and ] are commonly used off label for orthostatic hypotension related to autonomic dysfunction. Sublingual ] or ] injections may be used off-label for drooling. ] and ] are often used for depression related to PD, but there is a risk of ] with the SSRI or SNRI antidepressants.{{sfn|Tanner|Ostrem|2024}} Doxepin and rasagline may reduce physical fatigue in PD.{{sfn|Elbers|Verhoef|van Wegen|Berendse|2015}} Other treatments have received government approval, such as the first FDA-approved treatment for PD psychosis, ]. Although its efficacy is inferior to off-label ], it has significantly fewer side effects.{{sfn|Rissardo|Durante|Sharon|Caprara|2022|p=1}} | |||
| Nutrients have been used in clinical studies and are widely used by people with Parkinson's disease in order to partially treat Parkinson's disease or slow down its deterioration. The L-dopa precursor L-tyrosine was shown to relieve an average of 70% of symptoms.<ref>{{cite journal | author=(unknown) | title=(unknown) | journal=] | year=1986 | volume=302 | issue= | pages=435 | url= }}</ref> Ferrous iron, the essential cofactor for L-dopa biosynthesis was shown to relieve between 10% and 60% of symptoms in 110 out of 110 patients.<ref>{{cite journal | author=W. Birkmayer and J. G. D. Birkmayer | title=Iron, a new aid in the treatment of Parkinson patients | journal=] | year=1986 | volume=67 | issue=3–4 | pages=287–292 | url=http://www.springerlink.com/link.asp?id=tp15r2g8u6327731}}</ref> | |||
| <!-- this ref needs info adding if it is to be kept--><ref>{{cite journal | author=(unknown) | title=Early diagnosis and preventive therapy in Parkinson's disease | journal=(unknown) | year=1989 | pages=323}}</ref> Another complementary approach is Dopavite, a nutritional supplement which contains both of these substances and all the other nutrients required for dopamine formation. However, the efficacy of this nutritional supplement has not been validated in clinical trials. | |||
| ===Invasive interventions=== | |||
| More limited efficacy has been obtained with the use of THFA, NADH, and pyridoxine—coenzymes and coenzyme precursors involved in dopamine biosynthesis{{fact}}. Vitamin C and vitamin E in large doses are commonly used by patients in order to theoretically lessen the cell damage that occurs in Parkinson's disease. This is because the enzymes superoxide dismutase and catalase require these vitamins in order to nullify the superoxide anion, a toxin commonly produced in damaged cells. However, in the randomized controlled trial, DATATOP of patients with early PD, no beneficial effect for vitamin E compared to placebo was seen<ref>{{cite journal | author = | title = Effects of tocopherol and deprenyl on the progression of disability in early Parkinson's disease. The Parkinson Study Group. | journal = N Engl J Med | volume = 328 | issue = 3 | pages = 176-83 | year = 1993 | id = PMID 8417384}}</ref> | |||
| {{Further|Deep brain stimulation}} | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Surgery for Parkinson's first appeared in the 19th century and by the 1960s had evolved into ] that lesioned the ], ] or ] (a ]).{{sfn|Lozano|Tam|Lozano|2018|pp=1-2}} The discovery of <small>L</small>-DOPA for PD treatment caused ablative therapies to largely disappear.{{sfn|Lozano|Tam|Lozano|2018|p=2}}{{sfn|Bronstein|Tagliati|Alterman|Lozano|2011|p=165}} Ablative surgeries experienced a resurgence in the 1990s but were quickly superseded by newly-developed ] (DBS).{{sfn|Bronstein|Tagliati|Alterman|Lozano|2011|p=165}} Although ] and ] surgeries have been developed for pallidotomies and ], their use remains rare.{{sfn|Lozano|Tam|Lozano|2018|p=6}}{{sfn|Moosa|Martínez-Fernández|Elias|Del Alamo|2019|pp=1244-1249}} | |||
| DBS involves the implantation of ] called ]s, which sends electrical impulses to specific parts of the brain.{{sfn|Limousin|Foltynie|2019|p=234}} DBS for the ] and ] has high efficacy for up to 2 years, but longterm efficacy is unclear and likely decreases with time.{{sfn|Limousin|Foltynie|2019|p=234}} DBS typically targets rigidity and tremor,{{sfn|Bronstein|Tagliati|Alterman|Lozano|2011|p=168}} and is recommended for PD patients who are intolerant or do not respond to medication.{{sfn|Bronstein|Tagliati|Alterman|Lozano|2011|p=169}} Cognitive impairment is the most common exclusion criteria.{{sfn|Bronstein|Tagliati|Alterman|Lozano|2011|p=166}} | |||
| Coenzyme Q10 has more recently been used for similar reasons. MitoQ is a newly developed synthetic substance that is similar in structure and function to coenzyme Q10. However, proof of benefit has not been demonstrated yet. | |||
| === |
===Rehabilitation=== | ||
| {{Further|Management of Parkinson's disease#Rehabilitation}} | |||
| Regular physical exercise and/or therapy, including in forms such as yoga, tai chi, and dance can be beneficial to the patient for maintaining and improving mobility, flexibility, balance and a range of motion. | |||
| ] ride of this PD patient, is often recommended.]] | |||
| Although pharmacological therapies can improve symptoms, patients' autonomy and ability to perform everyday tasks is still reduced by PD. As a result, rehabilitation is often useful. However, the scientific support for any single rehabilitation treatment is limited.{{sfn|Tofani|Ranieri|Fabbrini|Berardi|2020|p=891}} | |||
| Exercise programs are often recommended, with preliminary evidence of efficacy.{{sfn|Ernst|Folkerts|Gollan|Lieker|2023}}{{Sfn|Crotty|Schwarzschild|2020|pp=1—2}}{{sfn|Ahlskog|2011|p=292}} Regular ] with or without physical therapy can be beneficial to maintain and improve mobility, flexibility, strength, gait speed, and quality of life.{{sfn|Ernst|Folkerts|Gollan|Lieker|2023}} Aerobic, mind-body, and resistance training may be beneficial in alleviating PD-associated depression and anxiety.{{sfn|Ahlskog|2011|p=292}}{{sfn|Costa|Prati|de Oliveira|Brito|2024}} ] may increase ] and strength, facilitating daily tasks that require grasping objects.{{sfn|Ramazzina|Bernazzoli|Costantino|2017|pp=620-623}} | |||
| ==Prognosis== | |||
| PD is not by itself a fatal disease, but it does get worse with time. The average life expectancy of a PD patient is generally the same as for people who do not have the disease{{fact}}. However, in the late stages of the disease, PD may cause complications such as choking, pneumonia, and falls that can lead to death. | |||
| The progression of symptoms in PD may take 20 years or more. In some people, however, the disease progresses more quickly. There is no way to predict what course the disease will take for an individual person. One commonly used system for describing how the symptoms of PD progress is called the ]. | |||
| In improving flexibility and range of motion for people experiencing rigidity, generalized relaxation techniques such as gentle rocking have been found to decrease excessive muscle tension. Other effective techniques to promote relaxation include slow rotational movements of the extremities and trunk, rhythmic initiation, ], and ].{{Sfn|O'Sullivan|Schmitz|2007|pp=873, 876}} Deep diaphragmatic breathing may also improve chest-wall mobility and ] decreased by the stooped posture and respiratory dysfunctions of advanced Parkinson's.{{Sfn|O'Sullivan|Schmitz|2007|p=880}} Rehabilitation techniques targeting gait and the challenges posed by bradykinesia, shuffling, and decreased arm swing include ], ], and ] exercises.{{Sfn|O'Sullivan|Schmitz|2007|p=879}} | |||
| Another commonly used scale is the (UPDRS). This much more complicated scale has multiple ratings that measure mental functioning, behavior, and mood; activities of daily living; and motor function. Both the Hoehn and Yahr scale and the UPDRS are used to measure how individuals are faring and how much treatments are helping them. It should be noted that neither scale is specific to Parkinson's Disease; that patients with other illnesses can score in the Parkinson's range. | |||
| ] such as the ] may reduce the effect of speech disorders associated with PD.{{sfn|McDonnell|Rischbieth|Schammer|Seaforth|2018|pp=607-609}}{{sfn|Pu|Huang|Kong|Wang|2021|pp=1-2}} ] is another rehabilitation strategy and can improve quality of life by enabling PD patients to find engaging activities and communal roles, adapt to their living environment, and improving domestic and work abilities.{{sfn|Tofani|Ranieri|Fabbrini|Berardi|2020|pp=891, 900}} | |||
| With appropriate treatment, most people with PD can live productive lives for many years after diagnosis. | |||
| ===Diet=== | |||
| ==Notable Parkinson's sufferers== | |||
| Parkinson's poses digestive problems like constipation and ], and a balanced diet with periodical nutritional assessments is recommended to avoid weight loss or gain and minimize the consequences of gastrointestinal dysfunction. In particular, a Mediterranean diet is advised and may slow disease progression.{{sfn|Lister|2020|pp=99-100}}{{sfn|Barichella|Cereda|Pezzoli|2009|pp=1888}} As it can compete for uptake with ] derived from protein, levodopa should be taken 30 minutes before meals to minimize such competition. Low protein diets may also be needed by later stages.{{sfn|Barichella|Cereda|Pezzoli|2009|pp=1888}} As the disease advances, swallowing difficulties often arise. Using ]s for liquid intake and an upright posture when eating may be useful; both measures reduce the risk of choking. ] can be used to deliver food directly into the stomach.{{sfn|Barichella|Cereda|Pezzoli|2009|pp=1887}}{{sfn|Pasricha|Guerrero-Lopez|Kuo|2024|p=212}} Increased water and fiber intake is used to treat constipation.{{sfn|Pasricha|Guerrero-Lopez|Kuo|2024|p=216}} | |||
| ===Palliative care=== | |||
| One famous sufferer of young-onset Parkinson's is ], who has written a book about his experience of the disease and established '']'' to develop a cure for Parkinson's disease within this decade. | |||
| As Parkinson's is incurable, palliative care aims to improve the quality of life for both the patient and family by alleviating the symptoms and stress associated with illness.{{sfn|Ghoche|2012|pp=S2-S3}}{{sfn|Wilcox|2010|p=26}}{{sfn|Ferrell|Connor|Cordes|Dahlin|2007|p=741}} Early integration of palliative care into the disease course is recommended, rather than delaying until later stages.{{sfn|Ghoche|2012|pp=S2-S3}} Palliative care specialists can help with physical symptoms, emotional factors such as loss of function and jobs, depression, fear, as well as existential concerns.{{sfn|Ghoche|2012|p=S3}} Palliative care team members also help guide patients and families on difficult decisions caused by disease progression, such as wishes for a ], ] or ], use of ], and entering ] care.{{sfn|Casey|2013|pp=20-22}}{{sfn|Bernat|Beresford|2013|pp=135, 137, 138}} | |||
| ==Prognosis== | |||
| The film '']'' (starring ] and ] and based on genuine cases reported by ]) deals sensitively and largely accurately with a similar disease, ]. | |||
| {{See also|Unified Parkinson's disease rating scale}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="float:right; margin-left:1em; font-size:90%; line-height:1.4em; width:350px;" | |||
| |+ Prognosis of PD subtypes{{sfn|Corcoran|Kluger|2021|p=956}}{{sfn|Fereshtehnejad|Zeighami|Dagher|Postuma|2017|p=1967}} | |||
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#011E41;color:white;text-align:center;" |Parkinson's subtype | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#011E41;color:white;text-align:center;" |Mean years post-diagnosis until: | |||
| |- | |||
| ! style="background:#011E41;color:white;" |Severe cognitive or movement abnormalities{{efn|group=note|Defined as the onset of development of recurrent falls, wheelchair dependence, dementia, or facility placement.{{sfn|Corcoran|Kluger|2021|p=956}}}} | |||
| ! style="background:#011E41;color:white;" |Death | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Mild-motor predominant | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 14.3 | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 20.2 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Intermediate | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 8.2 | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 13.1 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Diffuse malignant | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 3.5 | |||
| |style="text-align:center;"| 8.1 | |||
| |- | |||
| |} | |||
| As Parkinson's is a ] with multiple ], prognostication can be difficult and prognoses can be highly variable.{{sfn|Corcoran|Kluger|2021|p=956}}{{sfn|Tolosa|Garrido|Scholz|Poewe|2021|p=385}} On average, life expectancy is reduced in those with Parkinson's, with younger age of onset resulting in greater life expectancy decreases.{{sfn|Dommershuijsen|Darweesh|Ben-Shlomo|Kluger|2023|pp=2–3}} Although PD subtype categorization is controversial, the 2017 Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative study identified three broad scorable subtypes of increasing severity and more rapid progression: mild-motor predominant, intermediate, and diffuse malignant. Mean years of survival post-diagnosis were 20.2, 13.1, and 8.1.{{sfn|Corcoran|Kluger|2021|p=956}} | |||
| Around 30% of Parkinson's patients develop dementia, and is 12 times more likely to occur in elderly patients of those with severe PD.{{sfn|Murueta-Goyena|Muiño|Gómez-Esteban|2017|p=26}} Dementia is less likely to arise in patients with tremor-dominant PD.{{sfn|Murueta-Goyena|Muiño|Gómez-Esteban|2017|p=27}} Parkinson's disease dementia is associated with a reduced ] in people with PD and their ]s, increased mortality, and a higher probability of needing ].{{sfn|Caballol|Martí|Tolosa|2007|p=S358}} | |||
| Other famous sufferers include ], artist ], evangelist ], former US Attorney General ], boxer ], dictators ], ] and ], and numerous actors such as ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| The incidence rate of falls in Parkinson's patients is approximately 45 to 68%, thrice that of healthy individuals, and half of such falls result in serious secondary injuries. Falls increase ] and ].{{sfn|Murueta-Goyena|Muiño|Gómez-Esteban|2024|p=395}} Around 90% of those with PD develop ], which worsens with disease progression and can hinder communication.{{sfn|Atalar|Oguz|Genc|2023|p=163}} Additionally, over 80% of PD patients develop dysphagia: consequent inhalation of gastric and oropharyngeal secretions can lead to ].{{sfn|Chua|Wang|Chan|Chan|2024|p=1}} Aspiration pneumonia is responsible for 70% of deaths in those with PD.{{sfn|Corcoran|Muiño|Kluger|2021|p=1}} | |||
| More are shown under ] | |||
| == |
==Epidemiology== | ||
| ], possibly due to exposure to pesticides and industrial waste.]] | |||
| <!--See http://en.wikipedia.org/Wikipedia:Footnotes for an explanation of how to generate footnotes or references using the <ref(erences/)> tags--> | |||
| As of 2024, Parkinson's is the second most common neurodegenerative disease and the fastest-growing in total number of cases.{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=283}}{{Sfn|Varden|Walker|O'Callaghan|2024|p=1}} As of 2023, global ] was estimated to be 1.51 per 1000.{{Sfn|Zhu|Cui|Zhang|Yan|2024|p=e464}} Although it is around 40% more common in men,{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=286}} age is the dominant predeterminant of Parkinson's.{{Sfn|Deliz|Tanner|Gonzalez-Latapi|2024|p=166}} Consequently, as ] has increased, Parkinson's disease prevalence has also risen, with an estimated increase in cases by 74% from 1990 to 2016.{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=284}} The total number is predicted to rise to over 12 million patients by 2040.{{Sfn|Dorsey|Sherer|Okun|Bloem|2018|p=S4}} Some label this a ].{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=284}} | |||
| <div class="references-small"><references/></div> | |||
| ''Some of this article contains text from the public domain document at http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/parkinsons_disease/detail_parkinsons_disease.htm'' | |||
| This increase may be due to a number of global factors, including prolonged life expectancy, increased industrialisation, and ].{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=284}} Although genetics is the sole factor in a minority of cases, most cases of Parkinson's are likely a result of ]: ] with ] have found Parkinson's ] to be just 30%.{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=286}} The influence of multiple genetic and environmental factors complicates epidemiological efforts.{{Sfn|Deliz|Tanner|Gonzalez-Latapi|2024|p=165}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{commons|Category:Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| Relative to Europe and North America, disease prevalence is lower in Africa but similar in Latin America.{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=285}} Although China is predicted to have nearly half of the global Parkinson's population by 2030,{{Sfn|Li|Ma|Cui|He|2019|p=1}} estimates of prevalence in Asia vary.{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=285}} Potential explanations for these geographic differences include genetic variation, environmental factors, ], and life expectancy.{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=285}} Although PD incidence and prevalence may vary by race and ethnicity, significant disparities in care, diagnosis, and study participation limit ] and lead to conflicting results.{{Sfn|Ben-Shlomo|Darweesh|Llibre-Guerra|Marras|2024|p=285}}{{Sfn|Deliz|Tanner|Gonzalez-Latapi|2024|p=165}} Within the United States, high rates of PD have been identified in the ], the ], and agricultural regions of other states: collectively termed the "PD belt".{{Sfn|Deliz|Tanner|Gonzalez-Latapi|2024|pp=164–165}} The association between rural residence and Parkinson's has been hypothesized to be caused by environmental factors like herbicides, pesticides, and industrial waste.{{Sfn|Deliz|Tanner|Gonzalez-Latapi|2024|pp=164–165}}{{Sfn|Huang|Bargues-Carot|Riaz|Wickham|2022|pp=1–2}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ==History== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|History of Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| ] | |||
| | align = left | |||
| ] | |||
| | total_width = 360 | |||
| ] | |||
| | image1 = Jean-Martin Charcot.jpg | |||
| ] | |||
| | alt1 = | |||
| ] | |||
| | image2 = Photographs of a Parkinson patient Pierre D.jpg | |||
| ] | |||
| | alt2 = | |||
| ] | |||
| | footer = In 1877, ] (left) named the disease for ], credited as the first to comprehensively describe it. Patient Pierre D. (right) served as the model for ]' widely distributed illustration of Parkinson's disease.{{Sfn|Lewis|Plun-Favreau|Rowley|Spillane|2020|p=389}}}} | |||
| ] | |||
| In 1817, English physician ] published the first full medical description of the disease as a neurological syndrome in his monograph ''An Essay on the Shaking Palsy''.{{Sfn|Goetz|2011|pp=1–2}}{{Sfn|Lees|2007|p=S327}} He presented six clinical cases, including three he had observed on the streets near ] in ].{{Sfn|Goetz|2011|p=2}} Parkinson described three cardinal symptoms: tremor, postural instability and "paralysis" (undistinguished from rigidity or bradykinesia), and speculated that the disease was caused by trauma to the ].{{Sfn|Louis|1997|p=1069}}{{Sfn|Lees|2007|p=S328}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| There was little discussion or investigation of the "shaking palsy" until 1861, when Frenchman ]—regarded as the father of ]—began expanding Parkinson's description, adding bradykinesia as one of the four cardinal symptoms.{{Sfn|Louis|1997|p=1069}}{{Sfn|Goetz|2011|p=2}}{{Sfn|Lees|2007|p=S328}} In 1877, Charcot renamed the disease after Parkinson, as not all patients displayed the tremor suggested by "shaking palsy".{{Sfn|Goetz|2011|p=2}}{{Sfn|Lees|2007|p=S328}} Subsequent neurologists who made early advances to the understanding of Parkinson's include ], ], ], and ].{{Sfn|Lees|2007|p=S329}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] (pictured), details a disease with strikingly parkinsonian symptoms.]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Although Parkinson is typically credited with the first detailed description of PD, many previous texts reference some of the disease's clinical signs.{{Sfn|Bereczki|2010|p=290}} In his essay, Parkinson himself acknowledged partial descriptions by ], ], ], and others.{{Sfn|Lees|2007|p=S328}} Possible earlier but incomplete descriptions include a ] Egyptian ], the ] text '']'', ], and a discussion of tremors by ].{{Sfn|Lees|2007|p=S328}}{{Sfn|Blonder|2018|pp=3–4}} Multiple ] texts may include references to PD, including a discussion in the ]'s Internal Classic ({{Circa|425–221 BC}}) of a disease with symptoms of tremor, stiffness, staring, and stooped posture.{{Sfn|Blonder|2018|pp=3–4}} In 2009, a systematic description of PD was found in the Hungarian medical text ''Pax corporis'' written by Ferenc Pápai Páriz in 1690, some 120 years before Parkinson. Although Páriz correctly described all four cardinal signs, it was only published in Hungarian and was not widely distributed.{{Sfn|Bereczki|2010|pp=290–293}}{{Sfn|Blonder|2018|p=3}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| In 1912, ] described microscopic particles in affected brains, later named Lewy bodies.{{Sfn|Sousa-Santos|Pozzobon|Teixeira|2024|pp=1–2}} In 1919, ] reported that the substantia nigra was the main brain structure affected, corroborated by ] in 1938.{{Sfn|Lees|2007|p=S331}} The underlying changes in dopamine signaling were identified in the 1950s, largely by ] and ].{{Sfn|Fahn|2008|p=S500—S501, S504–S505}} In 1997, Polymeropoulos and colleagues at the ] discovered the first gene for PD,{{sfn|Polymeropoulos|Lavedan|Leroy|Ide|1997}} ''SNCA'', which encodes alpha-synuclein. Alpha-synuclein was in turn found to be the main component of Lewy bodies by ], ], ], and others.{{Sfn|Schulz-Schaeffer|2010|p=131}} Anticholinergics and surgery were the only treatments until the use of levodopa,{{Sfn|Lanska|2010|p=507}}{{Sfn|Guridi|Lozano|1997|pp=1180–1183}} which, although first synthesized by ] in 1911,{{Sfn|Fahn|2008|p=S497}} did not enter clinical use until 1967.{{Sfn|Fahn|2008|p=S501}} By the late 1980s, deep brain stimulation introduced by ] and colleagues at ], France, emerged as an additional treatment.{{Sfn|Coffey|2009|pp=209–210}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Society and culture== | |||
| ] | |||
| ]—as depicted here by French anatomist ] in 1888—can harm social well-being.]] | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Social impact=== | |||
| ] | |||
| For some people with PD, masked facial expressions and difficulty moderating facial expressions of emotion or recognizing other people's facial expressions can impact social well-being.{{sfn|Prenger|Madray|Van Hedger|Anello|2020|p=2}} As the condition progresses, tremor, other motor symptoms, difficulty communicating, or mobility issues may interfere with social engagement, causing individuals with PD to feel isolated.{{sfn|Crooks|Carter|Wilson|Wynne|2023|p=2,7}} Public perception and awareness of PD symptoms such as shaking, hallucinating, slurring speech, and being off balance is lacking in some countries and can lead to stigma.{{sfn|Crooks|Carter|Wilson|Wynne|2023|p=2}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Cost=== | |||
| ] | |||
| The economic cost of Parkinson's to both individuals and society is high.{{sfn|Schiess|Cataldi|Okun|Fothergill-Misbah|2022|p=931}} Globally, most government health insurance plans do not cover Parkinson's therapies, requiring patients to pay out-of-pocket.{{sfn|Schiess|Cataldi|Okun|Fothergill-Misbah|2022|p=931}} Indirect costs include lifetime earnings losses due to premature death, productivity losses, and caregiver burdens.{{sfn|Yang|Hamilton|Kopil|Beck|2020|p=1}} The duration and progessive nature of PD can place a heavy burden on caregivers:{{sfn|Schiess|Cataldi|Okun|Fothergill-Misbah|2022|p=933}} family members like spouses dedicate around 22 hours per week to care.{{sfn|Yang|Hamilton|Kopil|Beck|2020|p=1}} | |||
| ] | |||
| In 2010, the total economic burden of Parkinson's across Europe, including indirect and direct medical costs, was estimated to be €13.9 billion (US $14.9 billion) in 2010.{{sfn|Schiess|Cataldi|Okun|Fothergill-Misbah|2022|p=929}} The total burden in the United States was estimated to be $51.9 billion in 2017, and is project to surpass $79 billion by 2037.{{sfn|Yang|Hamilton|Kopil|Beck|2020|p=1}} However, as of 2022, no rigorous economic surveys had been performed for low or middle income nations.{{sfn|Schiess|Cataldi|Okun|Fothergill-Misbah|2022|p=930}} Regardless, preventative care has been identified as crucial to prevent the rapidly increasing incidence of Parkinson's from overwhelming national health systems.{{sfn|Schiess|Cataldi|Okun|Fothergill-Misbah|2022|p=933}} | |||
| ===Advocacy=== | |||
| ] signs a pledge from the ]]] | |||
| The birthday of James Parkinson, 11 April, has been designated as World Parkinson's Day.<ref name="pmid18175393">{{Harvnb|Lees|2007|pages=S327–S334}}</ref> A red tulip was chosen by international organizations as the symbol of the disease in 2005; it represents the 'James Parkinson' tulip ], registered in 1981 by a Dutch horticulturalist.{{sfn|GlaxoSmithKline}} | |||
| Advocacy organizations include the ], which has provided more than $180 million in care, research, and support services since 1982,{{sfn|National Parkinson Foundation}} ], which has distributed more than $115 million for research and nearly $50 million for education and advocacy programs since its founding in 1957 by William Black;{{sfn|Time 1960}}{{sfn|Parkinson's Disease Foundation}} the ], founded in 1961;{{sfn|American Parkinson Disease Association}} and the European Parkinson's Disease Association, founded in 1992.{{sfn|European Parkinson's Disease Association}} | |||
| ===Notable cases=== | |||
| {{Main|List of people diagnosed with Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| ] and boxer ] (center) are pictured in 2002 speaking before the ] to urge increased funding for Parkinson's research.]] | |||
| In the 21st century, the diagnosis of Parkinson's among notable figures has increased the public's understanding of the disorder.{{sfn|Parkinson's Foundation}} Actor ] was diagnosed with PD at 29 years old,{{sfn|The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research}} and has used his diagnosis to increase awareness of the disease.{{sfn|Davis|2007}} To illustrate the effects of the disease, Fox has appeared without medication in television roles and before the ] without medication.{{sfn|Brockes|2009}} ], which he founded in 2000, has raised over $2 billion for Parkinson's research.{{sfn|Burleson|Breen|2023}} | |||
| Boxer ] showed signs of PD when he was 38, but was undiagnosed until he was 42, and has been called the "world's most famous Parkinson's patient". | |||
| {{sfn|Brey|2006}} Whether he had PD or ] is unresolved.{{sfn|Matthews|2006|p=10–23}} Cyclist and Olympic medalist ], diagnosed with Parkinson's at 40, started the ] in 2004 to support PD research.{{sfn|Macur|2008}}{{sfn|Davis Phinney Foundation}} | |||
| Several historical figures have been theorized to have had Parkinson's, often framed in the industriousness and inflexibility of the so-called "Parkinsonian personality".{{sfn|Luca|Nicoletti|Mostile|Zappia|2018|pp=1–2}} For instance, English philosopher ] was diagnosed with "shaking palsy"—assumed to have been Parkinson's—but continued writing works such as '']''.{{sfn|McCrum|2017}}{{sfn|Kinsley|2014}}{{sfn|Raudino|2011|pp=945–949}} ] is widely believed to have had Parkinson's, and the condition may have influenced his decision making.{{sfn|Gupta|Kim|Agarwal|Lieber|2015|pp=1447–1452}}{{sfn|Boettcher|Bonney|Smitherman|Sughrue|2015|p=E8}}{{sfn|Lieberman|1996|p=95}} ] was also reported to have died from the disorder.{{sfn|Glass|2016}} | |||
| ==Clinical research== | |||
| {{Main|Research in Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| ] conducts Parkinson's research aboard the ] in 2018]] | |||
| As of 2024, no disease-modifying therapies exist that reverse or slow the progression of Parkinson's.{{Sfn|Crotty|Schwarzschild|2020|p=1}}{{Sfn|Fabbri|Rascol|Foltynie|Carroll|2024|p=2}} Active research directions include the search for new ]s of the disease and development and trial of ], ] transplants, and ] agents.{{sfn|Poewe|Seppi|Tanner|Halliday|2017}} Improved treatments will likely combine therapeutic strategies to manage symptoms and enhance outcomes.{{sfn|Pardo-Moreno|García-Morales|Suleiman-Martos|Rivas-Domínguez|2023|p=1}} Reliable ] are needed for early diagnosis, and research criteria for their identification have been established.{{sfn|Li|Le|2020|p=183}}{{sfn|Heinzel|Berg|Gasser|Chen|2019}} | |||
| ===Neuroprotective treatments=== | |||
| {{See also|Anti-α-synuclein drug}} | |||
| ] that prevent alpha-synuclein oligomerization and aggregation or promote their clearance are under active investigation, and potential therapeutic strategies include ] and ] like ] and ].{{sfn|Pardo-Moreno|García-Morales|Suleiman-Martos|Rivas-Domínguez|2023|pp=12-13}}{{sfn|Alfaidi|Barker|Kuan|2024|p=1}}{{sfn|Jasutkar|Oh|Mouradian|2022|p=208}} While immunotherapies show promise, their effiacy is often inconsistent.{{sfn|Alfaidi|Barker|Kuan|2024|p=1}} Anti-inflammatory drugs that target ] and the ] offer another potential therapeutic approach.{{sfn|Pardo-Moreno|García-Morales|Suleiman-Martos|Rivas-Domínguez|2023|pp=10-11}} | |||
| As the ] in PD is often disrupted and produces toxic compounds, ] might restore a healthy microbiome and alleviate various motor and non-motor symptoms.{{sfn|Pardo-Moreno|García-Morales|Suleiman-Martos|Rivas-Domínguez|2023|pp=12-13}} ]—] that enhance the growth, maturation, and survival of neurons—show modest results but require invasive surgical administration. ] may represent a more feasible delivery platform.{{sfn|Pardo-Moreno|García-Morales|Suleiman-Martos|Rivas-Domínguez|2023|p=13}} ] may restore the calcium imbalance present in Parkinson's, and are being investigated as a neuroprotective treatment.{{sfn|Pardo-Moreno|García-Morales|Suleiman-Martos|Rivas-Domínguez|2023|p=10}} Other therapies, like ], may reduce the abnormal accumulation of iron in PD.{{sfn|Pardo-Moreno|García-Morales|Suleiman-Martos|Rivas-Domínguez|2023|p=10}} | |||
| ===Cell-based therapies=== | |||
| {{Main|Cell-based therapies for Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | total_width = 400 | |||
| | image1 = Parkinson's induced pluripotent stem cell.jpg | |||
| | alt1 = Researchers at Argonne National Laboratory examining induced pluripotent stem cells | |||
| | image2 = Efficient-Conversion-of-Astrocytes-to-Functional-Midbrain-Dopaminergic-Neurons-Using-a-Single-pone.0028719.s002.ogv | |||
| | alt2 = The action potentials of an astrocyte converted into a dopaminergic neuron | |||
| | footer = Researchers at ] examine ] (iPSCs) for use in Parkinson's and other diseases: the ] of one such iPSC differentiated into a ] are visible at right. | |||
| }} | |||
| In contrast to other neurodegenerative disorders, many Parkinson's symptoms can be attributed to the loss of a single cell type. Consequently, dopaminergic neuron regeneration is a promising therapeutic approach.{{Sfn|Parmar|Grealish|Henchcliffe|2020|pp=103}} Although most initial research sought to generate dopaminergic neuron precursor cells from fetal brain tissue,{{Sfn|Parmar|Grealish|Henchcliffe|2020|pp=103-104}} ]—particularly ] (iPSCs)—have become an increasingly popular tissue source.{{Sfn|Parmar|Grealish|Henchcliffe|2020|pp=106}}{{Sfn|Henchcliffe|Parmar|2018|pp=134}} | |||
| Both fetal and iPSC-derived DA neurons have been transplanted into patients in clinical trials.{{Sfn|Parmar|Grealish|Henchcliffe|2020|pp=106, 108}}{{sfn|Schweitzer|Song|Herrington|Park|2020|p=1926}} Although some patients see improvements, the results are highly variable. Adverse effects, such as ] arising from excess dopamine release by the transplanted tissues, have also been observed.{{Sfn|Parmar|Grealish|Henchcliffe|2020|pp=105, 109}}{{Sfn|Henchcliffe|Parmar|2018|pp=132}} | |||
| ===Gene therapy=== | |||
| {{Main|Gene therapy in Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| ] for Parkinson's seeks to restore the healthy function of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra by delivering genetic material—typically through a viral vector—to these diseased cells.{{sfn|Van Laar|Van Laar|San Sebastian|Merola|2021|p=S174}}{{sfn|Hitti|Yang|Gonzalez-Alegre|Baltuch|2019|p=16}} This material may deilver a functional, ] version of a gene, or ] a pathological variants.{{sfn|Hitti|Yang|Gonzalez-Alegre|Baltuch|2019|pp=16-17}} Experimental gene therapies for PD have aimed to increase the expression of ] or enzymes involved in dopamine synthesis, like ].{{sfn|Van Laar|Van Laar|San Sebastian|Merola|2021|p=S174, S176}} The one-time delivery of genes circumvents the recurrent invasive administration required to administer some peptides and proteins to the brain.{{sfn|Hitti|Yang|Gonzalez-Alegre|Baltuch|2019|p=21}} MicroRNAs are an emerging PD gene therapy platform that may serve as an alternative to viral vectors.{{sfn|Shaheen|Shaheen|Osama|Nashwan|2024|pp=5-6}} | |||
| ==Notes and references== | |||
| ===Notes=== | |||
| {{reflist|group=note}} | |||
| ===Citations=== | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ===Works cited=== | |||
| ====Books==== | |||
| {{Refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Parkinson's Disease |vauthors=Bhattacharyya KB |date=2017 |publisher=International Review of Neurobiology |veditors=Bhatia KP, Chaudhuri KR, Stamelou M |pages=1–23 |chapter=Chapter One - Hallmarks of Clinical Aspects of Parkinson's Disease Through Centuries}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bernat |first1=James L. |last2=Beresford |first2=Richard |title=Ethical and Legal Issues in Neurology |date=2013 |publisher=Newnes |isbn=978-0-444-53504-7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YTY3AAAAQBAJ |language=en}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Neuroscience in medicine |vauthors=Cooper G, Eichhorn G, Rodnitzky RL |publisher=Humana Press |year=2008 |isbn=978-1-6032-7454-8 |veditors=Conn PM |chapter=Parkinson's disease |ref=none}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Anxiety in Older People: Clinical and Research Perspectives |vauthors=Dissanayaka NN |date=8 March 2021 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-1-1088-2636-5 |veditors=Byrne GJ, Panchana NA |pages=139–156 |chapter=Chapter 9: Anxiety in Parkinson's Disease |doi=10.1017/9781139087469.009 |s2cid=87250745}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Ferri's differential diagnosis: a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders |vauthors=Ferri FF |date=2010 |publisher=Elsevier/Mosby |isbn=978-0-3230-7699-9 |edition=2nd |chapter=Chapter P}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Handbook of Clinical Neurology |vauthors=Lanska DJ |date=2010 |publisher=History of Neurology |series=3 |volume=95 |pages=501–546 |chapter=Chapter 33: The history of movement disorders |doi=10.1016/S0072-9752(08)02133-7 |pmid=19892136|isbn=978-0-444-52009-8 }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Physical Rehabilitation |vauthors=O'Sullivan SB, Schmitz TJ |publisher=F.A. Davis |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-8036-1247-1 |edition=5th |chapter=Parkinson's Disease}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Lange Clinical Neurology |vauthors=Simon RP, Greenberg D, Aminoff MJ |publisher=McGraw-Hill |year=2017 |isbn=978-1-2598-6172-7 |edition=10th}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |url=https://exonpublications.com/index.php/exon/issue/view/9 |title=Parkinson's Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects |date=December 2018 |publisher=Codon Publications |isbn=978-0-9944-3816-4 |veditors=Stoker TB, Greenland JC |ref=none}} | |||
| ** {{Cite book |title=Parkinson's disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects |vauthors=Dallapiazza RF, De Vloo PD, Fomenko A, Lee DJ, Hamani C, Munhoz RP, Hodaie M, Lozano AM, Fasano A, Kalia SK |date=2018 |publisher=Codon Publications |isbn=978-0-9944-3816-4 |veditors=Stoker TB, Greenland JC |chapter=Chapter 8: Considerations for Patient and Target Selection in Deep Brain Stimulation surgery for Parkinson's disease |doi=10.15586/codonpublications.parkinsonsdisease.2018.ch8 |pmid=30702838 |chapter-url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536714 |s2cid=81155324}} | |||
| ** {{Cite book |title=Parkinson's disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects |vauthors=Greenland JC, Barker RA |date=2018 |publisher=Codon Publications |isbn=978-0-9944-3816-4 |veditors=Stoker TB, Greenland JC |pages=109–128 |chapter=Chapter 6: The Differential Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease |doi=10.15586/codonpublications.parkinsonsdisease.2018.ch6 |pmid=30702839 |chapter-url=https://exonpublications.com/index.php/exon/article/view/191/348 |s2cid=80908095}} | |||
| ** {{Cite book |title=Parkinson's Disease: Pathogenesis and clinical aspects |vauthors=Stoker TB, Torsney KM, Barker RA |date=2018 |isbn=978-0-9944-3816-4 |veditors=Stoker TB, Greenland JC |pages=45–64 |chapter=Chapter 3: Pathological mechanisms and clinical aspects of GBA1 mutation-associated Parkinson's disease |doi=10.15586/codonpublications.parkinsonsdisease.2018.ch3 |pmid=30702840 |ref=none |chapter-url=https://exonpublications.com/index.php/exon/article/view/188/342 |s2cid=92170834}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Parkinson's disease and movement disorders |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7817-7881-7 |veditors=Tolosa E, Jankovic E |ref=none}} | |||
| ** {{Cite book |title=Parkinson's disease and movement disorders |vauthors=Dickson DV |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7817-7881-7 |veditors=Tolosa E, Jankovic JJ |chapter=Neuropathology of movement disorders}} | |||
| ** {{Cite book |title=Parkinson's disease and movement disorders |vauthors=Fung VS, Thompson PD |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7817-7881-7 |veditors=Tolosa E, Jankovic E |chapter=Rigidity and spasticity |ref=none}} | |||
| ** {{Cite book |title=Parkinson's disease and movement disorders |vauthors=Tolosa E, Katzenschlager R |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7817-7881-7 |veditors=Tolosa E, Jankovic JJ |chapter=Pharmacological management of Parkinson's disease}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=International Neurology |vauthors=Truong DD, Bhidayasiri R |date=2016 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |isbn=978-1-1187-7736-7 |veditors=Lisak RP, Truong DD, Carroll WM, Bhidayasiri R |chapter=50: Parkinson's disease |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mRl6DAAAQBAJ&pg=PA188}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |title=StatPearls |vauthors=Vertes AC, Beato MR, Sonne J, Khan Suheb MZ |date=June 2023 |publisher=StatPearls Publishing |location=Treasure Island (FL) |chapter=Parkinson-Plus Syndrome |pmid=36256760 |access-date=2 May 2024 |chapter-url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK585113/}} | |||
| *{{Cite book|veditors=Bernat JL, Beresford R|vauthors=Lorenzl S, Nubling G, Perrar KM, Voltz |date=August 2013 |title=Handbook of Clinical Neurology|chapter=Palliative treatment of chronic neurologic disorders|volume=118|pages=133–139|pmid=24182372}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |title=Parkinson's Disease |publisher=Royal College of Physicians |year=2006 |isbn=978-1-8601-6283-1 |editor-last=The National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions |location=London |pages=113–133 |chapter=Non-motor features of Parkinson's disease |chapter-url=http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG35/Guidance/pdf/English |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100924153546/http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG35/Guidance/pdf/English |archive-date=24 September 2010 |url-status=live|ref={{Harvid|The National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions}}}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ====Journal articles==== | |||
| {{Refbegin|20em}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Binde CD, Tvete IF, Gåsemyr J, Natvig B, Klemp M |date=September 2018 |title=A multiple treatment comparison meta-analysis of monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors for Parkinson's disease |journal=British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology |volume=84 |issue=9 |pages=1917–1927 |doi=10.1111/bcp.13651 |pmc=6089809 |pmid=29847694}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |vauthors=Caballol N, Martí MJ, Tolosa E |title=Cognitive dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson disease |journal=Mov. Disord. |volume=22 |issue= Suppl 17|pages=S358–66 |date=September 2007 |pmid=18175397 |doi=10.1002/mds.21677 |s2cid=3229727 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Henchcliffe C, Parmar M |year=2018 |title=Repairing the Brain: Cell Replacement Using Stem Cell-Based Technologies |journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease |volume=8 |issue=s1 |pages=S131–S137 |doi=10.3233/JPD-181488 |pmc=6311366 |pmid=30584166}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Panicker N, Ge P, Dawson VL, Dawson TM |date=April 2021 |title=The cell biology of Parkinson's disease |journal=The Journal of Cell Biology |volume=220 |issue=4 |doi=10.1083/jcb.202012095 |pmc=8103423 |pmid=33749710 |ref=none}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Parmar M, Grealish S, Henchcliffe C |date=February 2020 |title=The future of stem cell therapies for Parkinson disease |journal=Nature Reviews. Neuroscience |volume=21 |issue=2 |pages=103–115 |doi=10.1038/s41583-019-0257-7 |pmid=31907406 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Tolosa E, Garrido A, Scholz SW, Poewe W |date=May 2021 |title=Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease |journal=The Lancet. Neurology |volume=20 |issue=5 |pages=385–397 |doi=10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00030-2 |pmc=8185633 |pmid=33894193 |ref=none}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Blauwendraat C, Nalls MA, Singleton AB |date=February 2020 |title=The genetic architecture of Parkinson's disease |journal=The Lancet. Neurology |volume=19 |issue=2 |pages=170–178 |doi=10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30287-X |pmc=8972299 |pmid=31521533}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Winiker K, Kertscher B |date=2023 |title=Behavioural interventions for swallowing in subjects with Parkinson's disease: A mixed methods systematic review |journal=International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders |volume=58 |issue=4 |pages=1375–1404 |doi=10.1111/1460-6984.12865 |pmid=36951546 |ref=none |doi-access=free}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Islam MS, Azim F, Saju H, Zargaran A, Shirzad M, Kamal M, Fatema K, Rehman S, Azad MA, Ebrahimi-Barough S |date=September 2021 |title=Pesticides and Parkinson's disease: Current and future perspective |journal=Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy |volume=115 |page=101966 |doi=10.1016/j.jchemneu.2021.101966 |pmc=8842749 |pmid=33991619 |ref=none}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Hansen D, Ling H, Lashley T, Holton JL, Warner TT |date=April 2019 |title=Review: Clinical, neuropathological and genetic features of Lewy body dementias |journal=Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology |volume=45 |issue=7 |pages=635–654 |doi=10.1111/nan.12554 |pmid=30977926}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Wallace ER, Segerstrom SC, van Horne CG, Schmitt FA, Koehl LM |date=2022 |title=Meta-Analysis of Cognition in Parkinson's Disease Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia Progression |journal=Neuropsychology Review |volume=32 |issue=1 |pages=149–160 |doi=10.1007/s11065-021-09502-7 |pmid=33860906}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Dolgacheva LP, Zinchenko VP, Goncharov NV |date=2022 |title=Molecular and Cellular Interactions in Pathogenesis of Sporadic Parkinson Disease |journal=International Journal of Molecular Sciences |volume=23 |issue=21 |page=13043 |doi=10.3390/ijms232113043 |doi-access=free |pmid=36361826|pmc=9657547 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Leta V, Urso D, Batzu L, Lau YH, Mathew D, Boura I, Raeder V, Falup-Pecurariu C, van Wamelen D, Chaudhuri KR|date=2022 |title=Viruses, parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease: the past, present and future |journal=Journal of Neural Transmission |volume=129 |issue=9 |pages=1119–1132 |doi=10.1007/s00702-022-02536-y |pmid=36036863|pmc=9422946 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Limphaibool N, Iwanowski P, Holstad MJ, Kobylarek D, Kozubski W |date=2019 |title=Infectious Etiologies of Parkinsonism: Pathomechanisms and Clinical Implications |journal=Frontiers in Neurology |volume=10 |page=652 |doi=10.3389/fneur.2019.00652 |doi-access=free |pmid=31275235|pmc=6593078 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Bologna M, Truong D, Jankovic J |date=2022 |title=The etiopathogenetic and pathophysiological spectrum of parkinsonism |journal=Journal of the Neurological Sciences |volume=433 |pages=1–8 |doi=10.1016/j.jns.2021.120012 |pmid=34642022}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Prajjwal P, Kolanu ND, Reddy YB, Ahmed A, Marsool MD, Santoshi K, Pattani HH, John J, Chandrasekar KK, Hussin OA |date=2024 |title=Association of Parkinson's disease to Parkinson's plus syndromes, Lewy body dementia, and Alzheimer's dementia |journal=Health Science Reports |volume=7 |issue=4 |pages=e2019 |doi=10.1002/hsr2.2019 |pmid=38562616|pmc=10982460 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Olfatia N, Shoeibia A, Litvanb I |date=2019 |title=Progress in the treatment of Parkinson-Plus syndromes |journal=Parkinsonism & Related Disorders |volume=59 |pages=101–110 |doi=10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.10.006 |pmid=30314846}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Calabresi P, Mechelli A, Natale G, Volpicelli-Daley L, Di Lazzaro G, Ghiglieri V |date=2023 |title=Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies: from overt neurodegeneration back to early synaptic dysfunction |journal=Cell Death & Disease |volume=14 |issue=3 |page=176 |doi=10.1038/s41419-023-05672-9 |pmid=36859484|pmc=9977911 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Ramesh SD, Arachchige AS |date=2023 |title=Depletion of dopamine in Parkinson's disease and relevant therapeutic options: A review of the literature |journal=AIMS Neuroscience |volume=10 |issue=3 |pages=200–231 |doi=10.3934/Neuroscience.2023017 |pmid=37841347|pmc=10567584 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Ascherio A, Schwarzschild MA |date=2016 |title=The epidemiology of Parkinson's disease: risk factors and prevention |journal=Lancet Neurology |volume=15 |issue=12 |pages=1257–1272 |doi=10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30230-7 |pmid=27751556}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Crotty GF, Schwarzschild MA |date=2020 |title=Chasing Protection in Parkinson's Disease: Does Exercise Reduce Risk and Progression? |journal=Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience |volume=12 |page=186 |doi=10.3389/fnagi.2020.00186 |doi-access=free |pmid=32636740|pmc=7318912 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Singh A, Tripathi P, Singh S |date=2021 |title=Neuroinflammatory responses in Parkinson's disease: relevance of Ibuprofen in therapeutics |journal=Inflammopharmacology |volume=29 |issue=1 |pages=5–14 |doi=10.1007/s10787-020-00764-w |pmid=33052479}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Fabbri M, Rascol O, Foltynie T, Carroll C, Postuma RB, Porcher R, Corvol JC |date=2024 |title=Advantages and Challenges of Platform Trials for Disease Modifying Therapies in Parkinson's Disease |journal=Movement Disorders |volume=39 |issue=9 |pages=1468–1477 |doi=10.1002/mds.29899 |pmid=38925541}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Kamal H, Tan GC, Ibrahim SF, Shaikh MF, Mohamed IN, Mohamed RM, Hamid AA, Ugusman A, Kumar J |date=2020 |title=Alcohol Use Disorder, Neurodegeneration, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease: Interplay Between Oxidative Stress, Neuroimmune Response and Excitotoxicity |journal=Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience |volume=14 |page=282 |doi=10.3389/fncel.2020.00282 |doi-access=free |pmid=33061892|pmc=7488355 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Lin J, Pang D, Li C, Ou R, Yu Y, Cui Y, Huang J, Shang H |date=2024 |title=Calcium channel blockers and Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis |journal=Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders |volume=17 |pages=1–8 |doi=10.1177/17562864241252713 |pmid=38770432|pmc=11104025 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Grotewolda N, Albina RL |date=2024 |title=Update: Protective and risk factors for Parkinson disease |journal=Parkinsonism and Related Disorders |volume=125 |pages=1–12 |doi=10.1016/j.parkreldis.2024.107026 |pmid=38879999}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Rose KN, Schwarzschild MS, Gomperts SN |date=2024 |title=Clearing the Smoke: What Protects Smokers from Parkinson's Disease? |journal=Movement Disorders |volume=39 |issue=2 |pages=267–272 |doi=10.1002/mds.29707 |pmid=38226487|pmc=10923097 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Ren X, Chen J |date=2020 |title=Caffeine and Parkinson's Disease: Multiple Benefits and Emerging Mechanisms |journal=Frontiers in Neuroscience |volume=14 |pages=1–12 |doi=10.3389/fnins.2020.602697 |doi-access=free |pmid=33390888|pmc=7773776 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Ben-Shlomo Y, Darweesh S, Llibre-Guerra J, Marras C, Luciano MS, Tanner C |date=2024 |title=The epidemiology of Parkinson's disease |journal=The Lancet |volume=403 |issue=10423 |pages=283–292|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01419-8 |pmid=38245248 |pmc=11123577 |pmc-embargo-date=January 20, 2025 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Deliz JR, Tanner CM, Gonzalez-Latapi P |date=2024 |title=Epidemiology of Parkinson's Disease: An Update |journal=Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports |volume=24 |issue=6 |pages=163–179|doi=10.1007/s11910-024-01339-w |pmid=38642225 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Dorsey ER, Sherer T, Okun MS, Bloem BR |date=2018 |title=The Emerging Evidence of the Parkinson Pandemic |journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease |volume=8 |issue=s1 |pmid=30584159 |pages=S3–S8|doi=10.3233/JPD-181474 |pmc=6311367 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Li G, Ma J, Cui S, He Y, Xiao Q, Liu J, Chen S |date=2019 |title=Parkinson's disease in China: a forty-year growing track of bedside work |journal=Translational Neurodegeneration |volume=8 |issue=1 |page=22 |doi=10.1186/s40035-019-0162-z |doi-access=free |pmid=31384434 |pmc=6668186 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Varden R, Walker R, O'Callaghan A |date=2024 |title=No trend to rising rates: A review of Parkinson's prevalence studies in the United Kingdom |journal=Parkinsonism & Related Disorders |volume=128 |pmid=38876845 |pages=1–6|doi=10.1016/j.parkreldis.2024.107015 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Zhu J, Cui Y, Zhang J, Yan R, Su D, Zhao D, Wang A, Feng T |date=2024 |title=Temporal trends in the prevalence of Parkinson's disease from 1980 to 2023: a systematic review and meta-analysis |journal=The Lancet: Healthy Longetivity |volume=5 |pmid=38876845 |pages=e464–e479|doi=10.1016/j.parkreldis.2024.107015 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Goetz CG |date=2011 |title=The history of Parkinson's disease: early clinical descriptions and neurological therapies |journal=Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine |volume=1 |issue=1 |pages=a008862 |doi=10.1101/cshperspect.a008862 |pmid=22229124|pmc=3234454 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Lees AJ |date=2007 |title=Unresolved issues relating to the shaking palsy on the celebration of James Parkinson's 250th birthday |journal=Movement Disorders |volume=22 |issue=S17 |pages=S327–S334 |doi=10.1002/mds.21684 |pmid=18175393}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Louis ED |date=1997 |title=The shaking palsy, the first forty-five years: a journey through the British literature |journal=Movement Disorders |volume=12 |issue=6 |pages=1068–1072 |doi=10.1002/mds.870120638 |pmid=9399240}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Lewis PA, Plun-Favreau H, Rowley M, Spillane J |date=2020 |title=Pierre D. and the first photographs of Parkinson's disease |journal=Movement Disorders |volume=35 |issue=3 |pages=389–391 |doi=10.1002/mds.27965 |pmid=31975439|pmc=7155099 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Bereczki D |date=2010 |title=The description of all four cardinal signs of Parkinson's disease in a Hungarian medical text published in 1690 |journal=Parkinsonism & Related Disorders |volume=16 |issue=4 |pmid=19948422 |pages=290–293|doi=10.1016/j.parkreldis.2009.11.006 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Blonder LX |date=2018 |title=Historical and cross-cultural perspectives on Parkinson's disease |journal=Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine |volume=15 |issue=3 |pmid=29738310 |pages=1–15|doi=10.1515/jcim-2016-0065 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Coffey RJ |date=2009 |title=Deep brain stimulation devices: a brief technical history and review |journal=Artificial Organs |volume=33 |issue=3 |pages=208–220 |doi=10.1111/j.1525-1594.2008.00620.x |pmid=18684199}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Sousa-Santos PE, Pozzobon PM, Teixeira IL |date=2024 |title=Frederic Lewy: how the two World Wars changed his life, work, and name |journal=Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatri |volume=82 |issue=3 |pages=001–002 |doi=10.1055/s-0044-1779692 |pmid=38467394|pmc=10927365 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Fahn S |date=2008 |title=The history of dopamine and levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease |journal=Movement Disorders |volume=23 |issue=S3 |pages=S497–S508 |doi=10.1002/mds.22028 |pmid=18781671}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Schulz-Schaeffer |first=WJ |date=2010 |title=The synaptic pathology of alpha-synuclein aggregation in dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia |journal=Acta Neuropathologica |volume=120 |issue=2 |pages=131–143 |doi=10.1007/s00401-010-0711-0 |pmid=20563819|pmc=2892607 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |vauthors=Guridi J, Lozano AM |date=1997 |title=A brief history of pallidotomy |journal=Neurosurgery |volume=41 |issue=5 |pages=1169–1180 |doi=10.1097/00006123-199711000-00029 |pmid=9361073}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Tolosa E, Garrido A, Scholz SW, Poewe W|date=May 2021|title=Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease|journal=Lancet Neurology|volume=20|issue=5 |pages=385–397|doi=10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00030-2 |pmid=33894193|pmc=8185633 }} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Corcoran J, Kluger BM|date=September 2023|title=Prognosis in chronic progressive neurologic disease: a narrative review|journal=Annals of Palliative Medicine|volume=12|issue=5|pages=952–962|doi=10.21037/apm-22-1338 |doi-access=free |pmid=37691335}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Fereshtehnejad SM, Zeighami Y, Dagher A, Postuma RB|date=July 2017|title=Clinical criteria for subtyping Parkinson's disease: biomarkers and longitudinal progression|journal=Brain|volume=140|issue=7|pages=1959–1976|doi=10.1093/brain/awx118 |pmid=28549077}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Dommershuijsen LJ, Darweesh SK, Ben-Shlomo Y, Kluger BM, Bloem BR|date=October 2023|title=The elephant in the room: critical reflections on mortality rates among individuals with Parkinson's disease|journal=npj Parkinson's Disease|volume=9|issue=1 |page=145 |doi=10.1038/s41531-023-00588-9 |pmid=37857675|pmc=10587193 }} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Murueta-Goyena A, Muiño O, Gómez-Esteban JC|date=April 2024|title=Prognostic factors for falls in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review|journal=Acta Neurologica Belgica|volume=124|issue=2 |pages=395–406|doi=10.1007/s13760-023-02428-2 |pmid=38015306|pmc=10965733 }} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Murueta-Goyena A, Muiño O, Gómez-Esteban JC|date=March 2017|title=Dementia in Parkinson's disease|journal=Journal of the Neurological Sciences|volume=374|pages=26–31|doi=10.1016/j.jns.2017.01.012 |pmid=28088312}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Chua WY, Wang JD, Chan CK, Chan L, Tan E|date=September 2024|title=Risk of aspiration pneumonia and hospital mortality in Parkinson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis|journal=European Journal of Neurology|volume=31 |issue=12 |pages=e16449|doi=10.1111/ene.16449 |pmid=39236309|doi-access=free|pmc=11555015 }} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Won JH, Byun SJ, Oh B, Park SJ, Seo HG|title=Cognitive dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson disease|journal=Scientific Reports|volume=22|issue=S17|pages=S358–S366|date=September 2007|doi=10.1002/mds.21677 |pmid=18175397}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Corcoran J, Kluger BM|date=2021|title=Risk and mortality of aspiration pneumonia in Parkinson's disease: a nationwide database study|journal=Scientific Reports|volume=11|issue=1 |page=6597 |doi=10.1038/s41598-021-86011-w |pmid=33758213|pmc=7988066 |bibcode=2021NatSR..11.6597W }} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Atalar MS, Oguz O, Genc G|date=2023|title=Hypokinetic Dysarthria in Parkinson's Disease: A Narrative Review|journal=The Medical Bulletin of Sisle Etfal Hospital|volume=57|issue=2|pages=163–170|doi=10.14744/SEMB.2023.29560 |pmid=37899809|pmc=10600629 }} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Huang M, Bargues-Carot A, Riaz Z, Wickham H, Zenitsky G, Jin H, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy A, Kanthasamy AG|date=September 2022|title=Impact of Environmental Risk Factors on Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Neuroinflammation, Protein Misfolding, and Oxidative Stress in the Etiopathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease|journal=International Journal of Molecular Sciences|volume=23|issue=10808|page=10808 |doi=10.3390/ijms231810808 |doi-access=free |pmid=36142718|pmc=9505762 }} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Luca A, Nicoletti A, Mostile G, Zappia M|date=2018|title=The Parkinsonian Personality: More Than Just a "Trait"|journal=Frontiers in Neurology|volume=9|issue=1191|page=1191 |doi=10.3389/fneur.2018.01191 |doi-access=free |pmid=30697187|pmc=6340987 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Rana AQ, Ahmed US, Chaudry ZM, Vasan S|date=May 2015|title=Parkinson's disease: a review of non-motor symptoms|journal=Expert Reviews Neurotherapeutics|volume=15|issue=5|pages=549–462|doi=10.1586/14737175.2015.1038244 |pmid=25936847}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Biundo R, Weis L, Antonini A|date=September 2016|title=Cognitive decline in Parkinson's disease: the complex picture|journal=npj Parkinson's Disease|volume=2|number=16018|page=16018 |doi=10.1038/npjparkd.2016.18 |pmid=28725699|pmc=5516581 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Gonzalez-Latapi P, Bayram E, Litvan I, Marras C |date=May 2021 |title=Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson's Disease: Epidemiology, Clinical Profile, Protective and Risk Factors |journal=Behavioral Sciences |volume=11 |issue=5 |page=74 |doi=10.3390/bs11050074 |pmc=8152515 |pmid=34068064 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Zhu M, Li M, Ye D, Jiang W, Lei T, Shu K|date=March 2016|title=Sensory symptoms in Parkinson's disease: Clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment|journal=Journal of Neuroscience Research|volume=94 |issue=8|pages=685–692|doi=10.1002/jnr.23729 |pmid=26948282}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Corrà MF, Vila-Chã N, Sardoeira A, Hansen C, Sousa AP, Reis I, Sambayeta F, Damásio J, Calejo M, Schicketmueller A, Laranjinha I, Salgado P, Taipa R, Magalhães R, Correia M, Maetzler W, Maia LF |date=January 2023 |title=Peripheral neuropathy in Parkinson's disease: prevalence and functional impact on gait and balance |journal=Brain |volume=146 |issue=1 |pages=225–236 |doi=10.1093/brain/awac026 |pmc=9825570 |pmid=35088837}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Weil RS, Schrag AE, Warren JD, Crutch SJ, Lees AJ, Morris HR|date=July 2016|title=Visual dysfunction in Parkinson's disease|journal=Brain |volume=146 |issue=139|pages= 2827–2843|doi=10.1093/brain/aww175 |pmid=27412389|pmc=5091042 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Pfeiffer RF|date=October 2020|title=Autonomic Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease|journal=Neurotherapeutics |volume=17 |issue=4|pages=1464–1479|doi=10.1007/s13311-020-00897-4 |pmid=32789741|pmc=7851208 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Palma JA, Kaufmann H |date=March 2018 |title=Treatment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies |journal=Movement Disorders |volume=33 |issue=3 |pages=372–390 |doi=10.1002/mds.27344 |pmc=5844369 |pmid=29508455}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Han MN, Finkelstein DI, McQuade RM, Diwakarla S |date=January 2022 |title=Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease: Current and Potential Therapeutics |journal=Journal of Personalized Medicine |volume=12 |issue=2|page=144 |doi=10.3390/jpm12020144 |pmc=8875119 |pmid=35207632 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Aarslanda D, Krambergera MG|date=2015|title=Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease|journal=Journal of Personalized Medicine |volume=5|issue=3 |pages=659–667|doi=10.3233/JPD-150604 |pmid=26406147}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Niemann N, Billnitzer A, Jankovic J |date=January 2021 |title=Parkinson's disease and skin |journal=Parkinsonism & Related Disorders |volume=82 |pages=61–76 |doi=10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.11.017 |pmid=33248395}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Almikhlafi MA |date=January 2024 |title=A review of the gastrointestinal, olfactory, and skin abnormalities in patients with Parkinson's disease |journal=Neurosciences |volume=29 |issue=1 |pages=4–9 |doi=10.17712/nsj.2024.1.20230062 |doi-broken-date=1 November 2024 |pmc=10827020 |pmid=38195133}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Stefani A, Högl B|date=January 2020|title=Sleep in Parkinson's disease|journal=Neuropsychopharmacology|volume=45|issue=1|pages=121–128|doi=10.1038/s41386-019-0448-y |pmid=31234200|pmc=6879568 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Bollu PC, Sahota P |date=2017 |title=Sleep and Parkinson Disease |journal=Missouri Medicine |volume=114 |issue=5 |pages=381–386 |pmc=6140184 |pmid=30228640}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Dodet P, Houot M, Leu-Semenescu S, Corvol JC, Lehéricy S, Mangone G, Vidailhet M, Roze E, Arnulf I |date=February 2024 |title=Sleep disorders in Parkinson's disease, an early and multiple problem |journal=npj Parkinson's Disease |volume=10 |issue=1 |page=46 |doi=10.1038/s41531-024-00642-0 |pmc=10904863 |pmid=38424131}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Moustafa AA, Chakravarthy S, Phillips JR, Gupta A, Keri S, Polner B, Frank MJ, Jahanshahi M|date=September 2016|title=Motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease: A unified framework|journal=Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews|volume=68|pages=727–740|doi=10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.07.010 |pmid=27422450|url=https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1511483/ }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Mirelman A, Bonato P, Camicioli R, Ellis TD, Giladi N, Hamilton JL, Hass CJ, Hausdorff JM, Pelosin E, Almeida QJ|date=April 2019|title=Gait impairments in Parkinson's disease|journal=Lancet Neurology|volume=17|issue=7|pages=697–708|doi=10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30044-4 |pmid=30975519}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Sveinbjornsdottir S |date=October 2016 |title=The clinical symptoms of Parkinson's disease |journal=Journal of Neurochemistry |volume=139 |issue=Suppl 1 |pages=318–324 |doi=10.1111/jnc.13691 |pmid=27401947 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Abusrair AH, Elsekaily W, Bohlega S |date=13 September 2022 |title=Tremor in Parkinson's Disease: From Pathophysiology to Advanced Therapies |journal=Tremor and Other Hyperkinetic Movements |volume=12 |issue=1 |page=29 |doi=10.5334/tohm.712 |pmc=9504742 |pmid=36211804 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Bologna M, Paparella G, Fasano A, Hallett M, Berardelli A|date=December 2019|title=Evolving concepts on bradykinesia|journal=Brain|volume=143|issue=3|pages=727–750|doi=10.1093/brain/awz344 |pmid=31834375|pmc=8205506 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Ferreira-Sánchez MD, Moreno-Verdú M, Cano-de-la-Cuerda R |date=February 2020 |title=Quantitative Measurement of Rigidity in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review |journal=Sensors |volume=20 |issue=3 |page=880 |bibcode=2020Senso..20..880F |doi=10.3390/s20030880 |pmc=7038663 |pmid=32041374 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Palakurthi B, Burugupally SP|date=September 2019|title=Postural Instability in Parkinson's Disease: A Review|journal=Brain Sciences|volume=9|issue=239|page=239 |doi=10.3390/brainsci9090239 |doi-access=free |pmid=31540441|pmc=6770017 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|vauthors=Yang W, Hamilton JL, Kopil C, Beck JC, Tanner CM, Albin RL, Dorsey ER, Dahodwala N, Cintina I, Hogan P, Thompson T|date=July 2020|title=Current and projected future economic burden of Parkinson's disease in the U.S.|journal=npj Parkinson's Disease|volume=6|page=15 |doi=10.1038/s41531-020-0117-1 |pmid=32665974|pmc=7347582 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|vauthors=Cunha M, Almeida H, Guimarães I, Ferreira LN|date=July 2020|title=Current and projected future economic burden of Parkinson's disease in the U.S.|journal=Journal of Public Health}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|vauthors=Schiess N, Cataldi R, Okun MS, Fothergill-Misbah N, Dorsey ER, Bloem BR, Barretto M, Bhidayasiri R, Brown R, Chishimba L, Chowdhary N, Coslov M, Cubo E, Di Rocco A, Dolhun R, Dowrick C, Fung VS, Gershanik OS, Gifford L, Gordon J, Khalil H, Kühn AA, Lew S, Lim SY, Marano MM, Micallef J, Mokaya J, Moukheiber E, Nwabuobi L, Okubadejo N, Pal PK, Shah H, Shalash A, Sherer T, Siddiqui B, Thompson T, Ullrich A, Walker R, Dua T|date=September 2022|title=Six Action Steps to Address Global Disparities in Parkinson Disease: A World Health Organization Priority|journal=JAMA|volume=79|issue=9|pages=929–936|doi=10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.1783 |pmid=35816299|hdl=10576/33335 |url=https://repository.ubn.ru.nl//bitstream/handle/2066/282658/282658.pdf }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Prenger MT, Madray R, Van Hedger K, Anello M, MacDonald PA |date=2020 |title=Social Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease |journal=Parkinson's Disease |volume=2020 |page=8846544 |doi=10.1155/2020/8846544 |pmc=7790585 |pmid=33489081 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Crooks S, Carter G, Wilson CB, Wynne L, Stark P, Doumas M, Rodger M, O'Shea E, Mitchell G |date=2023 |title=Exploring public perceptions and awareness of Parkinson's disease: A scoping review |journal=PLOS ONE |volume=18 |issue=9 |pages=e0291357 |bibcode=2023PLoSO..1891357C |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0291357 |pmc=10503766 |pmid=37713383 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Raudino F|date=2011|title=The Parkinson disease before James Parkinson|journal=History of Neurology|volume=33|pages=945–949}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Gupta R, Kim C, Agarwal N, Lieber B, Monaco EA|title=Understanding the Influence of Parkinson Disease on Adolf Hitler's Decision-Making during World War II|journal=World Neurosurgery|volume=84|issue=5|pages=1447–1452|date=2015 |doi=10.1016/j.wneu.2015.06.014 |pmid=26093359}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Boettcher L, Bonney P, Smitherman A, Sughrue M|title=Hitler's parkinsonism|journal=Neurosurgical Focus|volume=39|issue=1|pages=E8|date=2015|doi=10.3171/2015.4.FOCUS1563 |pmid=26126407 }} | |||
| *{{cite journal|url=http://www.aan.com/elibrary/neurologynow/?event=home.showArticle&id=ovid.com:/bib/ovftdb/01222928-200602020-00003|title=Muhammad Ali's Message: Keep Moving Forward|date=April 2006 |journal=Neurology Now|vauthors=Brey RL |volume=2 |issue=2|page = 8 |doi=10.1097/01222928-200602020-00003 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110927022505/http://www.aan.com/elibrary/neurologynow/?event=home.showArticle&id=ovid.com%3A%2Fbib%2Fovftdb%2F01222928-200602020-00003 |archive-date=27 September 2011 |access-date= 22 August 2020}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|title=Ali's Fighting Spirit|date=April 2006|journal=Neurology Now| vauthors= Matthews W |volume=2|issue=2|pages=10–23|doi=10.1097/01222928-200602020-00004|s2cid=181104230}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Dorsey ER, Bloem BR|date=January 2024|title=Parkinson's Disease Is Predominantly an Environmental Disease|journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease|volume=14|issue=3|pages=103–115|doi=10.3233/JPD-230357 |pmid=38217613|pmc=11091623 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Bandres-Ciga S, Diez-Fairen M, Kim JJ, Singleton AB|date=April 2020|title=Genetics of Parkinson's disease: An introspection of its journey towards precision medicine|journal=Neurobiology of Disease|volume=137|pages=1–9|doi=10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104782 |pmid=31991247|pmc=7064061 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Toffoli M, Vieira SR, Schapira AH|date=June 2020|title=Genetic causes of PD: A pathway to disease modification|journal=Neuropharmacology | |||
| |volume=170|pages=1–13|doi=10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108022 |pmid=32119885|url=https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10095601/ }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Dorsey ER, Zafar M, Lettenberger SE, Pawlik ME, Kinel D, Frissen M, Schneider RB, Kieburtz K, Tanner CM, De Miranda BR, Goldman SM, Bloem BR |date=2023 |title=Trichloroethylene: An Invisible Cause of Parkinson's Disease? |journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=203–218 |doi=10.3233/JPD-225047 |pmc=10041423 |pmid=36938742}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Chen C, Turnbull DM, Reeve AK|date=May 2019|title=Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease—Cause or Consequence?|journal=Biology|volume=8|issue=2|page=38 |doi=10.3390/biology8020038 |doi-access=free |pmid=31083583|pmc=6627981 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Morris HR, Spillantini MG, Sue CM, Williams-Gray CH |date=January 2024 |title=The pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease |url=https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10189143 |journal=Lancet |volume=403 |issue=10423 |pages=293–304 |doi=10.1016/s0140-6736(23)01478-2 |pmid=38245249}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Gogna T, Housden BE, Houldsworth A|date=September 2024|title=Exploring the Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease and the Efficacy of Antioxidant Treatment|journal=Antioxidants|volume=13|issue=1138|page=1138 |doi=10.3390/antiox13091138 |doi-access=free |pmid=39334797|pmc=11429442 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Brundin P, Melki R|date=October 2017|title=Prying into the Prion Hypothesis for Parkinson's Disease|journal=Journal of Neuroscience|volume=37|issue=41|pages=9808–9818|doi=10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1788-16.2017 |pmid=29021298|pmc=5637113 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Salles PA, Tirapegui JM, Chaná-Cuevas P |date=22 March 2024 |title=Genetics of Parkinson's disease: Dominant forms and GBA |journal=Neurology Perspectives |volume=4 |issue=3 |page=100153 |doi=10.1016/j.neurop.2024.100153 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Farrow SL, Gokuladhas S, Schierding W, Pudjihartono M, Perry JK, Cooper AA, O'Sullivan JM|date=October 2024 |title=Identification of 27 allele-specific regulatory variants in Parkinson's disease using a massively parallel reporter assay|journal=npj Parkinson's Disease |volume=10|issue=1 |page=44 |doi=10.1038/s41531-024-00659-5 |pmid=38413607|pmc=10899198 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Smith L, Schapira AH |date=April 2022 |title=''GBA'' Variants and Parkinson Disease: Mechanisms and Treatments |journal=Cells |volume=11 |issue=8 |page=1261 |doi=10.3390/cells11081261 |pmc=9029385 |pmid=35455941 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Goldstein DS|title=The catecholaldehyde hypothesis: where MAO fits in|date=February 2020|journal=Journal of Neural Transmission|volume=127|issue=2|pages=169–177|doi=10.1007/s00702-019-02106-9 |pmid=31807952|pmc=10680281 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Goldstein DS|title=The Catecholaldehyde Hypothesis for the Pathogenesis of Catecholaminergic Neurodegeneration: What We Know and What We Do Not Know|date=June 2021|journal=International Journal of Molecular Sciences|volume=22|issue=11 |page=5999 |doi=10.3390/ijms22115999 |doi-access=free |pmid=34206133|pmc=8199574 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Santos-Lobato BL |date=April 2024 |title=Towards a methodological uniformization of environmental risk studies in Parkinson's disease |journal=npj Parkinson's Disease |volume=10 |issue=1 |page=86 |doi=10.1038/s41531-024-00709-y |pmc=11024193 |pmid=38632283}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=De Mirandaa BR, Goldmanb SM, Millerc GW, Greenamyred JT, Dorseye ER|date=April 2024 |title=Preventing Parkinson's Disease: An Environmental Agenda|journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease|volume=12|issue=1|pages=45–68|doi=10.3233/JPD-212922 |pmid=34719434|pmc=8842749 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Langston JW|date=March 2017|title=The MPTP Story|journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease|volume=7|issue=1|pages=S11–S19|doi=10.3233/JPD-179006 |pmid=28282815|pmc=5345642 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Dorsey ER, De Mirandab BR, Horsager J, Borghammer P|date=April 2024|title=The Body, the Brain, the Environment, and Parkinson's Disease|journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease|volume=14|issue=3 |pages=363–381|doi=10.3233/JPD-240019 |pmid=38607765|pmc=11091648 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Bloem BR, Boonstra TA |date=December 2023 |title=The inadequacy of current pesticide regulations for protecting brain health: the case of glyphosate and Parkinson's disease |journal=The Lancet. Planetary Health |volume=7 |issue=12 |pages=e948–e949 |doi=10.1016/s2542-5196(23)00255-3 |pmid=37949088}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Delic V, Beck KD, Pang KC, Citron BA |date=April 2020 |title=Biological links between traumatic brain injury and Parkinson's disease |journal=Acta Neuropathologica Communications |volume=8 |issue=1 |page=45 |doi=10.1186/s40478-020-00924-7 |pmc=7137235 |pmid=32264976 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Coleman C, Martin I |date=16 December 2022 |title=Unraveling Parkinson's Disease Neurodegeneration: Does Aging Hold the Clues? |journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease |volume=12 |issue=8 |pages=2321–2338 |doi=10.3233/JPD-223363 |pmc=9837701 |pmid=36278358}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Wu S, Schekman RW|date=September 2024|title=Intercellular transmission of alpha-synuclein|journal=Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience|volume=17|pages=1–12|doi=10.3389/fnmol.2024.1470171 |doi-access=free |pmid=39324117|pmc=11422390 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Ho H, Wing SS|date=November 2024|title=α-Synuclein ubiquitination – functions in proteostasis and development of Lewy bodies|journal=Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience|volume=17|pages=1–19|doi=10.3389/fnmol.2024.1498459 |doi-access=free |pmid=39600913|pmc=11588729 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Rietdijk CD, Perez-Pardo P, Garssen J, van Wezel RJ, Kraneveld AD|date=February 2017|title=Exploring Braak's Hypothesis of Parkinson's Disease|journal=Frontiers in Neurology|volume=8|page=37 |doi=10.3389/fneur.2017.00037 |doi-access=free |pmid=28243222|pmc=5304413 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Borsche M, Pereira SL, Klein C, Grünewald A|date=February 2021|title=Mitochondria and Parkinson's Disease: Clinical, Molecular, and Translational Aspects|journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease|volume=11|issue=1|pages=45–60|doi=10.3233/JPD-201981 |pmid=33074190|pmc=7990451 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Tan E, Chao Y, West A, Chan L, Poewe W, Jankovic J|date=April 2020|title=Parkinson disease and the immune system - associations, mechanisms and therapeutics|journal=Nature Reviews Neurology|volume=16|issue=6|pages=303–318|doi=10.1038/s41582-020-0344-4 |pmid=32332985}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Kobylecki C|date=July 2020|title=Update on the diagnosis and management of Parkinson's disease|journal=Clinical Medicine|volume=20|issue=4|pages=393–398|doi=10.7861/clinmed.2020-0220 |pmid=32675145|pmc=7385761}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=de Bie RM, Clarke CE, Espay AJ, Fox SH, Lang AE|date=March 2020|title=Initiation of pharmacological therapy in Parkinson's disease: when, why, and how|journal=Lancet Neurology|volume=19|issue=5|pages=452–461|doi=10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30036-3 |pmid=32171387}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Ferrell B, Connor SR, Cordes A, Dahlin CM, Fine PG, Hutton N, Leenay M, Lentz J, Person JL, Meier DE, Zuroski K |date=June 2007 |title=The national agenda for quality palliative care: the National Consensus Project and the National Quality Forum |journal=Journal of Pain and Symptom Management |volume=33 |issue=6 |pages=737–744 |doi=10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.02.024 |pmid=17531914 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |title=Ethical and Legal Issues in Neurology |vauthors=Lorenzl S, Nübling G, Perrar KM, Voltz R |publisher=Elsevier |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-4445-3501-6 |series=Handbook of Clinical Neurology |volume=118 |pages=133–139 |chapter=Palliative treatment of chronic neurologic disorders |doi=10.1016/B978-0-444-53501-6.00010-X |pmid=24182372}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Ghoche R |date=December 2012 |title=The conceptual framework of palliative care applied to advanced Parkinson's disease |journal=Parkinsonism & Related Disorders |volume=18 |issue=Suppl 3 |pages=S2–S5 |doi=10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.06.012 |pmid=22771241}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Wilcox SK |date=January 2010 |title=Extending palliative care to patients with Parkinson's disease |journal=British Journal of Hospital Medicine |volume=71 |issue=1 |pages=26–30 |doi=10.12968/hmed.2010.71.1.45969 |pmid=20081638}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Moens K, Higginson IJ, Harding R |date=October 2014 |title=Are there differences in the prevalence of palliative care-related problems in people living with advanced cancer and eight non-cancer conditions? A systematic review |journal=Journal of Pain and Symptom Management |volume=48 |issue=4 |pages=660–677 |doi=10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2013.11.009 |pmid=24801658 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Casey G |date=August 2013 |title=Parkinson's disease: a long and difficult journey |journal=Nursing New Zealand |volume=19 |issue=7 |pages=20–24 |pmid=24195263}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Lister T|date=May 2020|title=Nutrition and Lifestyle Interventions for Managing Parkinson's Disease: A Narrative Review|journal=Journal of Movement Disorders|volume=13|issue=2|pages=97–104|doi=10.14802/jmd.20006 |pmid=32498495|pmc=7280935}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Barichella M, Cereda E, Pezzoli G|date=October 2009|title=Major nutritional issues in the management of Parkinson's disease|journal=Movement Disorders|volume=24|issue=13|pages=1881–1892|doi=10.1002/mds.22705 |pmid=19691125|hdl=2434/67795 |hdl-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Pasricha TS, Guerrero-Lopez IL, Kuo B|date=March 2024|title=Management of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease: A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Presentation, Workup, and Treatment|journal=Movement Disorders|volume=58|issue=3|pages=211–220|pmid=38260966}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=McDonnell MN, Rischbieth B, Schammer TT, Seaforth C, Shaw AJ, Phillips AC|date=May 2018|title=Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT)-BIG to improve motor function in people with Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis|journal=Clinical Rehabilitation|volume=32|issue=5|pages=607–618|doi=10.1177/0269215517734385 |pmid=28980476}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Pu T, Huang M, Kong X, Wang M, Chen X, Feng X, Wei C, Weng X, Xu F|date=December 2021|title=Lee Silverman Voice Treatment to Improve Speech in Parkinson's Disease: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis|journal=Parkinson's Disease|volume=2021|pages=1–10|doi=10.1155/2021/3366870 |doi-access=free |pmid=35070257|pmc=8782619}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Tofani M, Ranieri A, Fabbrini G, Berardi A, Pelosin E, Valente D, Fabbrini A, Costanzo M, Galeoto G|date=October 2020|title=Efficacy of Occupational Therapy Interventions on Quality of Life in Patients with Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis|journal=Movement Disorders|volume=7|issue=8|pages=891–901|doi=10.1002/mdc3.13089 |pmid=33163559|pmc=7604677}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Ernst M, Folkerts AK, Gollan R, Lieker E, Caro-Valenzuela J, Adams A, Cryns N, Monsef I, Dresen A, Roheger M, Eggers C, Skoetz N, Kalbe E |date=1 January 2023 |title=Physical exercise for people with Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis |journal=The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews |volume=2024 |issue=4 |pages=CD013856 |doi=10.1002/14651858.CD013856.pub3|pmc=9815433 |pmid=38588457}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Ahlskog JE |date=July 2011 |title=Does vigorous exercise have a neuroprotective effect in Parkinson disease? |journal=Neurology |volume=77 |issue=3 |pages=288–294 |doi=10.1212/wnl.0b013e318225ab66 |pmc=3136051 |pmid=21768599}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Costa V, Prati JM, de Oliveira BS, Brito TS, da Rocha F, Gianlorenço T, Carolyna A|date=November 2024 |title=Physical Exercise for Treating the Anxiety and Depression Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis |url=https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/08919887241237223 |journal=Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology|volume=37 |issue=6 |pages=415–435 |doi=10.1177/08919887241237223|pmid=38445606|issn=0891-9887}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Ramazzina I, Bernazzoli B, Costantino C |date=March 2017 |title=Systematic review on strength training in Parkinson's disease: an unsolved question |journal=Clinical Interventions in Aging |volume=12 |pages=619–628 |doi=10.2147/CIA.S131903 |pmc=5384725 |pmid=28408811 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Limousin P, Foltynie T|date=April 2019|title=Long-term outcomes of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease|journal=Nature Reviews Neurology|volume=14|issue=4|pages=234–242|doi=10.1038/s41582-019-0145-9 |pmid=30778210}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Bronstein JM, Tagliati M, Alterman RL, Lozano AM, Volkmann J, Stefani A, Horak FB, Okun MS, Foote KD, Krack P, Pahwa R, Henderson JM, Hariz MI, Bakay RA, Rezai A, Marks WJ, Moro E, Vitek JL, Weaver FM, Gross RE, DeLong MR |date=February 2011 |title=Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: an expert consensus and review of key issues |journal=Archives of Neurology |volume=68 |issue=2 |page=165 |doi=10.1001/archneurol.2010.260 |pmc=4523130 |pmid=20937936 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Lozano CS, Tam J, Lozano AM|date=January 2018|title=The changing landscape of surgery for Parkinson's Disease|journal=Movement Disorders|volume=33|issue=1|pages=36–47|doi=10.1002/mds.27228 |pmid=29194808}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Connolly BS, Lang AE |date=April 2014 |title=Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: a review |journal=JAMA |volume=311 |issue=16 |pages=1670–1683 |doi=10.1001/jama.2014.3654 |pmid=24756517 |s2cid=205058847}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Moosa S, Martínez-Fernández R, Elias WJ, Del Alamo M, Eisenberg HM, Fishman PS|date=September 2019|title=The role of high-intensity focused ultrasound as a symptomatic treatment for Parkinson's disease|journal=Movement Disorders|volume=34|issue=9|pages=1243–1251|doi=10.1002/mds.27779 |pmid=31291491}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Tambasco N, Romoli M, Calabresi P|date=October 2018|title=Levodopa in Parkinson's Disease: Current Status and Future Developments|journal=Current Neuropharmacology|volume=16|issue=8|pages=1239–1252|doi=10.2174/1570159X15666170510143821 |pmid=28494719|pmc=6187751 }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=LeWitt PA, Fahn S|date=April 2016|title=Levodopa therapy for Parkinson disease: A look backward and forward|journal=Neurology|volume=86|issue=14|pages=S3–S12|doi=10.1212/WNL.0000000000002509 |pmid=28494719}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Leta V, Klingelhoefer L, Longardner K, Campagnolo M, Levent HÇ, Aureli F, Metta V, Bhidayasiri R, Chung-Faye G, Falup-Pecurariu C, Stocchi F, Jenner P, Warnecke T, Ray Chaudhuri K, ((International Parkinson and Movement Disorders Society Non-Motor Parkinson's Disease Study Group))|date=May 2023|title=Gastrointestinal barriers to levodopa transport and absorption in Parkinson's disease|journal=European Journal of Neurology|volume=30|issue=5|pages=1465–1480|doi=10.1111/ene.15734 |pmid=36757008}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Oertel WH |date=13 March 2017 |title=Recent advances in treating Parkinson's disease |journal=F1000Research|volume=6 |page=260 |doi=10.12688/f1000research.10100.1 |pmc=5357034 |pmid=28357055 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Horowski R, Löschmann PA|date=February 2019|title=Classical dopamine agonists|journal=Journal of Neural Transmission|volume=126|issue=4|pages=449–454|doi=10.1007/s00702-019-01989-y |pmid=30805732}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Jing X, Yang H, Taximaimaiti R, Wang X|date=2023|title=Advances in the Therapeutic Use of Non-Ergot Dopamine Agonists in the Treatment of Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease|journal=Current Neuropharmacology|volume=21|issue=5|pages=1224–1240|doi=10.2174/1570159X20666220915091022 |pmid=36111769|pmc=10286583}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Tan Y, Jenner P, Chen S|date=2022|title=Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease: Past, Present, and Future|journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease|volume=12|issue=2|pages=477–493|doi=10.3233/JPD-212976 |pmid=34957948|pmc=8925102}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Robakis D, Fahn S|date=June 2015|title=Defining the Role of the Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for Parkinson's Disease|journal=CNS Drugs|volume=29|issue=6|pages=433–441|doi=10.1007/s40263-015-0249-8 |pmid=26164425}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Alborghetti M, Nicoletti F |date=2019 |title=Different Generations of Type-B Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Parkinson's Disease: From Bench to Bedside |journal=Current Neuropharmacology |volume=17 |issue=9 |pages=861–873 |doi=10.2174/1570159X16666180830100754 |pmc=7052841 |pmid=30160213}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Armstrong MJ, Okun MS |date=February 2020 |title=Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review |journal=JAMA |volume=323 |issue=6 |pages=548–560 |doi=10.1001/jama.2019.22360 |pmid=32044947 |s2cid=211079287}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Rissardo JP, Durante I, Sharon I, Caprara AL|date=September 2022|title=Pimavanserin and Parkinson's Disease Psychosis: A Narrative Review|journal=Brain Sciences|volume=23 |issue=12|pages=1–11|pmid=36291220}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Elbers RG, Verhoef J, van Wegen EE, Berendse HW, Kwakkel G |date=October 2015 |title=Interventions for fatigue in Parkinson's disease |journal=The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews |type=Review |volume=2015 |issue=10 |pages=CD010925 |doi=10.1002/14651858.CD010925.pub2 |pmc=9240814 |pmid=26447539 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Seppi K, Ray Chaudhuri K, Coelho M, Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, Perez Lloret S, Weintraub D, Sampaio C|title=Update on treatments for nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson's disease—an evidence-based medicine review |journal=Movement Disorders |date=February 2019 |volume=34 |issue=2 |pages=180–198 |doi=10.1002/mds.27602|pmid=30653247 |pmc=6916382 }} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Gouda NA, Elkamhawy A, Cho J|title=Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Parkinson's Disease and Future Prospects: A 2021 Update|journal=Biomedicines|date=February 2022 |volume=10|issue=2 |page=371 |doi=10.3390/biomedicines10020371 |doi-access=free |pmid=35203580|pmc=8962417}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Jasutkar HG, Oh SE, Mouradian MM|title=Therapeutics in the Pipeline Targeting α-Synuclein for Parkinson's Disease|journal=Pharmacological Reviews|date=January 2022|volume=74|issue=1|pages=207–237|doi=10.1124/pharmrev.120.000133 |pmid=35017177|pmc=11034868}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Pardo-Moreno T, García-Morales V, Suleiman-Martos S, Rivas-Domínguez A, Mohamed-Mohamed H, Ramos-Rodríguez JJ, Melguizo-Rodríguez L, González-Acedo A|title=Current Treatments and New, Tentative Therapies for Parkinson's Disease|journal=Pharmaceutics|date=February 2023|volume=15|issue=3|page=770 |doi=10.3390/pharmaceutics15030770 |doi-access=free |pmid=36986631|hdl=10481/81647|hdl-access=free}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Shaheen N, Shaheen A, Osama M, Nashwan AJ, Bharmauria V, Flouty O|date=October 2024|title=MicroRNAs regulation in Parkinson's disease, and their potential role as diagnostic and therapeutic targets|journal=npj Parkinson's Disease Volume|volume=10|issue=3|pages=1–11|pmid=39369002}} | |||
| *{{cite journal|vauthors=Van Laar AD, Van Laar VS, San Sebastian W, Merola A, Elder JB, Lonser RR, Bankiewicz KS|date=2021|title=An Update on Gene Therapy Approaches for Parkinson's Disease: Restoration of Dopaminergic Function|journal=Journal of Parkinson's Disease|volume=11|issue=S2|pages=S173–S182|doi=10.3233/JPD-212724 |pmid=34366374|pmc=8543243}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Schweitzer JS, Song B, Herrington TM, Park TY, Lee N, Ko S, Jeon J, Cha Y, Kim K, Li Q, Henchcliffe C, Kaplitt M, Neff C, Rapalino O, Seo H, Lee IH, Kim J, Kim T, Petsko GA, Ritz J, Cohen BM, Kong SW, Leblanc P, Carter BS, Kim KS |date=May 2020 |title=Personalized iPSC-Derived Dopamine Progenitor Cells for Parkinson's Disease |journal=The New England Journal of Medicine |volume=382 |issue=20 |pages=1926–1932 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa1915872 |pmc=7288982 |pmid=32402162}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Alfaidi M, Barker RA, Kuan W|date=December 2024|title=An update on immune-based alpha-synuclein trials in Parkinson's disease|journal=Journal of Neurology|volume=272 |issue=1|pages=1–9|pmid= 39666171}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Poewe W, Seppi K, Tanner CM, Halliday GM, Brundin P, Volkmann J, Schrag AE, Lang AE |date=March 2017 |title=Parkinson disease |journal=Nature Reviews. Disease Primers |volume=3 |issue=1 |page=17013 |doi=10.1038/nrdp.2017.13 |pmid=28332488 |s2cid=11605091}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Li T, Le W|date=February 2020|title=Biomarkers for Parkinson's Disease: How Good Are They?|journal=Neuroscience Bulletin|volume=36|issue=2|pages=183–194|doi=10.1007/s12264-019-00433-1 |pmid=31646434|pmc=6977795}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Heinzel S, Berg D, Gasser T, Chen H, Yao C, Postuma RB |date=October 2019 |title=Update of the MDS research criteria for prodromal Parkinson's disease |journal=Movement Disorders |volume=34 |issue=10 |pages=1464–1470 |doi=10.1002/mds.27802 |pmid=31412427 |s2cid=199663713 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Hitti FL, Yang AI, Gonzalez-Alegre P, Baltuch GH |date=September 2019 |title=Human gene therapy approaches for the treatment of Parkinson's disease: An overview of current and completed clinical trials |journal=Parkinsonism & Related Disorders |volume=66 |pages=16–24 |doi=10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.07.018 |pmid=31324556 |s2cid=198132349}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |last1=Polymeropoulos |first1=Mihael H. |last2=Lavedan |first2=Christian |last3=Leroy |first3=Elisabeth |last4=Ide |first4=Susan E. |last5=Dehejia |first5=Anindya |last6=Dutra |first6=Amalia |last7=Pike |first7=Brian |last8=Root |first8=Holly |last9=Rubenstein |first9=Jeffrey |last10=Boyer |first10=Rebecca |last11=Stenroos |first11=Edward S. |last12=Chandrasekharappa |first12=Settara |last13=Athanassiadou |first13=Aglaia |last14=Papapetropoulos |first14=Theodore |last15=Johnson |first15=William G. |date=1997-06-27 |title=Mutation in the α-Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson's Disease |url=https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.276.5321.2045 |journal=Science|volume=276 |issue=5321 |pages=2045–2047 |doi=10.1126/science.276.5321.2045 |pmid=9197268 |issn=0036-8075}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Zaman V, Shields DC, Shams R, Drasites KP, Matzelle D, Haque A, Banik NL|date=June 2021|title=Cellular and molecular pathophysiology in the progression of Parkinson's disease|journal=Metabolic Brain Disease|volume=36|issue=5|pages=815–827|doi=10.1007/s11011-021-00689-5 |pmid=33599945|pmc=8170715}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Vázquez-Vélez GE, Zoghbi HY|date=July 2021|title=Parkinson's Disease Genetics and Pathophysiology|journal=Annual Review of Neuroscience|volume=44|pages=87–108|doi=10.1146/annurev-neuro-100720-034518 |pmid=34236893}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Warnecke T, Schäfer KH, Claus I, Del Tredici K, Jost WH|date=March 2022|title=Gastrointestinal involvement in Parkinson's disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management|journal=npj Parkinson's Disease|volume=8|pages=1–13|doi=10.1038/s41531-022-00295-x |pmid=35332158|pmc=8948218}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Miller KM, Mercado NM, Sortwell CE|date=April 2021|title=Synucleinopathy-associated pathogenesis in Parkinson's disease and the potential for brain-derived neurotrophic factor|journal=npj Parkinson's Disease|volume=7|issue=1|pages=1–9|doi=10.1038/s41531-021-00179-6 |pmid=33846345|pmc=8041900}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Borghammer P|date=January 2018|title=How does parkinson's disease begin? Perspectives on neuroanatomical pathways, prions, and histology|journal=Movement Disorders|volume=33|issue=1|pages=48–57|doi=10.1002/mds.27138 |pmid=28843014}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Zhang X, Gao F, Wang D, Li C, Fu Y, He W, Zhang J|date=October 2018|title=Tau Pathology in Parkinson's Disease|journal=Frontiers in Neurology|volume=9|pages=1–7|doi=10.3389/fneur.2018.00809 |doi-access=free |pmid=30333786|pmc=6176019}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Henderson MX, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM|date=September 2019|title=α-Synuclein pathology in Parkinson's disease and related α-synucleinopathies|journal=Neuroscience Letters|volume=709|pages=1–10|doi=10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134316 |pmid=31170426|pmc=7014913}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Ye H, Robak LA, Yu M, Cykowski M, Shulman JM|date=January 2023|title=Genetics and Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Syndrome|journal=Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease|volume=18|pages=95–121|doi=10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-031521-034145 |pmid=36100231|pmc=10290758}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Dickson DW|date=January 2018|title=Neuropathology of Parkinson disease|journal=Parkinsonism and Related Disorders|volume=46|issue=S1|pages=S30–S33|doi=10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.07.033 |pmid=28780180|pmc=5718208}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Chen R, Gu X, Wang X |date=April 2022 |title=α-Synuclein in Parkinson's disease and advances in detection |journal=Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry |volume=529 |pages=76–86 |doi=10.1016/j.cca.2022.02.006 |pmid=35176268}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Menšíková K, Matěj R, Colosimo C, Rosales R, Tučková L, Ehrmann J, Hraboš D, Kolaříková K, Vodička R, Vrtěl R, Procházka M, Nevrlý M, Kaiserová M, Kurčová S, Otruba P, Kaňovský P|date=January 2022 |title=Lewy body disease or diseases with Lewy bodies? |journal=npj Parkinson's Disease|volume=8|issue=1|page=1-11|pmid=35013341}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Koh J, Ito H |date=January 2017 |title=Differential diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders |journal=Nihon Rinsho. Japanese Journal of Clinical Medicine |volume=75 |issue=1 |pages=56–62 |pmid=30566295}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Ou Z, Pan J, Tang S, Duan D, Yu D, Nong H, Wang Z |date=7 December 2021 |title=Global Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived With Disability of Parkinson's Disease in 204 Countries/Territories From 1990 to 2019 |journal=Frontiers in Public Health |volume=9 |page=776847 |doi=10.3389/fpubh.2021.776847 |pmc=8688697 |pmid=34950630 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Tolosa E, Garrido A, Scholz SW, Poewe W|date=May 2022|title=Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease|journal=Lancet Neurology|volume=20|issue=5|pages=385–397|doi=10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00030-2 |pmid=33894193|pmc=8185633}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Heim B, Krismer F, De Marzi R, Seppi K|date=August 2017|title=Magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease|journal=Journal of Neural Transmission|volume=124|issue=8|pages=915–964|doi=10.1007/s00702-017-1717-8 |pmid=28378231|pmc=5514207}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Ugrumov M|date=June 2020|title=Development of early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease: Illusion or reality?|journal=CNS Neuroscience and Therapeutics|volume=26|issue=10|pages=997–1009|doi=10.1111/cns.13429 |pmid=32597012|pmc=7539842}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Rizzo G, Copetti M, Arcuti S, Martino D, Fontana A, Logroscino G|date=February 2016|title=Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis|journal=Neurology|volume=86|issue=6|pages=566–576|doi=10.1212/WNL.0000000000002350 |pmid=26764028}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|vauthors=Bidesi NS, Andersen IV, Windhorst AD, Shalgunov V, Herth MM|date=November 2021|title=The role of neuroimaging in Parkinson's disease|journal=Journal of Neurochemistry|volume=159|issue=4|pages=660–689|doi=10.1111/jnc.15516 |pmid=34532856|pmc=9291628}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Brooks DJ |date=April 2010 |title=Imaging approaches to Parkinson disease |journal=Journal of Nuclear Medicine |volume=51 |issue=4 |pages=596–609 |doi=10.2967/jnumed.108.059998 |pmid=20351351}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |vauthors=Suwijn SR, van Boheemen CJ, de Haan RJ, Tissingh G, Booij J, de Bie RM |date=2015 |title=The diagnostic accuracy of dopamine transporter SPECT imaging to detect nigrostriatal cell loss in patients with Parkinson's disease or clinically uncertain parkinsonism: a systematic review |journal=EJNMMI Research |volume=5 |pages=12 |doi=10.1186/s13550-015-0087-1 |pmc=4385258 |pmid=25853018 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Caproni S, Colosimo C|date=February 2020|title=Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Parkinson Disease|journal=Clinical Geriatric Medicine|volume=36|pages=13–24|doi=10.1016/j.cger.2019.09.014 |pmid=31733693}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal|vauthors=Lieberman A|date=April 1996|title=Adolf Hitler had post-encephalitic Parkinsonism|journal=Parkinsonism & Related Disorders|volume=2|issue=2|pages=95-103|pmid=18591024}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ====Web sources==== | |||
| {{Refbegin|30em}} | |||
| *{{Cite news |year=2010 |title=About EPDA |url=http://www.epda.eu.com/about-us |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100815232300/http://www.epda.eu.com/about-us |archive-date=15 August 2010 |access-date=9 August 2010 |publisher=European Parkinson's Disease Association|ref={{Harvid|European Parkinson's Disease Association}}}} | |||
| *{{Cite web |title=About PDF |url=http://www.pdf.org/en/about_pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110515204903/http://www.pdf.org/en/about_pdf |archive-date=15 May 2011 |access-date=24 July 2016 |publisher=Parkinson's Disease Foundation|ref={{Harvid|Parkinson's Disease Foundation}}}} | |||
| *{{Cite web |title=American Parkinson Disease Association: Home |url=http://www.apdaparkinson.org/userND/index.asp |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120510165933/http://www.apdaparkinson.org/userND/index.asp |archive-date=10 May 2012 |access-date=9 August 2010 |publisher=American Parkinson Disease Association|ref={{Harvid|American Parkinson Disease Association}}}} | |||
| *{{cite news | vauthors = Macur J |title=For the Phinney Family, a Dream and a Challenge |url= https://www.nytimes.com/2008/03/26/sports/othersports/26cycling.html |newspaper=The New York Times |access-date=25 May 2013 |date=26 March 2008 |quote=About 1.5 million Americans have received a diagnosis of Parkinson's disease, but only 5 to 10 percent learn of it before age 40, according to the National Parkinson Foundation. Davis Phinney was among the few. |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20141106025145/http://www.nytimes.com/2008/03/26/sports/othersports/26cycling.html |archive-date=6 November 2014}} | |||
| *{{cite web |title=Michael's Story |url=https://www.michaeljfox.org/michaels-story |website=The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research |access-date=7 May 2023|ref={{Harvid|The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research}}}} | |||
| *{{Cite web |title=National Parkinson Foundation – Mission |url=http://www.parkinson.org/About-Us/Mission |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101221103201/http://parkinson.org/About-Us/Mission |archive-date=21 December 2010 |access-date=28 March 2011|ref={{Harvid|National Parkinson Foundation}}}} | |||
| *{{cite web|url=https://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/statistics/notable-figures|title=Notable Figures with Parkinson's|publisher=Parkinson's Foundation|access-date=22 November 2023|ref={{Harvid|Parkinson's Foundation}}}} | |||
| * {{Wikicite|reference ={{Cite web |title=Parkinson's Disease |url=https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/parkinsons-disease#:~:text=Parkinson's%20disease%20(PD)%20is%20movement,the%20body%2C%20or%20impaired%20balance. |access-date=2 September 2024 |publisher=National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke}}|ref={{Harvid|National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke}}}} | |||
| *{{Cite web |date=1 April 2009 |title=Parkinson's – 'the shaking palsy' |url=http://www.gsk.com/infocus/parkinsons.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110514151652/http://www.gsk.com/infocus/parkinsons.htm |archive-date=14 May 2011 |publisher=GlaxoSmithKline|ref={{Harvid|GlaxoSmithKline}}}} | |||
| * {{Wikicite|reference ={{Cite web |title=Symptoms of PD |url=https://med.stanford.edu/parkinsons/symptoms-PD.html |access-date=2 September 2024 |website=Stanford Parkinson's Community Outreach |publisher=Stanford University School Medicine}}|ref={{Harvid|Stanford University School Medicine}}}} | |||
| *{{cite web|url=http://davisphinneyfoundation.org/dpf/who-we-are/|title=Who We Are|publisher=Davis Phinney Foundation|access-date=18 January 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120111054225/http://davisphinneyfoundation.org/dpf/who-we-are/|archive-date=11 January 2012|ref={{Harvid|Davis Phinney Foundation}}}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ====News publications==== | |||
| {{Refbegin}} | |||
| *{{cite news|last1=Burleson|first1=Nate|last2=Breen|first2=Kerry|date=9 November 2023|title=Michael J. Fox talks funding breakthrough research for Parkinson's disease|url=https://www.cbsnews.com/news/michael-j-fox-parkinsons-research-funded-by-his-foundation/|work=CBS News|access-date=23 November 2023}} | |||
| *{{cite news|last=Glass|first=Andrew|date=9 September 2016|title=Mao Zedong dies in Beijing at age 82, Sept. 9, 1976|url=https://www.politico.com/story/2016/09/mao-zedong-dies-in-beijing-at-age-82-sept-9-1976-227742|work=Politico|access-date=30 October 2023}} | |||
| *{{cite news|url= https://www.nytimes.com/1988/07/17/magazine/ali-still-magic.html|title=Ali: Still Magic|date=17 July 1988|vauthors=Tauber P |work=The New York Times|access-date=2 April 2011|url-status=live|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20161117151827/http://www.nytimes.com/1988/07/17/magazine/ali-still-magic.html|archive-date=17 November 2016}} | |||
| *{{cite news|last=McCrum|first=Robert|date=20 November 2017|title=The 100 best nonfiction books: No 94 – Leviathan by Thomas Hobbes (1651)|url=https://www.theguardian.com/books/2017/nov/20/the-100-best-nonfiction-books-no-94-leviathan-thomas-hobbes-1651|work=The Guardian|access-date=23 November 2023}} | |||
| *{{cite magazine|last=Kinsley|first=Michael|date=21 April 2014|title=Have You Lost Your Mind?|url=https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2014/04/28/have-you-lost-your-mind|magazine=The New Yorker|access-date=23 November 2023}} | |||
| *{{Cite magazine |date=18 January 1960 |title=Education: Joy in Giving |url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,828597,00.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110220012106/http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,828597,00.html |archive-date=20 February 2011 |access-date=2 April 2011 |magazine=Time|ref={{Harvid|Time 1960}}}} | |||
| *{{cite news| url= http://www.time.com/time/specials/2007/time100/article/0,28804,1595326_1615754_1615882,00.html| title=Michael J. Fox| date=3 May 2007| vauthors = Davis P| work=The Time 100| publisher=] |location=New York |access-date=2 April 2011 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110425013526/http://www.time.com/time/specials/2007/time100/article/0,28804,1595326_1615754_1615882,00.html| archive-date=25 April 2011 }} | |||
| *{{cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2009/apr/11/michael-j-fox-parkinsons|title='It's the gift that keeps on taking'|date=11 April 2009| vauthors = Brockes E |work=The Guardian|access-date=25 October 2010|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131008000425/http://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2009/apr/11/michael-j-fox-parkinsons|archive-date=8 October 2013}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| {{Medical condition classification and resources | |||
| | DiseasesDB = 9651 | |||
| | ICD11 = {{ICD11|8A00.0}} | |||
| | ICD10 = {{ICD10|G20}}, {{ICD10|F02.3}} | |||
| | ICD9 = {{ICD9|332}} | |||
| | ICDO = | |||
| | OMIM = 168600 | |||
| | OMIM_mult = {{OMIM|556500||none}} | |||
| | MedlinePlus = 000755 | |||
| | eMedicineSubj = neuro | |||
| | eMedicineTopic = 304 | |||
| | eMedicine_mult = {{EMedicine2|neuro|635}} in young<br/>{{EMedicine2|pmr|99}} rehab | |||
| |MeSH=D010300 | |||
| | GeneReviewsNBK = NBK1223 | |||
| | GeneReviewsName = Parkinson Disease Overview | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Antiparkinson}} | |||
| {{CNS diseases of the nervous system}} | |||
| {{Mental and behavioral disorders|selected=neurological}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Revision as of 07:57, 30 December 2024
Progressive neurodegenerative disease "Parkinson's" redirects here. For the medical journal, see Parkinson's Disease (journal). For other uses, see Parkinson's (disambiguation).Medical condition
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually, with non-motor issues becoming more prevalent as the disease progresses. Common motor symptoms include tremors, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), rigidity, and balance difficulties, collectively termed parkinsonism. In later stages, Parkinson's disease dementia, falls, and neuropsychiatric problems such as sleep abnormalities, psychosis, mood swings, or behavioral changes may arise.
Most cases of Parkinson's disease are sporadic, though contributing factors have been identified. Pathophysiology involves progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the substantia nigra, a midbrain region that provides dopamine to the basal ganglia, a system involved in voluntary motor control. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood but involves the aggregation of alpha-synuclein into Lewy bodies within neurons. Other potential factors involve genetic and environmental influences, medications, lifestyle, and prior health conditions.
Diagnosis is primarily based on signs and symptoms, typically motor-related, identified through neurological examination. Medical imaging techniques like positron emission tomography can support the diagnosis. Parkinson's typically manifests in individuals over 60, with about one percent affected. In those younger than 50, it is termed "early-onset PD".
No cure for Parkinson's is known, and treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms. Initial treatment typically includes L-DOPA, MAO-B inhibitors, or dopamine agonists. As the disease progresses, these medications become less effective and may cause involuntary muscle movements. Diet and rehabilitation therapies can help improve symptoms. Deep brain stimulation is used to manage severe motor symptoms when drugs are ineffective. There is little evidence for treatments addressing non-motor symptoms, such as sleep disturbances and mood instability. Life expectancy for those with PD is near-normal but is decreased for early-onset.
Classification and terminology
See also: Parkinsonism and Parkinson-plus syndromeParkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease affecting both the central and peripheral nervous systems, characterized by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra region of the brain. It is classified as a synucleinopathy due to the abnormal accumulation of the protein alpha-synuclein, which aggregates into Lewy bodies within affected neurons.
The loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra initially presents as movement abnormalities, leading to Parkinson's further categorization as a movement disorder. In 30% of cases, disease progression leads to the cognitive decline known as Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD). Alongside dementia with Lewy bodies, PDD is one of the two subtypes of Lewy body dementia.
The four cardinal motor symptoms of Parkinson's—bradykinesia (slowed movements), postural instability, rigidity, and tremor—are called parkinsonism. These four symptoms are not exclusive to Parkinson's and can occur in many other conditions, including HIV infection and recreational drug use. Neurodegenerative diseases that feature parkinsonism but have distinct differences are grouped under the umbrella of Parkinson-plus syndromes or, alternatively, atypical parkinsonian disorders. Parkinson's disease can be attributed to genetic factors or be idiopathic, in which there is no clearly identifiable cause. The latter, also called sporadic Parkinson's, makes up some 85–90% of cases.
Signs and symptoms
Main article: Signs and symptoms of Parkinson's diseaseMotor
See also: Parkinsonism
 Motor symptoms include a stooping posture, the "Parkinsonian gait", and micrographia—jagged, diminutive handwriting.
Motor symptoms include a stooping posture, the "Parkinsonian gait", and micrographia—jagged, diminutive handwriting.
Although a wide spectrum of motor and non-motor symptoms appear in Parkinson's, the cardinal features remain tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability, collectively termed parkinsonism. Appearing in 70–75 percent of PD patients, tremor is often the predominant motor symptom. Resting tremor is the most common, but kinetic tremors—occurring during voluntary movements—and postural tremor—preventing upright, stable posture—also occur. Tremor largely affects the hands and feet: a classic parkinsonian tremor is "pill-rolling", a resting tremor in which the thumb and index finger make contact in a circular motion at 4–6 Hz frequency.
Bradykinesia describes difficulties in motor planning, beginning, and executing, resulting in overall slowed movement with reduced amplitude that affects sequential and simultaneous tasks. Bradykinesia can also lead to hypomimia, reduced facial expressions. Rigidity, also called rigor, refers to a feeling of stiffness and resistance to passive stretching of muscles that occurs in up to 89 percent of cases. Postural instability typically appears in later stages, leading to impaired balance and falls. Postural instability also leads to a forward stooping posture.
Beyond the cardinal four, other motor deficits, termed secondary motor symptoms, commonly occur. Notably, gait disturbances result in the Parkinsonian gait, which includes shuffling and paroxysmal deficits, where a normal gait is interrupted by rapid footsteps—known as festination—or sudden stops, impairing balance and causing falls. Most PD patients experience speech problems, including stuttering, hypophonic, "soft" speech, slurring, and festinating speech (rapid and poorly intelligible). Handwriting is commonly altered in Parkinson's, decreasing in size—known as micrographia—and becoming jagged and sharply fluctuating. Grip and dexterity are also impaired.
Non-motor
Neuropsychiatric and cognitive
| Symptom | |
|---|---|
| Prevalence (%) | |
| Anxiety | 40–50 |
| Apathy | 40 |
| Depression | 20–40 |
| Impulse control disorders | 36–60 |
| Psychosis | 15–30 |
Neuropsychiatric symptoms like anxiety, apathy, depression, hallucinations, and impulse control disorders occur in up to 60% of those with Parkinson's. They often precede motor symptoms and vary with disease progression. Non-motor fluctuations, including dysphoria, fatigue, and slowness of thought, are also common. Some neuropsychiatric symptoms are not directly caused by neurodegeneration but rather by its pharmacological management.
Cognitive impairments rank among the most prevalent and debilitating non-motor symptoms. These deficits may emerge in the early stages or before diagnosis, and their prevalence and severity tend to increase with disease progression. Ranging from mild cognitive impairment to severe Parkinson's disease dementia, these impairments include executive dysfunction, slowed cognitive processing speed, and disruptions in time perception and estimation.
Autonomic

Autonomic nervous system failures, known as dysautonomia, can appear at any stage of Parkinson's. They are among the most debilitating symptoms and greatly reduce quality of life. Although almost all PD patients suffer cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction, only some are symptomatic. Chiefly, orthostatic hypotension—a sustained blood pressure drop of at least 20 mmHg systolic or 10 mmHg diastolic after standing—occurs in 30–50 percent of cases. This can result in lightheadedness or fainting: subsequent falls are associated with higher morbidity and mortality.
Other autonomic failures include gastrointestinal issues like chronic constipation, impaired stomach emptying and subsequent nausea, excessive salivation, and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing): all greatly reduce quality of life. Dysphagia, for instance, can prevent pill swallowing and lead to aspiration pneumonia. Urinary incontinence, sexual dysfunction, and thermoregulatory dysfunction—including heat and cold intolerance and excessive sweating—also frequently occur.
Other non-motor symptoms
Sensory deficits appear in up to 90 percent of patients and are usually present at early stages. Nociceptive and neuropathic pain are common, with peripheral neuropathy affecting up to 55 percent of individuals. Visual impairments are also frequently observed, including deficits in visual acuity, color vision, eye coordination, and visual hallucinations. An impaired sense of smell is also prevalent. PD patients often struggle with spatial awareness, recognizing faces and emotions, and may experience challenges with reading and double vision.
Sleep disorders are highly prevalent in PD, affecting up to 98%. These disorders include insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, restless legs syndrome, REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), and sleep-disordered breathing, many of which can be worsened by medication. RBD may begin years before the initial motor symptoms. Individual presentation of symptoms varies, although most people affected by PD show an altered circadian rhythm at some point of disease progression.
PD is also associated with a variety of skin disorders that include melanoma, seborrheic dermatitis, bullous pemphigoid, and rosacea. Seborrheic dermatitis is recognized as a premotor feature that indicates dysautonomia and demonstrates that PD can be detected not only by changes of nervous tissue, but tissue abnormalities outside the nervous system as well.
Causes
Main article: Causes of Parkinson's disease
 The protein alpha-synuclein aggregates into Lewy bodies and neurites. Structural model of alpha-synuclein (left), photomicrograph of Lewy bodies (right).
The protein alpha-synuclein aggregates into Lewy bodies and neurites. Structural model of alpha-synuclein (left), photomicrograph of Lewy bodies (right).
As of 2024, the cause of neurodegeneration in Parkinson's remains unclear, though it is believed to result from the interplay of genetic and environmental factors. The majority of cases are sporadic with no clearly identifiable cause, while approximately 5–10 percent are familial. Around a third of familial cases can be attributed to a single monogenic cause.
Molecularly, abnormal aggregation of alpha-synuclein is considered a key contributor to PD pathogenesis, although the trigger for this aggregation remains debated. Proteostasis disruption and the dysfunction of cell organelles, including endosomes, lysosomes, and mitochondria, are implicated in pathogenesis. Additionally, maladaptive immune and inflammatory responses are potential contributors. The substantial heterogeneity in PD presentation and progression suggests the involvement of multiple interacting triggers and pathogenic pathways.
Genetic

Parkinson's can be narrowly defined as a genetic disease, as rare inherited gene variants have been firmly linked to monogenic PD, and the majority of sporadic cases carry variants that increase PD risk. PD heritability is estimated to range from 22 to 40 percent. Around 15 percent of diagnosed individuals have a family history, of which 5–10 percent can be attributed to a causative risk gene mutation. However, carrying one of these mutations may not lead to disease. Rates of familial PD vary by ethnicity: monogenic PD occurs in up to 40% of Arab-Berber patients and 20% of Ashkenazi Jewish patients.
As of 2024, around 90 genetic risk variants across 78 genomic loci have been identified. Notable risk variants include SNCA (which encodes alpha-synuclein), LRRK2, and VPS35 for autosomal dominant inheritance, and PRKN, PINK1, and DJ1 for autosomal recessive inheritance. LRRK2 is the most common autosomal dominant variant, responsible for 1–2 percent of all PD cases and 40 percent of familial cases. Parkin variants are associated with nearly half of recessive, early-onset monogenic PD. Mutations in the GBA1 gene, linked to Gaucher's disease, are found in 5–15 percent of PD cases. The GBA1 variant frequently leads to cognitive decline.
Environmental
See also: Environmental health and Exposome
The limited heritability of Parkinson's strongly suggests environmental factors are involved, though identifying these risk factors and establishing causality is challenging due to PD's decade-long prodromal period. However, environmental toxicants such as air pollution, pesticides, and industrial solvents like trichloroethylene are strongly linked to Parkinson's.
Certain pesticides—like paraquat, glyphosate, and rotenone—are the most established environmental toxicants for Parkinson's and are likely causal. PD prevalence is strongly associated with local pesticide use, and many pesticides are mitochondrial toxins. Paraquat, for instance, structurally resembles metabolized MPTP, which selectively kills dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting mitochondrial complex 1 and is widely used to model PD. Pesticide exposure after diagnosis may also accelerate disease progression. Without pesticide exposure, an estimated 20 percent of all PD cases would be prevented.
Hypotheses
Prionic hypothesis
See also: PrionThe hallmark of Parkinson's is the formation of protein aggregates, beginning with alpha-synuclein fibrils and followed by Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites. The prion hypothesis suggests that alpha-synuclein aggregates are pathogenic and can spread to neighboring, healthy neurons and seed new aggregates. Some propose that the heterogeneity of PD may stem from different "strains" of alpha-synuclein aggregates and varying anatomical sites of origin. Alpha-synuclein propagation has been demonstrated in cell and animal models and is the most popular explanation for the progressive spread through specific neuronal systems. However, therapeutic efforts to clear alpha-synuclein have failed. Additionally, postmortem brain tissue analysis shows that alpha-synuclein pathology does not clearly progress through the nearest neural connections.
Braak's hypothesis
Main article: Parkinson's disease and gut-brain axis § Braak's hypothesisIn 2002, Heiko Braak and colleagues proposed that Parkinson's disease begins outside the brain and is triggered by a "neuroinvasion" of some unknown pathogen. The pathogen enters through the nasal cavity and is swallowed into the digestive tract, initiating Lewy pathology in both areas. This alpha-synuclein pathology may then travel from the gut to the central nervous system through the vagus nerve. This theory could explain the presence of Lewy pathology in both the enteric nervous system and olfactory tract neurons, as well as clinical symptoms like loss of small and gastrointestinal problems. It has also been suggested that environmental toxicants might be ingested in a similar manner to trigger PD.
Catecholaldehyde hypothesis
Main article: Catecholaldehyde hypothesis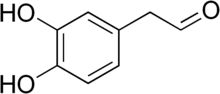
The enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO) plays a central role in the metabolism of the neurotransmitter dopamine and other catecholamines. The catecholaldehyde hypothesis argues that the oxidation of dopamine by MAO into 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL) and hydrogen peroxide and the subsequent abnormal accumulation thereof leads to neurodegeneration. The theory posits that DOPAL interacts with alpha-synuclein and causes it to aggregate.
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Whether mitochondrial dysfunction is a cause or consequence of PD pathology remains unclear. Impaired ATP production, increased oxidative stress, and reduced calcium buffering may contribute to neurodegeneration. The finding that MPP—a respiratory complex I inhibitor and MPTP metabolite—caused parkinsonian symptoms strongly implied that mitochondria contributed to PD pathogenesis. Alpha-synuclein and toxicants like rotenone similarly disrupt respiratory complex I. Additionally, faulty gene variants involved in familial Parkinson's—including PINK1 and Parkin—prevent the elimination of dysfunctional mitochondria through mitophagy.
Neuroinflammation
Some hypothesize that neurodegeneration arises from a chronic neuroinflammatory state created by local activated microglia and infiltrating immune cells. Mitochondrial dysfunction may also drive immune activation, particularly in monogenic PD. Some autoimmune disorders increase the risk of developing PD, supporting an autoimmune contribution. Additionally, influenza and herpes simplex virus infections increase the risk of PD, possibly due to a viral protein resembling alpha-synuclein. Parkinson's risk is also decreased with immunosuppressants.
Pathophysiology
Main article: Pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease has two hallmark pathophysiological processes: the abnormal aggregation of alpha-synuclein that leads to Lewy pathology, and the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. The death of these neurons reduces available dopamine in the striatum, which in turn affects circuits controlling movement in the basal ganglia. By the time motor symptoms appear, 50–80 percent of all dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra have degenerated.
However, cell death and Lewy pathology are not limited to the substantia nigra. The six-stage Braak system holds that alpha-synuclein pathology begins in the olfactory bulb or outside the central nervous system in the enteric nervous system before ascending the brain stem. In the third Braak stage, Lewy body pathology appears in the substantia nigra, and, by the sixth step, Lewy pathology has spread to the limbic and neocortical regions. Although Braak staging offers a strong basis for PD progression, the Lewy pathology around 50 percent patients do not adhere to the predicted model. Indeed, Lewy pathology is highly variable and may be entirely absent in some PD patients.
Alpha-synuclein pathology
Further information: Protein aggregation and Lewy body
Alpha-synuclein is an intracellular protein typically localized to presynaptic terminals and involved in synaptic vesicle trafficking, intracellular transport, and neurotransmitter release. When misfolded, it can aggregate into oligomers and proto-fibrils that in turn lead to Lewy body formation. Due to their lower molecular weight, oligomers and proto-fibrils may disseminate and be transmitted to other cells more rapidly.
Lewy bodies consist of a fibrillar exterior and granular core. Although alpha-synuclein is the dominant proteinaceous component, the core contains mitochondrial and autophagosomal membrane components, suggesting a link with organelle dysfunction. It is unclear whether Lewy bodies themselves contribute to or are simply the result of PD pathogenesis: alpha-synuclein oligomers can independently mediate cell damage, and neurodegeneration can precede Lewy body formation.
Pathways involved in neurodegeneration
See also: Neurodegeneration § MechanismsThree major pathways—vesicular trafficking, lysosomal degradation, and mitochondrial maintenance—are known to be affected by and contribute to Parkinson's pathogenesis, with all three linked to alpha-synuclein. High risk gene variants also impair all three of these processes. All steps of vesicular trafficking are impaired by alpha-synuclein. It blocks endoplasmic reticulum (ER) vesicles from reaching the Golgi—leading to ER stress—and Golgi vesicles from reaching the lysosome, preventing alpha-synuclein degradation and leading to its build-up. Risky gene variants, chiefly GBA, further compromise lysosomal function. Although the mechanism is not well established, alpha-synuclein can impair mitochondrial function and cause subsequent oxidative stress. Mitochondrial dysfunction can in turn lead to further alpha-synuclein accumulation in a positive feedback loop. Microglial activation, possibly caused by alpha-synuclein, is also strongly indicated.
Risk factors
Positive risk factors
As 90 percent of Parkinson's cases are sporadic, the identification of the risk factors that may influence disease progression or severity is critical. The most significant risk factor in developing PD is age, with a prevalence of 1 percent in those aged over 65 and approximately 4.3 percent in age over 85. Traumatic brain injury significant increases PD risk, especially if recent. Dairy consumption correlates with a higher risk, possibly due to contaminants like heptachlor epoxide. Although the connection is unclear, melanoma diagnosis is associated with an approximately 45 percent risk increase. There is also an association between methamphetamine use and PD risk.
Protective factors

Although no compounds or activities have been mechanistically established as neuroprotective for Parkinson's, several factors have been found to be associated with a decreased risk. Tobacco use and smoking is strongly associated with a decreased risk, reducing the chance of developing PD by up to 70%. Various tobacco and smoke components have been hypothesized to be neuroprotective, including nicotine, carbon monoxide, and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors. Consumption of coffee, tea, or caffeine is also strongly associated with neuroprotection. Prescribed adrenergic antagonists like terazosin may reduce risk.
Although findings have varied, usage of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen may be neuroprotective. Calcium channel blockers may also have a protective effect, with a 22% risk reduction reported. Higher blood concentrations of urate—a potent antioxidant—have been proposed to be neuroprotective. Although longitudinal studies observe a slight decrease in PD risk among those who consume alcohol—possibly due to alcohol's urate-increasing effect—alcohol abuse may increase risk.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Parkinson's disease is largely clinical, relying on medical history and examination of symptoms, with an emphasis on symptoms that appear in later stages. Although early stage diagnosis is not reliable, prodromal diagnosis may consider previous family history of Parkinson's and possible early symptoms like rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder (RBD), reduced sense of smell, and gastrointestinal issues. Isolated RBD is a particularly significant sign as 90% of those affected will develop some form of neurodegenerative parkinsonism. Diagnosis in later stages requires the manifestation of parkinsonism, specifically bradykinesia and rigidity or tremor. Further support includes other motor and non-motor symptoms and genetic profiling.
A PD diagnosis is typically confirmed by two of the following criteria: responsiveness to levodopa, resting tremor, levodopa-induced dyskinesia, or with dopamine transporter single-proton emission computed tomography. If these criteria are not met, atypical parkinsonism is considered. However, definitive diagnoses can only be made post-mortem through pathological analysis. Misdiagnosis is common, with a reported error rate of near 25 percent, and diagnoses often change during follow-ups. Diagnosis can be further complicated by multiple overlapping conditions.
Imaging

Diagnosis can be aided by molecular imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). As both conventional MRI and computed tomography (CT) scans are usually normal in patients with early PD, they can be used to exclude other pathologies that cause parkinsonism. Diffusion MRI can differentiate PD from multiple systems atrophy (MSA). Emerging MRI techniques of at least 3.0 T field strength—including neuromelanin-MRI, 1H-MRSI, and resting state fMRI—may detect abnormalities in the substantia nigra, nigrostriatal pathway, and elsewhere.
Unlike MRI, PET and SPECT use radioisotopes for imaging. Both techniques can aid diagnosis by characterizing PD-associated alterations in the metabolism and transport of dopamine in the basal ganglia. Largely used outside the United States, iodine-123-meta-iodobenzylguanidine myocardial scintigraphy can assess heart muscle denervation to support a PD diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis

Differential diagnosis of Parkinson's is among the most difficult in neurology. Differentiating early PD from atypical parkinsonian disorders is a major difficulty. In their initial stages, PD can be difficult to distinguish from the atypical neurodegenerative parkinsonisms, including MSA, dementia with Lewy bodies, and the tauopathies progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. Other conditions that may present similarly to PD include vascular parkinsonism, Alzheimer's disease, and frontotemporal dementia.
The International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society has proposed a set of criteria that, unlike the standard Queen's Square Brain Bank Criteria, includes non-exclusionary "red-flag" clinical features that may not suggest Parkinson's. A large number of "red flags" have been proposed and adopted for various conditions that might mimic the symptoms of PD. Diagnostic tests, including gene sequencing, molecular imaging techniques, and assessment of smell may also distinguish PD. MRI is particularly powerful due to several unique features for atypical parkinsonisms. Key distinguishing symptoms and features include:
| Disorder | Distinguishing symptoms and features |
|---|---|
| Corticobasal syndrome | Levodopa resistance, myoclonus, dystonia, corticosensory loss, alien limb phenomenon, apraxia, and non-fluent aphasia |
| Dementia with Lewy bodies | Levodopa resistance, cognitive predominance before motor symptoms, and fluctuating cognitive symptoms |
| Essential tremor | Tremor that worsens with action, normal SPECT scan |
| Multiple system atrophy | Levodopa resistance, rapidly progressive, autonomic failure, stridor, present Babinski sign, cerebellar ataxia, and specific MRI findings like the "Hot Cross Bun" |
| Progressive supranuclear palsy | Levodopa resistance, restrictive vertical gaze, pseudobulbar crying, eyelid twitching, specific MRI findings, and early and different postural difficulties |
Management
Main article: Management of Parkinson's diseaseAs of 2024, no disease-modifying therapies exist that reverse or slow neurodegeneration, processes respectively termed neurorestoration and neuroprotection. Patients are typically managed with a holistic approach that combines lifestyle modifications with physical therapy. Current pharmacological interventions purely target symptoms, by either increasing endogenous dopamine levels or directly mimicking dopamine's effect on the patient's brain. These include dopamine agonists, MAO-B inhibitors, and levodopa: the most widely used and effective drug. The optimal time to initiate pharmacological treatment is debated, but initial dopamine agonist and MAO-B inhibitor treatment and later levodopa therapy is common. Invasive procedures such as deep brain stimulation may be used for patients that do not respond to medication.
Medications
Levodopa

Levodopa (L-DOPA) is the most widely used and the most effective therapy—the gold standard—for Parkinson's treatment. The compound occurs naturally and is the immediate precursor for dopamine synthesis in the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Levodopa administration reduces the dopamine deficiency, alleviating parkinsonian symptoms.
Despite its efficacy, levodopa poses several challenges and has been called the "pharmacologist's nightmare". Its metabolism outside the brain by aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AAAD) and catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) can cause nausea and vomiting; inhibitors like carbidopa, entacapone, and benserazide are usually taken with levodopa to mitigate these effects. Symptoms may become unresponsive to levodopa, with sudden changes between a state of mobility ("ON time") and immobility ("OFF time"). Long-term levodopa use may also induce dyskinesia and motor fluctuations. Although this often causes levodopa use to be delayed to later stages, earlier administration leads to improved motor function and quality of life.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists are an alternative or complement for levodopa therapy. They activate dopamine receptors in the striatum, with reduced risk of motor fluctuations and dyskinesia. Ergot dopamine agonists were commonly used, but have been largely replaced with non-ergot compounds due to severe adverse effects like pulmonary fibrosis and cardiovascular issues. Non-ergot agonists are efficacious in both early and late stage Parkinson's, The agonist apomorphine is often used for drug-resistant OFF time in later-stage PD. However, after five years of use, impulse control disorders may occur in over 40 percent of PD patients taking dopamine agonists. A problematic, narcotic-like withdrawal effect may occur when agonist use is reduced or stopped. Compared to levodopa, dopamine agonists are more likely to cause fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and hallucinations.
MAO-B inhibitors
MAO-B inhibitors—such as safinamide, selegiline and rasagiline—increase the amount of dopamine in the basal ganglia by inhibiting the activity of monoamine oxidase B, an enzyme that breaks down dopamine. These compounds mildly alleviate motor symptoms when used as monotherapy but can also be used with levodopa and can be used at any disease stage. When used with levodopa, time spent in the off phase is reduced. Selegiline has been shown to delay the need for initial levodopa, suggesting that it might be neuroprotective and slow the progression of the disease. Common side effects are nausea, dizziness, insomnia, sleepiness, and (in selegiline and rasagiline) orthostatic hypotension. MAO-Bs are known to increase serotonin and cause a potentially dangerous condition known as serotonin syndrome.
Other drugs
Treatments for non-motor symptoms of PD have not been well studied and many medications are used off-label. A diverse range of symptoms beyond those related to motor function can be treated pharmaceutically. Examples include cholinesterase inhibitors for cognitive impairment and modafinil for excessive daytime sleepiness. Fludrocortisone, midodrine and droxidopa are commonly used off label for orthostatic hypotension related to autonomic dysfunction. Sublingual atropine or botulinum toxin injections may be used off-label for drooling. SSRIs and SNRIs are often used for depression related to PD, but there is a risk of serotonin syndrome with the SSRI or SNRI antidepressants. Doxepin and rasagline may reduce physical fatigue in PD. Other treatments have received government approval, such as the first FDA-approved treatment for PD psychosis, pimavanserin. Although its efficacy is inferior to off-label clozapine, it has significantly fewer side effects.
Invasive interventions
Further information: Deep brain stimulation
Surgery for Parkinson's first appeared in the 19th century and by the 1960s had evolved into ablative brain surgery that lesioned the basal ganglia, thalamus or globus pallidus (a pallidotomy). The discovery of L-DOPA for PD treatment caused ablative therapies to largely disappear. Ablative surgeries experienced a resurgence in the 1990s but were quickly superseded by newly-developed deep brain stimulation (DBS). Although gamma knife and high-intensity focused ultrasound surgeries have been developed for pallidotomies and thalamotomies, their use remains rare.
DBS involves the implantation of electrodes called neurostimulators, which sends electrical impulses to specific parts of the brain. DBS for the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus interna has high efficacy for up to 2 years, but longterm efficacy is unclear and likely decreases with time. DBS typically targets rigidity and tremor, and is recommended for PD patients who are intolerant or do not respond to medication. Cognitive impairment is the most common exclusion criteria.
Rehabilitation
Further information: Management of Parkinson's disease § Rehabilitation
Although pharmacological therapies can improve symptoms, patients' autonomy and ability to perform everyday tasks is still reduced by PD. As a result, rehabilitation is often useful. However, the scientific support for any single rehabilitation treatment is limited.
Exercise programs are often recommended, with preliminary evidence of efficacy. Regular physical exercise with or without physical therapy can be beneficial to maintain and improve mobility, flexibility, strength, gait speed, and quality of life. Aerobic, mind-body, and resistance training may be beneficial in alleviating PD-associated depression and anxiety. Strength training may increase manual dexterity and strength, facilitating daily tasks that require grasping objects.
In improving flexibility and range of motion for people experiencing rigidity, generalized relaxation techniques such as gentle rocking have been found to decrease excessive muscle tension. Other effective techniques to promote relaxation include slow rotational movements of the extremities and trunk, rhythmic initiation, diaphragmatic breathing, and meditation. Deep diaphragmatic breathing may also improve chest-wall mobility and vital capacity decreased by the stooped posture and respiratory dysfunctions of advanced Parkinson's. Rehabilitation techniques targeting gait and the challenges posed by bradykinesia, shuffling, and decreased arm swing include pole walking, treadmill walking, and marching exercises.
Speech therapies such as the Lee Silverman voice treatment may reduce the effect of speech disorders associated with PD. Occupational therapy is another rehabilitation strategy and can improve quality of life by enabling PD patients to find engaging activities and communal roles, adapt to their living environment, and improving domestic and work abilities.
Diet
Parkinson's poses digestive problems like constipation and prolonged emptying of stomach contents, and a balanced diet with periodical nutritional assessments is recommended to avoid weight loss or gain and minimize the consequences of gastrointestinal dysfunction. In particular, a Mediterranean diet is advised and may slow disease progression. As it can compete for uptake with amino acids derived from protein, levodopa should be taken 30 minutes before meals to minimize such competition. Low protein diets may also be needed by later stages. As the disease advances, swallowing difficulties often arise. Using thickening agents for liquid intake and an upright posture when eating may be useful; both measures reduce the risk of choking. Gastrostomy can be used to deliver food directly into the stomach. Increased water and fiber intake is used to treat constipation.
Palliative care
As Parkinson's is incurable, palliative care aims to improve the quality of life for both the patient and family by alleviating the symptoms and stress associated with illness. Early integration of palliative care into the disease course is recommended, rather than delaying until later stages. Palliative care specialists can help with physical symptoms, emotional factors such as loss of function and jobs, depression, fear, as well as existential concerns. Palliative care team members also help guide patients and families on difficult decisions caused by disease progression, such as wishes for a feeding tube, noninvasive ventilator or tracheostomy, use of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and entering hospice care.
Prognosis
See also: Unified Parkinson's disease rating scale| Parkinson's subtype | Mean years post-diagnosis until: | |
|---|---|---|
| Severe cognitive or movement abnormalities | Death | |
| Mild-motor predominant | 14.3 | 20.2 |
| Intermediate | 8.2 | 13.1 |
| Diffuse malignant | 3.5 | 8.1 |
As Parkinson's is a heterogeneous condition with multiple etiologies, prognostication can be difficult and prognoses can be highly variable. On average, life expectancy is reduced in those with Parkinson's, with younger age of onset resulting in greater life expectancy decreases. Although PD subtype categorization is controversial, the 2017 Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative study identified three broad scorable subtypes of increasing severity and more rapid progression: mild-motor predominant, intermediate, and diffuse malignant. Mean years of survival post-diagnosis were 20.2, 13.1, and 8.1.
Around 30% of Parkinson's patients develop dementia, and is 12 times more likely to occur in elderly patients of those with severe PD. Dementia is less likely to arise in patients with tremor-dominant PD. Parkinson's disease dementia is associated with a reduced quality of life in people with PD and their caregivers, increased mortality, and a higher probability of needing nursing home care.
The incidence rate of falls in Parkinson's patients is approximately 45 to 68%, thrice that of healthy individuals, and half of such falls result in serious secondary injuries. Falls increase morbidity and mortality. Around 90% of those with PD develop hypokinetic dysarthria, which worsens with disease progression and can hinder communication. Additionally, over 80% of PD patients develop dysphagia: consequent inhalation of gastric and oropharyngeal secretions can lead to aspiration pneumonia. Aspiration pneumonia is responsible for 70% of deaths in those with PD.
Epidemiology

As of 2024, Parkinson's is the second most common neurodegenerative disease and the fastest-growing in total number of cases. As of 2023, global prevalence was estimated to be 1.51 per 1000. Although it is around 40% more common in men, age is the dominant predeterminant of Parkinson's. Consequently, as global life expectancy has increased, Parkinson's disease prevalence has also risen, with an estimated increase in cases by 74% from 1990 to 2016. The total number is predicted to rise to over 12 million patients by 2040. Some label this a pandemic.
This increase may be due to a number of global factors, including prolonged life expectancy, increased industrialisation, and decreased smoking. Although genetics is the sole factor in a minority of cases, most cases of Parkinson's are likely a result of gene-environment interactions: concordance studies with twins have found Parkinson's heritability to be just 30%. The influence of multiple genetic and environmental factors complicates epidemiological efforts.
Relative to Europe and North America, disease prevalence is lower in Africa but similar in Latin America. Although China is predicted to have nearly half of the global Parkinson's population by 2030, estimates of prevalence in Asia vary. Potential explanations for these geographic differences include genetic variation, environmental factors, health care access, and life expectancy. Although PD incidence and prevalence may vary by race and ethnicity, significant disparities in care, diagnosis, and study participation limit generalizability and lead to conflicting results. Within the United States, high rates of PD have been identified in the Midwest, the South, and agricultural regions of other states: collectively termed the "PD belt". The association between rural residence and Parkinson's has been hypothesized to be caused by environmental factors like herbicides, pesticides, and industrial waste.
History
Main article: History of Parkinson's disease
 In 1877, Jean-Martin Charcot (left) named the disease for James Parkinson, credited as the first to comprehensively describe it. Patient Pierre D. (right) served as the model for William Gowers' widely distributed illustration of Parkinson's disease.
In 1877, Jean-Martin Charcot (left) named the disease for James Parkinson, credited as the first to comprehensively describe it. Patient Pierre D. (right) served as the model for William Gowers' widely distributed illustration of Parkinson's disease.
In 1817, English physician James Parkinson published the first full medical description of the disease as a neurological syndrome in his monograph An Essay on the Shaking Palsy. He presented six clinical cases, including three he had observed on the streets near Hoxton Square in London. Parkinson described three cardinal symptoms: tremor, postural instability and "paralysis" (undistinguished from rigidity or bradykinesia), and speculated that the disease was caused by trauma to the spinal cord.
There was little discussion or investigation of the "shaking palsy" until 1861, when Frenchman Jean-Martin Charcot—regarded as the father of neurology—began expanding Parkinson's description, adding bradykinesia as one of the four cardinal symptoms. In 1877, Charcot renamed the disease after Parkinson, as not all patients displayed the tremor suggested by "shaking palsy". Subsequent neurologists who made early advances to the understanding of Parkinson's include Armand Trousseau, William Gowers, Samuel Kinnier Wilson, and Wilhelm Erb.

Although Parkinson is typically credited with the first detailed description of PD, many previous texts reference some of the disease's clinical signs. In his essay, Parkinson himself acknowledged partial descriptions by Galen, William Cullen, Johann Juncker, and others. Possible earlier but incomplete descriptions include a Nineteenth Dynasty Egyptian papyrus, the ayurvedic text Charaka Samhita, Ecclesiastes 12:3, and a discussion of tremors by Leonardo da Vinci. Multiple traditional Chinese medicine texts may include references to PD, including a discussion in the Yellow Emperor's Internal Classic (c. 425–221 BC) of a disease with symptoms of tremor, stiffness, staring, and stooped posture. In 2009, a systematic description of PD was found in the Hungarian medical text Pax corporis written by Ferenc Pápai Páriz in 1690, some 120 years before Parkinson. Although Páriz correctly described all four cardinal signs, it was only published in Hungarian and was not widely distributed.
In 1912, Frederic Lewy described microscopic particles in affected brains, later named Lewy bodies. In 1919, Konstantin Tretiakoff reported that the substantia nigra was the main brain structure affected, corroborated by Rolf Hassler in 1938. The underlying changes in dopamine signaling were identified in the 1950s, largely by Arvid Carlsson and Oleh Hornykiewicz. In 1997, Polymeropoulos and colleagues at the NIH discovered the first gene for PD, SNCA, which encodes alpha-synuclein. Alpha-synuclein was in turn found to be the main component of Lewy bodies by Spillantini, Trojanowski, Goedert, and others. Anticholinergics and surgery were the only treatments until the use of levodopa, which, although first synthesized by Casimir Funk in 1911, did not enter clinical use until 1967. By the late 1980s, deep brain stimulation introduced by Alim Louis Benabid and colleagues at Grenoble, France, emerged as an additional treatment.
Society and culture

Social impact
For some people with PD, masked facial expressions and difficulty moderating facial expressions of emotion or recognizing other people's facial expressions can impact social well-being. As the condition progresses, tremor, other motor symptoms, difficulty communicating, or mobility issues may interfere with social engagement, causing individuals with PD to feel isolated. Public perception and awareness of PD symptoms such as shaking, hallucinating, slurring speech, and being off balance is lacking in some countries and can lead to stigma.
Cost
The economic cost of Parkinson's to both individuals and society is high. Globally, most government health insurance plans do not cover Parkinson's therapies, requiring patients to pay out-of-pocket. Indirect costs include lifetime earnings losses due to premature death, productivity losses, and caregiver burdens. The duration and progessive nature of PD can place a heavy burden on caregivers: family members like spouses dedicate around 22 hours per week to care.
In 2010, the total economic burden of Parkinson's across Europe, including indirect and direct medical costs, was estimated to be €13.9 billion (US $14.9 billion) in 2010. The total burden in the United States was estimated to be $51.9 billion in 2017, and is project to surpass $79 billion by 2037. However, as of 2022, no rigorous economic surveys had been performed for low or middle income nations. Regardless, preventative care has been identified as crucial to prevent the rapidly increasing incidence of Parkinson's from overwhelming national health systems.
Advocacy

The birthday of James Parkinson, 11 April, has been designated as World Parkinson's Day. A red tulip was chosen by international organizations as the symbol of the disease in 2005; it represents the 'James Parkinson' tulip cultivar, registered in 1981 by a Dutch horticulturalist.
Advocacy organizations include the National Parkinson Foundation, which has provided more than $180 million in care, research, and support services since 1982, Parkinson's Disease Foundation, which has distributed more than $115 million for research and nearly $50 million for education and advocacy programs since its founding in 1957 by William Black; the American Parkinson Disease Association, founded in 1961; and the European Parkinson's Disease Association, founded in 1992.
Notable cases
Main article: List of people diagnosed with Parkinson's disease
In the 21st century, the diagnosis of Parkinson's among notable figures has increased the public's understanding of the disorder. Actor Michael J. Fox was diagnosed with PD at 29 years old, and has used his diagnosis to increase awareness of the disease. To illustrate the effects of the disease, Fox has appeared without medication in television roles and before the United States Congress without medication. The Michael J. Fox Foundation, which he founded in 2000, has raised over $2 billion for Parkinson's research.
Boxer Muhammad Ali showed signs of PD when he was 38, but was undiagnosed until he was 42, and has been called the "world's most famous Parkinson's patient". Whether he had PD or parkinsonism related to boxing is unresolved. Cyclist and Olympic medalist Davis Phinney, diagnosed with Parkinson's at 40, started the Davis Phinney Foundation in 2004 to support PD research.
Several historical figures have been theorized to have had Parkinson's, often framed in the industriousness and inflexibility of the so-called "Parkinsonian personality". For instance, English philosopher Thomas Hobbes was diagnosed with "shaking palsy"—assumed to have been Parkinson's—but continued writing works such as Leviathan. Adolf Hitler is widely believed to have had Parkinson's, and the condition may have influenced his decision making. Mao Zedong was also reported to have died from the disorder.
Clinical research
Main article: Research in Parkinson's disease
As of 2024, no disease-modifying therapies exist that reverse or slow the progression of Parkinson's. Active research directions include the search for new animal models of the disease and development and trial of gene therapy, stem cell transplants, and neuroprotective agents. Improved treatments will likely combine therapeutic strategies to manage symptoms and enhance outcomes. Reliable biomarkers are needed for early diagnosis, and research criteria for their identification have been established.
Neuroprotective treatments
See also: Anti-α-synuclein drugAnti-alpha-synuclein drugs that prevent alpha-synuclein oligomerization and aggregation or promote their clearance are under active investigation, and potential therapeutic strategies include small molecules and immunotherapies like vaccines and monoclonal antibodies. While immunotherapies show promise, their effiacy is often inconsistent. Anti-inflammatory drugs that target NLRP3 and the JAK-STAT signaling pathway offer another potential therapeutic approach.
As the gut microbiome in PD is often disrupted and produces toxic compounds, fecal microbiota transplants might restore a healthy microbiome and alleviate various motor and non-motor symptoms. Neurotrophic factors—peptides that enhance the growth, maturation, and survival of neurons—show modest results but require invasive surgical administration. Viral vectors may represent a more feasible delivery platform. Calcium channel blockers may restore the calcium imbalance present in Parkinson's, and are being investigated as a neuroprotective treatment. Other therapies, like deferiprone, may reduce the abnormal accumulation of iron in PD.
Cell-based therapies
Main article: Cell-based therapies for Parkinson's disease Researchers at Argonne National Laboratory examine induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) for use in Parkinson's and other diseases: the action potentials of one such iPSC differentiated into a dopaminergic neuron are visible at right.
Researchers at Argonne National Laboratory examine induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) for use in Parkinson's and other diseases: the action potentials of one such iPSC differentiated into a dopaminergic neuron are visible at right.
In contrast to other neurodegenerative disorders, many Parkinson's symptoms can be attributed to the loss of a single cell type. Consequently, dopaminergic neuron regeneration is a promising therapeutic approach. Although most initial research sought to generate dopaminergic neuron precursor cells from fetal brain tissue, pluripotent stem cells—particularly induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)—have become an increasingly popular tissue source.
Both fetal and iPSC-derived DA neurons have been transplanted into patients in clinical trials. Although some patients see improvements, the results are highly variable. Adverse effects, such as dyskinesia arising from excess dopamine release by the transplanted tissues, have also been observed.
Gene therapy
Main article: Gene therapy in Parkinson's diseaseGene therapy for Parkinson's seeks to restore the healthy function of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra by delivering genetic material—typically through a viral vector—to these diseased cells. This material may deilver a functional, wildtype version of a gene, or knockdown a pathological variants. Experimental gene therapies for PD have aimed to increase the expression of growth factors or enzymes involved in dopamine synthesis, like tyrosine hydroxylase. The one-time delivery of genes circumvents the recurrent invasive administration required to administer some peptides and proteins to the brain. MicroRNAs are an emerging PD gene therapy platform that may serve as an alternative to viral vectors.
Notes and references
Notes
- These inhibitors do not cross the blood brain barrier and thus do not prevent levodopa metabolism there.
- Defined as the onset of development of recurrent falls, wheelchair dependence, dementia, or facility placement.
Citations
- ^ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
- Ferri 2010, Chapter P.
- Koh & Ito 2017.
- Ou et al. 2021.
- Ramesh & Arachchige 2023, pp. 200–201, 203.
- Calabresi et al. 2023, pp. 1, 5.
- Wallace et al. 2022, p. 149.
- Hansen et al. 2019, p. 635.
- Bhattacharyya 2017, p. 7.
- Stanford University School Medicine.
- Bologna, Truong & Jankovic 2022, pp. 1–6.
- Limphaibool et al. 2019, pp. 1–2.
- Leta et al. 2022, p. 1122.
- Langston 2017, p. S11.
- Prajjwal et al. 2024, pp. 1–3.
- Olfatia, Shoeibia & Litvanb 2019, p. 101.
- Dolgacheva, Zinchenko & Goncharov 2022, p. 2.
- ^ Abusrair, Elsekaily & Bohlega 2022, p. 2.
- ^ Moustafa et al. 2016, p. 730.
- Abusrair, Elsekaily & Bohlega 2022, p. 4.
- ^ Sveinbjornsdottir 2016, p. 319.
- Bologna et al. 2019, pp. 727–729.
- Ferreira-Sánchez, Moreno-Verdú & Cano-de-la-Cuerda 2020, p. 1.
- Moustafa et al. 2016, p. 728.
- Palakurthi & Burugupally 2019, pp. 1–2.
- Palakurthi & Burugupally 2019, pp. 1, 4.
- Moustafa et al. 2016, pp. 727–728.
- Moustafa et al. 2016, p. 731.
- Mirelman et al. 2019, p. 1.
- Moustafa et al. 2016, p. 734.
- Moustafa et al. 2016, p. 732.
- Moustafa et al. 2016, p. 733.
- Aarslanda & Krambergera 2015, pp. 660, 662.
- Aarslanda & Krambergera 2015, pp. 659–660.
- Weintraub & Mamikonyan 2019, p. 661. sfn error: no target: CITEREFWeintraubMamikonyan2019 (help)
- Aarslanda & Krambergera 2015, p. 660.
- ^ Biundo, Weis & Antonini 2016, p. 1.
- ^ Gonzalez-Latapi et al. 2021, p. 74.
- Palma & Kaufmann 2018, pp. 372–373.
- Pfeiffer 2020, p. 1464.
- ^ Palma & Kaufmann 2018, p. 373.
- Palma & Kaufmann 2020, pp. 1465–1466. sfn error: no target: CITEREFPalmaKaufmann2020 (help)
- Pfeiffer 2020, p. 1467.
- Han et al. 2022, p. 2.
- Pfeiffer 2020, p. 1468.
- Pfeiffer 2020, pp. 1471–1473.
- ^ Zhu et al. 2016, p. 685.
- Corrà et al. 2023, pp. 225–226.
- Zhu et al. 2016, p. 688.
- Zhu et al. 2016, p. 687.
- Weil et al. 2016, pp. 2828, 2831–2832.
- Stefani & Högl 2020, p. 121.
- Dodet et al. 2024, p. 1.
- Bollu & Sahota 2017, pp. 381–382.
- Niemann, Billnitzer & Jankovic 2021, p. 61.
- Almikhlafi 2024, p. 7.
- ^ Morris et al. 2024.
- ^ Toffoli, Vieira & Schapira 2020, p. 1.
- ^ Brundin & Melki 2017, p. 9808.
- Ho & Wing 2024, pp. 1–2.
- Toffoli, Vieira & Schapira 2020, p. 2.
- ^ Salles, Tirapegui & Chaná-Cuevas 2024, p. 2.
- Farrow et al. 2024, p. 1.
- Bandres-Ciga et al. 2020, p. 2.
- ^ Tanner & Ostrem 2024. sfn error: no target: CITEREFTannerOstrem2024 (help)
- Toffoli, Vieira & Schapira 2020, pp. 1–2.
- Smith & Schapira 2022, pp. 1–15.
- ^ De Mirandaa et al. 2024, p. 46.
- Dorsey & Bloem 2024, pp. 453–454.
- ^ Dorsey & Bloem 2024, p. 454.
- Bloem & Boonstra 2023, p. e948–e949.
- ^ Rietdijk et al. 2017, p. 1.
- Dorsey & Bloem 2024, pp. 453–455.
- Langston 2017, p. S14.
- Santos-Lobato 2024, p. 1.
- Wu & Schekman 2024, p. 1.
- Brundin & Melki 2017, p. 9809.
- Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, p. 96.
- Dickson 2018, p. S31.
- Wu & Schekman 2024, pp. 1–2.
- Brundin & Melki 2017, p. 9812.
- ^ Dorsey et al. 2024, p. 363.
- ^ Rietdijk et al. 2017, p. 2.
- Rietdijk et al. 2017, p. 3.
- Dorsey et al. 2024, pp. 363–364, 371–372.
- Goldstein 2020, p. 169.
- Goldstein 2021, pp. 1–3.
- Chen, Turnbull & Reeve 2019, pp. 1, 15.
- Chen, Turnbull & Reeve 2019, pp. 1, 4–5, 15.
- Chen, Turnbull & Reeve 2019, p. 2.
- Borsche et al. 2021, p. 45.
- Chen, Turnbull & Reeve 2019, p. 2, 13.
- Chen, Turnbull & Reeve 2019, pp. 6–7, 8, 15.
- Borsche et al. 2021, pp. 47–49.
- Tan et al. 2020, p. 303.
- Tan et al. 2020, p. 304.
- Pardo-Moreno et al. 2023, p. 3.
- ^ Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, p. 88.
- ^ Dickson 2018, p. S32.
- ^ Ye et al. 2023, p. 98.
- Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, p. 93.
- ^ Henderson, Trojanowski & Lee 2019, p. 2.
- Ye et al. 2023, p. 96.
- ^ Chen, Gu & Wang 2022.
- Menšíková et al. 2022, p. 8.
- ^ Borghammer 2018, p. 5.
- Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, p. 95.
- Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, p. 89.
- Menšíková et al. 2022, p. 6.
- ^ Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, pp. 96–99.
- Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, pp. 96–97.
- Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, pp. 98–99.
- Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, p. 99.
- Vázquez-Vélez & Zoghbi 2021, p. 100.
- Ye et al. 2023, p. 112.
- Ascherio & Schwarzschild 2016, p. 1257.
- Coleman & Martin 2022, pp. 2321–2322.
- Ascherio & Schwarzschild 2016, p. 1260.
- Delic et al. 2020, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Ascherio & Schwarzschild 2016, p. 1259.
- ^ Crotty & Schwarzschild 2020, p. 1.
- ^ Fabbri et al. 2024, p. 2.
- Ascherio & Schwarzschild 2016, p. 1262.
- Grotewolda & Albina 2024, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Grotewolda & Albina 2024, p. 2.
- Rose, Schwarzschild & Gomperts 2024, pp. 268–269.
- ^ Grotewolda & Albina 2024, p. 3.
- Ren & Chen 2020, p. 1.
- Singh, Tripathi & Singh 2021, p. 10.
- Ascherio & Schwarzschild 2016, pp. 1265–1266.
- Lin et al. 2024, p. 1.
- Ascherio & Schwarzschild 2016, p. 1263.
- Ascherio & Schwarzschild 2016, p. 1261.
- Kamal et al. 2020, p. 8.
- Armstrong & Okun 2020, p. 548.
- ^ Rizzo et al. 2016, p. 1.
- Ugrumov 2020, p. 997.
- ^ Armstrong & Okun 2020, p. 551.
- ^ Tolosa et al. 2021, p. 391.
- ^ Armstrong & Okun 2020, pp. 551–552.
- ^ Heim et al. 2017, p. 916.
- Bidesi et al. 2021, p. 660.
- Brooks 2010, p. 597.
- ^ Tolosa et al. 2021, p. 392.
- Bidesi et al. 2021, p. 665.
- Suwijn et al. 2015.
- Bidesi et al. 2021, pp. 664–672.
- Armstrong & Okun 2020, p. 552.
- Heim et al. 2017, p. 915.
- Tolosa et al. 2021, p. 389.
- Caproni & Colosimo 2020, p. 21.
- Tolosa et al. 2021, p. 390.
- Caproni & Colosimo 2020, pp. 15, 21.
- Tolosa et al. 2021, pp. 390–391.
- Caproni & Colosimo 2020, p. 14.
- Simon, Greenberg & Aminoff 2017.
- Greenland & Barker 2018.
- ^ Connolly & Lang 2014.
- de Bie et al. 2020, p. 3.
- ^ de Bie et al. 2020, pp. 1, 3.
- ^ Kobylecki 2020, p. 395.
- de Bie et al. 2020, p. 4.
- ^ Limousin & Foltynie 2019, p. 234.
- ^ Bronstein et al. 2011, p. 169.
- Tambasco, Romoli & Calabresi 2018, p. 1239.
- LeWitt & Fahn 2016, p. S5-S6.
- Tambasco, Romoli & Calabresi 2018, pp. 1239–1240.
- Tambasco, Romoli & Calabresi 2018, p. 1240.
- Leta et al. 2023, p. 1466.
- Leta et al. 2023, pp. 1466–1468.
- Tambasco, Romoli & Calabresi 2018, p. 1241.
- Leta et al. 2023, p. 1468.
- Jing et al. 2023, p. 1224.
- de Bie et al. 2020, pp. 1, 3–4.
- ^ Jing et al. 2023, p. 1225.
- ^ Jing et al. 2023, p. 1226.
- Kobylecki 2020, p. 396.
- ^ de Bie et al. 2020, p. 1.
- Robakis & Fahn 2015, pp. 433–434.
- Robakis & Fahn 2015, p. 433.
- Binde et al. 2018, p. 1924.
- Tan, Jenner & Chen 2022, p. 477.
- ^ Alborghetti & Nicoletti 2019.
- Armstrong & Okun 2020.
- Robakis & Fahn 2015, p. 435.
- The National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions.
- Seppi et al. 2019, pp. 183, 185, 188.
- Elbers et al. 2015.
- Rissardo et al. 2022, p. 1.
- Lozano, Tam & Lozano 2018, pp. 1–2.
- Lozano, Tam & Lozano 2018, p. 2.
- ^ Bronstein et al. 2011, p. 165.
- Lozano, Tam & Lozano 2018, p. 6.
- Moosa et al. 2019, pp. 1244–1249.
- Bronstein et al. 2011, p. 168.
- Bronstein et al. 2011, p. 166.
- Tofani et al. 2020, p. 891.
- ^ Ernst et al. 2023.
- Crotty & Schwarzschild 2020, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Ahlskog 2011, p. 292.
- Costa et al. 2024.
- Ramazzina, Bernazzoli & Costantino 2017, pp. 620–623.
- O'Sullivan & Schmitz 2007, pp. 873, 876.
- O'Sullivan & Schmitz 2007, p. 880.
- O'Sullivan & Schmitz 2007, p. 879.
- McDonnell et al. 2018, pp. 607–609.
- Pu et al. 2021, pp. 1–2.
- Tofani et al. 2020, pp. 891, 900.
- Lister 2020, pp. 99–100.
- ^ Barichella, Cereda & Pezzoli 2009, pp. 1888.
- Barichella, Cereda & Pezzoli 2009, pp. 1887.
- Pasricha, Guerrero-Lopez & Kuo 2024, p. 212.
- Pasricha, Guerrero-Lopez & Kuo 2024, p. 216.
- ^ Ghoche 2012, pp. S2–S3.
- Wilcox 2010, p. 26.
- Ferrell et al. 2007, p. 741.
- Ghoche 2012, p. S3.
- Casey 2013, pp. 20–22.
- Bernat & Beresford 2013, pp. 135, 137, 138.
- ^ Corcoran & Kluger 2021, p. 956.
- Fereshtehnejad et al. 2017, p. 1967.
- Tolosa et al. 2021, p. 385.
- Dommershuijsen et al. 2023, pp. 2–3.
- Murueta-Goyena, Muiño & Gómez-Esteban 2017, p. 26.
- Murueta-Goyena, Muiño & Gómez-Esteban 2017, p. 27.
- Caballol, Martí & Tolosa 2007, p. S358.
- Murueta-Goyena, Muiño & Gómez-Esteban 2024, p. 395.
- Atalar, Oguz & Genc 2023, p. 163.
- Chua et al. 2024, p. 1.
- Corcoran, Muiño & Kluger 2021, p. 1. sfn error: no target: CITEREFCorcoranMuiñoKluger2021 (help)
- Ben-Shlomo et al. 2024, p. 283.
- Varden, Walker & O'Callaghan 2024, p. 1.
- Zhu et al. 2024, p. e464.
- ^ Ben-Shlomo et al. 2024, p. 286.
- Deliz, Tanner & Gonzalez-Latapi 2024, p. 166.
- ^ Ben-Shlomo et al. 2024, p. 284.
- Dorsey et al. 2018, p. S4.
- ^ Deliz, Tanner & Gonzalez-Latapi 2024, p. 165.
- ^ Ben-Shlomo et al. 2024, p. 285.
- Li et al. 2019, p. 1.
- ^ Deliz, Tanner & Gonzalez-Latapi 2024, pp. 164–165.
- Huang et al. 2022, pp. 1–2.
- Lewis et al. 2020, p. 389.
- Goetz 2011, pp. 1–2.
- Lees 2007, p. S327.
- ^ Goetz 2011, p. 2.
- ^ Louis 1997, p. 1069.
- ^ Lees 2007, p. S328.
- Lees 2007, p. S329.
- Bereczki 2010, p. 290.
- ^ Blonder 2018, pp. 3–4.
- Bereczki 2010, pp. 290–293.
- Blonder 2018, p. 3.
- Sousa-Santos, Pozzobon & Teixeira 2024, pp. 1–2.
- Lees 2007, p. S331.
- Fahn 2008, p. S500—S501, S504–S505.
- Polymeropoulos et al. 1997.
- Schulz-Schaeffer 2010, p. 131.
- Lanska 2010, p. 507.
- Guridi & Lozano 1997, pp. 1180–1183.
- Fahn 2008, p. S497.
- Fahn 2008, p. S501.
- Coffey 2009, pp. 209–210.
- Prenger et al. 2020, p. 2.
- Crooks et al. 2023, p. 2,7.
- Crooks et al. 2023, p. 2.
- ^ Schiess et al. 2022, p. 931.
- ^ Yang et al. 2020, p. 1.
- ^ Schiess et al. 2022, p. 933.
- Schiess et al. 2022, p. 929.
- Schiess et al. 2022, p. 930.
- Lees 2007, pp. S327–S334
- GlaxoSmithKline.
- National Parkinson Foundation.
- Time 1960.
- Parkinson's Disease Foundation.
- American Parkinson Disease Association.
- European Parkinson's Disease Association.
- Parkinson's Foundation.
- The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research.
- Davis 2007.
- Brockes 2009.
- Burleson & Breen 2023.
- Brey 2006.
- Matthews 2006, p. 10–23.
- Macur 2008.
- Davis Phinney Foundation.
- Luca et al. 2018, pp. 1–2.
- McCrum 2017.
- Kinsley 2014.
- Raudino 2011, pp. 945–949.
- Gupta et al. 2015, pp. 1447–1452.
- Boettcher et al. 2015, p. E8.
- Lieberman 1996, p. 95.
- Glass 2016.
- Poewe et al. 2017.
- Pardo-Moreno et al. 2023, p. 1.
- Li & Le 2020, p. 183.
- Heinzel et al. 2019.
- ^ Pardo-Moreno et al. 2023, pp. 12–13.
- ^ Alfaidi, Barker & Kuan 2024, p. 1.
- Jasutkar, Oh & Mouradian 2022, p. 208.
- Pardo-Moreno et al. 2023, pp. 10–11.
- Pardo-Moreno et al. 2023, p. 13.
- ^ Pardo-Moreno et al. 2023, p. 10.
- Parmar, Grealish & Henchcliffe 2020, pp. 103.
- Parmar, Grealish & Henchcliffe 2020, pp. 103–104.
- Parmar, Grealish & Henchcliffe 2020, pp. 106.
- Henchcliffe & Parmar 2018, pp. 134.
- Parmar, Grealish & Henchcliffe 2020, pp. 106, 108.
- Schweitzer et al. 2020, p. 1926.
- Parmar, Grealish & Henchcliffe 2020, pp. 105, 109.
- Henchcliffe & Parmar 2018, pp. 132.
- Van Laar et al. 2021, p. S174.
- Hitti et al. 2019, p. 16.
- Hitti et al. 2019, pp. 16–17.
- Van Laar et al. 2021, p. S174, S176.
- Hitti et al. 2019, p. 21.
- Shaheen et al. 2024, pp. 5–6.
Works cited
Books
- Bhattacharyya KB (2017). "Chapter One - Hallmarks of Clinical Aspects of Parkinson's Disease Through Centuries". In Bhatia KP, Chaudhuri KR, Stamelou M (eds.). Parkinson's Disease. International Review of Neurobiology. pp. 1–23.
- Bernat JL, Beresford R (2013). Ethical and Legal Issues in Neurology. Newnes. ISBN 978-0-444-53504-7.
- Cooper G, Eichhorn G, Rodnitzky RL (2008). "Parkinson's disease". In Conn PM (ed.). Neuroscience in medicine. Humana Press. ISBN 978-1-6032-7454-8.
- Dissanayaka NN (8 March 2021). "Chapter 9: Anxiety in Parkinson's Disease". In Byrne GJ, Panchana NA (eds.). Anxiety in Older People: Clinical and Research Perspectives. Cambridge University Press. pp. 139–156. doi:10.1017/9781139087469.009. ISBN 978-1-1088-2636-5. S2CID 87250745.
- Ferri FF (2010). "Chapter P". Ferri's differential diagnosis: a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders (2nd ed.). Elsevier/Mosby. ISBN 978-0-3230-7699-9.
- Lanska DJ (2010). "Chapter 33: The history of movement disorders". Handbook of Clinical Neurology. 3. Vol. 95. History of Neurology. pp. 501–546. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(08)02133-7. ISBN 978-0-444-52009-8. PMID 19892136.
- O'Sullivan SB, Schmitz TJ (2007). "Parkinson's Disease". Physical Rehabilitation (5th ed.). F.A. Davis. ISBN 978-0-8036-1247-1.
- Simon RP, Greenberg D, Aminoff MJ (2017). Lange Clinical Neurology (10th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-1-2598-6172-7.
- Stoker TB, Greenland JC, eds. (December 2018). Parkinson's Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects. Codon Publications. ISBN 978-0-9944-3816-4.
- Dallapiazza RF, De Vloo PD, Fomenko A, Lee DJ, Hamani C, Munhoz RP, et al. (2018). "Chapter 8: Considerations for Patient and Target Selection in Deep Brain Stimulation surgery for Parkinson's disease". In Stoker TB, Greenland JC (eds.). Parkinson's disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects. Codon Publications. doi:10.15586/codonpublications.parkinsonsdisease.2018.ch8. ISBN 978-0-9944-3816-4. PMID 30702838. S2CID 81155324.
- Greenland JC, Barker RA (2018). "Chapter 6: The Differential Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease". In Stoker TB, Greenland JC (eds.). Parkinson's disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects. Codon Publications. pp. 109–128. doi:10.15586/codonpublications.parkinsonsdisease.2018.ch6. ISBN 978-0-9944-3816-4. PMID 30702839. S2CID 80908095.
- Stoker TB, Torsney KM, Barker RA (2018). "Chapter 3: Pathological mechanisms and clinical aspects of GBA1 mutation-associated Parkinson's disease". In Stoker TB, Greenland JC (eds.). Parkinson's Disease: Pathogenesis and clinical aspects. pp. 45–64. doi:10.15586/codonpublications.parkinsonsdisease.2018.ch3. ISBN 978-0-9944-3816-4. PMID 30702840. S2CID 92170834.
- Tolosa E, Jankovic E, eds. (2007). Parkinson's disease and movement disorders. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-7881-7.
- Dickson DV (2007). "Neuropathology of movement disorders". In Tolosa E, Jankovic JJ (eds.). Parkinson's disease and movement disorders. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-7881-7.
- Fung VS, Thompson PD (2007). "Rigidity and spasticity". In Tolosa E, Jankovic E (eds.). Parkinson's disease and movement disorders. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-7881-7.
- Tolosa E, Katzenschlager R (2007). "Pharmacological management of Parkinson's disease". In Tolosa E, Jankovic JJ (eds.). Parkinson's disease and movement disorders. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-7881-7.
- Truong DD, Bhidayasiri R (2016). "50: Parkinson's disease". In Lisak RP, Truong DD, Carroll WM, Bhidayasiri R (eds.). International Neurology. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-1187-7736-7.
- Vertes AC, Beato MR, Sonne J, Khan Suheb MZ (June 2023). "Parkinson-Plus Syndrome". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 36256760. Retrieved 2 May 2024.
- Lorenzl S, Nubling G, Perrar KM, Voltz (August 2013). "Palliative treatment of chronic neurologic disorders". In Bernat JL, Beresford R (eds.). Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 118. pp. 133–139. PMID 24182372.
- The National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions, ed. (2006). "Non-motor features of Parkinson's disease". Parkinson's Disease. London: Royal College of Physicians. pp. 113–133. ISBN 978-1-8601-6283-1. Archived from the original on 24 September 2010.
Journal articles
- Binde CD, Tvete IF, Gåsemyr J, Natvig B, Klemp M (September 2018). "A multiple treatment comparison meta-analysis of monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors for Parkinson's disease". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 84 (9): 1917–1927. doi:10.1111/bcp.13651. PMC 6089809. PMID 29847694.
- Caballol N, Martí MJ, Tolosa E (September 2007). "Cognitive dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson disease". Mov. Disord. 22 (Suppl 17): S358–66. doi:10.1002/mds.21677. PMID 18175397. S2CID 3229727.
- Henchcliffe C, Parmar M (2018). "Repairing the Brain: Cell Replacement Using Stem Cell-Based Technologies". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 8 (s1): S131 – S137. doi:10.3233/JPD-181488. PMC 6311366. PMID 30584166.
- Panicker N, Ge P, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (April 2021). "The cell biology of Parkinson's disease". The Journal of Cell Biology. 220 (4). doi:10.1083/jcb.202012095. PMC 8103423. PMID 33749710.
- Parmar M, Grealish S, Henchcliffe C (February 2020). "The future of stem cell therapies for Parkinson disease". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 21 (2): 103–115. doi:10.1038/s41583-019-0257-7. PMID 31907406.
- Tolosa E, Garrido A, Scholz SW, Poewe W (May 2021). "Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease". The Lancet. Neurology. 20 (5): 385–397. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00030-2. PMC 8185633. PMID 33894193.
- Blauwendraat C, Nalls MA, Singleton AB (February 2020). "The genetic architecture of Parkinson's disease". The Lancet. Neurology. 19 (2): 170–178. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30287-X. PMC 8972299. PMID 31521533.
- Winiker K, Kertscher B (2023). "Behavioural interventions for swallowing in subjects with Parkinson's disease: A mixed methods systematic review". International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders. 58 (4): 1375–1404. doi:10.1111/1460-6984.12865. PMID 36951546.
- Islam MS, Azim F, Saju H, Zargaran A, Shirzad M, Kamal M, et al. (September 2021). "Pesticides and Parkinson's disease: Current and future perspective". Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy. 115: 101966. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2021.101966. PMC 8842749. PMID 33991619.
- Hansen D, Ling H, Lashley T, Holton JL, Warner TT (April 2019). "Review: Clinical, neuropathological and genetic features of Lewy body dementias". Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology. 45 (7): 635–654. doi:10.1111/nan.12554. PMID 30977926.
- Wallace ER, Segerstrom SC, van Horne CG, Schmitt FA, Koehl LM (2022). "Meta-Analysis of Cognition in Parkinson's Disease Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia Progression". Neuropsychology Review. 32 (1): 149–160. doi:10.1007/s11065-021-09502-7. PMID 33860906.
- Dolgacheva LP, Zinchenko VP, Goncharov NV (2022). "Molecular and Cellular Interactions in Pathogenesis of Sporadic Parkinson Disease". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 23 (21): 13043. doi:10.3390/ijms232113043. PMC 9657547. PMID 36361826.
- Leta V, Urso D, Batzu L, Lau YH, Mathew D, Boura I, et al. (2022). "Viruses, parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease: the past, present and future". Journal of Neural Transmission. 129 (9): 1119–1132. doi:10.1007/s00702-022-02536-y. PMC 9422946. PMID 36036863.
- Limphaibool N, Iwanowski P, Holstad MJ, Kobylarek D, Kozubski W (2019). "Infectious Etiologies of Parkinsonism: Pathomechanisms and Clinical Implications". Frontiers in Neurology. 10: 652. doi:10.3389/fneur.2019.00652. PMC 6593078. PMID 31275235.
- Bologna M, Truong D, Jankovic J (2022). "The etiopathogenetic and pathophysiological spectrum of parkinsonism". Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 433: 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2021.120012. PMID 34642022.
- Prajjwal P, Kolanu ND, Reddy YB, Ahmed A, Marsool MD, Santoshi K, et al. (2024). "Association of Parkinson's disease to Parkinson's plus syndromes, Lewy body dementia, and Alzheimer's dementia". Health Science Reports. 7 (4): e2019. doi:10.1002/hsr2.2019. PMC 10982460. PMID 38562616.
- Olfatia N, Shoeibia A, Litvanb I (2019). "Progress in the treatment of Parkinson-Plus syndromes". Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 59: 101–110. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.10.006. PMID 30314846.
- Calabresi P, Mechelli A, Natale G, Volpicelli-Daley L, Di Lazzaro G, Ghiglieri V (2023). "Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies: from overt neurodegeneration back to early synaptic dysfunction". Cell Death & Disease. 14 (3): 176. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-05672-9. PMC 9977911. PMID 36859484.
- Ramesh SD, Arachchige AS (2023). "Depletion of dopamine in Parkinson's disease and relevant therapeutic options: A review of the literature". AIMS Neuroscience. 10 (3): 200–231. doi:10.3934/Neuroscience.2023017. PMC 10567584. PMID 37841347.
- Ascherio A, Schwarzschild MA (2016). "The epidemiology of Parkinson's disease: risk factors and prevention". Lancet Neurology. 15 (12): 1257–1272. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30230-7. PMID 27751556.
- Crotty GF, Schwarzschild MA (2020). "Chasing Protection in Parkinson's Disease: Does Exercise Reduce Risk and Progression?". Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience. 12: 186. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2020.00186. PMC 7318912. PMID 32636740.
- Singh A, Tripathi P, Singh S (2021). "Neuroinflammatory responses in Parkinson's disease: relevance of Ibuprofen in therapeutics". Inflammopharmacology. 29 (1): 5–14. doi:10.1007/s10787-020-00764-w. PMID 33052479.
- Fabbri M, Rascol O, Foltynie T, Carroll C, Postuma RB, Porcher R, et al. (2024). "Advantages and Challenges of Platform Trials for Disease Modifying Therapies in Parkinson's Disease". Movement Disorders. 39 (9): 1468–1477. doi:10.1002/mds.29899. PMID 38925541.
- Kamal H, Tan GC, Ibrahim SF, Shaikh MF, Mohamed IN, Mohamed RM, et al. (2020). "Alcohol Use Disorder, Neurodegeneration, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease: Interplay Between Oxidative Stress, Neuroimmune Response and Excitotoxicity". Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 14: 282. doi:10.3389/fncel.2020.00282. PMC 7488355. PMID 33061892.
- Lin J, Pang D, Li C, Ou R, Yu Y, Cui Y, et al. (2024). "Calcium channel blockers and Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders. 17: 1–8. doi:10.1177/17562864241252713. PMC 11104025. PMID 38770432.
- Grotewolda N, Albina RL (2024). "Update: Protective and risk factors for Parkinson disease". Parkinsonism and Related Disorders. 125: 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2024.107026. PMID 38879999.
- Rose KN, Schwarzschild MS, Gomperts SN (2024). "Clearing the Smoke: What Protects Smokers from Parkinson's Disease?". Movement Disorders. 39 (2): 267–272. doi:10.1002/mds.29707. PMC 10923097. PMID 38226487.
- Ren X, Chen J (2020). "Caffeine and Parkinson's Disease: Multiple Benefits and Emerging Mechanisms". Frontiers in Neuroscience. 14: 1–12. doi:10.3389/fnins.2020.602697. PMC 7773776. PMID 33390888.
- Ben-Shlomo Y, Darweesh S, Llibre-Guerra J, Marras C, Luciano MS, Tanner C (2024). "The epidemiology of Parkinson's disease". The Lancet. 403 (10423): 283–292. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01419-8. PMC 11123577. PMID 38245248.
- Deliz JR, Tanner CM, Gonzalez-Latapi P (2024). "Epidemiology of Parkinson's Disease: An Update". Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 24 (6): 163–179. doi:10.1007/s11910-024-01339-w. PMID 38642225.
- Dorsey ER, Sherer T, Okun MS, Bloem BR (2018). "The Emerging Evidence of the Parkinson Pandemic". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 8 (s1): S3 – S8. doi:10.3233/JPD-181474. PMC 6311367. PMID 30584159.
- Li G, Ma J, Cui S, He Y, Xiao Q, Liu J, et al. (2019). "Parkinson's disease in China: a forty-year growing track of bedside work". Translational Neurodegeneration. 8 (1): 22. doi:10.1186/s40035-019-0162-z. PMC 6668186. PMID 31384434.
- Varden R, Walker R, O'Callaghan A (2024). "No trend to rising rates: A review of Parkinson's prevalence studies in the United Kingdom". Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 128: 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2024.107015. PMID 38876845.
- Zhu J, Cui Y, Zhang J, Yan R, Su D, Zhao D, et al. (2024). "Temporal trends in the prevalence of Parkinson's disease from 1980 to 2023: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The Lancet: Healthy Longetivity. 5: e464 – e479. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2024.107015. PMID 38876845.
- Goetz CG (2011). "The history of Parkinson's disease: early clinical descriptions and neurological therapies". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine. 1 (1): a008862. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a008862. PMC 3234454. PMID 22229124.
- Lees AJ (2007). "Unresolved issues relating to the shaking palsy on the celebration of James Parkinson's 250th birthday". Movement Disorders. 22 (S17): S327 – S334. doi:10.1002/mds.21684. PMID 18175393.
- Louis ED (1997). "The shaking palsy, the first forty-five years: a journey through the British literature". Movement Disorders. 12 (6): 1068–1072. doi:10.1002/mds.870120638. PMID 9399240.
- Lewis PA, Plun-Favreau H, Rowley M, Spillane J (2020). "Pierre D. and the first photographs of Parkinson's disease". Movement Disorders. 35 (3): 389–391. doi:10.1002/mds.27965. PMC 7155099. PMID 31975439.
- Bereczki D (2010). "The description of all four cardinal signs of Parkinson's disease in a Hungarian medical text published in 1690". Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 16 (4): 290–293. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2009.11.006. PMID 19948422.
- Blonder LX (2018). "Historical and cross-cultural perspectives on Parkinson's disease". Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine. 15 (3): 1–15. doi:10.1515/jcim-2016-0065. PMID 29738310.
- Coffey RJ (2009). "Deep brain stimulation devices: a brief technical history and review". Artificial Organs. 33 (3): 208–220. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1594.2008.00620.x. PMID 18684199.
- Sousa-Santos PE, Pozzobon PM, Teixeira IL (2024). "Frederic Lewy: how the two World Wars changed his life, work, and name". Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatri. 82 (3): 001–002. doi:10.1055/s-0044-1779692. PMC 10927365. PMID 38467394.
- Fahn S (2008). "The history of dopamine and levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease". Movement Disorders. 23 (S3): S497 – S508. doi:10.1002/mds.22028. PMID 18781671.
- Schulz-Schaeffer WJ (2010). "The synaptic pathology of alpha-synuclein aggregation in dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia". Acta Neuropathologica. 120 (2): 131–143. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0711-0. PMC 2892607. PMID 20563819.
- Guridi J, Lozano AM (1997). "A brief history of pallidotomy". Neurosurgery. 41 (5): 1169–1180. doi:10.1097/00006123-199711000-00029. PMID 9361073.
- Tolosa E, Garrido A, Scholz SW, Poewe W (May 2021). "Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease". Lancet Neurology. 20 (5): 385–397. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00030-2. PMC 8185633. PMID 33894193.
- Corcoran J, Kluger BM (September 2023). "Prognosis in chronic progressive neurologic disease: a narrative review". Annals of Palliative Medicine. 12 (5): 952–962. doi:10.21037/apm-22-1338. PMID 37691335.
- Fereshtehnejad SM, Zeighami Y, Dagher A, Postuma RB (July 2017). "Clinical criteria for subtyping Parkinson's disease: biomarkers and longitudinal progression". Brain. 140 (7): 1959–1976. doi:10.1093/brain/awx118. PMID 28549077.
- Dommershuijsen LJ, Darweesh SK, Ben-Shlomo Y, Kluger BM, Bloem BR (October 2023). "The elephant in the room: critical reflections on mortality rates among individuals with Parkinson's disease". npj Parkinson's Disease. 9 (1): 145. doi:10.1038/s41531-023-00588-9. PMC 10587193. PMID 37857675.
- Murueta-Goyena A, Muiño O, Gómez-Esteban JC (April 2024). "Prognostic factors for falls in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review". Acta Neurologica Belgica. 124 (2): 395–406. doi:10.1007/s13760-023-02428-2. PMC 10965733. PMID 38015306.
- Murueta-Goyena A, Muiño O, Gómez-Esteban JC (March 2017). "Dementia in Parkinson's disease". Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 374: 26–31. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2017.01.012. PMID 28088312.
- Chua WY, Wang JD, Chan CK, Chan L, Tan E (September 2024). "Risk of aspiration pneumonia and hospital mortality in Parkinson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis". European Journal of Neurology. 31 (12): e16449. doi:10.1111/ene.16449. PMC 11555015. PMID 39236309.
- Won JH, Byun SJ, Oh B, Park SJ, Seo HG (September 2007). "Cognitive dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson disease". Scientific Reports. 22 (S17): S358 – S366. doi:10.1002/mds.21677. PMID 18175397.
- Corcoran J, Kluger BM (2021). "Risk and mortality of aspiration pneumonia in Parkinson's disease: a nationwide database study". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 6597. Bibcode:2021NatSR..11.6597W. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86011-w. PMC 7988066. PMID 33758213.
- Atalar MS, Oguz O, Genc G (2023). "Hypokinetic Dysarthria in Parkinson's Disease: A Narrative Review". The Medical Bulletin of Sisle Etfal Hospital. 57 (2): 163–170. doi:10.14744/SEMB.2023.29560. PMC 10600629. PMID 37899809.
- Huang M, Bargues-Carot A, Riaz Z, Wickham H, Zenitsky G, Jin H, et al. (September 2022). "Impact of Environmental Risk Factors on Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Neuroinflammation, Protein Misfolding, and Oxidative Stress in the Etiopathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 23 (10808): 10808. doi:10.3390/ijms231810808. PMC 9505762. PMID 36142718.
- Luca A, Nicoletti A, Mostile G, Zappia M (2018). "The Parkinsonian Personality: More Than Just a "Trait"". Frontiers in Neurology. 9 (1191): 1191. doi:10.3389/fneur.2018.01191. PMC 6340987. PMID 30697187.
- Rana AQ, Ahmed US, Chaudry ZM, Vasan S (May 2015). "Parkinson's disease: a review of non-motor symptoms". Expert Reviews Neurotherapeutics. 15 (5): 549–462. doi:10.1586/14737175.2015.1038244. PMID 25936847.
- Biundo R, Weis L, Antonini A (September 2016). "Cognitive decline in Parkinson's disease: the complex picture". npj Parkinson's Disease. 2 (16018): 16018. doi:10.1038/npjparkd.2016.18. PMC 5516581. PMID 28725699.
- Gonzalez-Latapi P, Bayram E, Litvan I, Marras C (May 2021). "Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson's Disease: Epidemiology, Clinical Profile, Protective and Risk Factors". Behavioral Sciences. 11 (5): 74. doi:10.3390/bs11050074. PMC 8152515. PMID 34068064.
- Zhu M, Li M, Ye D, Jiang W, Lei T, Shu K (March 2016). "Sensory symptoms in Parkinson's disease: Clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment". Journal of Neuroscience Research. 94 (8): 685–692. doi:10.1002/jnr.23729. PMID 26948282.
- Corrà MF, Vila-Chã N, Sardoeira A, Hansen C, Sousa AP, Reis I, et al. (January 2023). "Peripheral neuropathy in Parkinson's disease: prevalence and functional impact on gait and balance". Brain. 146 (1): 225–236. doi:10.1093/brain/awac026. PMC 9825570. PMID 35088837.
- Weil RS, Schrag AE, Warren JD, Crutch SJ, Lees AJ, Morris HR (July 2016). "Visual dysfunction in Parkinson's disease". Brain. 146 (139): 2827–2843. doi:10.1093/brain/aww175. PMC 5091042. PMID 27412389.
- Pfeiffer RF (October 2020). "Autonomic Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease". Neurotherapeutics. 17 (4): 1464–1479. doi:10.1007/s13311-020-00897-4. PMC 7851208. PMID 32789741.
- Palma JA, Kaufmann H (March 2018). "Treatment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies". Movement Disorders. 33 (3): 372–390. doi:10.1002/mds.27344. PMC 5844369. PMID 29508455.
- Han MN, Finkelstein DI, McQuade RM, Diwakarla S (January 2022). "Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease: Current and Potential Therapeutics". Journal of Personalized Medicine. 12 (2): 144. doi:10.3390/jpm12020144. PMC 8875119. PMID 35207632.
- Aarslanda D, Krambergera MG (2015). "Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease". Journal of Personalized Medicine. 5 (3): 659–667. doi:10.3233/JPD-150604. PMID 26406147.
- Niemann N, Billnitzer A, Jankovic J (January 2021). "Parkinson's disease and skin". Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 82: 61–76. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.11.017. PMID 33248395.
- Almikhlafi MA (January 2024). "A review of the gastrointestinal, olfactory, and skin abnormalities in patients with Parkinson's disease". Neurosciences. 29 (1): 4–9. doi:10.17712/nsj.2024.1.20230062 (inactive 1 November 2024). PMC 10827020. PMID 38195133.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - Stefani A, Högl B (January 2020). "Sleep in Parkinson's disease". Neuropsychopharmacology. 45 (1): 121–128. doi:10.1038/s41386-019-0448-y. PMC 6879568. PMID 31234200.
- Bollu PC, Sahota P (2017). "Sleep and Parkinson Disease". Missouri Medicine. 114 (5): 381–386. PMC 6140184. PMID 30228640.
- Dodet P, Houot M, Leu-Semenescu S, Corvol JC, Lehéricy S, Mangone G, et al. (February 2024). "Sleep disorders in Parkinson's disease, an early and multiple problem". npj Parkinson's Disease. 10 (1): 46. doi:10.1038/s41531-024-00642-0. PMC 10904863. PMID 38424131.
- Moustafa AA, Chakravarthy S, Phillips JR, Gupta A, Keri S, Polner B, et al. (September 2016). "Motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease: A unified framework". Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 68: 727–740. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.07.010. PMID 27422450.
- Mirelman A, Bonato P, Camicioli R, Ellis TD, Giladi N, Hamilton JL, et al. (April 2019). "Gait impairments in Parkinson's disease". Lancet Neurology. 17 (7): 697–708. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30044-4. PMID 30975519.
- Sveinbjornsdottir S (October 2016). "The clinical symptoms of Parkinson's disease". Journal of Neurochemistry. 139 (Suppl 1): 318–324. doi:10.1111/jnc.13691. PMID 27401947.
- Abusrair AH, Elsekaily W, Bohlega S (13 September 2022). "Tremor in Parkinson's Disease: From Pathophysiology to Advanced Therapies". Tremor and Other Hyperkinetic Movements. 12 (1): 29. doi:10.5334/tohm.712. PMC 9504742. PMID 36211804.
- Bologna M, Paparella G, Fasano A, Hallett M, Berardelli A (December 2019). "Evolving concepts on bradykinesia". Brain. 143 (3): 727–750. doi:10.1093/brain/awz344. PMC 8205506. PMID 31834375.
- Ferreira-Sánchez MD, Moreno-Verdú M, Cano-de-la-Cuerda R (February 2020). "Quantitative Measurement of Rigidity in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review". Sensors. 20 (3): 880. Bibcode:2020Senso..20..880F. doi:10.3390/s20030880. PMC 7038663. PMID 32041374.
- Palakurthi B, Burugupally SP (September 2019). "Postural Instability in Parkinson's Disease: A Review". Brain Sciences. 9 (239): 239. doi:10.3390/brainsci9090239. PMC 6770017. PMID 31540441.
- Yang W, Hamilton JL, Kopil C, Beck JC, Tanner CM, Albin RL, et al. (July 2020). "Current and projected future economic burden of Parkinson's disease in the U.S." npj Parkinson's Disease. 6: 15. doi:10.1038/s41531-020-0117-1. PMC 7347582. PMID 32665974.
- Cunha M, Almeida H, Guimarães I, Ferreira LN (July 2020). "Current and projected future economic burden of Parkinson's disease in the U.S.". Journal of Public Health.
- Schiess N, Cataldi R, Okun MS, Fothergill-Misbah N, Dorsey ER, Bloem BR, et al. (September 2022). "Six Action Steps to Address Global Disparities in Parkinson Disease: A World Health Organization Priority" (PDF). JAMA. 79 (9): 929–936. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.1783. hdl:10576/33335. PMID 35816299.
- Prenger MT, Madray R, Van Hedger K, Anello M, MacDonald PA (2020). "Social Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease". Parkinson's Disease. 2020: 8846544. doi:10.1155/2020/8846544. PMC 7790585. PMID 33489081.
- Crooks S, Carter G, Wilson CB, Wynne L, Stark P, Doumas M, et al. (2023). "Exploring public perceptions and awareness of Parkinson's disease: A scoping review". PLOS ONE. 18 (9): e0291357. Bibcode:2023PLoSO..1891357C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0291357. PMC 10503766. PMID 37713383.
- Raudino F (2011). "The Parkinson disease before James Parkinson". History of Neurology. 33: 945–949.
- Gupta R, Kim C, Agarwal N, Lieber B, Monaco EA (2015). "Understanding the Influence of Parkinson Disease on Adolf Hitler's Decision-Making during World War II". World Neurosurgery. 84 (5): 1447–1452. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2015.06.014. PMID 26093359.
- Boettcher L, Bonney P, Smitherman A, Sughrue M (2015). "Hitler's parkinsonism". Neurosurgical Focus. 39 (1): E8. doi:10.3171/2015.4.FOCUS1563. PMID 26126407.
- Brey RL (April 2006). "Muhammad Ali's Message: Keep Moving Forward". Neurology Now. 2 (2): 8. doi:10.1097/01222928-200602020-00003. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 22 August 2020.
- Matthews W (April 2006). "Ali's Fighting Spirit". Neurology Now. 2 (2): 10–23. doi:10.1097/01222928-200602020-00004. S2CID 181104230.
- Dorsey ER, Bloem BR (January 2024). "Parkinson's Disease Is Predominantly an Environmental Disease". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 14 (3): 103–115. doi:10.3233/JPD-230357. PMC 11091623. PMID 38217613.
- Bandres-Ciga S, Diez-Fairen M, Kim JJ, Singleton AB (April 2020). "Genetics of Parkinson's disease: An introspection of its journey towards precision medicine". Neurobiology of Disease. 137: 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104782. PMC 7064061. PMID 31991247.
- Toffoli M, Vieira SR, Schapira AH (June 2020). "Genetic causes of PD: A pathway to disease modification". Neuropharmacology. 170: 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108022. PMID 32119885.
- Dorsey ER, Zafar M, Lettenberger SE, Pawlik ME, Kinel D, Frissen M, et al. (2023). "Trichloroethylene: An Invisible Cause of Parkinson's Disease?". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 13 (2): 203–218. doi:10.3233/JPD-225047. PMC 10041423. PMID 36938742.
- Chen C, Turnbull DM, Reeve AK (May 2019). "Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease—Cause or Consequence?". Biology. 8 (2): 38. doi:10.3390/biology8020038. PMC 6627981. PMID 31083583.
- Morris HR, Spillantini MG, Sue CM, Williams-Gray CH (January 2024). "The pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease". Lancet. 403 (10423): 293–304. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(23)01478-2. PMID 38245249.
- Gogna T, Housden BE, Houldsworth A (September 2024). "Exploring the Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease and the Efficacy of Antioxidant Treatment". Antioxidants. 13 (1138): 1138. doi:10.3390/antiox13091138. PMC 11429442. PMID 39334797.
- Brundin P, Melki R (October 2017). "Prying into the Prion Hypothesis for Parkinson's Disease". Journal of Neuroscience. 37 (41): 9808–9818. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1788-16.2017. PMC 5637113. PMID 29021298.
- Salles PA, Tirapegui JM, Chaná-Cuevas P (22 March 2024). "Genetics of Parkinson's disease: Dominant forms and GBA". Neurology Perspectives. 4 (3): 100153. doi:10.1016/j.neurop.2024.100153.
- Farrow SL, Gokuladhas S, Schierding W, Pudjihartono M, Perry JK, Cooper AA, et al. (October 2024). "Identification of 27 allele-specific regulatory variants in Parkinson's disease using a massively parallel reporter assay". npj Parkinson's Disease. 10 (1): 44. doi:10.1038/s41531-024-00659-5. PMC 10899198. PMID 38413607.
- Smith L, Schapira AH (April 2022). "GBA Variants and Parkinson Disease: Mechanisms and Treatments". Cells. 11 (8): 1261. doi:10.3390/cells11081261. PMC 9029385. PMID 35455941.
- Goldstein DS (February 2020). "The catecholaldehyde hypothesis: where MAO fits in". Journal of Neural Transmission. 127 (2): 169–177. doi:10.1007/s00702-019-02106-9. PMC 10680281. PMID 31807952.
- Goldstein DS (June 2021). "The Catecholaldehyde Hypothesis for the Pathogenesis of Catecholaminergic Neurodegeneration: What We Know and What We Do Not Know". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22 (11): 5999. doi:10.3390/ijms22115999. PMC 8199574. PMID 34206133.
- Santos-Lobato BL (April 2024). "Towards a methodological uniformization of environmental risk studies in Parkinson's disease". npj Parkinson's Disease. 10 (1): 86. doi:10.1038/s41531-024-00709-y. PMC 11024193. PMID 38632283.
- De Mirandaa BR, Goldmanb SM, Millerc GW, Greenamyred JT, Dorseye ER (April 2024). "Preventing Parkinson's Disease: An Environmental Agenda". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 12 (1): 45–68. doi:10.3233/JPD-212922. PMC 8842749. PMID 34719434.
- Langston JW (March 2017). "The MPTP Story". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 7 (1): S11 – S19. doi:10.3233/JPD-179006. PMC 5345642. PMID 28282815.
- Dorsey ER, De Mirandab BR, Horsager J, Borghammer P (April 2024). "The Body, the Brain, the Environment, and Parkinson's Disease". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 14 (3): 363–381. doi:10.3233/JPD-240019. PMC 11091648. PMID 38607765.
- Bloem BR, Boonstra TA (December 2023). "The inadequacy of current pesticide regulations for protecting brain health: the case of glyphosate and Parkinson's disease". The Lancet. Planetary Health. 7 (12): e948 – e949. doi:10.1016/s2542-5196(23)00255-3. PMID 37949088.
- Delic V, Beck KD, Pang KC, Citron BA (April 2020). "Biological links between traumatic brain injury and Parkinson's disease". Acta Neuropathologica Communications. 8 (1): 45. doi:10.1186/s40478-020-00924-7. PMC 7137235. PMID 32264976.
- Coleman C, Martin I (16 December 2022). "Unraveling Parkinson's Disease Neurodegeneration: Does Aging Hold the Clues?". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 12 (8): 2321–2338. doi:10.3233/JPD-223363. PMC 9837701. PMID 36278358.
- Wu S, Schekman RW (September 2024). "Intercellular transmission of alpha-synuclein". Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. 17: 1–12. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2024.1470171. PMC 11422390. PMID 39324117.
- Ho H, Wing SS (November 2024). "α-Synuclein ubiquitination – functions in proteostasis and development of Lewy bodies". Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. 17: 1–19. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2024.1498459. PMC 11588729. PMID 39600913.
- Rietdijk CD, Perez-Pardo P, Garssen J, van Wezel RJ, Kraneveld AD (February 2017). "Exploring Braak's Hypothesis of Parkinson's Disease". Frontiers in Neurology. 8: 37. doi:10.3389/fneur.2017.00037. PMC 5304413. PMID 28243222.
- Borsche M, Pereira SL, Klein C, Grünewald A (February 2021). "Mitochondria and Parkinson's Disease: Clinical, Molecular, and Translational Aspects". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 11 (1): 45–60. doi:10.3233/JPD-201981. PMC 7990451. PMID 33074190.
- Tan E, Chao Y, West A, Chan L, Poewe W, Jankovic J (April 2020). "Parkinson disease and the immune system - associations, mechanisms and therapeutics". Nature Reviews Neurology. 16 (6): 303–318. doi:10.1038/s41582-020-0344-4. PMID 32332985.
- Kobylecki C (July 2020). "Update on the diagnosis and management of Parkinson's disease". Clinical Medicine. 20 (4): 393–398. doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0220. PMC 7385761. PMID 32675145.
- de Bie RM, Clarke CE, Espay AJ, Fox SH, Lang AE (March 2020). "Initiation of pharmacological therapy in Parkinson's disease: when, why, and how". Lancet Neurology. 19 (5): 452–461. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30036-3. PMID 32171387.
- Ferrell B, Connor SR, Cordes A, Dahlin CM, Fine PG, Hutton N, et al. (June 2007). "The national agenda for quality palliative care: the National Consensus Project and the National Quality Forum". Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 33 (6): 737–744. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.02.024. PMID 17531914.
- Lorenzl S, Nübling G, Perrar KM, Voltz R (2013). "Palliative treatment of chronic neurologic disorders". Ethical and Legal Issues in Neurology. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 118. Elsevier. pp. 133–139. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-53501-6.00010-X. ISBN 978-0-4445-3501-6. PMID 24182372.
- Ghoche R (December 2012). "The conceptual framework of palliative care applied to advanced Parkinson's disease". Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 18 (Suppl 3): S2 – S5. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.06.012. PMID 22771241.
- Wilcox SK (January 2010). "Extending palliative care to patients with Parkinson's disease". British Journal of Hospital Medicine. 71 (1): 26–30. doi:10.12968/hmed.2010.71.1.45969. PMID 20081638.
- Moens K, Higginson IJ, Harding R (October 2014). "Are there differences in the prevalence of palliative care-related problems in people living with advanced cancer and eight non-cancer conditions? A systematic review". Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 48 (4): 660–677. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2013.11.009. PMID 24801658.
- Casey G (August 2013). "Parkinson's disease: a long and difficult journey". Nursing New Zealand. 19 (7): 20–24. PMID 24195263.
- Lister T (May 2020). "Nutrition and Lifestyle Interventions for Managing Parkinson's Disease: A Narrative Review". Journal of Movement Disorders. 13 (2): 97–104. doi:10.14802/jmd.20006. PMC 7280935. PMID 32498495.
- Barichella M, Cereda E, Pezzoli G (October 2009). "Major nutritional issues in the management of Parkinson's disease". Movement Disorders. 24 (13): 1881–1892. doi:10.1002/mds.22705. hdl:2434/67795. PMID 19691125.
- Pasricha TS, Guerrero-Lopez IL, Kuo B (March 2024). "Management of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease: A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Presentation, Workup, and Treatment". Movement Disorders. 58 (3): 211–220. PMID 38260966.
- McDonnell MN, Rischbieth B, Schammer TT, Seaforth C, Shaw AJ, Phillips AC (May 2018). "Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT)-BIG to improve motor function in people with Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Clinical Rehabilitation. 32 (5): 607–618. doi:10.1177/0269215517734385. PMID 28980476.
- Pu T, Huang M, Kong X, Wang M, Chen X, Feng X, et al. (December 2021). "Lee Silverman Voice Treatment to Improve Speech in Parkinson's Disease: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis". Parkinson's Disease. 2021: 1–10. doi:10.1155/2021/3366870. PMC 8782619. PMID 35070257.
- Tofani M, Ranieri A, Fabbrini G, Berardi A, Pelosin E, Valente D, et al. (October 2020). "Efficacy of Occupational Therapy Interventions on Quality of Life in Patients with Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Movement Disorders. 7 (8): 891–901. doi:10.1002/mdc3.13089. PMC 7604677. PMID 33163559.
- Ernst M, Folkerts AK, Gollan R, Lieker E, Caro-Valenzuela J, Adams A, et al. (1 January 2023). "Physical exercise for people with Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2024 (4): CD013856. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013856.pub3. PMC 9815433. PMID 38588457.
- Ahlskog JE (July 2011). "Does vigorous exercise have a neuroprotective effect in Parkinson disease?". Neurology. 77 (3): 288–294. doi:10.1212/wnl.0b013e318225ab66. PMC 3136051. PMID 21768599.
- Costa V, Prati JM, de Oliveira BS, Brito TS, da Rocha F, Gianlorenço T, et al. (November 2024). "Physical Exercise for Treating the Anxiety and Depression Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology. 37 (6): 415–435. doi:10.1177/08919887241237223. ISSN 0891-9887. PMID 38445606.
- Ramazzina I, Bernazzoli B, Costantino C (March 2017). "Systematic review on strength training in Parkinson's disease: an unsolved question". Clinical Interventions in Aging. 12: 619–628. doi:10.2147/CIA.S131903. PMC 5384725. PMID 28408811.
- Limousin P, Foltynie T (April 2019). "Long-term outcomes of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease". Nature Reviews Neurology. 14 (4): 234–242. doi:10.1038/s41582-019-0145-9. PMID 30778210.
- Bronstein JM, Tagliati M, Alterman RL, Lozano AM, Volkmann J, Stefani A, et al. (February 2011). "Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: an expert consensus and review of key issues". Archives of Neurology. 68 (2): 165. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2010.260. PMC 4523130. PMID 20937936.
- Lozano CS, Tam J, Lozano AM (January 2018). "The changing landscape of surgery for Parkinson's Disease". Movement Disorders. 33 (1): 36–47. doi:10.1002/mds.27228. PMID 29194808.
- Connolly BS, Lang AE (April 2014). "Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: a review". JAMA. 311 (16): 1670–1683. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3654. PMID 24756517. S2CID 205058847.
- Moosa S, Martínez-Fernández R, Elias WJ, Del Alamo M, Eisenberg HM, Fishman PS (September 2019). "The role of high-intensity focused ultrasound as a symptomatic treatment for Parkinson's disease". Movement Disorders. 34 (9): 1243–1251. doi:10.1002/mds.27779. PMID 31291491.
- Tambasco N, Romoli M, Calabresi P (October 2018). "Levodopa in Parkinson's Disease: Current Status and Future Developments". Current Neuropharmacology. 16 (8): 1239–1252. doi:10.2174/1570159X15666170510143821. PMC 6187751. PMID 28494719.
- LeWitt PA, Fahn S (April 2016). "Levodopa therapy for Parkinson disease: A look backward and forward". Neurology. 86 (14): S3 – S12. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000002509. PMID 28494719.
- Leta V, Klingelhoefer L, Longardner K, Campagnolo M, Levent HÇ, Aureli F, et al. (May 2023). "Gastrointestinal barriers to levodopa transport and absorption in Parkinson's disease". European Journal of Neurology. 30 (5): 1465–1480. doi:10.1111/ene.15734. PMID 36757008.
- Oertel WH (13 March 2017). "Recent advances in treating Parkinson's disease". F1000Research. 6: 260. doi:10.12688/f1000research.10100.1. PMC 5357034. PMID 28357055.
- Horowski R, Löschmann PA (February 2019). "Classical dopamine agonists". Journal of Neural Transmission. 126 (4): 449–454. doi:10.1007/s00702-019-01989-y. PMID 30805732.
- Jing X, Yang H, Taximaimaiti R, Wang X (2023). "Advances in the Therapeutic Use of Non-Ergot Dopamine Agonists in the Treatment of Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease". Current Neuropharmacology. 21 (5): 1224–1240. doi:10.2174/1570159X20666220915091022. PMC 10286583. PMID 36111769.
- Tan Y, Jenner P, Chen S (2022). "Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease: Past, Present, and Future". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 12 (2): 477–493. doi:10.3233/JPD-212976. PMC 8925102. PMID 34957948.
- Robakis D, Fahn S (June 2015). "Defining the Role of the Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for Parkinson's Disease". CNS Drugs. 29 (6): 433–441. doi:10.1007/s40263-015-0249-8. PMID 26164425.
- Alborghetti M, Nicoletti F (2019). "Different Generations of Type-B Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Parkinson's Disease: From Bench to Bedside". Current Neuropharmacology. 17 (9): 861–873. doi:10.2174/1570159X16666180830100754. PMC 7052841. PMID 30160213.
- Armstrong MJ, Okun MS (February 2020). "Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review". JAMA. 323 (6): 548–560. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.22360. PMID 32044947. S2CID 211079287.
- Rissardo JP, Durante I, Sharon I, Caprara AL (September 2022). "Pimavanserin and Parkinson's Disease Psychosis: A Narrative Review". Brain Sciences. 23 (12): 1–11. PMID 36291220.
- Elbers RG, Verhoef J, van Wegen EE, Berendse HW, Kwakkel G (October 2015). "Interventions for fatigue in Parkinson's disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (Review). 2015 (10): CD010925. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010925.pub2. PMC 9240814. PMID 26447539.
- Seppi K, Ray Chaudhuri K, Coelho M, Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, Perez Lloret S, et al. (February 2019). "Update on treatments for nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson's disease—an evidence-based medicine review". Movement Disorders. 34 (2): 180–198. doi:10.1002/mds.27602. PMC 6916382. PMID 30653247.
- Gouda NA, Elkamhawy A, Cho J (February 2022). "Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Parkinson's Disease and Future Prospects: A 2021 Update". Biomedicines. 10 (2): 371. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10020371. PMC 8962417. PMID 35203580.
- Jasutkar HG, Oh SE, Mouradian MM (January 2022). "Therapeutics in the Pipeline Targeting α-Synuclein for Parkinson's Disease". Pharmacological Reviews. 74 (1): 207–237. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.120.000133. PMC 11034868. PMID 35017177.
- Pardo-Moreno T, García-Morales V, Suleiman-Martos S, Rivas-Domínguez A, Mohamed-Mohamed H, Ramos-Rodríguez JJ, et al. (February 2023). "Current Treatments and New, Tentative Therapies for Parkinson's Disease". Pharmaceutics. 15 (3): 770. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15030770. hdl:10481/81647. PMID 36986631.
- Shaheen N, Shaheen A, Osama M, Nashwan AJ, Bharmauria V, Flouty O (October 2024). "MicroRNAs regulation in Parkinson's disease, and their potential role as diagnostic and therapeutic targets". npj Parkinson's Disease Volume. 10 (3): 1–11. PMID 39369002.
- Van Laar AD, Van Laar VS, San Sebastian W, Merola A, Elder JB, Lonser RR, et al. (2021). "An Update on Gene Therapy Approaches for Parkinson's Disease: Restoration of Dopaminergic Function". Journal of Parkinson's Disease. 11 (S2): S173 – S182. doi:10.3233/JPD-212724. PMC 8543243. PMID 34366374.
- Schweitzer JS, Song B, Herrington TM, Park TY, Lee N, Ko S, et al. (May 2020). "Personalized iPSC-Derived Dopamine Progenitor Cells for Parkinson's Disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (20): 1926–1932. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915872. PMC 7288982. PMID 32402162.
- Alfaidi M, Barker RA, Kuan W (December 2024). "An update on immune-based alpha-synuclein trials in Parkinson's disease". Journal of Neurology. 272 (1): 1–9. PMID 39666171.
- Poewe W, Seppi K, Tanner CM, Halliday GM, Brundin P, Volkmann J, et al. (March 2017). "Parkinson disease". Nature Reviews. Disease Primers. 3 (1): 17013. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.13. PMID 28332488. S2CID 11605091.
- Li T, Le W (February 2020). "Biomarkers for Parkinson's Disease: How Good Are They?". Neuroscience Bulletin. 36 (2): 183–194. doi:10.1007/s12264-019-00433-1. PMC 6977795. PMID 31646434.
- Heinzel S, Berg D, Gasser T, Chen H, Yao C, Postuma RB (October 2019). "Update of the MDS research criteria for prodromal Parkinson's disease". Movement Disorders. 34 (10): 1464–1470. doi:10.1002/mds.27802. PMID 31412427. S2CID 199663713.
- Hitti FL, Yang AI, Gonzalez-Alegre P, Baltuch GH (September 2019). "Human gene therapy approaches for the treatment of Parkinson's disease: An overview of current and completed clinical trials". Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 66: 16–24. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2019.07.018. PMID 31324556. S2CID 198132349.
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, et al. (27 June 1997). "Mutation in the α-Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson's Disease". Science. 276 (5321): 2045–2047. doi:10.1126/science.276.5321.2045. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 9197268.
- Zaman V, Shields DC, Shams R, Drasites KP, Matzelle D, Haque A, et al. (June 2021). "Cellular and molecular pathophysiology in the progression of Parkinson's disease". Metabolic Brain Disease. 36 (5): 815–827. doi:10.1007/s11011-021-00689-5. PMC 8170715. PMID 33599945.
- Vázquez-Vélez GE, Zoghbi HY (July 2021). "Parkinson's Disease Genetics and Pathophysiology". Annual Review of Neuroscience. 44: 87–108. doi:10.1146/annurev-neuro-100720-034518. PMID 34236893.
- Warnecke T, Schäfer KH, Claus I, Del Tredici K, Jost WH (March 2022). "Gastrointestinal involvement in Parkinson's disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management". npj Parkinson's Disease. 8: 1–13. doi:10.1038/s41531-022-00295-x. PMC 8948218. PMID 35332158.
- Miller KM, Mercado NM, Sortwell CE (April 2021). "Synucleinopathy-associated pathogenesis in Parkinson's disease and the potential for brain-derived neurotrophic factor". npj Parkinson's Disease. 7 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1038/s41531-021-00179-6. PMC 8041900. PMID 33846345.
- Borghammer P (January 2018). "How does parkinson's disease begin? Perspectives on neuroanatomical pathways, prions, and histology". Movement Disorders. 33 (1): 48–57. doi:10.1002/mds.27138. PMID 28843014.
- Zhang X, Gao F, Wang D, Li C, Fu Y, He W, et al. (October 2018). "Tau Pathology in Parkinson's Disease". Frontiers in Neurology. 9: 1–7. doi:10.3389/fneur.2018.00809. PMC 6176019. PMID 30333786.
- Henderson MX, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (September 2019). "α-Synuclein pathology in Parkinson's disease and related α-synucleinopathies". Neuroscience Letters. 709: 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134316. PMC 7014913. PMID 31170426.
- Ye H, Robak LA, Yu M, Cykowski M, Shulman JM (January 2023). "Genetics and Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Syndrome". Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease. 18: 95–121. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-031521-034145. PMC 10290758. PMID 36100231.
- Dickson DW (January 2018). "Neuropathology of Parkinson disease". Parkinsonism and Related Disorders. 46 (S1): S30 – S33. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.07.033. PMC 5718208. PMID 28780180.
- Chen R, Gu X, Wang X (April 2022). "α-Synuclein in Parkinson's disease and advances in detection". Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry. 529: 76–86. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2022.02.006. PMID 35176268.
- Menšíková K, Matěj R, Colosimo C, Rosales R, Tučková L, Ehrmann J, et al. (January 2022). "Lewy body disease or diseases with Lewy bodies?". npj Parkinson's Disease. 8 (1): 1-11. PMID 35013341.
- Koh J, Ito H (January 2017). "Differential diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders". Nihon Rinsho. Japanese Journal of Clinical Medicine. 75 (1): 56–62. PMID 30566295.
- Ou Z, Pan J, Tang S, Duan D, Yu D, Nong H, et al. (7 December 2021). "Global Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived With Disability of Parkinson's Disease in 204 Countries/Territories From 1990 to 2019". Frontiers in Public Health. 9: 776847. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.776847. PMC 8688697. PMID 34950630.
- Tolosa E, Garrido A, Scholz SW, Poewe W (May 2022). "Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease". Lancet Neurology. 20 (5): 385–397. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00030-2. PMC 8185633. PMID 33894193.
- Heim B, Krismer F, De Marzi R, Seppi K (August 2017). "Magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease". Journal of Neural Transmission. 124 (8): 915–964. doi:10.1007/s00702-017-1717-8. PMC 5514207. PMID 28378231.
- Ugrumov M (June 2020). "Development of early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease: Illusion or reality?". CNS Neuroscience and Therapeutics. 26 (10): 997–1009. doi:10.1111/cns.13429. PMC 7539842. PMID 32597012.
- Rizzo G, Copetti M, Arcuti S, Martino D, Fontana A, Logroscino G (February 2016). "Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Neurology. 86 (6): 566–576. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000002350. PMID 26764028.
- Bidesi NS, Andersen IV, Windhorst AD, Shalgunov V, Herth MM (November 2021). "The role of neuroimaging in Parkinson's disease". Journal of Neurochemistry. 159 (4): 660–689. doi:10.1111/jnc.15516. PMC 9291628. PMID 34532856.
- Brooks DJ (April 2010). "Imaging approaches to Parkinson disease". Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 51 (4): 596–609. doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.059998. PMID 20351351.
- Suwijn SR, van Boheemen CJ, de Haan RJ, Tissingh G, Booij J, de Bie RM (2015). "The diagnostic accuracy of dopamine transporter SPECT imaging to detect nigrostriatal cell loss in patients with Parkinson's disease or clinically uncertain parkinsonism: a systematic review". EJNMMI Research. 5: 12. doi:10.1186/s13550-015-0087-1. PMC 4385258. PMID 25853018.
- Caproni S, Colosimo C (February 2020). "Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Parkinson Disease". Clinical Geriatric Medicine. 36: 13–24. doi:10.1016/j.cger.2019.09.014. PMID 31733693.
- Lieberman A (April 1996). "Adolf Hitler had post-encephalitic Parkinsonism". Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 2 (2): 95–103. PMID 18591024.
Web sources
- "About EPDA". European Parkinson's Disease Association. 2010. Archived from the original on 15 August 2010. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- "About PDF". Parkinson's Disease Foundation. Archived from the original on 15 May 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2016.
- "American Parkinson Disease Association: Home". American Parkinson Disease Association. Archived from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- Macur J (26 March 2008). "For the Phinney Family, a Dream and a Challenge". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 6 November 2014. Retrieved 25 May 2013.
About 1.5 million Americans have received a diagnosis of Parkinson's disease, but only 5 to 10 percent learn of it before age 40, according to the National Parkinson Foundation. Davis Phinney was among the few.
- "Michael's Story". The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- "National Parkinson Foundation – Mission". Archived from the original on 21 December 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2011.
- "Notable Figures with Parkinson's". Parkinson's Foundation. Retrieved 22 November 2023.
- "Parkinson's Disease". National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- "Parkinson's – 'the shaking palsy'". GlaxoSmithKline. 1 April 2009. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011.
- "Symptoms of PD". Stanford Parkinson's Community Outreach. Stanford University School Medicine. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- "Who We Are". Davis Phinney Foundation. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 18 January 2012.
News publications
- Burleson N, Breen K (9 November 2023). "Michael J. Fox talks funding breakthrough research for Parkinson's disease". CBS News. Retrieved 23 November 2023.
- Glass A (9 September 2016). "Mao Zedong dies in Beijing at age 82, Sept. 9, 1976". Politico. Retrieved 30 October 2023.
- Tauber P (17 July 1988). "Ali: Still Magic". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 17 November 2016. Retrieved 2 April 2011.
- McCrum R (20 November 2017). "The 100 best nonfiction books: No 94 – Leviathan by Thomas Hobbes (1651)". The Guardian. Retrieved 23 November 2023.
- Kinsley M (21 April 2014). "Have You Lost Your Mind?". The New Yorker. Retrieved 23 November 2023.
- "Education: Joy in Giving". Time. 18 January 1960. Archived from the original on 20 February 2011. Retrieved 2 April 2011.
- Davis P (3 May 2007). "Michael J. Fox". The Time 100. New York: Time. Archived from the original on 25 April 2011. Retrieved 2 April 2011.
- Brockes E (11 April 2009). "'It's the gift that keeps on taking'". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 8 October 2013. Retrieved 25 October 2010.
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
| Antiparkinson agents (N04) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dopaminergics |
| ||||||||||
| Anticholinergics | |||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Diseases of the nervous system, primarily CNS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brain/ encephalopathy |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Both/either |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mental disorders (Classification) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||



