| Revision as of 13:57, 12 June 2013 editShelfSkewed (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers292,462 editsm Disambiguate Archangelos to Archangelos, Rhodes← Previous edit | Revision as of 05:52, 17 July 2013 edit undoRjensen (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, File movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers227,279 edits →Sources: add citeNext edit → | ||
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
| ==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
| * Carabott, P.J. "The Temporary Italian Occupation of the Dodecanese: A Prelude to Permanency," ''Diplomacy and Statecraft," (1993) 4#2 pp 285-312. | |||
| ⚫ | * Calace, Francesca (a cura di), ''«Restituiamo la Storia» – dagli archivi ai territori. Architetture e modelli urbani nel Mediterraneo orientale.'' Gangemi, Roma, 2012 (collana PRIN 2006 «Restituiamo la Storia») | ||
| * Doumanis, Nicholas. "Italians as Good Colonizers": Speaking Subalterns and the Politics of Memory in the Dodecanese," in Ruth Ben-Ghiat and Mia Fuller, ed.s, ''Italian Colonialism''. New York: Palgarve Macmillian. 2005. ISBN 0-312-23649-2. | * Doumanis, Nicholas. "Italians as Good Colonizers": Speaking Subalterns and the Politics of Memory in the Dodecanese," in Ruth Ben-Ghiat and Mia Fuller, ed.s, ''Italian Colonialism''. New York: Palgarve Macmillian. 2005. ISBN 0-312-23649-2. | ||
| ==In Italian== | |||
| ⚫ | * Calace, Francesca (a cura di), ''«Restituiamo la Storia» – dagli archivi ai territori. Architetture e modelli urbani nel Mediterraneo orientale.'' Gangemi, Roma, 2012 (collana PRIN 2006 «Restituiamo la Storia») | ||
| * Tuccimei, Ercole. ''La Banca d'Italia in Africa'', Foreword by Arnaldo Mauri, Laterza, Bari, 1999. | * Tuccimei, Ercole. ''La Banca d'Italia in Africa'', Foreword by Arnaldo Mauri, Laterza, Bari, 1999. | ||
| *Pignataro, Luca. Le Isole Italiane dell'Egeo dall'8 settembre 1943 al termine della seconda guerra mondiale in "Clio. Rivista internazionale di studi storici", 3(2001). | *Pignataro, Luca. Le Isole Italiane dell'Egeo dall'8 settembre 1943 al termine della seconda guerra mondiale in "Clio. Rivista internazionale di studi storici", 3(2001). | ||
Revision as of 05:52, 17 July 2013
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Dodecanese" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
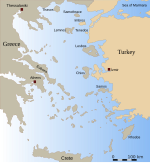
Template:Infobox Pref GR The Dodecanese (/doʊdɪkəˈniːz/; Template:Lang-el, Dodekánisa, [ðoðeˈkanisa]; literally 'twelve islands') are a group of 12 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the Aegean Sea, of which 26 are inhabited. Τhis island group generally defines the eastern limit of the Sea of Crete. They belong to the Southern Sporades island group. They have a rich history, and many of even the smallest inhabited islands boast dozens of Byzantine churches and medieval castles.
The most historically important and well-known is Rhodes (Rodos), which, for millennia, has been the island from which the region is controlled. Of the others, Kos and Patmos are historically more important; the remaining nine are Astipalea, Kalimnos, Karpathos, Kasos, Leros, Nisyros, Symi, Tilos and Kastellorizo. Other islands in the chain include Agathonisi, Alimia, Arkoi, Chalki, Farmakonisi, Gyali, Kinaros, Levitha, Lipsi, Nimos, Pserimos, Saria, Syrna and Telendos.
History
Pre-history and the Archaic Period
The Dodecanese have been inhabited since prehistoric times. In the Neopalatial period on Crete, the islands were heavily Minoanized (contact beginning in the second millennium BC). Following the downfall of the Minoans, the islands were ruled by the Mycenaean Greeks from circa 1400 BC, until the arrival of the Dorians circa 1100 BC. It is in the Dorian period that they began to prosper as an independent entity, developing a thriving economy and culture through the following centuries. By the early Archaic Period Rhodes and Kos emerged as the major islands in the group, and in the 6th century BC the Dorians founded three major cities on Rhodes (Lindos, Kameiros and Ialyssos). Together with the island of Kos and the cities of Knidos and Halicarnassos on the mainland of Asia Minor, these made up the Dorian Hexapolis.
Classical Period
This development was interrupted around 499 BC by the Persian Wars, during which the islands were captured by the Persians for a brief period. Following the defeat of the Persians by the Athenians in 478 BC, the cities joined the Athenian-dominated Delian League. When the Peloponnesian War broke out in 431 BC, they remained largely neutral although they were still members of the League.
By the time the Peloponnesian War ended in 404 BC, the Dodecanese were mostly removed from the larger Aegean conflicts, and had begun a period of relative quiet and prosperity. In 408 BC, the three cities of Rhodes had united to form one state, which built a new capital on the northern end of the island, also named Rhodes; this united Rhodes was to dominate the region for the coming millennia. Other islands in the Dodecanese also developed into significant economic and cultural centers; most notably, Kos served as the site of the school of medicine founded by Hippocrates.
However, the Peloponnesian War had so weakened the entire Greek civilization's military strength that it lay open to invasion. In 357 BC, the islands were conquered by the king Mausolus of Caria, then in 340 BC by the Persians. But this second period of Persian rule proved to be nearly as short as the first, and the islands became part of the rapidly growing Macedonian Empire as Alexander the Great swept through and defeated the Persians in 332 BC, to the great relief of the islands' inhabitants.
Following the death of Alexander, the islands, and even Rhodes itself, were split up among the many generals who contended to succeed him. The islands formed strong commercial ties with the Ptolemies in Egypt, and together they formed the Rhodo-Egyptian alliance which controlled trade throughout the Aegean in the 3rd century BC. Led by Rhodes, the islands developed into maritime, commercial and cultural centers: coins of Rhodes circulated almost everywhere in the Mediterranean, and the islands' schools of philosophy, literature and rhetoric were famous. The Colossus of Rhodes, built in 304 BC, perhaps best symbolized their wealth and power.
In 164 BC, Rhodes signed a treaty with Rome, and the islands became aligned to greater or lesser extent with the Roman Empire while mostly maintaining their autonomy. Rhodes quickly became a major schooling center for Roman noble families, and, as the islands (and particularly Rhodes) were important allies of Rome, they enjoyed numerous privileges and generally friendly relations. These were eventually lost in 42 BC, in the turmoil following the assassination of Julius Caesar in 44 BC, after which Cassius invaded and sacked the islands. Thereafter, they became part of the Roman Empire proper. Titus made Rhodes capital of the Provincia Insularum, and eventually the islands were joined with Crete as part of the 18th Province of the Roman Empire.

In the 1st century, Saint Paul visited the islands twice, and Saint John visited numerous times; they succeeded in converting the islands to Christianity, placing them among the first dominantly Christian regions. Saint John eventually came to reside among them, being exiled to Patmos, where he wrote his famous Revelation.
Middle Ages
Main article: Cibyrrhaeot ThemeAs the Roman Empire split in 395 AD into Eastern and Western halves, the islands became part of the Eastern part, which later evolved into the Byzantine Empire. They would remain there for nearly a thousand years, though these were punctuated by numerous invasions. It was during this period that they began to re-emerge as an independent entity, and the term Dodecanese itself dates to around the 8th century. Copious evidence of the Byzantine period remains on the islands today, most notably in hundreds of churches from the period which can be seen in various states of preservation.
In the 13th century, with the Fourth Crusade, Italians began invading portions of the Dodecanese, which had remained under the nominal power of the Empire of Nicea; Venetians (Querini, Cornaro) and Genoese families (Vignoli) each held some islands for brief periods, while Basilian monks ruled on Patmos and Leros. Finally, in the 14th century, the Byzantine era came to an end when the islands were taken by forces of the Knights Hospitaller (Knights of St. John): Rhodes was conquered in 1309, and the rest of the islands fell gradually over the next few decades. The Knights made Rhodes their stronghold, transforming its capital into a grandiose medieval city dominated by an impressive fortress, and scattered fortresses and citadels through the rest of the islands as well.
These massive fortifications proved sufficient to repel invasions by the Sultan of Egypt in 1444 and Mehmed II in 1480. Finally, however, the citadel at Rhodes fell to the large army of Suleiman the Magnificent in 1522, and the other islands were overrun within the year. The few remaining Knights fled to Malta.
Ottoman rule

Thus began a period of several hundred years in the Ottoman Empire. The Dodecanese formed a separate province within the Eyalet of the Archipelago. The population was allowed to retain a number of privileges provided it submitted to Ottoman rule. By Suleiman's edict, they paid a special tax in return for a special autonomous status that prohibited Ottoman generals from interfering in their civil affairs or mistreating the population. These guarantees, combined with a strategic location at the crossroads of Mediterranean shipping, allowed the islands to prosper. The overwhelmingly Greek population (only Rhodes and Kos had Turkish communities) leaned heavily towards Greece following its declaration of independence in 1822, and many of the islanders joined the Greek War of Independence, with the result that the northern portion of the Dodecanese (including Samos) became briefly the Greek provinces of the Eastern Sporades and Southern Sporades. Kasos in particular played a prominent role due to its skilled mariners, until its destruction by the Egyptians in 1824. Most of the islands were slated to become part of the new Greek state in the London Protocol of 1828, but when Greek independence was recognized in the London Protocol of 1830, the islands were left outside the new Kingdom of Greece. Indeed, the 19th century turned out to be one of the islands' most prosperous, and a number of mansions date from this era.
Italian rule
Further information: Italian colonists in the DodecaneseAfter the outbreak of the Italian-Turkish war over nearby Libya, the islands finally declared independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1912, proclaiming an independent state as the Federation of the Dodecanese Islands. This nascent state was quashed almost immediately by the invasion of Italy, which wanted the islands, and particularly the fortress of Rhodes, to control communication between Turkey and Libya. The Italians occupied all the Dodecanese except for Kastellorizo, which was later temporarily seized by France.
After the end of the war, according to the First Treaty of Lausanne, Italy maintained the occupation of the islands as guarantee for the execution of the treaty. The occupation continued after Italy declared war on the Ottoman Empire (21 August 1915) during the First World War.
The islands became an important naval base for Britain and France; Italy was allied with both nations during World War I. The Dodecanese were used as a staging area for numerous campaigns, most famously the one at Gallipoli. Some of the smaller islands were occupied by the French and British, but Rhodes remained under Italian occupation.
Following the war, the Tittoni–Venizelos agreement, signed on July 29, 1919 called for the smaller islands to join with Greece, while Italy maintained control of Rhodes. The treaty further outlined an exchange where Italy would receive Antalya for southwest Anatolia. The Greek defeat in the Greco-Turkish War and the foundation of modern Turkey prevented the exchange. Italy formally annexed the Dodecanese as the Possedimenti Italiani dell'Egeo under the terms of the Treaty of Lausanne. Mussolini embarked on a program of Italianization, hoping to make Rhodes a modern transportation hub that would serve as a focal point for the spread of Italian culture in the Levant. The islands were overwhelmingly Greek-speaking, with Turkish-speaking minority and even smaller Ladino-speaking Jewish minority. Immigrant Italian speakers were a nominal language community.

The Fascist program did have some positive effects in its attempts to modernize the islands, resulting in the eradication of malaria, the construction of hospitals, aqueducts, a power plant to provide Rhodes' capital with electric lighting and the establishment of the Dodecanese Cadastre. The main castle of the Knights of St. John was also rebuilt. The concrete-dominated Fascist architectural style detracted significantly from the islands' picturesque scenery (and also reminded the inhabitants of Italian rule), and has consequently been largely demolished or remodeled, apart from the famous example of the Leros town of Lakki, which remains a prime example of the architecture.
From 1936 to 1940 Cesare Maria De Vecchi acted as governor of the Italian Aegean Islands promoting the official use of the Italian language and favoring a process of italianization, interrupted by the beginning of World War II. In the 1936 Italian census of the Dodecanese islands, the total population was 129,135, of which 7,015 were Italians.

During World War II, Italy joined the Axis Powers, and used the Dodecanese as a naval staging area for its invasion of Crete in 1940. After the surrender of Italy in September 1943, the islands briefly became a battleground between the Germans and Allied forces, including the Italians (see Battle of Leros). The Germans prevailed in the Dodecanese Campaign, and although they were driven out of mainland Greece in 1944, the Dodecanese remained occupied until the end of the war in 1945, during which time nearly the entire Jewish population of 6,000 was deported and killed. Only 1,200 of these Ladino-speaking Jews survived by escaping to the nearby coast of Turkey.
Post-World War II
Following the war, the islands became a British military protectorate, and were almost immediately allowed to run their own civil affairs, upon which the islands became informally united with Greece, though under separate sovereignty and military control. Despite objections from Turkey, which desired the islands as well, they were formally united with Greece by the 1947 Peace Treaty with Italy, ending 740 years of foreign rule over the islands. As a legacy of its former status as a jurisdiction separate from Greece, it is still considered a separate "entity" for amateur radio purposes, essentially maintaining its status as an independent country "on the air." Amateur Radio call signs in the Dodecanese begin with the prefix SV5.
Today, Rhodes and the Dodecanese are popular travel destinations.
Administration
The Dodecanese Prefecture was one of the prefectures of Greece. As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the prefecture was abolished, and its territory was divided into 4 regional units of the South Aegean region:
Municipalities and communities
The prefecture was subdivided into the following municipalities and communities. These have been reorganised at the 2011 Kallikratis reform as well.
| Municipality | YPES code | Seat (if different) | Postal code | Area code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afantou | 1205 | 851 03 | 22410-50 through 53, 56, 57 | |
| Archangelos | 1202 | 851 02 | 22440-2 | |
| Astypalaia | 1203 | 859 00 | 22430-4 | |
| Attavyros | 1204 | Empona | 851 09 | 22460-5 |
| Chalki | 1227 | 851 10 | 22460-45 | |
| Dikaio | 1206 | Zipari | 853 00 | |
| Ialysos | 1208 | 851 01 | 22410-90 through 98 | |
| Irakleides | 1207 | Antimacheia | 853 02 | 22420-6 |
| Kallithea | 1209 | Kalythies | 851 05 | 22410-6, 84 through 87 |
| Kalymnos | 1210 | 852 00 | 22430-2, 50, 59 | |
| Kameiros | 1211 | Soroni | 851 06 | 22410-40 through 42 |
| Karpathos | 1212 | 858 00 | 22450-2 | |
| Kasos | 1213 | 857 00 | 22450-4 | |
| Kos | 1214 | 853 00 | 22420-2 | |
| Leipsoi | 1215 | 850 01 | 22470-4 | |
| Leros | 1216 | 854 00 | 22470-2 | |
| Lindos | 1217 | 851 07 | 22440-2,3 | |
| Megisti/Kastellorizo | 1218 | 851 11 | 22460-49 | |
| Nisyros | 1219 | 853 03 | 22420-3 | |
| Patmos | 1222 | 855 00 | 22470-3 | |
| Petaloudes | 1223 | Kremasti | 851 04 | 22410-90 through 98 |
| Rhodes | 1224 | 851 00 | 22410-2,3,4,6,7,8 | |
| South Rhodes | 1220 | Gennadi | 851 09 | 22440-4 |
| Symi | 1225 | 856 00 | 22460-70 through 72 | |
| Tilos | 1226 | 850 02 | 22460-44 | |
| Community | YPES code | Seat (if different) | Postal code | Area code |
| Agathonisi | 1201 | Agathonissi | 850 01 | 22470 |
| Olympos | 1221 | 857 00 | 22450 |
Provinces

- Province of Patmos – Patmos
- Province of Kalymnos – Kalymnos
- Province of Kos – Kos
- Province of Rhodes – Rhodes City
- Province of Karpathos & Kasos – Karpathos
Note: Provinces no longer hold any legal status in Greece (except for the only autonomous province being the monastic republic of the Holy Mountain).
Footnotes
a: Note that in the Middle Ages, the term "Dodecanese" was used by the Byzantines and the Latins for the Cyclades. Until the 19th century, the modern Dodecanese were not differentiated from the other Southern Sporades. They became a distinct group as the "Twelve Islands" only through the Italian occupation from 1912 on.
See also
References
- Peter Saundry, C.Michael Hogan & Steve Baum. 2011. Sea of Crete. Encyclopedia of Earth. Eds.M.Pidwirny & C.J.Cleveland. National Council for Science and Environment. Washington DC.
- The Dodecanese and the East Aegean ... - Google Books. p. 436. ISBN 978-1-85828-883-3. Retrieved 2009-07-19.
- Ahrweiler, Hélène (1966), Byzance et la mer. La Marine de Guerre, la politique et les institutiones maritimes de Byzance aux VIIe–XVe siècles (in French), Paris, p. 80
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "Τα Δωδεκάνησα την παραμονή της Επανάστασης του 1821" (in Greek). Rhodes Central Municipal Library. Retrieved 2011-01-21.
Sources
- Carabott, P.J. "The Temporary Italian Occupation of the Dodecanese: A Prelude to Permanency," Diplomacy and Statecraft," (1993) 4#2 pp 285-312.
- Doumanis, Nicholas. "Italians as Good Colonizers": Speaking Subalterns and the Politics of Memory in the Dodecanese," in Ruth Ben-Ghiat and Mia Fuller, ed.s, Italian Colonialism. New York: Palgarve Macmillian. 2005. ISBN 0-312-23649-2.
In Italian
- Calace, Francesca (a cura di), «Restituiamo la Storia» – dagli archivi ai territori. Architetture e modelli urbani nel Mediterraneo orientale. Gangemi, Roma, 2012 (collana PRIN 2006 «Restituiamo la Storia»)
- Tuccimei, Ercole. La Banca d'Italia in Africa, Foreword by Arnaldo Mauri, Laterza, Bari, 1999.
- Pignataro, Luca. Le Isole Italiane dell'Egeo dall'8 settembre 1943 al termine della seconda guerra mondiale in "Clio. Rivista internazionale di studi storici", 3(2001).
- Pignataro, Luca. Il tramonto del Dodecaneso italiano 1945-1950 in "Clio. Rivista internazionale di studi storici", 4(2001)
- Pignataro, Luca. Ombre sul Dodecaneso italiano, in “Nuova Storia Contemporanea”, XII, 3(2008), pp. 61–94
- Pignataro, Luca. Il Dodecaneso italiano, con appendice fotografica, in "Nuova Storia Contemporanea" 2(2010)
- Pignataro, Luca. La presenza cattolica in Dodecaneso tra 1924 e 1937, in "Nova Historica" 32(2010)
- Pignataro, Luca. Il collegio rabbinico di Rodi, in "Nuova Storia Contemporanea", 6(2011)
- Pignataro, Luca. I naufraghi del Pentcho, in "Nuova Storia Contemporanea", 1(2012)
- Pignataro, Luca. Il Dodecaneso italiano 1912-1947, vol. I: L’occupazione iniziale 1912-1922, Chieti, Solfanelli, 2011
External links
- Dodecanese The Official website of the Greek National Tourism Organisation
| Dodecanese Islands | |
|---|---|
| The 12 major islands | |
| Minor islands |
|
| Related articles | |
| Greek islands: Aegean Islands, Saronic Islands, Crete, Cyclades, Dodecanese, Euboea, North Aegean Islands, Sporades, Ionian Islands, Echinades | |
| Prefectures of Greece | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
36°22′23″N 27°13′05″E / 36.373°N 27.218°E / 36.373; 27.218
Categories: