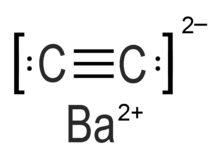
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Barium ethynediide | |
| Other names Barium acetylide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | BaC2 |
| Molar mass | 161.35 g/mol |
| Appearance | black crystalline solid |
| Density | 3.75 g/cm |
| Related compounds | |
| Other cations | Calcium carbide; Strontium carbide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Barium carbide (also referred to as barium ethynediide or barium acetylide) is a chemical compound in the carbide family having the chemical formula BaC2.
Preparation
Barium carbide can be synthesized as an impure compound by reducing barium carbonate powder with metallic magnesium in the presence of carbon. Barium carbide can also be made by reducing carbon dioxide with hot barium metal at 600°C. These methods are used because of their high yield, and because the carbide is used to make acetylene. It can also be prepared by heating a barium amalgam and carbon powder mixture in a hydrogen current. The pure compound is prepared by reducing barium oxide with carbon at high temperature.
Properties
Barium carbide reacts similarly to calcium carbide, but it's more fusible. When exposed to extreme heat, the barium will evaporate leaving behind crystals of graphite. It can also absorb the carbon in a solution at high temperature.
Hazards
Barium carbide can cause damage to the GI tract and irritation in the skin and eyes.
References
- ^ "Barium acetylide | C2Ba | ChemSpider". chemspider.com. Retrieved 2019-12-17.
- "Barium Carbide". American Elements. Retrieved 2019-12-11.
- Mishin, V. I.; Georgievskij, S. S.; Eksel', L. M.; Koval', A. I.; Afanas'eva, L. A.; Puchkov, L. D.; Ulybin, V. B. (1989-12-07). "Method for preparation of barium carbide labelled by carbon 14" (in Russian).
- Arrol, W. J.; Glascock, R. (1948). "308. The conversion of carbon dioxide into acetylene on the scale of 2—20 micromoles". J. Chem. Soc. 3: 1534–1537. doi:10.1039/JR9480001534. PMID 18101450.
- ^ "Barium Carbide, BaC2". barium.atomistry.com. Retrieved 2019-12-11.
- "Carbide". InfoPlease. Retrieved 2019-12-11.
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the carbide ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||