| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Chloro(iodo)methane | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 1730802 |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.915 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
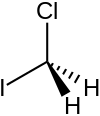
| Chemical formula | CH2ClI |
| Molar mass | 176.38 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 2.422 g mL |
| Boiling point | 108 to 109 °C (226 to 228 °F; 381 to 382 K) |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
8.9 μmol Pa kg |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.582 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms | 
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P305+P351+P338 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanes | |
| Related compounds | 2-Chloroethanol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Chloroiodomethane is the halomethane with the formula is CH
2ClI. It is a colorless liquid of use in organic synthesis. Together with other iodomethanes, chloroiodomethane is produced by some microorganisms.
Applications
Chloroiodomethane is used in cyclopropanation (Simmon-Smith reaction), where it often replaces diiodomethane because of higher yields and selectivity. It is also used in Mannich reaction, aminomethylation, epoxidation, ring opening and addition to terminal alkenes. It is a precursor to agent Ph3P=CHCl that can add a chloromethylene group (=CHCl). It reacts with organolithium compounds to give chloromethyl lithium (ClCH2Li).
Crystallography
It crystallizes orthorhombic crystal system with space group Pnma with lattice constants: a = 6.383, b = 6.706, c = 8.867 (.10 nm).
References
- ^ Miyano, Sotaro; Friestad, Gregory K. (2008). "Chloroiodomethane". E-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rc110.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- Fuse, Hiroyuki; Inoue, Hiroyuki; Murakami, Katsuji; Takimura, Osamu; Yamaoka, Yukiho (2003). "Production of free and organic iodine by Roseovarius spp.". FEMS Microbiology Letters. 229 (2): 189–94. doi:10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00839-5. PMID 14680698.
- Donald S. Matteson (2001). "Chloromethyllithium". EEROS. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rc117. ISBN 0471936235.
- Torrie B. H.; Binbrek O. S.; von Dreele R. (1993). "Crystal structure of chloroiodomethane". Mol. Phys. 79 (4): 869–874(6). Bibcode:1993MolPh..79..869T. doi:10.1080/00268979300101691.
External links
| Halomethanes | |
|---|---|
| Unsubstituted | |
| Monosubstituted | |
| Disubstituted | |
| Trisubstituted | |
| Tetrasubstituted | |
| * Chiral compound. | |
This article about an organic halide is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |