In geometry, a cuboid is a hexahedron with quadrilateral faces, meaning it is a polyhedron with six faces; it has eight vertices and twelve edges. A rectangular cuboid (sometimes also called a "cuboid") has all right angles and equal opposite rectangular faces. Etymologically, "cuboid" means "like a cube", in the sense of a convex solid which can be transformed into a cube (by adjusting the lengths of its edges and the angles between its adjacent faces). A cuboid is a convex polyhedron whose polyhedral graph is the same as that of a cube.
General cuboids have many different types. When all of the rectangular cuboid's edges are equal in length, it results in a cube, with six square faces and adjacent faces meeting at right angles. Along with the rectangular cuboids, parallelepiped is a cuboid with six parallelogram. Rhombohedron is a cuboid with six rhombus faces. A square frustum is a frustum with a square base, but the rest of its faces are quadrilaterals; the square frustum is formed by truncating the apex of a square pyramid. In attempting to classify cuboids by their symmetries, Robertson (1983) found that there were at least 22 different cases, "of which only about half are familiar in the shapes of everyday objects".
| Image | Name | Faces | Symmetry group |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Cube | 6 congruent squares | Oh, , (*432) order 48 |
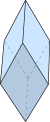 |
Trigonal trapezohedron | 6 congruent rhombi | D3d, , (2*3) order 12 |
 |
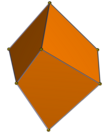
Rectangular cuboid | 3 pairs of rectangles | D2h, , (*222) order 8 |
 |
Right rhombic prism | 1 pair of rhombi, 4 congruent squares | |
 |
Right square frustum | 2 non-congruent squares, 4 congruent isosceles trapezoids |
C4v, , (*44) order 8 |
 |
Twisted trigonal trapezohedron | 6 congruent quadrilaterals | D3, , (223) order 6 |
 |
Right isosceles-trapezoidal prism | 1 pair of isosceles trapezoids; 1, 2 or 3 (congruent) square(s) |
?, ?, ? order 4 |
 |
Rhombohedron | 3 pairs of rhombi | Ci, , (×) order 2 |
 |
Parallelepiped | 3 pairs of parallelograms |

There exist quadrilateral-faced hexahedra which are non-convex.
See also
References
- ^ Robertson, Stewart A. (1984). Polytopes and Symmetry. Cambridge University Press. p. 75. ISBN 9780521277396.
- Branko Grünbaum has also used the word "cuboid" to describe a more general class of convex polytopes in three or more dimensions, obtained by gluing together polytopes combinatorially equivalent to hypercubes. See: Grünbaum, Branko (2003). Convex Polytopes. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Vol. 221 (2nd ed.). New York: Springer-Verlag. p. 59. doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-0019-9. ISBN 978-0-387-00424-2. MR 1976856.
- Dupuis, Nathan F. (1893). Elements of Synthetic Solid Geometry. Macmillan. p. 53. Retrieved December 1, 2018.
- Robertson, S. A. (1983). "Polyhedra and symmetry". The Mathematical Intelligencer. 5 (4): 57–60. doi:10.1007/BF03026511. MR 0746897.
| Convex polyhedra | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platonic solids (regular) | |||||
| Archimedean solids (semiregular or uniform) | |||||
| Catalan solids (duals of Archimedean) |
| ||||
| Dihedral regular | |||||
| Dihedral uniform |
| ||||
| Dihedral others | |||||
| Degenerate polyhedra are in italics. | |||||