| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
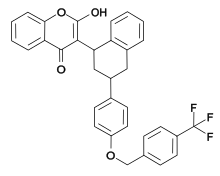
| IUPAC name 2-Hydroxy-3-methoxy)phenyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl] chromen-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.102.053 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3027 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C33H25F3O4 |
| Molar mass | 542.554 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Flocoumafen is a fluorinated, second-generation anticoagulant of the 4-hydroxycoumarin vitamin K antagonist type. It is a second generation (i.e., high potency) chemical in this class, used commercially as a rodenticide. It has a very high toxicity and is restricted to indoor use and sewers (in the UK). This restriction is mainly due to the increased risk to non-target species, especially due to its tendency to bio-accumulate in exposed organisms. Studies have shown that rodents resistant to first-generation anticoagulants can be adequately controlled with flocoumafen. It was synthesized in 1984 by Shell International Chemical.
Toxicity
In most rodents, the LD50 is 1 mg/kg, but it can vary between species: from 0.12 mg/kg in the common vole (Microtus arvalis) to more than 10 mg/kg in the Cairo spiny mouse (Acomys cahirinus). For dogs the LD50 is 0.075-0.25 mg/kg.
Antidote
The antidote to flocoumafen is vitamin K1, which must be administered over a period of several weeks or even months.
References
- ^ Watt, Barbara E.; Proudfoot, Alex T.; Bradberry, Sally M.; Vale, J Allister (2005). "Anticoagulant Rodenticides". Toxicological Reviews. 24 (4): 259–269. doi:10.2165/00139709-200524040-00005. PMID 16499407.
- ^ Flocoumafen -- A new anticoagulant rodenticide
- "Flocoumafen: Antidote and Emergency Treatment". PubChem.
External links
| Pest control: Rodenticides | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulants / Vitamin K antagonists |
| ||||||||
| Convulsants | |||||||||
| Calciferols | |||||||||
| Inorganic compounds | |||||||||
| Organochlorine | |||||||||
| Organophosphorus | |||||||||
| Carbamates | |||||||||
| Others | |||||||||