 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
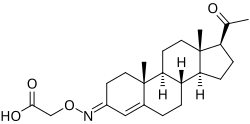
| Other names | P4-3-CMO; Progesterone 3-carboxymethyloxime; Progesterone 3-(O-carboxymethyl)oxime; 3-(O-Carboxymethyl-oximino)progesterone; oxy]acetic acid |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Neurosteroid |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.875 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H33NO4 |
| Molar mass | 387.520 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Progesterone carboxymethyloxime, or progesterone 3-(O-carboxymethyl)oxime (P4-3-CMO), is a progestin which was never marketed. It is an oral prodrug of progesterone with improved pharmacokinetic properties. The compound was developed in an attempt to address the poor oral pharmacokinetics of progesterone, including its very low bioavailability and short biological half-life. These properties of progesterone are thought to be caused by its low water solubility and high metabolic clearance rate due to rapid degradation in the intestines and liver. Drugs with low aqueous solubility are not absorbed well in the intestines because their dissolution in water is limited.
P4-3-CMO (as the potassium salt) showed water solubility that was increased by more than four orders of magnitude relative to progesterone (solubility = 9.44 mol/L and 0.0006 mol/L, respectively). In addition, it showed an in vitro terminal half-life in rat liver microsomes that was 363-fold longer than that of progesterone (half-life = 795.5 minutes and 2.2 minutes, respectively). As such, P4-3-CMO could have both improved absorption and increased metabolic stability relative to progesterone. However, the compound has not been further assessed nor studied in humans.
See also
- List of neurosteroids § Inhibitory > Synthetic > Pregnanes
- List of progestogen esters § Oximes of progesterone derivatives
References
- ^ Basu K, Mitra AK (November 1990). "Effects of 3-hydrazone modification on the metabolism and protein binding of progesterone". International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 65 (1–2): 109–114. doi:10.1016/0378-5173(90)90015-V. ISSN 0378-5173.
- ^ Basu K, Kildsig DO, Mitra AK (November 1988). "Synthesis and kinetic stability studies of progesterone derivatives". International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 47 (1–3): 195–203. doi:10.1016/0378-5173(88)90231-1. ISSN 0378-5173.
- Singh H, Jindal DP, Yadav MR, Kumar M (1991). "Heterosteroids and drug research". Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. 28: 233–300. doi:10.1016/S0079-6468(08)70366-7. ISBN 9780444812759. PMID 1843548.
- Liu R (18 January 2008). Water-Insoluble Drug Formulation, Second Edition. CRC Press. pp. 105–. ISBN 978-1-4200-0955-2.
This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |