Star in the constellation Cassiopeia
Not to be confused with Rho Cassiopeiae .
R Cassiopeiae
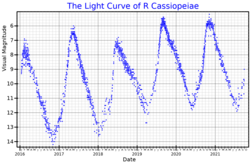
visual band light curve of R Cassiopeiae, from AAVSO data
Observation dataEpoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0
Constellation
Cassiopeia
Right ascension
23 58 24.87003
Declination
+51° 23′ 19.70″
Apparent magnitude (V)
4.4 to 13.5
Characteristics
Spectral type
M6e–M10e
U−B color index
+0.08
B−V color index
+1.83
Variable type
Mira
Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv )−22.94±0.72 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: 81.920±0.403 mas /yr Dec.: 18.760±0.358 mas /yr Parallax (π)5.3417 ± 0.2449 mas Distance 176 pc Details Mass 0.59 M ☉ Radius 263 R ☉ Luminosity 8,960 L ☉ Temperature 2,812 K Other designations R Cas , BD +50°4202, HD 224490, HIP 118188, HR 9066, SAO 35938, ADS 17135, CCDM J23584+5123 Database references SIMBAD data
R Cassiopeiae is a variable star in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia . It is located approximately 574 light years distant from the Sun, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −23 km/s. This is a pulsating Mira-type variable star with a brightness varies from magnitude +4.4 down to +13.5 with a period of 433.6 days. At its maximum, R Cassiopeiae is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued star.
This aging red giant star has a stellar classification that varies from M6e to M10e, where the 'e' suffix indicates emission features in the spectrum . Currently on the asymptotic giant branch , it has 59% of the mass of the Sun with an oxygen rich chemical abundance. Having exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core , the star has expanded to 263 times the Sun's radius . On average, the star is radiating 3,837 times the luminosity of the Sun from its swollen photosphere with an effective temperature ranging around 2,812 K. It is losing mass at the rate of 1.3×10 M ☉ /yr and is surrounded by a dusty circumstellar shell that extends out to 2.8′ .
See also
References
"Download Data" . aavso.org . AAVSO. Retrieved 1 October 2021.^ Brown, A. G. A. ; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties" . Astronomy & Astrophysics 616 . A1. arXiv :1804.09365 . Bibcode :2018A&A...616A...1G . doi :10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 .Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR .
^ Samus, N. N.; et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports . 5.1. 61 (1): 80–88. Bibcode :2017ARep...61...80S . doi :10.1134/S1063772917010085 . S2CID 125853869 .
^ Ducati, J. R. (2002). "Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues . 2237 : 0. Bibcode :2002yCat.2237....0D .
^ Famaey, B.; et al. (January 2005). "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters". Astronomy and Astrophysics . 430 (1): 165–186. arXiv :astro-ph/0409579 . Bibcode :2005A&A...430..165F . doi :10.1051/0004-6361:20041272 . S2CID 17804304 .
^ McDonald, I.; De Beck, E.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Lagadec, E. (2018). "Pulsation-triggered dust production by asymptotic giant branch stars" . Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society . 481 (4): 4984. arXiv :1809.07965 . Bibcode :2018MNRAS.481.4984M . doi :10.1093/mnras/sty2607 . S2CID 118969263 .
^ Takeuti, Mine; et al. (2013). "A Method to Estimate the Masses of Asymptotic Giant Branch Variable Stars" . Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan . 65 (3): 60. Bibcode :2013PASJ...65...60T . doi :10.1093/pasj/65.3.60 .
"R Cas" . SIMBAD Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2019-08-17.Assaf, K. A. (December 2018). "Multi-epoch Proper Motion Magnetic Field Comparison of SiO Masers around R Cas" . The Astrophysical Journal . 869 (1): 19. Bibcode :2018ApJ...869...80A . doi :10.3847/1538-4357/aaea65 . 80.
^ Ueta, T.; et al. (May 2010). "The interface between the stellar wind and interstellar medium around R Cassiopeiae revealed by far-infrared imaging". Astronomy and Astrophysics . 514 : 6. arXiv :0911.4918 . Bibcode :2010A&A...514A..16U . doi :10.1051/0004-6361/200913455 . S2CID 54745858 . A16.
Categories :
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.
**DISCLAIMER** We are not affiliated with Wikipedia, and Cloudflare.
The information presented on this site is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.
You should always have a personal consultation with a healthcare professional before making changes to your diet, medication, or exercise routine.
AI helps with the correspondence in our chat.
We participate in an affiliate program. If you buy something through a link, we may earn a commission 💕
↑