| Revision as of 00:55, 7 January 2015 editTylerDurden8823 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers42,903 edits Pickwickian syndrome does not appear to be the preferred term. Obesity hypoventilation is a better term anyway as it is descriptive of the problem← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:45, 17 December 2024 edit undoHeadbomb (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Page movers, File movers, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers, Template editors454,509 edits →Prostacyclin and thromboxane: | Misc citation tidying. | Use this tool. Report bugs. | #UCB_Gadget | Add: pages, issue, volume, journal, title, date, pmid, authors 1-1. Changed bare reference to CS1/2. Removed parameters. | Use this tool. Report bugs. | #UCB_Gadget | ||
| (753 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Increased blood pressure in lung arteries}} | |||
| {{Infobox disease | |||
| {{Infobox medical condition (new) | |||
| | Name = Pulmonary arterial hypertension | |||
| | name = Pulmonary hypertension | |||
| | Image = Plexiform_lesion_-_Pulmonary_hypertension.jpg | |||
| | synonyms = Ayerza syndrome<ref name=GHR2016/> | |||
| | Caption = ] showing a plexiform lesion of the ], as seen in irreversible pulmonary hypertension. ]. | |||
| | image = Pulmonary Hypertension.png | |||
| | DiseasesDB = 10998 | |||
| | caption = Pulmonary hypertension | |||
| | ICD10 = {{ICD10|I|27|0|i|26}}, {{ICD10|I|27|2|i|26}} | |||
| | field = ], ] | |||
| | ICD9 = {{ICD9|416.0}} | |||
| | symptoms = Chest pain, fatigue<ref name="www.nhlbi.nih.gov"/> | |||
| | ICDO = | |||
| | complications = | |||
| | OMIM = | |||
| | onset = 20 to 60 years old<ref name=NHLBI23PHRisk/> | |||
| | MedlinePlus = 000112 | |||
| | duration = Long term<ref name="Humbert-2022"/> | |||
| | eMedicineSubj = radio | |||
| | types = | |||
| | eMedicineTopic = 583 | |||
| | causes = Unknown<ref name="Humbert-2022"/> | |||
| | eMedicine_mult = {{eMedicine2|med|1962}} | |||
| | risks = Family history, ], ], ], ] use, ], ], living at high ]s<ref name=NHLBI23PHCa/><ref name=NHLBI23PHRisk/> | |||
| | MeshID = D006976 | |||
| | diagnosis = Following ruling out other potential causes<ref name="Humbert-2022"/> | |||
| | differential = | |||
| | prevention = | |||
| | treatment = ], various medications, ]<ref name="Humbert-2022"/><ref name=NHLBI23PHTx/> | |||
| | medication = ], ], ], ], ], ], ]<ref name="Humbert-2022"/> | |||
| | prognosis = | |||
| | frequency = 1,000 new cases a year (US)<ref name=GHR2016/> | |||
| | deaths = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| <!-- Definition and symptoms --> | |||
| '''Pulmonary hypertension''' (PH) is an increase of blood pressure in the ], ], or pulmonary capillaries, together known as the ] ], leading to ], ], ], ] and other symptoms. Pulmonary hypertension can be a severe disease with a markedly decreased exercise tolerance and ]. It was first identified by Ernst von Romberg in 1891.<ref>{{cite journal|last=von Romberg |first=Ernst |title=Über Sklerose der Lungenarterie|journal=Dtsch Arch Klin Med |language=German|year=1891–1892|volume=48|pages=197–206}}</ref> According to the most recent classification, it can be one of six different types (see below).<ref name=Dana>{{cite journal |author=Simonneau G, Robbins I, Beghetti M, ''et al.'' |title=Updated Clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension |journal=J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. |volume=54 |issue=1 Suppl S |pages=S43-S54 |date=30 June 2009 |pmid=19555858 |doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.012 | url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0735109709012169}}</ref> | |||
| '''Pulmonary hypertension''' ('''PH''' or '''PHTN''') is a condition of increased ] in the ].<ref name=NHLBI23PH>{{harvnb|NHLBI|What Is Pulmonary Hypertension?|2023}}</ref> Symptoms include ], ], tiredness, chest pain, ], and a ].<ref name=NHLBI23PH/><ref name=GHR2016/> The condition may make it difficult to exercise.<ref name=NHLBI23PH/> Onset is typically gradual.<ref name=NHLBI23PHDiag>{{cite web |title=Diagnosis |date=March 24, 2022 |work=Health Topics: Pulmonary Hypertension |publisher=National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. National Library of Medicine |url=https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/pulmonary-hypertension/diagnosis}}</ref> | |||
| <!-- Definition --> | |||
| According to the definition at the 6th World Symposium of Pulmonary Hypertension in 2018, a patient is deemed to have pulmonary hypertension if the pulmonary mean arterial pressure is greater than 20mmHg at rest, revised down from a purely arbitrary 25mmHg, and ] (PVR) greater than 3 Wood units. | |||
| <!-- Cause and diagnosis --> | |||
| The cause is often unknown.<ref name="Humbert-2022">{{cite journal | vauthors = Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, Badagliacca R, Berger RM, Brida M, Carlsen J, Coats AJ, Escribano-Subias P, Ferrari P, Ferreira DS, Ghofrani HA, Giannakoulas G, Kiely DG, Mayer E, Meszaros G, Nagavci B, Olsson KM, Pepke-Zaba J, Quint JK, Rådegran G, Simonneau G, Sitbon O, Tonia T, Toshner M, Vachiery JL, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Delcroix M, Rosenkranz S | display-authors = 6 | title = 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension | journal = European Heart Journal | volume = 43 | issue = 38 | pages = 3618–3731 | date = October 2022 | pmid = 36017548 | doi = 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac237 }}</ref> Risk factors include a family history, prior ] (blood clots in the lungs), ], ], ] use, ], ], living at high ]s, and problems with the ].<ref name=NHLBI23PHCa>{{cite web |title=Causes and Risk Factors |date=24 March 2022 |work=Health Topics: Pulmonary Hypertension |publisher=National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. National Library of Medicine |url=https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/pulmonary-hypertension/causes}}</ref><ref name="NHLBI23PHRisk">{{cite web |date=2 August 2011 |title=Who Is at Risk for Pulmonary Hypertension? |url=https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pah/atrisk |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170731041125/https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pah/atrisk |archive-date=31 July 2017 |access-date=30 July 2017 |website=NHLBI – NIH}}</ref> The underlying mechanism typically involves ] and subsequent remodeling of the ] in the ].<ref name=NHLBI23PHCa/> Diagnosis involves first ruling out other potential causes.<ref name="Humbert-2022"/> | |||
| <!-- Prevention and treatment --> | |||
| {{As of|2022}} there was no cure for pulmonary hypertension,<ref name=NHLBI23PHTx>{{cite web |title=Treatment |date=24 March 2022 |work=Health Topics: Pulmonary Hypertension |publisher=National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. National Library of Medicine |url=https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/pulmonary-hypertension/treatment}}</ref> although research to find a cure is ongoing. Treatment depends on the type of disease.<ref name=NHLBI23PHTx/> A number of ] such as ], ], and ] may be used.<ref name="Humbert-2022"/> Medications specifically used to treat pulmonary hypertension include ], ], ], ], ], ], and ], tadalafil, selexipag, riociguat.<ref name="Humbert-2022"/> ] may be an option in severe cases.<ref name=NHLBI23PHTx/> | |||
| <!-- Epidemiology and history --> | |||
| The frequency of occurrence is estimated at 1,000 new cases per year in the United States.<ref name=NHLBI23PHRisk/><ref name=GHR2016>{{cite web|title=Pulmonary arterial hypertension|url=https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/pulmonary-arterial-hypertension|website=Genetics Home Reference|access-date=30 July 2017|language=en|date=January 2016|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170728014636/https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/pulmonary-arterial-hypertension|archive-date=28 July 2017}}</ref> Females are more often affected than males.<ref name=GHR2016/> Onset is typically between 20 and 60 years of age.<ref name=NHLBI23PHRisk/> Pulmonary hypertension was identified by Ernst von Romberg in 1891.<ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = von Romberg E |title=Über Sklerose der Lungenarterie|journal=Dtsch Arch Klin Med |language=de|year=1891–1892|volume=48|pages=197–206}}</ref><ref name="Humbert-2022"/> | |||
| {{TOC limit|3}} | |||
| ==Classification== | |||
| According to WHO classification there are 5 groups of PH, where Group I (pulmonary arterial hypertension) is further subdivided into Group I<nowiki>' and Group I''</nowiki> classes.<ref name=Simonneau098/><ref name="Simonneau-2013"/> The WHO classification system in 2022 (with adaptations from the more recent ESC/ERS guidelines shown in italics) can be summarized as follows:<ref name="Humbert-2022"/><ref name="Simonneau-2013"/><ref name="Galiè-2016"/> | |||
| '''WHO Group I''' – ] (PAH) | |||
| * Caused by narrowing and thickening of tiny arteries of the lung<ref name="ALA">{{cite web | title = Learn About Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension | work = PAH | publisher = ] | url = https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pulmonary-arterial-hypertension/learn-about-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension | access-date = 2023-08-01}}</ref> | |||
| * ] in most cases (heritable in some cases)<ref name="ALA" /> | |||
| * ] (], ], ], ], ] mutations) | |||
| * Drug- and toxin-induced (e.g., ], ], or ] use<ref name="Kolaitis-2021">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kolaitis NA, Zamanian RT, de Jesus Perez VA, Badesch DB, Benza RL, Burger CD, Chakinala MM, Elwing JM, Feldman J, Lammi MR, Mathai SC, McConnell JW, Presberg KW, Robinson JC, Sager J, Shlobin OA, Simon MA, Kawut SM, Glidden DV, Singer JP, De Marco T | display-authors = 6 | title = Clinical Differences and Outcomes between Methamphetamine-associated and Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in the Pulmonary Hypertension Association Registry | journal = Annals of the American Thoracic Society | volume = 18 | issue = 4 | pages = 613–622 | date = April 2021 | pmid = 33064950 | pmc = 8174020 | doi = 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202007-774OC | doi-access = free }}</ref> ) | |||
| * Associated conditions:], ], ], ]s, ] | |||
| '''WHO Group I'''' – ] (PVOD), ] (PCH) | |||
| * Idiopathic | |||
| * Heritable (] mutations) | |||
| * Drugs, toxins and radiation-induced | |||
| * Associated conditions:connective tissue disease, HIV infection | |||
| '''WHO Group I"''' – Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the ] | |||
| '''WHO Group II''' – Pulmonary hypertension secondary to ] disease | |||
| * Left ventricular ] | |||
| * Left ventricular ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * Congenital/acquired left heart inflow/outflow tract obstruction and congenital ] | |||
| * Congenital/acquired pulmonary venous ] | |||
| '''WHO Group III''' – Pulmonary hypertension due to ], chronic ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * Mixed restrictive and obstructive pattern ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] ] disorders | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| '''WHO Group IV''' – Chronic arterial obstruction | |||
| * ] (CTEPH) | |||
| * Other pulmonary artery obstructions | |||
| ** ] or other tumor within the blood vessels | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** Congenital pulmonary artery ] | |||
| ** ] (]) | |||
| '''WHO Group V''' – Pulmonary hypertension with unclear or ] mechanisms | |||
| * ]s: chronic ] (including ]) | |||
| * ]s: ], pulmonary Langerhans cell ]: ], ], ] | |||
| * ]s: ], ], ]s | |||
| * Others: pulmonary tumoral thrombotic microangiopathy, ], ], segmental pulmonary hypertension (pulmonary hypertension restricted to one or more ] of the ]) | |||
| ==Signs and symptoms== | ==Signs and symptoms== | ||
| The symptoms of pulmonary hypertension include the following:<ref name="www.nhlbi.nih.gov">{{Cite web|title = What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary Hypertension? – NHLBI, NIH|url = http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pah/signs|website = www.nhlbi.nih.gov|access-date = 2015-12-30|url-status = live|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160105180434/http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pah/signs|archive-date = 2016-01-05}}</ref><ref name="Galiè-2016">{{cite journal | vauthors = Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Beghetti M, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Hansmann G, Klepetko W, Lancellotti P, Matucci M, McDonagh T, Pierard LA, Trindade PT, Zompatori M, Hoeper M | display-authors = 6 | title = 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) | journal = European Heart Journal | volume = 37 | issue = 1 | pages = 67–119 | date = January 2016 | pmid = 26320113 | doi = 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317 | collaboration = ESC Scientific Document Group | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="McLaughlin-2009">{{cite journal | vauthors = McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, McGoon MD, Park MH, Rosenson RS, Rubin LJ, Tapson VF, Varga J | display-authors = 6 | title = ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 53 | issue = 17 | pages = 1573–1619 | date = April 2009 | pmid = 19389575 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.01.004 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| {{unreferenced section|date=June 2013}} | |||
| {{columns-list|colwidth=30em| | |||
| Because symptoms may develop very gradually, patients may delay seeing a physician for years. Common symptoms are ], ], non-productive ], ], fainting or ], peripheral edema (swelling around the ankles and feet), and rarely ]. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (] rate increased) | |||
| * Right-sided abdominal pain | |||
| * Poor ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (legs/ankles) | |||
| * ] | |||
| }} | |||
| Less common signs/symptoms include non-productive cough and exercise-induced nausea and vomiting.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/> Coughing up of blood may occur in some patients, particularly those with specific subtypes of pulmonary hypertension such as heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension, ] and ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Diller GP, Gatzoulis MA | title = Pulmonary vascular disease in adults with congenital heart disease | journal = Circulation | volume = 115 | issue = 8 | pages = 1039–1050 | date = February 2007 | pmid = 17325254 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.592386 | doi-access = free }}</ref> ] venous ] typically presents with shortness of breath while lying flat or sleeping (] or ]), while pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) typically does not.<ref name="Fang-2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Fang JC, DeMarco T, Givertz MM, Borlaug BA, Lewis GD, Rame JE, Gomberg-Maitland M, Murali S, Frantz RP, McGlothlin D, Horn EM, Benza RL | display-authors = 6 | title = World Health Organization Pulmonary Hypertension group 2: pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease in the adult--a summary statement from the Pulmonary Hypertension Council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation | journal = The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation | volume = 31 | issue = 9 | pages = 913–933 | date = September 2012 | pmid = 22884380 | doi = 10.1016/j.healun.2012.06.002 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| Other typical signs of pulmonary hypertension include an accentuated pulmonary component of the second heart sound, a right ventricular ], and ] indicating a ]. Signs of systemic congestion resulting from ] include ], ], and ].<ref name="Galiè-2016"/><ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/><ref name="evi">{{Cite book|title = Evidence-Based Cardiology|url = https://books.google.com/books?id=tjgJzBWDneYC|publisher = John Wiley & Sons|date = 2011|page = 70.3 (figure)|isbn = 978-1-4443-5945-9| vauthors = Yusuf S, Cairns J, Camm J, Fallen EL, Gersh BJ |url-status = live|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160430061345/https://books.google.com/books?id=tjgJzBWDneYC|archive-date = 2016-04-30}}</ref> Evidence of ] and ] is also sought and, if present, is consistent with the presence of pulmonary hypertension.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/><ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/><ref name="emed">{{Cite web|title = Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Clinical Presentation: History, Physical Examination, Complications|url = http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/301450-clinical#b2|website = emedicine.medscape.com|access-date = 2015-12-30|url-status = live|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20151101111008/http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/301450-clinical#b2|archive-date = 2015-11-01}}</ref> | |||
| ] ''venous'' ] typically presents with shortness of breath while lying flat or sleeping (] or ]), while pulmonary ''arterial'' hypertension (PAH) typically does not. | |||
| ==Causes== | |||
| A detailed family history is established to determine whether the disease might be ]. A history of exposure to drugs such as ], ], ] leading to ], and tobacco leading to ] are considered significant. | |||
| Pulmonary hypertension is a pathophysiologic condition with many possible causes. Indeed, this condition frequently accompanies severe heart or lung conditions.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/> A 1973 ] meeting was the first attempt to classify pulmonary hypertension by its cause, and a distinction was made between primary PH (resulting from a disease of the pulmonary arteries) and secondary PH (resulting secondary to other, non-vascular causes). Further, primary PH was divided into the "arterial plexiform", "veno-occlusive" and "thromboembolic" forms.<ref>{{cite book |vauthors=Hatano S, Strasser R | title=Primary pulmonary hypertension | publisher=World Health Organization | location=Geneva | year=1975}}</ref> In 1998, a second conference at ] addressed the causes of secondary PH.<ref>{{cite book |vauthors=Rich S, Rubin LJ, Abenhail L, etal | title=Executive summary from the World Symposium on Primary Pulmonary Hypertension (Evian, France, September 6–10, 1998) | publisher=The World Health Organization | location=Geneva | year=1998 |url=https://www.who.int/ncd/cvd/pph.html | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20020408173726/http://www.who.int/ncd/cvd/pph.html | archive-date=April 8, 2002}}</ref> Subsequent third,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Simonneau G, Galiè N, Rubin LJ, Langleben D, Seeger W, Domenighetti G, Gibbs S, Lebrec D, Speich R, Beghetti M, Rich S, Fishman A | display-authors = 6 | title = Clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 43 | issue = 12 Suppl S | pages = 5S–12S | date = June 2004 | pmid = 15194173 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.02.037 | doi-access = free }}</ref> fourth,<ref name=Simonneau098>{{cite journal | vauthors = Simonneau G, Robbins IM, Beghetti M, Channick RN, Delcroix M, Denton CP, Elliott CG, Gaine SP, Gladwin MT, Jing ZC, Krowka MJ, Langleben D, Nakanishi N, Souza R | display-authors = 6 | title = Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 54 | issue = 1 Suppl | pages = S43–S54 | date = June 2009 | pmid = 19555858 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.012 | doi-access = free }}</ref> and fifth (2013)<ref name="Simonneau-2013">{{cite journal | vauthors = Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Krishna Kumar R, Landzberg M, Machado RF, Olschewski H, Robbins IM, Souza R | display-authors = 6 | title = Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 62 | issue = 25 Suppl | pages = D34–D41 | date = December 2013 | pmid = 24355639 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.029 | doi-access = free }}</ref> World Symposia on PAH have further defined the classification of PH. The classification continues to evolve based on improved understanding of the disease mechanisms.{{citation needed|date=December 2018}} | |||
| Most recently in 2022, the WHO guidelines were updated by the ] (ESC) and ] (ERS).<ref name="Humbert-2022"/> These guidelines are endorsed by the ], and provide the current framework for understanding and treatment of pulmonary hypertension.<ref name=Humbert-2022/> | |||
| A ] is performed to look for typical signs of pulmonary hypertension, including a split S2, and loud P2 (pulmonic valve closure sound) and (para)sternal heave indicating a hypertrophied right atrium. Signs of systemic congestion resulting from right sided heart failure are jugular venous distension, pedal ], ], ], ] etc. Evidence of ] and ] is also sought and, if present, is consistent with the presence of pulmonary hypertension. | |||
| ===Genetics=== | |||
| ==Causes and classification== | |||
| A 1973 meeting organized by the ] was the first to attempt classification of pulmonary hypertension. A distinction was made between primary and secondary PH, and primary PH was divided in the "arterial plexiform", "veno-occlusive" and "thromboembolic" forms.<ref>{{cite book | author=Hatano S, Strasser R | title=Primary pulmonary hypertension | publisher=World Health Organization | location=Geneva | year=1975}}</ref> A second conference in 1998 at ] also addressed the causes of secondary PH (i.e. those due to other medical conditions),<ref>{{cite book | author=Rich S, Rubin LJ, Abenhail L ''et al.'' | title=Executive summary from the World Symposium on Primary Pulmonary Hypertension (Evian, France, September 6–10, 1998) | publisher=The World Health Organization | location=Geneva | year=1998 |url=http://www.who.int/ncd/cvd/pph.html | archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20020408173726/http://www.who.int/ncd/cvd/pph.html | archivedate=April 8, 2002}}</ref> and in 2008, the 4th World Symposium on Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension was convened in Dana Point to modify the classification based on new understandings of disease mechanisms. The revised system developed by this group provides the current framework for understanding pulmonary hypertension.<ref name=Dana/> The system includes several improvements over the former 2004 Venice Classification system. | |||
| Mutations in several genes have been associated with this condition<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Rabinovitch M | title = Molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = The Journal of Clinical Investigation | volume = 122 | issue = 12 | pages = 4306–4313 | date = December 2012 | pmid = 23202738 | pmc = 3533531 | doi = 10.1172/JCI60658 }}</ref><ref name=Hadinnapola2017>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hadinnapola C, Bleda M, Haimel M, Screaton N, Swift A, Dorfmüller P, Preston SD, Southwood M, Hernandez-Sanchez J, Martin J, Treacy C, Yates K, Bogaard H, Church C, Coghlan G, Condliffe R, Corris PA, Gibbs S, Girerd B, Holden S, Humbert M, Kiely DG, Lawrie A, Machado R, MacKenzie Ross R, Moledina S, Montani D, Newnham M, Peacock A, Pepke-Zaba J, Rayner-Matthews P, Shamardina O, Soubrier F, Southgate L, Suntharalingam J, Toshner M, Trembath R, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Wilkins MR, Wort SJ, Wharton J, Gräf S, Morrell NW | display-authors = 6 | title = Phenotypic Characterization of ''EIF2AK4'' Mutation Carriers in a Large Cohort of Patients Diagnosed Clinically With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension | journal = Circulation | volume = 136 | issue = 21 | pages = 2022–2033 | date = November 2017 | pmid = 28972005 | pmc = 5700414 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028351 }}</ref> these include bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2 (]) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha kinase 4 gene (]). 80% of familial pulmonary arterial hypertension and 20% of sporadic variants have mutations in BMPR2.<ref name="Hassoun 2021">{{cite journal |last1=Hassoun |first1=Paul M. |title=Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension |journal=New England Journal of Medicine |date=16 December 2021 |volume=385 |issue=25 |pages=2361–2376 |doi=10.1056/NEJMra2000348|pmid=34910865 }}</ref> BMPR2 is involved in ] proliferation and remodeling. Other mutations associated with PAH include ] (which encodes activin receptor–like kinase 1) and ] encoding endoglin, two proteins which also participate in BMPR2 signaling.<ref name="Hassoun 2021" /> The SMAD transcription factor family, including ], ], and ] are involved in signaling pathways downstream from BMPR2 and are also implicated in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension.<ref name="Hassoun 2021" /> | |||
| The Dana Point 2008 Updated Clinical Classification system can be summarized as follows:<ref name=Dana/> | |||
| * WHO Group I - Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) | |||
| ** ] PAH | |||
| ** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ], ] (with or without ]) | |||
| *** Unknown | |||
| ** Drug- and toxin-induced | |||
| ** Associated with | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** ]s | |||
| *** ] | |||
| *** Chronic ] (including ]) | |||
| ** Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the ] | |||
| ** WHO Group I' - ] (PVOD) and/or ] (PCH) | |||
| * WHO Group II - Pulmonary hypertension owing to ] disease | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * WHO Group III - Pulmonary hypertension owing to ] and/or ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** Other ] with mixed restrictive and obstructive pattern | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] ] disorders | |||
| ** ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * WHO Group IV - Chronic ] pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) | |||
| * WHO Group V - Pulmonary hypertension with unclear ] mechanisms | |||
| ** ]s: ], ] | |||
| ** ]s: ], pulmonary Langerhans cell ]: ], ], ] | |||
| ** ]s: ], ], ]s | |||
| ** Others: tumoral ], ], ] on ] | |||
| ==Pathogenesis== | ==Pathogenesis== | ||
| ] (on left side)]] | |||
| {{refimprove section|date=January 2015}} | |||
| ] showing ] in pulmonary hypertensive with marked thickening of the walls]] | |||
| Whatever the initial cause, pulmonary ''arterial'' hypertension (WHO Group I) involves the ] connected to and within the lungs. This makes it harder for the heart to pump blood through the ], much as it is harder to make water flow through a narrow pipe as opposed to a wide one. Over time, the affected blood vessels become stiffer and thicker, in a process known as ]. This further increases the blood pressure within the lungs and impairs their blood flow. In common with other types of pulmonary hypertension, the increased workload of the heart causes ] of the ], making the heart less able to pump blood through the lungs, ultimately causing ] (a condition known as ]). The right ventricle is normally part of a low pressure system, with pressures that are around one-sixth of those that the ] normally encounters. As such, the right ventricle cannot cope as well to higher pressures, and although hypertrophy of the heart muscle helps initially, it ultimately leads to a situation where the right ventricular muscle cannot get enough oxygen to meet its needs and right heart failure follows. As the blood flowing through the lungs decreases, the left side of the heart receives less blood. This blood may also carry less oxygen than normal. Therefore it becomes harder and harder for the left side of the heart to pump to supply sufficient ] to the rest of the body, especially during physical activity. | |||
| The pathogenesis of pulmonary ''arterial'' hypertension (WHO Group I) involves the ] connected to and within the lungs. This makes it harder for the heart to pump blood through the ], as it is much harder to make water flow through a narrow pipe as opposed to a wide one. Over time, the affected blood vessels become stiffer and thicker, in a process known as ]. The mechanisms involved in this narrowing process include ], ], and ] (excessive cellular proliferation, fibrosis, and reduced apoptosis/programmed cell death in the vessel walls, caused by ], disordered ] and dysregulation of certain ]).<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Jacob AS, Nielsen DH, Gianelly RE | title = Fatal ventricular fibrillation following verapamil in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome with atrial fibrillation | journal = Annals of Emergency Medicine | volume = 14 | issue = 2 | pages = 159–160 | date = February 1985 | pmid = 3970402 | pmc = 3970402 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.025 }}</ref><ref name="Vonk-Noordegraaf A 2013">{{cite journal | vauthors = Vonk-Noordegraaf A, Haddad F, Chin KM, Forfia PR, Kawut SM, Lumens J, Naeije R, Newman J, Oudiz RJ, Provencher S, Torbicki A, Voelkel NF, Hassoun PM | display-authors = 6 | title = Right heart adaptation to pulmonary arterial hypertension: physiology and pathobiology | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 62 | issue = 25 Suppl | pages = D22–D33 | date = December 2013 | pmid = 24355638 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.027 | doi-access = free }}</ref> This further increases the blood pressure within the lungs and impairs their blood flow. In common with other types of pulmonary hypertension, these changes result in an increased workload for the right side of the heart.<ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/><ref name="Galie N 2009">{{cite journal | vauthors = Galiè N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA, Beghetti M, Corris P, Gaine S, Gibbs JS, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Jondeau G, Klepetko W, Opitz C, Peacock A, Rubin L, Zellweger M, Simonneau G | display-authors = 6 | title = Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension | journal = The European Respiratory Journal | volume = 34 | issue = 6 | pages = 1219–1263 | date = December 2009 | pmid = 19749199 | doi = 10.1183/09031936.00139009 | doi-access = free }}</ref> The ] is normally part of a low pressure system, with systolic ventricular pressures that are lower than those that the left ventricle normally encounters. As such, the right ventricle cannot cope as well with higher pressures, and although right ventricular adaptations (] and increased contractility of the heart muscle) initially help to preserve ], ultimately these compensatory mechanisms are insufficient; the right ventricular muscle cannot get enough oxygen to meet its needs and ] follows.<ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/><ref name="Vonk-Noordegraaf A 2013"/><ref name="Galie N 2009"/> As the blood flowing through the lungs decreases, the left side of the heart receives less blood. This blood may also carry less oxygen than normal. Therefore, it becomes harder and harder for the left side of the heart to supply sufficient ] to the rest of the body, especially during physical activity.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Yuan JX, Rubin LJ | title = Pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: the need for multiple hits | journal = Circulation | volume = 111 | issue = 5 | pages = 534–538 | date = February 2005 | pmid = 15699271 | doi = 10.1161/01.CIR.0000156326.48823.55 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Tuder RM, Marecki JC, Richter A, Fijalkowska I, Flores S | title = Pathology of pulmonary hypertension | journal = Clinics in Chest Medicine | volume = 28 | issue = 1 | pages = 23–42, vii | date = March 2007 | pmid = 17338926 | pmc = 1924722 | doi = 10.1016/j.ccm.2006.11.010 }}</ref><ref name=Simonneau098/> During the end-systolic volume phase of the cardiac cycle, the Gaussian curvature and the mean curvature of right ventricular endocardial wall of PH patients was found to be significantly different as compared to controls.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bordones-Crom A, Patnaik SS, Menon PG, Murali S, Finol E | title = Morphological Analysis of the Right Ventricular Endocardial Wall in Pulmonary Hypertension | journal = Journal of Biomechanical Engineering | volume = 143 | issue = 7 | date = July 2021 | pmid = 33704381 | doi = 10.1115/1.4050457 | s2cid = 232193407 }}</ref> | |||
| In PVOD (WHO Group I'), pulmonary blood vessel narrowing occurs preferentially (though not exclusively) in post-capillary venous blood vessels.<ref name="Montani-2009">{{cite journal | vauthors = Montani D, Price LC, Dorfmuller P, Achouh L, Jaïs X, Yaïci A, Sitbon O, Musset D, Simonneau G, Humbert M | display-authors = 6 | title = Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease | journal = The European Respiratory Journal | volume = 33 | issue = 1 | pages = 189–200 | date = January 2009 | pmid = 19118230 | doi = 10.1183/09031936.00090608 | doi-access = free }}</ref> PVOD shares several characteristics with PAH, but there are also some important differences, for example differences in prognosis and response to medical therapy.<ref name="Montani-2016">{{cite journal |last1=Montani |first1=David |last2=Lau |first2=Edmund M. |last3=Dorfmüller |first3=Peter |last4=Girerd |first4=Barbara |last5=Jaïs |first5=Xavier |last6=Savale |first6=Laurent |last7=Perros |first7=Frederic |last8=Nossent |first8=Esther |last9=Garcia |first9=Gilles |last10=Parent |first10=Florence |last11=Fadel |first11=Elie |last12=Soubrier |first12=Florent |last13=Sitbon |first13=Olivier |last14=Simonneau |first14=Gérald |last15=Humbert |first15=Marc |title=Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease |journal=European Respiratory Journal |date=May 2016 |volume=47 |issue=5 |pages=1518–1534 |doi=10.1183/13993003.00026-2016}}</ref> | |||
| Pathogenesis in pulmonary hypertension owing to left heart disease (WHO Group II) is completely different in that constriction or damage to the pulmonary blood vessels is not the issue. Instead, the left heart fails to pump blood efficiently, leading to pooling of blood in the lungs and back pressure within the pulmonary system. This causes ] and ]s. | |||
| Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn occurs when the circulatory system of a newborn baby fails to adapt to life outside the womb; it is characterized by high resistance to blood flow through the lungs, ] and severe ].<ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/> | |||
| In hypoxic pulmonary hypertension (WHO Group III), the low levels of oxygen are thought to cause narrowing of the pulmonary arteries. This phenomenon is called ] and it is initially a protective response designed to stop too much blood flowing to areas of the lung that are damaged and do not contain oxygen. When the damage is widespread and prolonged, this hypoxia-mediated vasoconstriction occurs across a large portion of the pulmonary vascular bed. | |||
| Pathogenesis in pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease (WHO Group II) is completely different in that constriction or damage to the pulmonary blood vessels is not the issue. Instead, the left heart fails to pump blood efficiently, leading to pooling of blood in the lungs and back pressure within the pulmonary system. This causes ] and ]s.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Guazzi M, Galiè N | title = Pulmonary hypertension in left heart disease | journal = European Respiratory Review | volume = 21 | issue = 126 | pages = 338–346 | date = December 2012 | pmid = 23204122 | pmc = 9487233 | doi = 10.1183/09059180.00004612 | doi-access = free }}</ref> In the absence of pulmonary blood vessel narrowing, the increased back pressure is described as 'isolated post-capillary pulmonary hypertension' (older terms include 'passive' or 'proportionate' pulmonary hypertension or 'pulmonary venous hypertension'). However, in some patients, the raised pressure in the pulmonary vessels triggers a superimposed component of vessel narrowing, which further increases the workload of the right side of the heart. This is referred to as 'post-capillary pulmonary hypertension with a pre-capillary component' or 'combined post-capillary and pre-capillary pulmonary hypertension' (older terms include 'reactive' or 'out-of-proportion' pulmonary hypertension).<ref name="Galiè-2016"/><ref name="Fang-2012"/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Vachiéry JL, Adir Y, Barberà JA, Champion H, Coghlan JG, Cottin V, De Marco T, Galiè N, Ghio S, Gibbs JS, Martinez F, Semigran M, Simonneau G, Wells A, Seeger W | display-authors = 6 | title = Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart diseases | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 62 | issue = 25 Suppl | pages = D100–D108 | date = December 2013 | pmid = 24355634 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.033 | hdl-access = free | doi-access = free | hdl = 11585/534481 }}</ref> | |||
| In chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (WHO Group IV), the blood vessels are blocked or narrowed with recurrent blood clots, and these clots can lead to release of substances that cause the blood vessels to constrict. This combination of blocked or narrowed vessels and vasoconstriction once again increases the resistance to blood flow and so the pressure within the system rises. | |||
| In pulmonary hypertension due to lung diseases and/or hypoxia (WHO Group III), low levels of oxygen in the ] (due to respiratory disease or living at high altitude) cause constriction of the pulmonary arteries. This phenomenon is called ] and it is initially a protective response to stop too much blood flowing to areas of the lung that are damaged and do not contain oxygen. When the alveolar hypoxia is widespread and prolonged, this hypoxia-mediated vasoconstriction occurs across a large portion of the pulmonary vascular bed and leads to an increase in pulmonary arterial pressure, with thickening of the pulmonary vessel walls contributing to the development of sustained pulmonary hypertension.<ref name=Simonneau098/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Shanks N, Macklin J, Coles S | title = Comparison of oral erythromycin ethylsuccinate and clavulanate-potentiated amoxicillin in the treatment of acute respiratory tract infections | journal = Clinical Therapeutics | volume = 11 | issue = 6 | pages = 812–819 | year = 2009 | pmid = 2692823 | pmc = 2692823 | doi = 10.1016/j.coph.2009.02.006 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sommer N, Dietrich A, Schermuly RT, Ghofrani HA, Gudermann T, Schulz R, Seeger W, Grimminger F, Weissmann N | display-authors = 6 | title = Regulation of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction: basic mechanisms | journal = The European Respiratory Journal | volume = 32 | issue = 6 | pages = 1639–1651 | date = December 2008 | pmid = 19043010 | doi = 10.1183/09031936.00013908 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Stenmark KR, Fagan KA, Frid MG | title = Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: cellular and molecular mechanisms | journal = Circulation Research | volume = 99 | issue = 7 | pages = 675–691 | date = September 2006 | pmid = 17008597 | doi = 10.1161/01.RES.0000243584.45145.3f | doi-access = free }}</ref> Prolonged hypoxia also induces the transcription factor ], which directly activates downstream growth factor signaling that causes irreversible proliferation and remodeling of pulmonary arterial endothelial cells, leading to chronic pulmonary arterial hypertension.{{citation needed|date=August 2020}} | |||
| ==Molecular pathology== | |||
| The molecular mechanism of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is not known yet, but it is believed that the endothelial dysfunction results in a decrease in the synthesis of endothelium-derived vasodilators such as ] and ]. Moreover, there’s a stimulation of the synthesis of vasoconstrictors such as ] and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). These results in a severe vasoconstriction and smooth muscle and ] hypertrophy characteristic of patients with PAH.<ref>Budhiraja R, Tuder RM, Hassoun. PM. Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. ''Circulation''. 2004;109:159–165.</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| In normal conditions, the ] produces nitric oxide from L-arginine in presence of oxygen. Adenylate-cyclase and gualynate-cyclase are activated in presence of nitric oxide and these enzymes produce ] and ] respectively. The cGMP is produced by a type of guanylate cyclase (which is a kind of pyrophosphate-liase cyclase): the soluble guanylate cyclase (or sGC), that catalyzes the formation of cGMP from GTP. sGC is a heterodimer made up of one α subunit and one β sub-unit in each chain. It also contains a prosthetic ], required for NO binding. The union of NO and sGC produces a conformational enzyme change that stimulates cGMP production.<ref name="tesi">Fosfodiesterasas del AMPc y del GMPc en el cerebro: Expresión en procesos neuroinflamatorios y neurodegenerativos. URL: http://www.tesisenred.net/bitstream/handle/10803/891/03.ERI_METODOS.pdf?sequence=4. Viewed 3 November 2012.</ref> | |||
| In chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, or CTEPH (WHO Group IV), the initiating event is thought to be blockage or narrowing of the pulmonary blood vessels with unresolved blood clots; these clots can lead to increased pressure and ] in the rest of the pulmonary circulation, precipitating structural changes in the vessel walls (remodeling) similar to those observed in other types of severe pulmonary hypertension. This combination of vessel occlusion and vascular remodeling once again increases the resistance to blood flow and so the pressure within the system rises.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = McNeil K, Dunning J | title = Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) | journal = Heart | volume = 93 | issue = 9 | pages = 1152–1158 | date = September 2007 | pmid = 17699182 | pmc = 1955041 | doi = 10.1136/hrt.2004.053603 }}</ref><ref name="Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hy">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hoeper MM, Mayer E, Simonneau G, Rubin LJ | title = Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension | journal = Circulation | volume = 113 | issue = 16 | pages = 2011–2020 | date = April 2006 | pmid = 16636189 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.602565 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| In the vascular endothelium, cGMP activates cGMP kinase or ] (protein kinase G), which is an enzyme that belongs to a type of serine/threonine - specific protein ]. PKG is a dimer composed of two similar polypeptides chains that share a common molecular structure. Each subunit contains a catalytic domain and regulatory domain. GMP-kinase activates potassium channels and subsequently the inhibition of calcium channels. Thus, this process leads to a reduction of intracellular calcium and finally a vasodilation.<ref name="ReferenceA">Ghofrani HA, Pepke-Zaba J, Barbera JA, et al. Nitric oxide pathway and phosphodiesterase inhibitors in pulmonary arterial hypertension. ''J Am Coll Cardiol''. 2004;43:68S–72S.</ref> | |||
| ===Molecular pathology=== | |||
| Phosphodiesterase type V (]), which is abundant in the pulmonary tissue, is a metalohydrolase that hydrolyzes the cyclic bond of cGMP in the presence of divalent cations (Zn<sup>2+</sup>). Actually, Zn<sup>2+</sup> union is necessary for PDE5 activity. In the N-terminal region (regulatory domain) of PDE5 there is an aminoacid sequence (residues 142-526) that joins cGMP. This sequence of PDE5 is divided in two domains; GAF-A and GAF-B; but only GAF-A has the necessary affinity to bind cGMP. This union increases the catalytic activity and it is stabilized by a close serine phosphorylation (performed by a kinase). Consequently, the concentration of cGMP decreases and the vasodilation is stopped.<ref name="tesi" /> | |||
| ] | |||
| The molecular mechanism of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is not known yet, but it is believed that the endothelial dysfunction results in a decrease in the synthesis of endothelium-derived vasodilators such as ] and ].<ref name="Budhiraja-2004">{{cite journal | vauthors = Budhiraja R, Tuder RM, Hassoun PM | title = Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension | journal = Circulation | volume = 109 | issue = 2 | pages = 159–165 | date = January 2004 | pmid = 14734504 | doi = 10.1161/01.CIR.0000102381.57477.50 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Moreover, there is a stimulation of the synthesis of vasoconstrictors such as ] and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). These result in a severe vasoconstriction and ] and ] hypertrophy characteristic of patients with PAH.<ref name="Budhiraja-2004"/> | |||
| ====Nitric oxide-soluble guanylate cyclase pathway==== | |||
| Patients with PAH produce less NO and others vasodilators and produce more vasoconstrictors. Consequently, this molecular pathway doesn’t work properly and it results in a constant vasoconstriction. For this reason, NO and PDE5 inhibitors such as tadalafil or sildenafil are possible therapies.<ref name="ReferenceA"/> Tadalafil, for example, causes a vasodilation mediated by nitric oxide in the pulmonary endothelium. | |||
| In normal conditions, the vascular ] produces nitric oxide from L-arginine in the presence of oxygen.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Förstermann U, Münzel T | title = Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: from marvel to menace | journal = Circulation | volume = 113 | issue = 13 | pages = 1708–1714 | date = April 2006 | pmid = 16585403 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.602532 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| This nitric oxide diffuses into neighboring cells (including vascular smooth muscle cells and platelets), where it increases the activity of the enzyme ], leading to increased formation of ] (cGMP) from guanosine triphosphate (GTP).<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Murad F | title = Shattuck Lecture. Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in cell signaling and drug development | journal = The New England Journal of Medicine | volume = 355 | issue = 19 | pages = 2003–2011 | date = November 2006 | pmid = 17093251 | doi = 10.1056/NEJMsa063904 | doi-access = free }}</ref> The cGMP then activates cGMP-dependent kinase or PKG (protein kinase G). Activated PKG promotes vasorelaxation (via a reduction of intracellular calcium levels), alters the expression of genes involved in smooth muscle cell contraction, ] and ], and inhibits ] activation.<ref name="Francis-2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Francis SH, Busch JL, Corbin JD, Sibley D | title = cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cGMP phosphodiesterases in nitric oxide and cGMP action | journal = Pharmacological Reviews | volume = 62 | issue = 3 | pages = 525–563 | date = September 2010 | pmid = 20716671 | pmc = 2964902 | doi = 10.1124/pr.110.002907 }}</ref> Nitric oxide–soluble guanylate cyclase signaling also leads to anti-inflammatory effects.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Zelia OP, Kovalenko FP | title = Comparative efficiency of infecting laboratory animals via intravenous and subcutaneous administration of Schistosoma mansoni cercaria | journal = Parazitologiia | volume = 20 | issue = 6 | pages = 461–465 | year = 2011 | pmid = 3103045 }}</ref> | |||
| ==Diagnosis== | |||
| ] | |||
| Because pulmonary hypertension can be of five major types, a series of tests must be performed to distinguish pulmonary ''arterial'' hypertension from ''venous, hypoxic, thromboembolic,'' or ''miscellaneous'' varieties. | |||
| Phosphodiesterase type 5 (]), which is abundant in the pulmonary tissue, hydrolyzes the cyclic bond of cGMP. Consequently, the concentration of cGMP (and thus PKG activity) decreases.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ghofrani HA, Pepke-Zaba J, Barbera JA, Channick R, Keogh AM, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Kneussl M, Grimminger F | display-authors = 6 | title = Nitric oxide pathway and phosphodiesterase inhibitors in pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 43 | issue = 12 Suppl S | pages = 68S–72S | date = June 2004 | pmid = 15194181 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.02.031 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="Francis-2010"/> | |||
| Further procedures are required to confirm the presence of pulmonary hypertension and exclude other possible diagnoses. These generally include ]s; ]s to exclude ], ] diseases, and liver disease; ] (ECG); ] measurements; ]s of the chest (followed by high-resolution ]ning if ] is suspected); and ventilation-perfusion or ]ning to exclude chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Biopsy of the lung is usually not indicated unless the pulmonary hypertension is thought to be due to an underlying interstitial lung disease; further, lung biopsies are fraught with risks of bleeding due to the high intrapulmonary blood pressure. Clinical improvement is often measured by a "six-minute walk test", i.e. the distance a patient can walk in six minutes. Stability and improvement in this measurement correlate with better survival. | |||
| ====Endothelin==== | |||
| ] | |||
| Diagnosis of PAH requires the presence of pulmonary hypertension. Although pulmonary arterial pressure can be estimated on the basis of ], pressure measurements with a ] through the right side of the heart provides the most definite assessment. PAOP (pulmonary artery occlusion pressure) and PVR (pulmonary vascular resistance) cannot be measured directly with ]. Therefore diagnosis of PAH requires right-sided ]. A Swan-Ganz catheter can also measure the ], which is far more important in measuring disease severity than the pulmonary arterial pressure. | |||
| ] is a peptide (comprising 21 amino acids) that is produced in endothelial cells. It acts on the endothelin receptors ETA and ETB in various cell types including vascular smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts, leading to vasoconstriction, hypertrophy, proliferation, inflammation, and fibrosis. It also acts on ETB receptors in endothelial cells; this leads to the release of both vasoconstrictors and vasodilators from those cells, and clears endothelin-1 from the system.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = McLaughlin VV, McGoon MD | title = Pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = Circulation | volume = 114 | issue = 13 | pages = 1417–1431 | date = September 2006 | pmid = 17000921 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.503540 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Fonseca C, Abraham D, Renzoni EA | title = Endothelin in pulmonary fibrosis | journal = American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology | volume = 44 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–10 | date = January 2011 | pmid = 20448055 | doi = 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0388TR }}</ref> | |||
| Normal pulmonary arterial pressure in a person living at sea level has a mean value of 8–20 mm Hg (1066–2666 Pa) at rest. Pulmonary hypertension is present when mean pulmonary artery pressure exceeds 25 mm Hg (3300 Pa) at rest.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Badesch|first=DB|author2=Champion, HC; Sanchez, MA; Hoeper, MM; Loyd, JE; Manes, A; McGoon, M; Naeije, R; Olschewski, H; Oudiz, RJ; Torbicki, A|title=Diagnosis and assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.|journal=Journal of the American College of Cardiology|date=Jun 30, 2009|volume=54|issue=1 Suppl|pages=S55-66|doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.011|pmid=19555859|url=http://content.onlinejacc.org/article.aspx?articleid=1139838}}</ref> ''Mean'' pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) should not be confused with systolic pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP), which is often reported on ] reports. A systolic pressure of 40 mm Hg typically implies a ''mean'' pressure of more than 25 mm Hg. Roughly, mPAP = 0.61•sPAP + 2. | |||
| ====Prostacyclin and thromboxane==== | |||
| ] is synthesized from arachidonic acid in endothelial cells. In vascular smooth muscle cells, prostacyclin binds mainly to the prostaglandin I receptor. This sends a signal to increase adenylate cyclase activity, which leads to increased synthesis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). This in turn leads to increased cAMP-dependent protein kinase or ] (protein kinase A) activity, ultimately promoting vasodilation and inhibiting cell proliferation. Prostacyclin signaling also leads to anti-thrombotic, anti-fibrotic, and anti-inflammatory effects. Levels of cAMP (which mediates most of the biological effects of prostacyclin) are reduced by ] 3 and 4.<ref name="Archer SL 2010">{{cite journal | pmid=2869481 | date=1986 | last1=Wood | first1=S. F. | title=Astemizole and terfenadine compared in hay fever | journal=The Practitioner | volume=230 | issue=1411 | pages=41–44 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gomberg-Maitland M, Olschewski H | title = Prostacyclin therapies for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = The European Respiratory Journal | volume = 31 | issue = 4 | pages = 891–901 | date = April 2008 | pmid = 18378784 | doi = 10.1183/09031936.00097107 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| The vasoconstrictor thromboxane is also synthesized from arachidonic acid. In PAH, the balance is shifted away from synthesis of prostacyclin toward synthesis of thromboxane.<ref name="Archer SL 2010"/> | |||
| ====Other pathways==== | |||
| The three pathways described above are all targeted by currently available medical therapies for PAH. However, several other pathways have been identified that are also altered in PAH and are being investigated as potential targets for future therapies. For example, the ] enzyme ] (PDK) is pathologically activated in PAH, causing a metabolic shift from ] to ] and leading to increased cell proliferation and impaired apoptosis.<ref name="Archer SL 2010"/><ref name="Gomberg-Maitland M 2013">{{cite journal | vauthors = Lenfant M | title = | journal = Biochimie | volume = 54 | issue = 2 | pages = 283–285 | year = 2013 | pmid = 4117578 | pmc = 4117578 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.026 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide, a potent vasodilator with anti-inflammatory and immune-modulatory roles, is reduced in PAH, while expression of its receptor is increased.<ref name="Archer SL 2010"/><ref name="Gomberg-Maitland M 2013"/> | |||
| Plasma levels of ], which promotes vasoconstriction, hypertrophy and proliferation, are increased in patients with PAH, although the role played by serotonin in the pathogenesis of PAH remains uncertain.<ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/><ref name="Archer SL 2010"/> The expression or activity of several growth factors (including ], ], ], and ]) is increased and contributes to vascular remodeling in PAH.<ref name="Archer SL 2010"/> Other factors underlying the proliferative state of pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells include ]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lawrie A | title = The role of the osteoprotegerin/tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand axis in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = Vascular Pharmacology | volume = 63 | issue = 3 | pages = 114–117 | date = December 2014 | pmid = 25446166 | doi = 10.1016/j.vph.2014.10.002 }}</ref> and ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Braithwaite AT, Marriott HM, Lawrie A | title = Divergent Roles for TRAIL in Lung Diseases | journal = Frontiers in Medicine | volume = 5 | page = 212 | date = 2018 | pmid = 30101145 | pmc = 6072839 | doi = 10.3389/fmed.2018.00212 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Focusing only on the pulmonary vasculature provides an incomplete picture of PAH; the ability of the right ventricle to adapt to the increased workload varies between patients and is an important determinant of survival. The molecular pathology of PAH in the right ventricle is therefore also being investigated, and recent research has shifted to consider the cardiopulmonary unit as a single system rather than two separate systems. Importantly, right ventricular remodeling is associated with increased apoptosis; this is in contrast to pulmonary vascular remodeling which involves inhibition of apoptosis.<ref name="Vonk-Noordegraaf A 2013"/> | |||
| Even though the primary cause of PAH is unknown, ] and ] have been shown to have a key role in vascular remodeling.<ref name = Ranchoux2016>{{cite journal |vauthors=Ranchoux B, Meloche J, Paulin R, Boucherat O, Provencher S, Bonnet S |title=DNA Damage and Pulmonary Hypertension |journal=Int J Mol Sci |volume=17 |issue=6 |pages=990 |date=June 2016 |pmid=27338373 |pmc=4926518 |doi=10.3390/ijms17060990 |doi-access=free}}</ref> These factors are known to cause ], and may also promote the proliferative and ]-resistant phenotype that is observed in PAH vascular cells.<ref name = Ranchoux2016/> Elevated levels of DNA damage have been reported to occur in PAH lungs and remodeled arteries, and also in animal models of PH, indicating that DNA damage likely contributes to PAH pathogenesis.<ref name = Ranchoux2016/> | |||
| ==Diagnosis== | |||
| ] pulse tracing demonstrates a prominent a wave without a c or v wave being observed. The ] (fourth left interspace and cardiac apex) show a murmur of tricuspid insufficiency and ventricular and atrial gallops.]] | |||
| ] ] | |||
| In terms of the diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension, it has five major types, and a series of tests must be performed to distinguish pulmonary arterial hypertension from venous, hypoxic, thromboembolic, or unclear multifactorial varieties. PAH is diagnosed after exclusion of other possible causes of pulmonary hypertension.<ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/> | |||
| ===Physical examination=== | ===Physical examination=== | ||
| A ] is performed to look for typical signs of pulmonary hypertension (described ]),<ref name="nih">{{Cite web|title = How Is Pulmonary Hypertension Diagnosed? – NHLBI, NIH|url = http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pah/diagnosis|website = www.nhlbi.nih.gov|access-date = 2015-12-30|url-status = live|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160105180446/http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pah/diagnosis|archive-date = 2016-01-05}}</ref> and a detailed family history is established to determine whether the disease might be ].<ref>{{Cite book | vauthors = Austin ED, Phillips III JA, Loyd JE | chapter = Pulmonary arterial hypertension| chapter-url = http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/pulmonary-arterial-hypertension | veditors = Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LH, Gripp KW, Amemiya A | title = Genetics Home Reference|date = 2015-12-28|access-date = 2015-12-30|url-status = live|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20151224100323/http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/pulmonary-arterial-hypertension|archive-date = 2015-12-24}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book | chapter-url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1485/ |id=NBK1485 |publisher = University of Washington, Seattle|date = January 1993|location = Seattle (WA)|pmid = 20301658| vauthors = Austin ED, Loyd JE, Phillips JA | chapter = Heritable Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Overview | title = GeneReviews | veditors = Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJ, Bird TD, Fong C, Mefford HC }}</ref><ref name="Hoeper-2013">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hoeper MM, Bogaard HJ, Condliffe R, Frantz R, Khanna D, Kurzyna M, Langleben D, Manes A, Satoh T, Torres F, Wilkins MR, Badesch DB | display-authors = 6 | title = Definitions and diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 62 | issue = 25 Suppl | pages = D42–D50 | date = December 2013 | pmid = 24355641 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.032 | doi-access = free }}</ref> A history of exposure to drugs such as ] (a ] derivative), ], ], ], ] leading to ], and ] leading to ] is considered significant.<ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/><ref>{{Cite book|title = Drug Safety Data: How to Analyze, Summarize and Interpret to Determine Risk|url = https://books.google.com/books?id=Rj7KAcOspvcC|publisher = Jones & Bartlett Learning|date = 2010-10-25|page = 86|isbn = 978-0-7637-6912-3| vauthors = Klepper MJ, Cobert B |url-status = live|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160504000601/https://books.google.com/books?id=Rj7KAcOspvcC|archive-date = 2016-05-04}}</ref><ref name="Simonneau-2013"/> Use of ] during pregnancy (particularly late pregnancy) is associated with an increased risk of the baby developing ].<ref name="Simonneau-2013" /> | |||
| A ] is performed to look for typical signs of pulmonary hypertension. These include altered ], such as a widely split S<sub>2</sub> or second heart sound, a loud P<sub>2</sub> or ] closure sound (part of the second heart sound), (para)sternal heave, possible S<sub>3</sub> or ], and ]. Other signs include an elevated ], ] (swelling of the ankles and feet), ] (abdominal swelling due to the accumulation of fluid), ], and ]. | |||
| ===Echocardiography=== | ===Echocardiography=== | ||
| A ] of ] for predicting right heart catheterization reported a ] and |
If pulmonary hypertension is suspected based on the above assessments, echocardiography is performed as the next step.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/><ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/><ref name="Hoeper-2013"/> A ] of ] for predicting the results of right heart catheterization reported a ] of 88% and 56%, respectively.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Taleb M, Khuder S, Tinkel J, Khouri SJ | title = The diagnostic accuracy of Doppler echocardiography in assessment of pulmonary artery systolic pressure: a meta-analysis | journal = Echocardiography | volume = 30 | issue = 3 | pages = 258–265 | date = March 2013 | pmid = 23227919 | doi = 10.1111/echo.12061 | s2cid = 7460778 }}</ref> Thus, Doppler echocardiography can suggest the presence of pulmonary hypertension, but right heart catheterization (described below) remains the gold standard for diagnosis of PAH.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/><ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/> | ||
| Echocardiography can also help to detect congenital heart disease as a cause of pulmonary hypertension.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/> | |||
| ===Exclude other diseases=== | |||
| If the echocardiogram is compatible with a diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension, common causes of pulmonary hypertension (left heart disease and lung disease) are considered and further tests are performed accordingly. These tests generally include ] (ECG), ] including lung diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide and ] measurements, ] of the chest and high-resolution computed tomography (CT) scanning.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/><ref name="McLaughlin-2009"/><ref name="Hoeper-2013"/><ref>{{cite web |title=How Is Pulmonary Hypertension Diagnosed? |url=https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/node/4225 |publisher=National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute }}</ref> | |||
| ==== Ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy ==== | |||
| If heart disease and lung disease have been excluded, a ventilation/perfusion scan is performed to rule out CTEPH. If unmatched perfusion defects are found, further evaluation by CT pulmonary angiography, right heart catheterization, and selective pulmonary angiography is performed.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/><ref name="Hoeper-2013"/> | |||
| ===CT scan=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Signs of pulmonary hypertension on ] of the chest are: | |||
| * Enlargement of the ] (measured at its bifurcation). It is, however, a poor predictor of pulmonary hypertension in patients with ].<ref name=Radiopaedia>{{cite web |url= https://radiopaedia.org/articles/pulmonary-hypertension-1 |title= Pulmonary hypertension |website= ] | vauthors = Gaillard F |access-date= 2018-03-12}}</ref> | |||
| :*A diameter of more than 27 mm for women and 29 mm for men is suggested as a ].<ref name=Radiopaedia/> | |||
| :*A ] of 31.6 mm may be a more statistically robust in individuals without ].<ref name=Radiopaedia/> | |||
| * Increased ratio of the diameter of the main pulmonary artery (pulmonary trunk) to the ] (measured at its bifurcation). | |||
| :*A ratio of 1.0 is suggested as a cutoff in adults.<ref name=Radiopaedia/> | |||
| :*Cutoff ~1.09 in children.<ref name=Radiopaedia/> | |||
| * Increased diameter ratio of segmental arteries to bronchi. This finding in three or four lobes, in the presence of a dilated pulmonary trunk (≥29 mm), and absence of significant structural lung disease confers a specificity of 100% for pulmonary hypertension.<ref name=Radiopaedia/> | |||
| * Mural calcification in central pulmonary arteries is most frequently seen in patients with ].<ref name=Radiopaedia/> | |||
| ===Right heart catheterization=== | |||
| Although pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP) can be estimated on the basis of ],<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bossone E, D'Andrea A, D'Alto M, Citro R, Argiento P, Ferrara F, Cittadini A, Rubenfire M, Naeije R | display-authors = 6 | title = Echocardiography in pulmonary arterial hypertension: from diagnosis to prognosis | journal = Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography | volume = 26 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–14 | date = January 2013 | pmid = 23140849 | doi = 10.1016/j.echo.2012.10.009 }}</ref> pressure measurements with a Swan-Ganz catheter inserted through the right side of the heart provide the most definite assessment. Pulmonary hypertension is defined as a mean PAP of at least 20 mm Hg (3300 Pa) at rest, and PAH is defined as precapillary pulmonary hypertension (i.e. mean PAP ≥ 20 mm Hg with pulmonary arterial occlusion pressure ≤ 15 mm Hg and pulmonary vascular resistance > 3 Wood Units).<ref name="Hoeper-2013"/> PAOP and PVR cannot be measured directly with echocardiography. Therefore, diagnosis of PAH requires right-sided cardiac catheterization. A Swan-Ganz catheter can also measure the cardiac output; this can be used to calculate the cardiac index, which is far more important in measuring disease severity than the pulmonary arterial pressure.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/><ref>{{cite encyclopedia |title=Swan-Ganz – right heart catheterization |date=2022 |encyclopedia=Medical Encyclopedia |publisher=MedlinePlus, National Library of Medicine |url=https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003870.htm}}</ref> | |||
| ''Mean'' PAP (mPAP) should not be confused with systolic PAP (sPAP), which is often reported on echocardiogram reports. A systolic pressure of 40 mm Hg typically implies a mean pressure of more than 25 mm Hg. Roughly, mPAP = 0.61•sPAP + 2.<ref>{{cite book | vauthors = Khouri SJ, Pandya U | date = 2012 | chapter = Pulmonary hypertension. | veditors = Garcia MJ | title = NonInvasive cardiovascular imaging: a multimodality approach | publisher = Lippincott Williams & Wilkins | pages = 655–668 }}</ref> Due to the invasive nature of this procedure, the use of computational fluid dynamics based hemodynamic indices have been postulated.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Piskin S, Patnaik SS, Han D, Bordones AD, Murali S, Finol EA | title = A canonical correlation analysis of the relationship between clinical attributes and patient-specific hemodynamic indices in adult pulmonary hypertension | journal = Medical Engineering & Physics | volume = 77 | pages = 1–9 | date = March 2020 | pmid = 32007361 | pmc = 7069525 | doi = 10.1016/j.medengphy.2020.01.006 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Pillalamarri NR, Piskin S, Patnaik SS, Murali S, Finol EA | title = Patient-Specific Computational Analysis of Hemodynamics in Adult Pulmonary Hypertension | journal = Annals of Biomedical Engineering | volume = 49 | issue = 12 | pages = 3465–3480 | date = December 2021 | pmid = 34799807 | pmc = 8684831 | doi = 10.1007/s10439-021-02884-y }}</ref> | |||
| ===Other=== | |||
| For people considered likely to have PAH based on the above tests, the specific associated condition is then determined based on the physical examination, medical/family history and further specific diagnostic tests (for example, ] tests to detect underlying connective tissue disease, HIV infection or hepatitis, ] to confirm the presence of portal hypertension, echocardiography/cardiac ] for congenital heart disease, laboratory tests for schistosomiasis, and high-resolution CT for PVOD and pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis). Routine lung biopsy is discouraged in patients with PAH, because of the risk to the patient and because the findings are unlikely to alter the diagnosis and treatment.<ref name="Galiè-2016"/><ref name="Galie N 2009"/><ref name="Hoeper-2013"/> | |||
| ==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
| Treatment of pulmonary hypertension is determined by whether the PH is arterial, venous, hypoxic, thromboembolic, or miscellaneous. If it is caused by left heart disease, the treatment is to optimize left ventricular function by the use of medication or to repair/replace the ] or ].<ref>{{Cite web|title = How Is Pulmonary Hypertension Treated? – NHLBI, NIH|url = https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pah/treatment|website = www.nhlbi.nih.gov|access-date = 2015-12-30|url-status = live|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160105180457/http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pah/treatment|archive-date = 2016-01-05}}</ref> Patients with left heart failure or ] lung diseases (groups II or III pulmonary hypertension) should not routinely be treated with vasoactive agents including prostanoids, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, or endothelin antagonists, as these are approved for the different condition called primary pulmonary arterial hypertension.<ref name="ACCPandATSfive">{{Citation |author1 = American College of Chest Physicians |author1-link = American College of Chest Physicians |author2 = American Thoracic Society |author2-link = American Thoracic Society |date = September 2013 |title = Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question |publisher = American College of Chest Physicians and American Thoracic Society |work = ]: an initiative of the ] |url = http://www.choosingwisely.org/doctor-patient-lists/american-college-of-chest-physicians-and-american-thoracic-society/ |access-date = 6 January 2013 |url-status = live |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20131103063427/http://www.choosingwisely.org/doctor-patient-lists/american-college-of-chest-physicians-and-american-thoracic-society/ |archive-date = 3 November 2013 }}, which cites | |||
| Treatment is determined by whether the PH is arterial, venous, hypoxic, thromboembolic, or miscellaneous. Since pulmonary ''venous'' hypertension is synonymous with ], the treatment is to optimize left ventricular function by the use of ]s, ]s, ]s etc., or to repair/replace the ] or ]. | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, McGoon MD, Park MH, Rosenson RS, Rubin LJ, Tapson VF, Varga J, Harrington RA, Anderson JL, Bates ER, Bridges CR, Eisenberg MJ, Ferrari VA, Grines CL, Hlatky MA, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Lichtenberg RC, Lindner JR, Moliterno DJ, Mukherjee D, Pohost GM, Rosenson RS, Schofield RS, Shubrooks SJ, Stein JH, Tracy CM, Weitz HH, Wesley DJ | display-authors = 6 | title = ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association: developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society, Inc., and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association | journal = Circulation | volume = 119 | issue = 16 | pages = 2250–2294 | date = April 2009 | pmid = 19332472 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192230 | doi-access = free }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Galiè N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA, Beghetti M, Corris P, Gaine S, Gibbs JS, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Jondeau G, Klepetko W, Opitz C, Peacock A, Rubin L, Zellweger M, Simonneau G | display-authors = 6 | title = Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) | journal = European Heart Journal | volume = 30 | issue = 20 | pages = 2493–2537 | date = October 2009 | pmid = 19713419 | doi = 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp297 | doi-access = free }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Hoeper MM, Barberà JA, Channick RN, Hassoun PM, Lang IM, Manes A, Martinez FJ, Naeije R, Olschewski H, Pepke-Zaba J, Redfield MM, Robbins IM, Souza R, Torbicki A, McGoon M | display-authors = 6 | title = Diagnosis, assessment, and treatment of non-pulmonary arterial hypertension pulmonary hypertension | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 54 | issue = 1 Suppl | pages = S85–S96 | date = June 2009 | pmid = 19555862 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.008 | doi-access = free }}</ref> To make the distinction, doctors at a minimum will conduct ] of the right heart, echocardiography, chest CT, a seven-minute walk test, and ].<ref name=ACCPandATSfive/> Using treatments for other kinds of pulmonary hypertension in patients with these conditions can harm the patient and wastes substantial medical resources.<ref name=ACCPandATSfive/> | |||
| High-dose ]s are useful in only 5% of IPAH patients who are ''vasoreactive'' by ]. Calcium channel blockers have been largely misused, being prescribed to many patients with non-vasoreactive PAH, leading to excess morbidity and mortality.<ref name=emed/> The criteria for vasoreactivity have changed. Only those patients whose ''mean'' pulmonary artery pressure falls by more than 10 mm Hg to less than 40 mm Hg with an unchanged or increased cardiac output when challenged with ], ], or ] are considered vasoreactive.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Barst RJ, McGoon M, Torbicki A, Sitbon O, Krowka MJ, Olschewski H, Gaine S | title = Diagnosis and differential assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 43 | issue = 12 Suppl S | pages = 40S–47S | date = June 2004 | pmid = 15194177 | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.02.032 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Of these, only half of the patients are responsive to calcium channel blockers in the long term.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sitbon O, Humbert M, Jaïs X, Ioos V, Hamid AM, Provencher S, Garcia G, Parent F, Hervé P, Simonneau G | display-authors = 6 | title = Long-term response to calcium channel blockers in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = Circulation | volume = 111 | issue = 23 | pages = 3105–3111 | date = June 2005 | pmid = 15939821 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.488486 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| Patients with left heart failure or ] lung diseases (groups II or III pulmonary hypertension) should not routinely be treated with vasoactive agents including prostanoids, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, or endothelin antagonists, as these are approved for the different condition called pulmonary arterial hypertension.<ref name="ACCPandATSfive">{{Citation |author1 = American College of Chest Physicians |author1-link = American College of Chest Physicians |author2 = American Thoracic Society |author2-link = American Thoracic Society |date = September 2013 |title = Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question |publisher = American College of Chest Physicians and American Thoracic Society |work = ]: an initiative of the ] |page = |url = http://www.choosingwisely.org/doctor-patient-lists/american-college-of-chest-physicians-and-american-thoracic-society/ |accessdate = 6 January 2013}}, which cites | |||
| *{{Cite journal | last1 = McLaughlin | first1 = V. V. | last2 = Archer | first2 = S. L. | last3 = Badesch | first3 = D. B. | last4 = Barst | first4 = R. J. | last5 = Farber | first5 = H. W. | last6 = Lindner | first6 = J. R. | last7 = Mathier | first7 = M. A. | last8 = McGoon | first8 = M. D. | last9 = Park | first9 = M. H. | last10 = Rosenson | first10 = R. S. | last11 = Rubin | first11 = L. J. | last12 = Tapson | first12 = V. F. | last13 = Varga | first13 = J. | last14 = Harrington | first14 = R. A. | last15 = Anderson | first15 = J. L. | last16 = Bates | first16 = E. R. | last17 = Bridges | first17 = C. R. | last18 = Eisenberg | first18 = M. J. | last19 = Ferrari | first19 = V. A. | last20 = Grines | first20 = C. L. | last21 = Hlatky | first21 = M. A. | last22 = Jacobs | first22 = A. K. | last23 = Kaul | first23 = S. | last24 = Lichtenberg | first24 = R. C. | last25 = Lindner | first25 = J. R. | last26 = Moliterno | first26 = D. J. | last27 = Mukherjee | first29 = R. S. | first28 = G. M. | last29 = Rosenson | last28 = Pohost | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192230 | last30 = Schofield | title = ACCF/AHA 2009 Expert Consensus Document on Pulmonary Hypertension: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association: Developed in Collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society, Inc., and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association | first30 = R. S. | first27 = D. | journal = Circulation | volume = 119 | issue = 16 | pages = 2250–2294 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19332472 | pmc = }}*{{Cite journal | last1 = Galie | first1 = N. | last2 = Hoeper | first2 = M. M. | last3 = Humbert | first3 = M. | last4 = Torbicki | first4 = A. | last5 = Vachiery | first5 = J. -L. | last6 = Barbera | first6 = J. A. | last7 = Beghetti | first7 = M. | last8 = Corris | first8 = P. | last9 = Gaine | first9 = S. | last10 = Gibbs | first10 = J. S. | last11 = Gomez-Sanchez | first11 = M. A. | last12 = Jondeau | first12 = G. | last13 = Klepetko | first13 = W. | last14 = Opitz | first14 = C. | last15 = Peacock | first15 = A. | last16 = Rubin | first16 = L. | last17 = Zellweger | first17 = M. | last18 = Simonneau | first18 = G.| last19 = Vahanian | first19 = A. | last20 = Auricchio | first20 = A. | last21 = Bax | first21 = J. | last22 = Ceconi | first22 = C. | last23 = Dean | first23 = V. | last24 = Filippatos | first24 = G. | last25 = Funck-Brentano | first25 = C. | last26 = Hobbs | first26 = R. | last27 = Kearney | first27 = P.| last28 = McDonagh | first28 = T. | last29 = McGregor | first29 = K. | last30 = Popescu | first30 = B. A.| author31 = ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG) | title = Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT)| doi = 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp297 | journal = European Heart Journal | volume = 30 | issue = 20 | pages = 2493–2537 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19713419| pmc = | displayauthors = 30 }}*{{Cite journal | last1 = Hoeper | first1 = M. M. | last2 = Barberà | first2 = J. A. | last3 = Channick | first3 = R. N. | last4 = Hassoun | first4 = P. M. | last5 = Lang | first5 = I. M. | last6 = Manes | first6 = A. | last7 = Martinez | first7 = F. J. | last8 = Naeije | first8 = R. | last9 = Olschewski | first9 = H. | last10 = Pepke-Zaba | first10 = J. | last11 = Redfield | first11 = M. M. | last12 = Robbins | first12 = I. M. | last13 = Souza | first13 = R. R. | last14 = Torbicki | first14 = A. | last15 = McGoon | first15 = M. | title = Diagnosis, Assessment, and Treatment of Non-Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Pulmonary Hypertension | doi = 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.008 | journal = Journal of the American College of Cardiology | volume = 54 | issue = 1 Suppl | pages = S85–S96 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19555862 | pmc = }}</ref> To make the distinction, doctors at a minimum will conduct ] of the right heart, echocardiography, chest CT, a six-minute walk test, and ].<ref name="ACCPandATSfive"/> Using treatments for other kinds of pulmonary hypertension in patients with these conditions can harm the patient and wastes substantial medical resources.<ref name="ACCPandATSfive"/> | |||
| A number of agents have recently been introduced for primary and secondary PAH. The trials supporting the use of these agents have been relatively small, and the only measure consistently used to compare their effectivity is the "six-minute walk test". Many have no data on mortality benefit or time to progression.<ref name=Torres07>{{cite journal | vauthors = Torres F | title = Systematic review of randomised, double-blind clinical trials of oral agents conducted in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = International Journal of Clinical Practice | volume = 61 | issue = 10 | pages = 1756–1765 | date = October 2007 | pmid = 17877662 | doi = 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01545.x | s2cid = 1191543 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| High dose ]s are useful in only 5% of IPAH patients who are ''vasoreactive'' by ]. Unfortunately, calcium channel blockers have been largely misused, being prescribed to many patients with non-vasoreactive PAH, leading to excess morbidity and mortality. The criteria for vasoreactivity have changed. Only those patients whose ''mean'' pulmonary artery pressure falls by more than 10 mm Hg to less than 40 mm Hg with an unchanged or increased cardiac output when challenged with ], ], or ] are considered vasoreactive.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Barst RJ, McGoon M, Torbicki A, ''et al.'' |title=Diagnosis and differential assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension |journal=J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. |volume=43 |issue=12 Suppl S |pages=40S–47S |date=June 2004 |pmid=15194177 |doi=10.1016/j.jacc.2004.02.032}}</ref> Of these, only half of the patients are responsive to ]s in the long term.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Sitbon O, Humbert M, Jaïs X, ''et al.'' |title=Long-term response to calcium channel blockers in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension |journal=Circulation |volume=111 |issue=23 |pages=3105–11 |date=June 2005 |pmid=15939821 |doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.488486 |url=http://circ.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/short/111/23/3105}}</ref> | |||
| ] (Winrevair) was approved for medical use in the United States in March 2024.<ref>{{cite press release | title=FDA Approves Merck's Winrevair (sotatercept-csrk), a First-in-Class Treatment for Adults with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH, WHO* Group 1) | publisher=Merck | date=27 March 2024 | url=https://www.merck.com/news/fda-approves-mercks-winrevair-sotatercept-csrk-a-first-in-class-treatment-for-adults-with-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-pah-who-group-1/ | access-date=27 March 2024}}</ref> | |||
| A number of agents have recently been introduced for primary and secondary PAH. The trials supporting the use of these agents have been relatively small, and the only measure consistently used to compare their effectivity is the "6 minute walk test". Many have no data on mortality benefit or time to progression.<ref name="pmid17877662">{{cite journal |author=Torres F |title=Systematic review of randomised, double-blind clinical trials of oral agents conducted in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension |journal=Int. J. Clin. Pract. |volume=61 |issue=10 |pages=1756–65 |year=2007 |pmid=17877662 |doi=10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01545.x|url=http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01545.x}}</ref> | |||
| '''Exercise-based rehabilitation''' | |||
| ===Vasoactive substances=== | |||
| Many pathways are involved in the abnormal proliferation and contraction of the ] cells of the pulmonary arteries in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Three of these pathways are important since they have been targeted with drugs — ]s, ] type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, and prostacyclin derivatives. | |||
| A 2023 Cochrane review found that exercise-based rehabilitation may lead to a large increase in exercise capacity and an improvement in ], without significantly increasing adverse events.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Morris NR, Kermeen FD, Jones AW, Lee JY, Holland AE | title = Exercise-based rehabilitation programmes for pulmonary hypertension | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2023 | issue = 3 | pages = CD011285 | date = March 2023 | pmid = 36947725 | pmc = 10032353 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD011285.pub3 | collaboration = Cochrane Airways Group }}</ref> | |||
| Because inexpensive generic drugs for this disease are not widely available, the World Health Organization does not include them in its model list of ]. | |||
| ===Vasoactive substances=== | |||
| Many pathways are involved in the abnormal proliferation and contraction of the ] cells of the pulmonary arteries in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Three of these pathways are important since they have been targeted with drugs – ]s, ] type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, and prostacyclin derivatives.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Raja SG, Raja SM | title = Treating pulmonary arterial hypertension: current treatments and future prospects | journal = Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease | volume = 2 | issue = 6 | pages = 359–370 | date = November 2011 | pmid = 23251761 | pmc = 3513893 | doi = 10.1177/2040622311420773 }}</ref> | |||
| ====Prostaglandins==== | ====Prostaglandins==== | ||
| ] (] I<sub>2</sub>) is commonly considered the most effective treatment for PAH. ] (synthetic |
] (] I<sub>2</sub>) is commonly considered the most effective treatment for PAH. ] (synthetic prostacyclin) is given via continuous infusion that requires a semi-permanent ]. This delivery system can cause ] and ]. Prostacyclin is unstable, and therefore has to be kept on ice during administration. Since it has a half-life of 3 to 5 minutes, the infusion has to be continuous, and interruption can be fatal.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Safdar Z | title = Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: the role of prostacyclin and prostaglandin analogs | journal = Respiratory Medicine | volume = 105 | issue = 6 | pages = 818–827 | date = June 2011 | pmid = 21273054 | doi = 10.1016/j.rmed.2010.12.018 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Other ]s have therefore been developed. ] can be given intravenously or subcutaneously, but the subcutaneous form can be very painful. An increased risk of sepsis with intravenous Remodulin has been reported by the ]. ] is also used in Europe intravenously and has a longer half life. Iloprost was the only inhaled form of prostacyclin approved for use in the US and Europe, until the inhaled form of treprostinil was approved by the FDA in July 2009.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=022387 | title=Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs }}</ref> | ||
| ====Endothelin receptor antagonists==== | ====Endothelin receptor antagonists==== | ||
| The dual (ET<sub>A</sub> and ET<sub>B</sub>) ] receptor antagonist ] |
Moderate quality evidence suggests that endothelin receptor antagonists improve exercise capacity and decrease symptoms severity.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Liu C, Chen J, Gao Y, Deng B, Liu K | title = Endothelin receptor antagonists for pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2021 | issue = 3 | pages = CD004434 | date = March 2021 | pmid = 33765691 | pmc = 8094512 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD004434.pub6 | collaboration = Cochrane Airways Group }}</ref> The dual (ET<sub>A</sub> and ET<sub>B</sub>) ] receptor antagonist ] was approved in 2001. ] is another ET<sub>A</sub> and ET<sub>B</sub> dual endothelin receptor blocker that is used.<ref name="Hassoun 2021" /> ] (Thelin) was approved for use in Canada, Australia, and the European Union,<ref name="Thelin">{{cite news |date=2008-05-30 |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/governmentFilingsNews/idUSBNG28335020070530 |title=UPDATE 1-Encysive gets Canadian approval for hypertension drug |newspaper=Reuters |access-date=2007-07-08 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070704163058/http://www.reuters.com/article/governmentFilingsNews/idUSBNG28335020070530 |archive-date=2007-07-04 }}</ref> but not in the United States. In 2010, Pfizer withdrew sitaxentan worldwide because of fatal liver complications.<ref>{{cite web |title=Citing Liver Damage, Pfizer Withdraws Thelin – CBS Detroit |url=https://www.cbsnews.com/detroit/news/citing-liver-damage-pfizer-withdraws-thelin/ |website=www.cbsnews.com |date=10 December 2010}}</ref> A similar drug, ] (which is a ET<sub>A</sub> endothelin receptor blocker) is sold under the brand name Letairis in the US by ].<ref>{{cite press release | title = U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approves Gilead's Letairis Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension | publisher = ] | date = 2007-06-15 | url = http://www.gilead.com/wt/sec/pr_1016053 | access-date = 2007-06-16 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20070927064048/http://www.gilead.com/wt/sec/pr_1016053 | archive-date = 2007-09-27 }}</ref> | ||
| ====Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors==== | ====Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors==== | ||
| The |
The US FDA approved ], a selective inhibitor of ] (PDE5), for the treatment of PAH in 2005. It is marketed for PAH as Revatio. In 2009, they also approved ], another PDE5 inhibitor, marketed under the name Adcirca.<ref>{{cite press release|date=2009-05-26|url=http://www.news-medical.net/news/2009/05/26/FDA-approves-Adcirca-(tadalafil)-tablets-for-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension.aspx|title=FDA approves Adcirca (tadalafil) tablets for pulmonary arterial hypertension|access-date=2010-12-06|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101203185840/http://www.news-medical.net/news/2009/05/26/FDA-approves-Adcirca-(tadalafil)-tablets-for-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension.aspx|archive-date=2010-12-03}}</ref> PDE5 inhibitors are believed to increase pulmonary artery vasodilation, and inhibit vascular remodeling, thus lowering pulmonary arterial pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Duarte JD, Hanson RL, Machado RF | title = Pharmacologic treatments for pulmonary hypertension: exploring pharmacogenomics | journal = Future Cardiology | volume = 9 | issue = 3 | pages = 335–349 | date = May 2013 | pmid = 23668740 | pmc = 3864092 | doi = 10.2217/fca.13.6 }}</ref> | ||
| Tadalafil is taken orally, as well as sildenafil, and it is rapidly absorbed (serum levels are detectable at 20 minutes). The T<sub>1/2</sub> (]) hovers around 17.5 hours in healthy subjects.<ref name="ciatacio2">{{cite journal | vauthors = Forgue ST, Patterson BE, Bedding AW, Payne CD, Phillips DL, Wrishko RE, Mitchell MI | title = Tadalafil pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects | journal = British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology | volume = 61 | issue = 3 | pages = 280–288 | date = March 2006 | pmid = 16487221 | pmc = 1885023 | doi = 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02553.x }}</ref> Moreover, if we consider pharmacoeconomic implications, patients that take tadalafil would pay two-thirds of the cost of sildenafil therapy.<ref name=Arif11>{{cite journal |vauthors=Arif SA, Poon H |title=Tadalafil: a long-acting phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension |journal=Clin Ther |volume=33 |issue=8 |pages=993–1004 |date=August 2011 |pmid=21762988 |doi=10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.06.008 }}</ref> However, there are some adverse effects of this drug such as headache, diarrhea, nausea, back pain, ], ] and ].<ref name="citacio4">{{cite journal | vauthors = Galiè N, Brundage BH, Ghofrani HA, Oudiz RJ, Simonneau G, Safdar Z, Shapiro S, White RJ, Chan M, Beardsworth A, Frumkin L, Barst RJ | display-authors = 6 | title = Tadalafil therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = Circulation | volume = 119 | issue = 22 | pages = 2894–2903 | date = June 2009 | pmid = 19470885 | doi = 10.1161/circulationaha.108.839274 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| The combination medication ] (Opsynvi) was approved for medical use in Canada in October 2021,<ref>{{cite press release | title=Opsynvi (macitentan and tadalafil) Becomes the First and Only Health Canada-Approved Once Daily Fixed Dose Combination Treatment for Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) | website=] | date=15 October 2021 | url=https://www.jnj.com/media-center/press-releases/opsynvi-macitentan-and-tadalafil-becomes-the-first-and-only-health-canada-approved-once-daily-fixed-dose-combination-treatment-for-patients-with-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-pah | access-date=25 March 2024}}</ref> and in the United States in March 2024.<ref>{{cite web | title = Approval Letter: Opsynvi (macitentan and tadalafil)| url = https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2024/218490Orig1s000ltr.pdf | publisher = U.S. Food and Drug Administration }}</ref><ref>{{cite press release | title=U.S. FDA Approves Opsynvi (macitentan and tadalafil) as the First and Only Once-Daily Single-Tablet Combination Therapy for Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) | website=] | date=22 March 2024 | url=https://www.jnj.com/media-center/press-releases/u-s-fda-approves-opsynvi-macitentan-and-tadalafil-as-the-first-and-only-once-daily-single-tablet-combination-therapy-for-patients-with-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-pah | access-date=25 March 2024}}</ref> | |||
| Tadalafil is taken orally, as well as sildenafil, and it is rapidly absorbed (serum levels are detectable at 20 minutes). The recommended dose is 40 mg in one single dose per day and the T<sub>1/2</sub> (]) hovers around 17.5 hours in healthy subjects.<ref name="ciatacio2">Forgue ST, Patterson BE, Bedding. AW, et al. Tadalafil pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects. ''Br J Clin Pharmacol''. 2005;61:280–288.</ref> Moreover, if we consider pharmacoeconomic implications, patients that take tadalafil would pay ⅔ of the cost of sildenafil therapy.<ref name="citacio3">Sally A. Arif, PharmD, BCPS (Department of Pharmacy Practice, Chicago College of Pharmacy, Midwestern University, Downers Grove, Illinois, and Department of Pharmacy, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois); and Henry Poon, PharmD, BCPS (Department of Pharmacy, James J. Peters VA Medical Center, Bronx, New York). Tadalafil: A Long-Acting Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. 2011;33:993–1004</ref> However, there are some adverse effects of this drug such as headache, diarrhea, nausea, back pain, ], ] and ].<ref name="citacio4">Galié N, Brundage BH, Ghofrani HA, et al. Tadalafil therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. ''Circulation''. 2009;119:2894–2903.</ref> | |||
| ====Activators of soluble guanylate cyclase==== | ====Activators of soluble guanylate cyclase==== | ||
| Soluble ] (sGC) is the intracellular receptor for ]. {{As of|April 2009}}, the sGC activators ] and ] were undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of PAH. |
Soluble ] (sGC) is the intracellular receptor for ]. {{As of|April 2009}}, the sGC activators ] and ] were undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of PAH.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lasker GF, Maley JH, Pankey EA, Kadowitz PJ | title = Targeting soluble guanylate cyclase for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension | journal = Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine | volume = 5 | issue = 2 | pages = 153–161 | date = April 2011 | pmid = 21510726 | pmc = 3108035 | doi = 10.1586/ers.11.9 }}</ref> | ||
| ===Surgical=== | ===Surgical=== | ||
| ] is a surgical procedure that creates a communication between the right and left ]. It relieves pressure on the right side of the heart, but at the cost of lower oxygen levels in blood ( |
] is a surgical procedure that creates a communication between the right and left ]. It relieves pressure on the right side of the heart, but at the cost of lower oxygen levels in blood (]). ] replaces a chronic condition with the ongoing need for treatment.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = George MP, Champion HC, Pilewski JM | title = Lung transplantation for pulmonary hypertension | journal = Pulmonary Circulation | volume = 1 | issue = 2 | pages = 182–191 | date = 2011 | pmid = 22034605 | pmc = 3198646 | doi = 10.4103/2045-8932.83455 | doi-access = free }}</ref> There is a post-surgical ] survival of just over five years.<ref name="SRTR">{{cite web |date=2006-05-01 |url=http://www.ustransplant.org/annual_reports/current/113_surv-new_dh.htm |title=2006 OPTN/SRTR Annual Report |publisher=US Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients |access-date=2007-03-28 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100605083802/http://www.ustransplant.org/annual_reports/current/113_surv-new_dh.htm |archive-date=2010-06-05 }}</ref> | ||
| ] (PTE) is a surgical procedure that is used for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. It is the surgical removal of an organized ] (clot) along with the lining of the pulmonary artery; it is a very difficult, major procedure that is currently performed in a few select centers.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cerveri I, D'Armini AM, Viganò M | title = Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy almost 50 years after the first surgical attempts | journal = Heart | volume = 89 | issue = 4 | pages = 369–370 | date = April 2003 | pmid = 12639858 | pmc = 1769265 | doi = 10.1136/heart.89.4.369 }}</ref> | |||
| ] cures pulmonary arterial hypertension, but leaves the patient with the complications of transplantation, and a post-surgical ] survival of just over five years.<ref name="SRTR">{{cite web |date=2006-05-01 |url=http://www.ustransplant.org/annual_reports/current/113_surv-new_dh.htm |title=2006 OPTN/SRTR Annual Report |publisher=US Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients |accessdate=2007-03-28}}</ref> | |||
| ] (PTE) is a surgical procedure that is used for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. It is the surgical removal of an organized ] (clot) along with the lining of the pulmonary artery; it is a very difficult, major procedure that is currently performed in a few select centers. | |||
| Treatment regimens for hypoxic and miscellaneous varieties of pulmonary hypertension have not been established. However, studies of several agents are currently enrolling patients. Many physicians will treat these diseases with the same medications as for PAH, until better options become available. Such treatment is called ]. | |||
| ===Monitoring=== | ===Monitoring=== | ||
| Established clinical practice guidelines dictate the frequency of pulmonary nodule evaluation and surveillance,<ref name=ACCPandATSfive/><ref>{{Citation |author1 = American College of Chest Physicians |author1-link = American College of Chest Physicians |author2 = American Thoracic Society |author2-link = American Thoracic Society |date = September 2013 |title = Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question |publisher = American College of Chest Physicians and American Thoracic Society |work = ]: an initiative of the ] |url = http://www.choosingwisely.org/doctor-patient-lists/american-college-of-chest-physicians-and-american-thoracic-society/ |access-date = 6 January 2013 |url-status = live |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20131103063427/http://www.choosingwisely.org/doctor-patient-lists/american-college-of-chest-physicians-and-american-thoracic-society/ |archive-date = 3 November 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| Patients are normally monitored through commonly available tests such as: | |||
| patients are normally monitored through commonly available tests such as:{{citation needed|date=October 2016}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{columns-list|colwidth=30em| | |||
| * ] tests | |||
| * ] |
* ] | ||
| * |
* ] tests | ||
| * ]s | |||
| * serial ] | |||
| * Serial ] tests | |||
| * ] or more advanced lung function studies | |||
| * Serial ] | |||
| * ] or more advanced lung function studies | |||
| * Six-minute walk test<ref>Guidelines: Six-minute Walk Test. Accessed: 2015</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| ==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
| ] | |||
| The ] IPAH registry from the 1980s showed an ''untreated'' median survival of 2–3 years from time of diagnosis, with the cause of death usually being right ventricular failure (]).{{citation needed|date=August 2013}} A recent outcome study of those patients who had started treatment with bosentan (Tracleer) showed that 89% patients were alive at 2 years.<ref name="pmid15684287">{{cite journal |author=McLaughlin VV, Sitbon O, Badesch DB, ''et al.'' |title=Survival with first-line bosentan in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension |journal=Eur. Respir. J. |volume=25 |issue=2 |pages=244–9 |year=2005 |pmid=15684287 |doi=10.1183/09031936.05.00054804| url=http://erj.ersjournals.com/cgi/content/full/25/2/244}}</ref> With new therapies, survival rates are increasing.<ref name="pmid11352291">{{cite journal |author=Nauser TD, Stites SW |title=Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension |journal=Am Fam Physician |volume=63 |issue=9 |pages=1789–98 |year=2001 |pmid=11352291 |url=http://www.aafp.org/afp/20010501/1789.html}}</ref> For 2,635 patients enrolled in The Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-term Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Disease Management (REVEAL Registry) from March 2006 to December 2009, 1-, 3-, 5-, and 7-year survival rates were 85%, 68%, 57%, and 49%, respectively. For patients with idiopathic/familial PAH, survival rates were 91%, 74%, 65%, and 59%.<ref name="Chest2012">{{cite journal | |||
| PAH is considered a universally fatal illness, although survival time may vary between individuals. The prognosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (WHO Group I) has an ''untreated'' median survival of 2–3 years from time of diagnosis, with the cause of death usually being right ventricular failure (]).<ref>{{Cite web|title = Pulmonary Hypertension. About Pulmonary Hypertension {{!}} Patient|url = http://patient.info/doctor/pulmonary-hypertension-pro|website = Patient|access-date = 2015-12-30|language = en-GB|url-status = live|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160102193628/http://patient.info/doctor/pulmonary-hypertension-pro|archive-date = 2016-01-02}}</ref> The survival time is variable and depends on many factors.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mouratoglou SA, Bayoumy AA, Noordegraaf AV | title = Prediction Models and Scores in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Review | journal = Current Pharmaceutical Design | volume = 27 | issue = 10 | pages = 1266–1276 | date = 2021 | pmid = 33155897 | doi = 10.2174/1381612824999201105163437 | s2cid = 226272078 }}</ref> A recent outcome study of those patients who had started treatment with ] (Tracleer) showed that 89% of patients were alive at 2 years.<ref name=McLaughlin05>{{cite journal | vauthors = McLaughlin VV, Sitbon O, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Black C, Galiè N, Rainisio M, Simonneau G, Rubin LJ | display-authors = 6 | title = Survival with first-line bosentan in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension | journal = The European Respiratory Journal | volume = 25 | issue = 2 | pages = 244–249 | date = February 2005 | pmid = 15684287 | doi = 10.1183/09031936.05.00054804 | doi-access = free }}</ref> With new therapies, survival rates are increasing. For 2,635 patients enrolled in The Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-term Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Disease Management (REVEAL Registry) from March 2006 to December 2009, 1-, 3-, 5-, and 7-year survival rates were 85%, 68%, 57%, and 49%, respectively. For patients with idiopathic/familial PAH, survival rates were 91%, 74%, 65%, and 59%.<ref name="Chest2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Benza RL, Miller DP, Barst RJ, Badesch DB, Frost AE, McGoon MD | title = An evaluation of long-term survival from time of diagnosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension from the REVEAL Registry | journal = Chest | volume = 142 | issue = 2 | pages = 448–456 | date = August 2012 | pmid = 22281797 | doi = 10.1378/chest.11-1460 }}</ref> Levels of mortality are very high in ] women with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension (WHO Group I). Pregnancy is sometimes described as contraindicated in these women.<ref name="Kaufman-2007">{{cite book | vauthors = Kaufman MH, Stead L, Feig R |title=First aid for the obstetrics & gynecology clerkship |url=https://archive.org/details/maxwellquickmedi00stea |url-access=limited |publisher=McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division |location=New York |year=2007 |page= |isbn=978-0-07-144874-1 }}</ref><ref name="Ghosh-2008">{{cite book | vauthors = Ghosh AK |title=Mayo Clinic Internal Medicine Review |edition=8th |url=https://archive.org/details/mayoclinicintern00ghos_466 |url-access=limited |publisher=Informa Healthcare |year=2008 |page= |isbn=978-1-4200-8478-8 }}</ref><ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110121035550/http://bja.oxfordjournals.org/content/87/2/295.full |date=2011-01-21 }} March 19, 2011</ref> | |||
| | title =An evaluation of long-term survival from time of diagnosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension from the REVEAL Registry. | |||
| | journal =Chest | |||
| | date =August 2012 | |||
| |author=Benza RL, Miller DP, Barst RJ, Badesch DB, Frost AE, McGoon MD. | |||
| | volume =142 | |||
| | issue =2 | |||
| | pages =448–56 | |||
| | url =http://journal.publications.chestnet.org/article.aspx?articleid=1262338 | |||
| | doi =10.1378/chest.11-1460 | |||
| | pmid =22281797 | |||
| | pmc = | |||
| }} </ref> | |||
| Levels of mortality are very high in ] women with severe pulmonary hypertension.<ref name="isbn0-7817-1937-2">{{cite book |title=Kelley's essentials of internal medicine |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |location=Hagerstwon, MD |year=2001 |pages=84 |isbn=0-7817-1937-2 |oclc= |doi= |accessdate=}}</ref> Pregnancy is sometimes described as contraindicated in these women.<ref name="isbn0-19-856978-5">{{cite book |author=Edward Benz; David Weatherall; David Warrell; Cox, Timothy J.; Firth, John B. |title=Oxford textbook of medicine |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=Oxford |year=2005 |pages=1101 |isbn=0-19-856978-5 |oclc= |doi= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="isbn0-07-144874-8">{{cite book |author=Kaufman, Matthew H.; Latha Stead; Feig, Robert |title=First aid for the obstetrics & gynecology clerkship |publisher=McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division |location=New York |year=2007 |pages=100 |isbn=0-07-144874-8 |oclc= |doi= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="isbn1-4200-8478-X">{{cite book |author=Ghosh, Amit K. |title=Mayo Clinic Internal Medicine Review: Eighth Edition (Mayo Clinic Internal Medicine Review) |publisher=Informa Healthcare |location= |year=2008 |pages=55 |isbn=1-4200-8478-X |oclc= |doi= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref> March 19, 2011</ref> | |||
| ==Epidemiology== | ==Epidemiology== | ||
| The epidemiology of IPAH is about 125–150 deaths per year in the U.S., and worldwide the incidence is similar at 4 cases per million. However, in parts of Europe (France), indications are 6 cases per million of IPAH. Females have a higher incidence rate than males (2–9:1).<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Oudiz RJ | title=Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology | website=Medscape Reference | date=6 February 2023 | url=https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/301450-overview#a6?form=fpf}}</ref> | |||
| Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension is a rare disease with an incidence of about 2-3 cases per million per year<ref name="Rudarakanchana">{{cite journal | last=Rudarakanchana | first=N |author2=Trembath RC, Morrell NW | title=New insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension | journal=Thorax | volume=56 | issue=11 | pages=888–890 | date=November 2001 | pmid=11641516 | pmc=1745964 | doi=10.1136/thorax.56.11.888}}</ref> and a prevalence of about 15 per million. Adult females are almost three times as likely to present with IPAH than adult males. The presentation of IPAH within children is more evenly split along gender lines. | |||
| Other forms of PH are far more common. In ], the incidence has been estimated to be 8 to 12% of all patients;<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = York M, Farber HW | title = Pulmonary hypertension: screening and evaluation in scleroderma | journal = Current Opinion in Rheumatology | volume = 23 | issue = 6 | pages = 536–544 | date = November 2011 | pmid = 21934501 | doi = 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32834ba6a7 | s2cid = 19528958 }}</ref> in ] it is rare.<ref>{{cite web| vauthors = Nannini C |title=Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis|website=MedScape.com|url=http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/573647_6|publisher=MedScape|access-date=31 December 2015|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160208104626/http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/573647_6|archive-date=8 February 2016}}</ref> However, in ] it is 4 to 14%,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mittoo S, Fell CD | title = Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus | journal = Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine | volume = 35 | issue = 2 | pages = 249–254 | date = April 2014 | pmid = 24668539 | doi = 10.1055/s-0034-1371537 | url = http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/825749 | access-date = 31 December 2015 | publisher = MedScape | url-status = live | s2cid = 24654448 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20151026125732/http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/825749 | archive-date = 26 October 2015 }}</ref> and in sickle cell disease, it ranges from 20 to 40%.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lee MT, Rosenzweig EB, Cairo MS | title = Pulmonary hypertension in sickle cell disease | journal = Clinical Advances in Hematology & Oncology | volume = 5 | issue = 8 | pages = 585, 645–653| date = August 2007 | pmid = 17982405 }}</ref> Up to 4% of people who develop a ] go on to develop chronic thromboembolic disease including pulmonary hypertension.<ref name="Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hy"/> A small percentage of patients with ] develop pulmonary hypertension with no other disease to explain the high pressure.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Minai OA, Chaouat A, Adnot S | title = Pulmonary hypertension in COPD: epidemiology, significance, and management: pulmonary vascular disease: the global perspective | journal = Chest | volume = 137 | issue = 6 Suppl | pages = 39S–51S | date = June 2010 | pmid = 20522579 | doi = 10.1378/chest.10-0087 }}</ref> On the other hand, ] is very commonly associated with right ] due to pulmonary hypertension.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Balachandran JS, Masa JF, Mokhlesi B | title = Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome Epidemiology and Diagnosis | journal = Sleep Medicine Clinics | volume = 9 | issue = 3 | pages = 341–347 | date = September 2014 | pmid = 25360072 | pmc = 4210766 | doi = 10.1016/j.jsmc.2014.05.007 }}</ref> | |||
| Other forms of PAH are far more common. In ] the incidence has been estimated to be 6 to 60% of all patients, in ] up to 21%, in ] 4 to 14%, in ] between 2 to 5%, in HIV about 0.5%, and in sickle cell disease ranging from 20 to 40%. | |||
| Diet pills such as ] produced an annual incidence of 25-50 per million per year. | |||
| ==Research== | |||
| Pulmonary venous hypertension is exceedingly common, since it occurs in most patients symptomatic with congestive heart failure. | |||
| For people that inherited the disease, gene therapy is being studied.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Reynolds PN | title = Gene therapy for pulmonary hypertension: prospects and challenges | journal = Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy | volume = 11 | issue = 2 | pages = 133–143 | date = February 2011 | pmid = 21219232 | doi = 10.1517/14712598.2011.542139 | s2cid = 23641857 }}</ref> | |||
| ==Culture and society== | |||
| Up to 4% of people who suffer a ] go on to develop chronic thromboembolic disease including pulmonary hypertension. | |||
| ===Notable cases=== | |||
| * ], American restaurateur<ref>{{cite web|title=Elaine Kaufman, famed Elaine's restaurateur, dies at age 81|url=http://www.nydailynews.com/new-york/famed-elaine-restaurateur-elaine-kaufman-dead-81-eatery-favorite-nyc-writers-actors-article-1.469449|website=Daily News|date=3 December 2010 |access-date=27 September 2016|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160828141155/http://www.nydailynews.com/new-york/famed-elaine-restaurateur-elaine-kaufman-dead-81-eatery-favorite-nyc-writers-actors-article-1.469449|archive-date=28 August 2016}}</ref> | |||
| * ], American Broadway and TV actress<ref>{{cite news| vauthors = Folkart BA |title=Ina Balin, 52; Movie and TV Actress Sought Lung Implant|url=https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-1990-06-21-mn-160-story.html|newspaper=Los Angeles Times|access-date=27 September 2016|date=21 June 1990|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160911105214/http://articles.latimes.com/1990-06-21/news/mn-160_1_ina-balin|archive-date=11 September 2016}}</ref> | |||
| * ], American singer-songwriter<ref name="Phull-2016">{{cite news|url=https://nypost.com/2016/07/26/shes-tethered-to-an-oxygen-tank-but-her-singing-career-is-soaring/|title=She's tethered to an oxygen tank, but her singing career is soaring| vauthors = Phull H |date=July 26, 2016|newspaper=New York Post|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160814062758/http://nypost.com/2016/07/26/shes-tethered-to-an-oxygen-tank-but-her-singing-career-is-soaring/|archive-date=August 14, 2016}}</ref><ref name="Insdorf-2013">{{cite news|url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/annette-insdorf/chloe-temtchine_b_4246594.html|title=The Challenges of Chloe Temtchine|vauthors=Insdorf A |date=November 10, 2013|work=The Huffington Post|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160918180418/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/annette-insdorf/chloe-temtchine_b_4246594.html|archive-date=September 18, 2016}}</ref> | |||
| * ], American singer<ref>"Autopsy: The Last Hours of Natalie Cole." ''Autopsy''. Nar. Eric Meyers. Exec. Prod. Ed Taylor and Michael Kelpie. Reelz, 27 May 2017. Television.</ref> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| Only about 1.1% of patients with ] develop pulmonary hypertension with no other disease to explain the high pressure. ] is usually associated with only very mild pulmonary hypertension, typically below the level of detection. On the other hand ] is very commonly associated with right ] due to pulmonary hypertension. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] (CAMPHOR) | ||
| ==References== | == References == | ||
| {{Reflist |
{{Reflist}} | ||
| == Further reading == | |||
| ===Sources=== | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |author=Rubin LJ, Badesch DB |title=Evaluation and management of the patient with pulmonary arterial hypertension |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=143 |issue=4 |pages=282–92 |year=2005 |pmid=16103472 |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/143/4/282 |doi=10.7326/0003-4819-143-4-200508160-00009}} | |||
| *{{cite web |title=Pulmonary arterial hypertension |date=2016 |work=Genetics: Genetic Conditions |publisher=MedlinePlus, National Library of Medicine |url=https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/pulmonary-arterial-hypertension/ |ref={{harvid|MedlinePlus|Pulmonary arterial hypertension|2016}} }} | |||
| *{{cite web |title=What Is Pulmonary Hypertension? |date=May 2023 |work=Health Topics: Pulmonary Hypertension |publisher=National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. National Library of Medicine |url=https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/pulmonary-hypertension |ref={{harvid|NHLBI|What Is Pulmonary Hypertension?|2023}} }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Rubin LJ, Badesch DB | title = Evaluation and management of the patient with pulmonary arterial hypertension | journal = Annals of Internal Medicine | volume = 143 | issue = 4 | pages = 282–292 | date = August 2005 | pmid = 16103472 | doi = 10.7326/0003-4819-143-4-200508160-00009 | s2cid = 28841269 | citeseerx = 10.1.1.463.8466 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Abman SH, Hansmann G, Archer SL, Ivy DD, Adatia I, Chung WK, Hanna BD, Rosenzweig EB, Raj JU, Cornfield D, Stenmark KR, Steinhorn R, Thébaud B, Fineman JR, Kuehne T, Feinstein JA, Friedberg MK, Earing M, Barst RJ, Keller RL, Kinsella JP, Mullen M, Deterding R, Kulik T, Mallory G, Humpl T, Wessel DL | display-authors = 6 | title = Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension: Guidelines From the American Heart Association and American Thoracic Society | journal = Circulation | volume = 132 | issue = 21 | pages = 2037–2099 | date = November 2015 | pmid = 26534956 | doi = 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000329 | s2cid = 7412370 | doi-access = free }} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | == External links == | ||
| * | |||
| {{Medical resources | |||
| | DiseasesDB = 10998 | |||
| | ICD10 = {{ICD10|I|27|0|i|26}}, {{ICD10|I|27|2|i|26}} | |||
| | ICD9 = {{ICD9|416.0}}, {{ICD9|416.8}} | |||
| | ICDO = | |||
| | OMIM = 178600 | |||
| | MedlinePlus = 000112 | |||
| | eMedicineSubj = radio | |||
| | eMedicineTopic = 583 | |||
| | eMedicine_mult = {{eMedicine2|med|1962}} | |||
| | MeshID = D006976 | |||
| |Orphanet=182090}} | |||
| {{commons category|Pulmonary hypertension}} | {{commons category|Pulmonary hypertension}} | ||
| {{Scholia|topic}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * from the ] (NHLBI) | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Vascular diseases}} | {{Vascular diseases}} | ||
| {{Respiratory pathology}} | {{Respiratory pathology}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:45, 17 December 2024
Increased blood pressure in lung arteries Medical condition| Pulmonary hypertension | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ayerza syndrome |
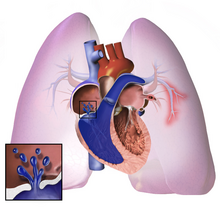 | |
| Pulmonary hypertension | |
| Specialty | Pulmonology, cardiology |
| Symptoms | Chest pain, fatigue |
| Usual onset | 20 to 60 years old |
| Duration | Long term |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risk factors | Family history, pulmonary embolism, HIV/AIDS, sickle cell disease, cocaine use, COPD, sleep apnea, living at high altitudes |
| Diagnostic method | Following ruling out other potential causes |
| Treatment | Supportive care, various medications, lung transplantation |
| Medication | Epoprostenol, treprostinil, iloprost, bosentan, ambrisentan, macitentan, sildenafil |
| Frequency | 1,000 new cases a year (US) |
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fainting, tiredness, chest pain, swelling of the legs, and a fast heartbeat. The condition may make it difficult to exercise. Onset is typically gradual. According to the definition at the 6th World Symposium of Pulmonary Hypertension in 2018, a patient is deemed to have pulmonary hypertension if the pulmonary mean arterial pressure is greater than 20mmHg at rest, revised down from a purely arbitrary 25mmHg, and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) greater than 3 Wood units.
The cause is often unknown. Risk factors include a family history, prior pulmonary embolism (blood clots in the lungs), HIV/AIDS, sickle cell disease, cocaine use, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, living at high altitudes, and problems with the mitral valve. The underlying mechanism typically involves inflammation and subsequent remodeling of the arteries in the lungs. Diagnosis involves first ruling out other potential causes.
As of 2022 there was no cure for pulmonary hypertension, although research to find a cure is ongoing. Treatment depends on the type of disease. A number of supportive measures such as oxygen therapy, diuretics, and medications to inhibit blood clotting may be used. Medications specifically used to treat pulmonary hypertension include epoprostenol, treprostinil, iloprost, bosentan, ambrisentan, macitentan, and sildenafil, tadalafil, selexipag, riociguat. Lung transplantation may be an option in severe cases.
The frequency of occurrence is estimated at 1,000 new cases per year in the United States. Females are more often affected than males. Onset is typically between 20 and 60 years of age. Pulmonary hypertension was identified by Ernst von Romberg in 1891.
Classification
According to WHO classification there are 5 groups of PH, where Group I (pulmonary arterial hypertension) is further subdivided into Group I' and Group I'' classes. The WHO classification system in 2022 (with adaptations from the more recent ESC/ERS guidelines shown in italics) can be summarized as follows:
WHO Group I – Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)
- Caused by narrowing and thickening of tiny arteries of the lung
- Idiopathic in most cases (heritable in some cases)
- Heritable (BMPR2, ALK1, SMAD9, caveolin 1, KCNK3 mutations)
- Drug- and toxin-induced (e.g., methamphetamine, amphetamine, or cocaine use )
- Associated conditions:Connective tissue disease, HIV infection, Portal hypertension, Congenital heart diseases, Schistosomiasis
WHO Group I' – Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD), pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis (PCH)
- Idiopathic
- Heritable (EIF2AK4 mutations)
- Drugs, toxins and radiation-induced
- Associated conditions:connective tissue disease, HIV infection
WHO Group I" – Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn
WHO Group II – Pulmonary hypertension secondary to left heart disease
- Left ventricular systolic dysfunction
- Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction
- Valvular heart disease
- Congenital/acquired left heart inflow/outflow tract obstruction and congenital cardiomyopathy
- Congenital/acquired pulmonary venous stenosis
WHO Group III – Pulmonary hypertension due to lung disease, chronic hypoxia
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Interstitial lung disease
- Mixed restrictive and obstructive pattern pulmonary diseases
- Sleep-disordered breathing
- Alveolar hypoventilation disorders
- Chronic exposure to high altitude
- Developmental abnormalities
WHO Group IV – Chronic arterial obstruction
- Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH)
- Other pulmonary artery obstructions
- Angiosarcoma or other tumor within the blood vessels
- Arteritis
- Congenital pulmonary artery stenosis
- Parasitic infection (hydatidosis)
WHO Group V – Pulmonary hypertension with unclear or multifactorial mechanisms
- Hematologic diseases: chronic hemolytic anemia (including sickle cell disease)
- Systemic diseases: sarcoidosis, pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis: lymphangioleiomyomatosis, neurofibromatosis, vasculitis
- Metabolic disorders: glycogen storage disease, Gaucher disease, thyroid diseases
- Others: pulmonary tumoral thrombotic microangiopathy, fibrosing mediastinitis, chronic kidney failure, segmental pulmonary hypertension (pulmonary hypertension restricted to one or more lobes of the lungs)
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of pulmonary hypertension include the following:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Chest pain
- Palpitations (heartbeat rate increased)
- Right-sided abdominal pain
- Poor appetite
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Swelling (legs/ankles)
- Cyanosis
Less common signs/symptoms include non-productive cough and exercise-induced nausea and vomiting. Coughing up of blood may occur in some patients, particularly those with specific subtypes of pulmonary hypertension such as heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension, Eisenmenger syndrome and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Pulmonary venous hypertension typically presents with shortness of breath while lying flat or sleeping (orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea), while pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) typically does not.
Other typical signs of pulmonary hypertension include an accentuated pulmonary component of the second heart sound, a right ventricular third heart sound, and parasternal heave indicating a hypertrophied right ventricle. Signs of systemic congestion resulting from right-sided heart failure include jugular venous distension, ascites, and hepatojugular reflux. Evidence of tricuspid insufficiency and pulmonic regurgitation is also sought and, if present, is consistent with the presence of pulmonary hypertension.
Causes
Pulmonary hypertension is a pathophysiologic condition with many possible causes. Indeed, this condition frequently accompanies severe heart or lung conditions. A 1973 World Health Organization meeting was the first attempt to classify pulmonary hypertension by its cause, and a distinction was made between primary PH (resulting from a disease of the pulmonary arteries) and secondary PH (resulting secondary to other, non-vascular causes). Further, primary PH was divided into the "arterial plexiform", "veno-occlusive" and "thromboembolic" forms. In 1998, a second conference at Évian-les-Bains addressed the causes of secondary PH. Subsequent third, fourth, and fifth (2013) World Symposia on PAH have further defined the classification of PH. The classification continues to evolve based on improved understanding of the disease mechanisms.
Most recently in 2022, the WHO guidelines were updated by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Respiratory Society (ERS). These guidelines are endorsed by the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation, and provide the current framework for understanding and treatment of pulmonary hypertension.
Genetics
Mutations in several genes have been associated with this condition these include bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2 (BMPR2) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha kinase 4 gene (EIF2AK4). 80% of familial pulmonary arterial hypertension and 20% of sporadic variants have mutations in BMPR2. BMPR2 is involved in endothelial proliferation and remodeling. Other mutations associated with PAH include ACVRL1 (which encodes activin receptor–like kinase 1) and ENG encoding endoglin, two proteins which also participate in BMPR2 signaling. The SMAD transcription factor family, including SMAD1, SMAD4, and SMAD9 are involved in signaling pathways downstream from BMPR2 and are also implicated in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Pathogenesis


The pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (WHO Group I) involves the narrowing of blood vessels connected to and within the lungs. This makes it harder for the heart to pump blood through the lungs, as it is much harder to make water flow through a narrow pipe as opposed to a wide one. Over time, the affected blood vessels become stiffer and thicker, in a process known as fibrosis. The mechanisms involved in this narrowing process include vasoconstriction, thrombosis, and vascular remodeling (excessive cellular proliferation, fibrosis, and reduced apoptosis/programmed cell death in the vessel walls, caused by inflammation, disordered metabolism and dysregulation of certain growth factors). This further increases the blood pressure within the lungs and impairs their blood flow. In common with other types of pulmonary hypertension, these changes result in an increased workload for the right side of the heart. The right ventricle is normally part of a low pressure system, with systolic ventricular pressures that are lower than those that the left ventricle normally encounters. As such, the right ventricle cannot cope as well with higher pressures, and although right ventricular adaptations (hypertrophy and increased contractility of the heart muscle) initially help to preserve stroke volume, ultimately these compensatory mechanisms are insufficient; the right ventricular muscle cannot get enough oxygen to meet its needs and right heart failure follows. As the blood flowing through the lungs decreases, the left side of the heart receives less blood. This blood may also carry less oxygen than normal. Therefore, it becomes harder and harder for the left side of the heart to supply sufficient oxygen to the rest of the body, especially during physical activity. During the end-systolic volume phase of the cardiac cycle, the Gaussian curvature and the mean curvature of right ventricular endocardial wall of PH patients was found to be significantly different as compared to controls.
In PVOD (WHO Group I'), pulmonary blood vessel narrowing occurs preferentially (though not exclusively) in post-capillary venous blood vessels. PVOD shares several characteristics with PAH, but there are also some important differences, for example differences in prognosis and response to medical therapy.
Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn occurs when the circulatory system of a newborn baby fails to adapt to life outside the womb; it is characterized by high resistance to blood flow through the lungs, right-to-left cardiac shunting and severe hypoxemia.
Pathogenesis in pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease (WHO Group II) is completely different in that constriction or damage to the pulmonary blood vessels is not the issue. Instead, the left heart fails to pump blood efficiently, leading to pooling of blood in the lungs and back pressure within the pulmonary system. This causes pulmonary edema and pleural effusions. In the absence of pulmonary blood vessel narrowing, the increased back pressure is described as 'isolated post-capillary pulmonary hypertension' (older terms include 'passive' or 'proportionate' pulmonary hypertension or 'pulmonary venous hypertension'). However, in some patients, the raised pressure in the pulmonary vessels triggers a superimposed component of vessel narrowing, which further increases the workload of the right side of the heart. This is referred to as 'post-capillary pulmonary hypertension with a pre-capillary component' or 'combined post-capillary and pre-capillary pulmonary hypertension' (older terms include 'reactive' or 'out-of-proportion' pulmonary hypertension).
In pulmonary hypertension due to lung diseases and/or hypoxia (WHO Group III), low levels of oxygen in the alveoli (due to respiratory disease or living at high altitude) cause constriction of the pulmonary arteries. This phenomenon is called hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and it is initially a protective response to stop too much blood flowing to areas of the lung that are damaged and do not contain oxygen. When the alveolar hypoxia is widespread and prolonged, this hypoxia-mediated vasoconstriction occurs across a large portion of the pulmonary vascular bed and leads to an increase in pulmonary arterial pressure, with thickening of the pulmonary vessel walls contributing to the development of sustained pulmonary hypertension. Prolonged hypoxia also induces the transcription factor HIF1A, which directly activates downstream growth factor signaling that causes irreversible proliferation and remodeling of pulmonary arterial endothelial cells, leading to chronic pulmonary arterial hypertension.
In chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, or CTEPH (WHO Group IV), the initiating event is thought to be blockage or narrowing of the pulmonary blood vessels with unresolved blood clots; these clots can lead to increased pressure and shear stress in the rest of the pulmonary circulation, precipitating structural changes in the vessel walls (remodeling) similar to those observed in other types of severe pulmonary hypertension. This combination of vessel occlusion and vascular remodeling once again increases the resistance to blood flow and so the pressure within the system rises.
Molecular pathology
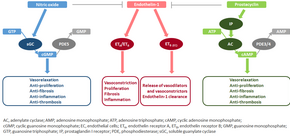
The molecular mechanism of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is not known yet, but it is believed that the endothelial dysfunction results in a decrease in the synthesis of endothelium-derived vasodilators such as nitric oxide and prostacyclin. Moreover, there is a stimulation of the synthesis of vasoconstrictors such as thromboxane and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). These result in a severe vasoconstriction and vascular smooth muscle and adventitial hypertrophy characteristic of patients with PAH.
Nitric oxide-soluble guanylate cyclase pathway
In normal conditions, the vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase produces nitric oxide from L-arginine in the presence of oxygen.
This nitric oxide diffuses into neighboring cells (including vascular smooth muscle cells and platelets), where it increases the activity of the enzyme soluble guanylate cyclase, leading to increased formation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). The cGMP then activates cGMP-dependent kinase or PKG (protein kinase G). Activated PKG promotes vasorelaxation (via a reduction of intracellular calcium levels), alters the expression of genes involved in smooth muscle cell contraction, migration and differentiation, and inhibits platelet activation. Nitric oxide–soluble guanylate cyclase signaling also leads to anti-inflammatory effects.
Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), which is abundant in the pulmonary tissue, hydrolyzes the cyclic bond of cGMP. Consequently, the concentration of cGMP (and thus PKG activity) decreases.
Endothelin
Endothelin-1 is a peptide (comprising 21 amino acids) that is produced in endothelial cells. It acts on the endothelin receptors ETA and ETB in various cell types including vascular smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts, leading to vasoconstriction, hypertrophy, proliferation, inflammation, and fibrosis. It also acts on ETB receptors in endothelial cells; this leads to the release of both vasoconstrictors and vasodilators from those cells, and clears endothelin-1 from the system.
Prostacyclin and thromboxane
Prostacyclin is synthesized from arachidonic acid in endothelial cells. In vascular smooth muscle cells, prostacyclin binds mainly to the prostaglandin I receptor. This sends a signal to increase adenylate cyclase activity, which leads to increased synthesis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). This in turn leads to increased cAMP-dependent protein kinase or PKA (protein kinase A) activity, ultimately promoting vasodilation and inhibiting cell proliferation. Prostacyclin signaling also leads to anti-thrombotic, anti-fibrotic, and anti-inflammatory effects. Levels of cAMP (which mediates most of the biological effects of prostacyclin) are reduced by phosphodiesterases 3 and 4. The vasoconstrictor thromboxane is also synthesized from arachidonic acid. In PAH, the balance is shifted away from synthesis of prostacyclin toward synthesis of thromboxane.
Other pathways
The three pathways described above are all targeted by currently available medical therapies for PAH. However, several other pathways have been identified that are also altered in PAH and are being investigated as potential targets for future therapies. For example, the mitochondrial enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK) is pathologically activated in PAH, causing a metabolic shift from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis and leading to increased cell proliferation and impaired apoptosis. Expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide, a potent vasodilator with anti-inflammatory and immune-modulatory roles, is reduced in PAH, while expression of its receptor is increased. Plasma levels of serotonin, which promotes vasoconstriction, hypertrophy and proliferation, are increased in patients with PAH, although the role played by serotonin in the pathogenesis of PAH remains uncertain. The expression or activity of several growth factors (including platelet-derived growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor) is increased and contributes to vascular remodeling in PAH. Other factors underlying the proliferative state of pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells include OPG and TRAIL. Focusing only on the pulmonary vasculature provides an incomplete picture of PAH; the ability of the right ventricle to adapt to the increased workload varies between patients and is an important determinant of survival. The molecular pathology of PAH in the right ventricle is therefore also being investigated, and recent research has shifted to consider the cardiopulmonary unit as a single system rather than two separate systems. Importantly, right ventricular remodeling is associated with increased apoptosis; this is in contrast to pulmonary vascular remodeling which involves inhibition of apoptosis.
Even though the primary cause of PAH is unknown, inflammation and oxidative stress have been shown to have a key role in vascular remodeling. These factors are known to cause DNA damage, and may also promote the proliferative and apoptosis-resistant phenotype that is observed in PAH vascular cells. Elevated levels of DNA damage have been reported to occur in PAH lungs and remodeled arteries, and also in animal models of PH, indicating that DNA damage likely contributes to PAH pathogenesis.
Diagnosis



In terms of the diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension, it has five major types, and a series of tests must be performed to distinguish pulmonary arterial hypertension from venous, hypoxic, thromboembolic, or unclear multifactorial varieties. PAH is diagnosed after exclusion of other possible causes of pulmonary hypertension.
Physical examination
A physical examination is performed to look for typical signs of pulmonary hypertension (described above), and a detailed family history is established to determine whether the disease might be heritable. A history of exposure to drugs such as benfluorex (a fenfluramine derivative), dasatinib, cocaine, methamphetamine, ethanol leading to cirrhosis, and tobacco leading to emphysema is considered significant. Use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors during pregnancy (particularly late pregnancy) is associated with an increased risk of the baby developing persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn.
Echocardiography
If pulmonary hypertension is suspected based on the above assessments, echocardiography is performed as the next step. A meta-analysis of Doppler echocardiography for predicting the results of right heart catheterization reported a sensitivity and specificity of 88% and 56%, respectively. Thus, Doppler echocardiography can suggest the presence of pulmonary hypertension, but right heart catheterization (described below) remains the gold standard for diagnosis of PAH. Echocardiography can also help to detect congenital heart disease as a cause of pulmonary hypertension.
Exclude other diseases
If the echocardiogram is compatible with a diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension, common causes of pulmonary hypertension (left heart disease and lung disease) are considered and further tests are performed accordingly. These tests generally include electrocardiography (ECG), pulmonary function tests including lung diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide and arterial blood gas measurements, X-rays of the chest and high-resolution computed tomography (CT) scanning.
Ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy
If heart disease and lung disease have been excluded, a ventilation/perfusion scan is performed to rule out CTEPH. If unmatched perfusion defects are found, further evaluation by CT pulmonary angiography, right heart catheterization, and selective pulmonary angiography is performed.
CT scan

Signs of pulmonary hypertension on CT scan of the chest are:
- Enlargement of the pulmonary trunk (measured at its bifurcation). It is, however, a poor predictor of pulmonary hypertension in patients with interstitial lung disease.
- A diameter of more than 27 mm for women and 29 mm for men is suggested as a cutoff.
- A cutoff of 31.6 mm may be a more statistically robust in individuals without interstitial lung disease.
- Increased ratio of the diameter of the main pulmonary artery (pulmonary trunk) to the ascending aorta (measured at its bifurcation).
- A ratio of 1.0 is suggested as a cutoff in adults.
- Cutoff ~1.09 in children.
- Increased diameter ratio of segmental arteries to bronchi. This finding in three or four lobes, in the presence of a dilated pulmonary trunk (≥29 mm), and absence of significant structural lung disease confers a specificity of 100% for pulmonary hypertension.
- Mural calcification in central pulmonary arteries is most frequently seen in patients with Eisenmenger's syndrome.
Right heart catheterization
Although pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP) can be estimated on the basis of echocardiography, pressure measurements with a Swan-Ganz catheter inserted through the right side of the heart provide the most definite assessment. Pulmonary hypertension is defined as a mean PAP of at least 20 mm Hg (3300 Pa) at rest, and PAH is defined as precapillary pulmonary hypertension (i.e. mean PAP ≥ 20 mm Hg with pulmonary arterial occlusion pressure ≤ 15 mm Hg and pulmonary vascular resistance > 3 Wood Units). PAOP and PVR cannot be measured directly with echocardiography. Therefore, diagnosis of PAH requires right-sided cardiac catheterization. A Swan-Ganz catheter can also measure the cardiac output; this can be used to calculate the cardiac index, which is far more important in measuring disease severity than the pulmonary arterial pressure. Mean PAP (mPAP) should not be confused with systolic PAP (sPAP), which is often reported on echocardiogram reports. A systolic pressure of 40 mm Hg typically implies a mean pressure of more than 25 mm Hg. Roughly, mPAP = 0.61•sPAP + 2. Due to the invasive nature of this procedure, the use of computational fluid dynamics based hemodynamic indices have been postulated.
Other
For people considered likely to have PAH based on the above tests, the specific associated condition is then determined based on the physical examination, medical/family history and further specific diagnostic tests (for example, serological tests to detect underlying connective tissue disease, HIV infection or hepatitis, ultrasonography to confirm the presence of portal hypertension, echocardiography/cardiac magnetic resonance imaging for congenital heart disease, laboratory tests for schistosomiasis, and high-resolution CT for PVOD and pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis). Routine lung biopsy is discouraged in patients with PAH, because of the risk to the patient and because the findings are unlikely to alter the diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of pulmonary hypertension is determined by whether the PH is arterial, venous, hypoxic, thromboembolic, or miscellaneous. If it is caused by left heart disease, the treatment is to optimize left ventricular function by the use of medication or to repair/replace the mitral valve or aortic valve. Patients with left heart failure or hypoxemic lung diseases (groups II or III pulmonary hypertension) should not routinely be treated with vasoactive agents including prostanoids, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, or endothelin antagonists, as these are approved for the different condition called primary pulmonary arterial hypertension. To make the distinction, doctors at a minimum will conduct cardiac catheterization of the right heart, echocardiography, chest CT, a seven-minute walk test, and pulmonary function testing. Using treatments for other kinds of pulmonary hypertension in patients with these conditions can harm the patient and wastes substantial medical resources.
High-dose calcium channel blockers are useful in only 5% of IPAH patients who are vasoreactive by Swan-Ganz catheter. Calcium channel blockers have been largely misused, being prescribed to many patients with non-vasoreactive PAH, leading to excess morbidity and mortality. The criteria for vasoreactivity have changed. Only those patients whose mean pulmonary artery pressure falls by more than 10 mm Hg to less than 40 mm Hg with an unchanged or increased cardiac output when challenged with adenosine, epoprostenol, or nitric oxide are considered vasoreactive. Of these, only half of the patients are responsive to calcium channel blockers in the long term.
A number of agents have recently been introduced for primary and secondary PAH. The trials supporting the use of these agents have been relatively small, and the only measure consistently used to compare their effectivity is the "six-minute walk test". Many have no data on mortality benefit or time to progression.
Sotatercept (Winrevair) was approved for medical use in the United States in March 2024.
Exercise-based rehabilitation
A 2023 Cochrane review found that exercise-based rehabilitation may lead to a large increase in exercise capacity and an improvement in health related quality of life, without significantly increasing adverse events.
Vasoactive substances
Many pathways are involved in the abnormal proliferation and contraction of the smooth muscle cells of the pulmonary arteries in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Three of these pathways are important since they have been targeted with drugs – endothelin receptor antagonists, phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, and prostacyclin derivatives.
Prostaglandins
Prostacyclin (prostaglandin I2) is commonly considered the most effective treatment for PAH. Epoprostenol (synthetic prostacyclin) is given via continuous infusion that requires a semi-permanent central venous catheter. This delivery system can cause sepsis and thrombosis. Prostacyclin is unstable, and therefore has to be kept on ice during administration. Since it has a half-life of 3 to 5 minutes, the infusion has to be continuous, and interruption can be fatal. Other prostanoids have therefore been developed. Treprostinil can be given intravenously or subcutaneously, but the subcutaneous form can be very painful. An increased risk of sepsis with intravenous Remodulin has been reported by the CDC. Iloprost is also used in Europe intravenously and has a longer half life. Iloprost was the only inhaled form of prostacyclin approved for use in the US and Europe, until the inhaled form of treprostinil was approved by the FDA in July 2009.
Endothelin receptor antagonists
Moderate quality evidence suggests that endothelin receptor antagonists improve exercise capacity and decrease symptoms severity. The dual (ETA and ETB) endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan was approved in 2001. Macitentan is another ETA and ETB dual endothelin receptor blocker that is used. Sitaxentan (Thelin) was approved for use in Canada, Australia, and the European Union, but not in the United States. In 2010, Pfizer withdrew sitaxentan worldwide because of fatal liver complications. A similar drug, ambrisentan (which is a ETA endothelin receptor blocker) is sold under the brand name Letairis in the US by Gilead Sciences.
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors
The US FDA approved sildenafil, a selective inhibitor of cGMP specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), for the treatment of PAH in 2005. It is marketed for PAH as Revatio. In 2009, they also approved tadalafil, another PDE5 inhibitor, marketed under the name Adcirca. PDE5 inhibitors are believed to increase pulmonary artery vasodilation, and inhibit vascular remodeling, thus lowering pulmonary arterial pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance.
Tadalafil is taken orally, as well as sildenafil, and it is rapidly absorbed (serum levels are detectable at 20 minutes). The T1/2 (biological half-life) hovers around 17.5 hours in healthy subjects. Moreover, if we consider pharmacoeconomic implications, patients that take tadalafil would pay two-thirds of the cost of sildenafil therapy. However, there are some adverse effects of this drug such as headache, diarrhea, nausea, back pain, dyspepsia, flushing and myalgia.
The combination medication macitentan/tadalafil (Opsynvi) was approved for medical use in Canada in October 2021, and in the United States in March 2024.
Activators of soluble guanylate cyclase
Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) is the intracellular receptor for NO. As of April 2009, the sGC activators cinaciguat and riociguat were undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of PAH.
Surgical
Atrial septostomy is a surgical procedure that creates a communication between the right and left atria. It relieves pressure on the right side of the heart, but at the cost of lower oxygen levels in blood (hypoxemia). Lung transplantation replaces a chronic condition with the ongoing need for treatment. There is a post-surgical median survival of just over five years.
Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy (PTE) is a surgical procedure that is used for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. It is the surgical removal of an organized thrombus (clot) along with the lining of the pulmonary artery; it is a very difficult, major procedure that is currently performed in a few select centers.
Monitoring
Established clinical practice guidelines dictate the frequency of pulmonary nodule evaluation and surveillance, patients are normally monitored through commonly available tests such as:
- Pulse oximetry
- Arterial blood gas tests
- Chest X-rays
- Serial ECG tests
- Serial echocardiography
- Spirometry or more advanced lung function studies
- Six-minute walk test
Prognosis

PAH is considered a universally fatal illness, although survival time may vary between individuals. The prognosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (WHO Group I) has an untreated median survival of 2–3 years from time of diagnosis, with the cause of death usually being right ventricular failure (cor pulmonale). The survival time is variable and depends on many factors. A recent outcome study of those patients who had started treatment with bosentan (Tracleer) showed that 89% of patients were alive at 2 years. With new therapies, survival rates are increasing. For 2,635 patients enrolled in The Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-term Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Disease Management (REVEAL Registry) from March 2006 to December 2009, 1-, 3-, 5-, and 7-year survival rates were 85%, 68%, 57%, and 49%, respectively. For patients with idiopathic/familial PAH, survival rates were 91%, 74%, 65%, and 59%. Levels of mortality are very high in pregnant women with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension (WHO Group I). Pregnancy is sometimes described as contraindicated in these women.
Epidemiology
The epidemiology of IPAH is about 125–150 deaths per year in the U.S., and worldwide the incidence is similar at 4 cases per million. However, in parts of Europe (France), indications are 6 cases per million of IPAH. Females have a higher incidence rate than males (2–9:1). Other forms of PH are far more common. In systemic scleroderma, the incidence has been estimated to be 8 to 12% of all patients; in rheumatoid arthritis it is rare. However, in systemic lupus erythematosus it is 4 to 14%, and in sickle cell disease, it ranges from 20 to 40%. Up to 4% of people who develop a pulmonary embolism go on to develop chronic thromboembolic disease including pulmonary hypertension. A small percentage of patients with COPD develop pulmonary hypertension with no other disease to explain the high pressure. On the other hand, obesity-hypoventilation syndrome is very commonly associated with right heart failure due to pulmonary hypertension.
Research
For people that inherited the disease, gene therapy is being studied.
Culture and society
Notable cases
- Elaine Kaufman, American restaurateur
- Ina Balin, American Broadway and TV actress
- Chloe Temtchine, American singer-songwriter
- Natalie Cole, American singer
See also
References
- ^ "Pulmonary arterial hypertension". Genetics Home Reference. January 2016. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ^ "What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary Hypertension? – NHLBI, NIH". www.nhlbi.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2016-01-05. Retrieved 2015-12-30.
- ^ "Who Is at Risk for Pulmonary Hypertension?". NHLBI – NIH. 2 August 2011. Archived from the original on 31 July 2017. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ^ Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, Badagliacca R, Berger RM, Brida M, et al. (October 2022). "2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension". European Heart Journal. 43 (38): 3618–3731. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehac237. PMID 36017548.
- ^ "Causes and Risk Factors". Health Topics: Pulmonary Hypertension. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. National Library of Medicine. 24 March 2022.
- ^ "Treatment". Health Topics: Pulmonary Hypertension. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. National Library of Medicine. 24 March 2022.
- ^ NHLBI & What Is Pulmonary Hypertension? 2023
- "Diagnosis". Health Topics: Pulmonary Hypertension. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. National Library of Medicine. March 24, 2022.
- von Romberg E (1891–1892). "Über Sklerose der Lungenarterie". Dtsch Arch Klin Med (in German). 48: 197–206.
- ^ Simonneau G, Robbins IM, Beghetti M, Channick RN, Delcroix M, Denton CP, et al. (June 2009). "Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 54 (1 Suppl): S43 – S54. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.012. PMID 19555858.
- ^ Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A, et al. (December 2013). "Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 62 (25 Suppl): D34 – D41. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.029. PMID 24355639.
- ^ Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. (ESC Scientific Document Group) (January 2016). "2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT)". European Heart Journal. 37 (1): 67–119. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317. PMID 26320113.
- ^ "Learn About Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension". PAH. American Lung Association. Retrieved 2023-08-01.
- Kolaitis NA, Zamanian RT, de Jesus Perez VA, Badesch DB, Benza RL, Burger CD, et al. (April 2021). "Clinical Differences and Outcomes between Methamphetamine-associated and Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in the Pulmonary Hypertension Association Registry". Annals of the American Thoracic Society. 18 (4): 613–622. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202007-774OC. PMC 8174020. PMID 33064950.
- ^ McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, et al. (April 2009). "ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 53 (17): 1573–1619. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.01.004. PMID 19389575.
- Diller GP, Gatzoulis MA (February 2007). "Pulmonary vascular disease in adults with congenital heart disease". Circulation. 115 (8): 1039–1050. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.592386. PMID 17325254.
- ^ Fang JC, DeMarco T, Givertz MM, Borlaug BA, Lewis GD, Rame JE, et al. (September 2012). "World Health Organization Pulmonary Hypertension group 2: pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease in the adult--a summary statement from the Pulmonary Hypertension Council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation". The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 31 (9): 913–933. doi:10.1016/j.healun.2012.06.002. PMID 22884380.
- Yusuf S, Cairns J, Camm J, Fallen EL, Gersh BJ (2011). Evidence-Based Cardiology. John Wiley & Sons. p. 70.3 (figure). ISBN 978-1-4443-5945-9. Archived from the original on 2016-04-30.
- ^ "Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Clinical Presentation: History, Physical Examination, Complications". emedicine.medscape.com. Archived from the original on 2015-11-01. Retrieved 2015-12-30.
- Hatano S, Strasser R (1975). Primary pulmonary hypertension. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- Rich S, Rubin LJ, Abenhail L, et al. (1998). Executive summary from the World Symposium on Primary Pulmonary Hypertension (Evian, France, September 6–10, 1998). Geneva: The World Health Organization. Archived from the original on April 8, 2002.
- Simonneau G, Galiè N, Rubin LJ, Langleben D, Seeger W, Domenighetti G, et al. (June 2004). "Clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 43 (12 Suppl S): 5S – 12S. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.02.037. PMID 15194173.
- Rabinovitch M (December 2012). "Molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 122 (12): 4306–4313. doi:10.1172/JCI60658. PMC 3533531. PMID 23202738.
- Hadinnapola C, Bleda M, Haimel M, Screaton N, Swift A, Dorfmüller P, et al. (November 2017). "Phenotypic Characterization of EIF2AK4 Mutation Carriers in a Large Cohort of Patients Diagnosed Clinically With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension". Circulation. 136 (21): 2022–2033. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028351. PMC 5700414. PMID 28972005.
- ^ Hassoun, Paul M. (16 December 2021). "Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension". New England Journal of Medicine. 385 (25): 2361–2376. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2000348. PMID 34910865.
- Jacob AS, Nielsen DH, Gianelly RE (February 1985). "Fatal ventricular fibrillation following verapamil in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome with atrial fibrillation". Annals of Emergency Medicine. 14 (2): 159–160. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.025. PMC 3970402. PMID 3970402.
- ^ Vonk-Noordegraaf A, Haddad F, Chin KM, Forfia PR, Kawut SM, Lumens J, et al. (December 2013). "Right heart adaptation to pulmonary arterial hypertension: physiology and pathobiology". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 62 (25 Suppl): D22 – D33. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.027. PMID 24355638.
- ^ Galiè N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA, et al. (December 2009). "Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension". The European Respiratory Journal. 34 (6): 1219–1263. doi:10.1183/09031936.00139009. PMID 19749199.
- Yuan JX, Rubin LJ (February 2005). "Pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: the need for multiple hits". Circulation. 111 (5): 534–538. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000156326.48823.55. PMID 15699271.
- Tuder RM, Marecki JC, Richter A, Fijalkowska I, Flores S (March 2007). "Pathology of pulmonary hypertension". Clinics in Chest Medicine. 28 (1): 23–42, vii. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2006.11.010. PMC 1924722. PMID 17338926.
- Bordones-Crom A, Patnaik SS, Menon PG, Murali S, Finol E (July 2021). "Morphological Analysis of the Right Ventricular Endocardial Wall in Pulmonary Hypertension". Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 143 (7). doi:10.1115/1.4050457. PMID 33704381. S2CID 232193407.
- Montani D, Price LC, Dorfmuller P, Achouh L, Jaïs X, Yaïci A, et al. (January 2009). "Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease". The European Respiratory Journal. 33 (1): 189–200. doi:10.1183/09031936.00090608. PMID 19118230.
- Montani, David; Lau, Edmund M.; Dorfmüller, Peter; Girerd, Barbara; Jaïs, Xavier; Savale, Laurent; Perros, Frederic; Nossent, Esther; Garcia, Gilles; Parent, Florence; Fadel, Elie; Soubrier, Florent; Sitbon, Olivier; Simonneau, Gérald; Humbert, Marc (May 2016). "Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease". European Respiratory Journal. 47 (5): 1518–1534. doi:10.1183/13993003.00026-2016.
- Guazzi M, Galiè N (December 2012). "Pulmonary hypertension in left heart disease". European Respiratory Review. 21 (126): 338–346. doi:10.1183/09059180.00004612. PMC 9487233. PMID 23204122.
- Vachiéry JL, Adir Y, Barberà JA, Champion H, Coghlan JG, Cottin V, et al. (December 2013). "Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart diseases". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 62 (25 Suppl): D100 – D108. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.033. hdl:11585/534481. PMID 24355634.
- Shanks N, Macklin J, Coles S (2009). "Comparison of oral erythromycin ethylsuccinate and clavulanate-potentiated amoxicillin in the treatment of acute respiratory tract infections". Clinical Therapeutics. 11 (6): 812–819. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2009.02.006. PMC 2692823. PMID 2692823.
- Sommer N, Dietrich A, Schermuly RT, Ghofrani HA, Gudermann T, Schulz R, et al. (December 2008). "Regulation of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction: basic mechanisms". The European Respiratory Journal. 32 (6): 1639–1651. doi:10.1183/09031936.00013908. PMID 19043010.
- Stenmark KR, Fagan KA, Frid MG (September 2006). "Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: cellular and molecular mechanisms". Circulation Research. 99 (7): 675–691. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000243584.45145.3f. PMID 17008597.
- McNeil K, Dunning J (September 2007). "Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH)". Heart. 93 (9): 1152–1158. doi:10.1136/hrt.2004.053603. PMC 1955041. PMID 17699182.
- ^ Hoeper MM, Mayer E, Simonneau G, Rubin LJ (April 2006). "Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension". Circulation. 113 (16): 2011–2020. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.602565. PMID 16636189.
- ^ Budhiraja R, Tuder RM, Hassoun PM (January 2004). "Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension". Circulation. 109 (2): 159–165. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000102381.57477.50. PMID 14734504.
- Förstermann U, Münzel T (April 2006). "Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: from marvel to menace". Circulation. 113 (13): 1708–1714. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.602532. PMID 16585403.
- Murad F (November 2006). "Shattuck Lecture. Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in cell signaling and drug development". The New England Journal of Medicine. 355 (19): 2003–2011. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa063904. PMID 17093251.
- ^ Francis SH, Busch JL, Corbin JD, Sibley D (September 2010). "cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cGMP phosphodiesterases in nitric oxide and cGMP action". Pharmacological Reviews. 62 (3): 525–563. doi:10.1124/pr.110.002907. PMC 2964902. PMID 20716671.
- Zelia OP, Kovalenko FP (2011). "Comparative efficiency of infecting laboratory animals via intravenous and subcutaneous administration of Schistosoma mansoni cercaria". Parazitologiia. 20 (6): 461–465. PMID 3103045.
- Ghofrani HA, Pepke-Zaba J, Barbera JA, Channick R, Keogh AM, Gomez-Sanchez MA, et al. (June 2004). "Nitric oxide pathway and phosphodiesterase inhibitors in pulmonary arterial hypertension". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 43 (12 Suppl S): 68S – 72S. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.02.031. PMID 15194181.
- McLaughlin VV, McGoon MD (September 2006). "Pulmonary arterial hypertension". Circulation. 114 (13): 1417–1431. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.503540. PMID 17000921.
- Fonseca C, Abraham D, Renzoni EA (January 2011). "Endothelin in pulmonary fibrosis". American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. 44 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2009-0388TR. PMID 20448055.
- ^ Wood, S. F. (1986). "Astemizole and terfenadine compared in hay fever". The Practitioner. 230 (1411): 41–44. PMID 2869481.
- Gomberg-Maitland M, Olschewski H (April 2008). "Prostacyclin therapies for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension". The European Respiratory Journal. 31 (4): 891–901. doi:10.1183/09031936.00097107. PMID 18378784.
- ^ Lenfant M (2013). "[Dihydrostreptomycin fixation on the ribosomes of E. coli]". Biochimie. 54 (2): 283–285. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.026. PMC 4117578. PMID 4117578.
- Lawrie A (December 2014). "The role of the osteoprotegerin/tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand axis in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension". Vascular Pharmacology. 63 (3): 114–117. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2014.10.002. PMID 25446166.
- Braithwaite AT, Marriott HM, Lawrie A (2018). "Divergent Roles for TRAIL in Lung Diseases". Frontiers in Medicine. 5: 212. doi:10.3389/fmed.2018.00212. PMC 6072839. PMID 30101145.
- ^ Ranchoux B, Meloche J, Paulin R, Boucherat O, Provencher S, Bonnet S (June 2016). "DNA Damage and Pulmonary Hypertension". Int J Mol Sci. 17 (6): 990. doi:10.3390/ijms17060990. PMC 4926518. PMID 27338373.
- "How Is Pulmonary Hypertension Diagnosed? – NHLBI, NIH". www.nhlbi.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2016-01-05. Retrieved 2015-12-30.
- Austin ED, Phillips III JA, Loyd JE (2015-12-28). "Pulmonary arterial hypertension". In Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LH, Gripp KW, Amemiya A (eds.). Genetics Home Reference. Archived from the original on 2015-12-24. Retrieved 2015-12-30.
- Austin ED, Loyd JE, Phillips JA (January 1993). "Heritable Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Overview". In Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJ, Bird TD, Fong C, Mefford HC (eds.). GeneReviews. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 20301658. NBK1485.
- ^ Hoeper MM, Bogaard HJ, Condliffe R, Frantz R, Khanna D, Kurzyna M, et al. (December 2013). "Definitions and diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 62 (25 Suppl): D42 – D50. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.032. PMID 24355641.
- Klepper MJ, Cobert B (2010-10-25). Drug Safety Data: How to Analyze, Summarize and Interpret to Determine Risk. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 86. ISBN 978-0-7637-6912-3. Archived from the original on 2016-05-04.
- Taleb M, Khuder S, Tinkel J, Khouri SJ (March 2013). "The diagnostic accuracy of Doppler echocardiography in assessment of pulmonary artery systolic pressure: a meta-analysis". Echocardiography. 30 (3): 258–265. doi:10.1111/echo.12061. PMID 23227919. S2CID 7460778.
- "How Is Pulmonary Hypertension Diagnosed?". National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
- ^ Gaillard F. "Pulmonary hypertension". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2018-03-12.
- Bossone E, D'Andrea A, D'Alto M, Citro R, Argiento P, Ferrara F, et al. (January 2013). "Echocardiography in pulmonary arterial hypertension: from diagnosis to prognosis". Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 26 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2012.10.009. PMID 23140849.
- "Swan-Ganz – right heart catheterization". Medical Encyclopedia. MedlinePlus, National Library of Medicine. 2022.
- Khouri SJ, Pandya U (2012). "Pulmonary hypertension.". In Garcia MJ (ed.). NonInvasive cardiovascular imaging: a multimodality approach. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 655–668.
- Piskin S, Patnaik SS, Han D, Bordones AD, Murali S, Finol EA (March 2020). "A canonical correlation analysis of the relationship between clinical attributes and patient-specific hemodynamic indices in adult pulmonary hypertension". Medical Engineering & Physics. 77: 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2020.01.006. PMC 7069525. PMID 32007361.
- Pillalamarri NR, Piskin S, Patnaik SS, Murali S, Finol EA (December 2021). "Patient-Specific Computational Analysis of Hemodynamics in Adult Pulmonary Hypertension". Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 49 (12): 3465–3480. doi:10.1007/s10439-021-02884-y. PMC 8684831. PMID 34799807.
- "How Is Pulmonary Hypertension Treated? – NHLBI, NIH". www.nhlbi.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2016-01-05. Retrieved 2015-12-30.
- ^ American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society (September 2013), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American College of Chest Physicians and American Thoracic Society, archived from the original on 3 November 2013, retrieved 6 January 2013, which cites
- McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, et al. (April 2009). "ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association: developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society, Inc., and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association". Circulation. 119 (16): 2250–2294. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192230. PMID 19332472.
- Galiè N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA, et al. (October 2009). "Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT)". European Heart Journal. 30 (20): 2493–2537. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehp297. PMID 19713419.
- Hoeper MM, Barberà JA, Channick RN, Hassoun PM, Lang IM, Manes A, et al. (June 2009). "Diagnosis, assessment, and treatment of non-pulmonary arterial hypertension pulmonary hypertension". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 54 (1 Suppl): S85 – S96. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.008. PMID 19555862.
- Barst RJ, McGoon M, Torbicki A, Sitbon O, Krowka MJ, Olschewski H, Gaine S (June 2004). "Diagnosis and differential assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 43 (12 Suppl S): 40S – 47S. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.02.032. PMID 15194177.
- Sitbon O, Humbert M, Jaïs X, Ioos V, Hamid AM, Provencher S, et al. (June 2005). "Long-term response to calcium channel blockers in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension". Circulation. 111 (23): 3105–3111. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.488486. PMID 15939821.
- Torres F (October 2007). "Systematic review of randomised, double-blind clinical trials of oral agents conducted in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 61 (10): 1756–1765. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01545.x. PMID 17877662. S2CID 1191543.
- "FDA Approves Merck's Winrevair (sotatercept-csrk), a First-in-Class Treatment for Adults with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH, WHO* Group 1)" (Press release). Merck. 27 March 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- Morris NR, Kermeen FD, Jones AW, Lee JY, Holland AE, et al. (Cochrane Airways Group) (March 2023). "Exercise-based rehabilitation programmes for pulmonary hypertension". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2023 (3): CD011285. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011285.pub3. PMC 10032353. PMID 36947725.
- Raja SG, Raja SM (November 2011). "Treating pulmonary arterial hypertension: current treatments and future prospects". Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease. 2 (6): 359–370. doi:10.1177/2040622311420773. PMC 3513893. PMID 23251761.
- Safdar Z (June 2011). "Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: the role of prostacyclin and prostaglandin analogs". Respiratory Medicine. 105 (6): 818–827. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2010.12.018. PMID 21273054.
- "Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs".
- Liu C, Chen J, Gao Y, Deng B, Liu K, et al. (Cochrane Airways Group) (March 2021). "Endothelin receptor antagonists for pulmonary arterial hypertension". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (3): CD004434. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004434.pub6. PMC 8094512. PMID 33765691.
- "UPDATE 1-Encysive gets Canadian approval for hypertension drug". Reuters. 2008-05-30. Archived from the original on 2007-07-04. Retrieved 2007-07-08.
- "Citing Liver Damage, Pfizer Withdraws Thelin – CBS Detroit". www.cbsnews.com. 10 December 2010.
- "U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approves Gilead's Letairis Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension" (Press release). Gilead Sciences. 2007-06-15. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- "FDA approves Adcirca (tadalafil) tablets for pulmonary arterial hypertension" (Press release). 2009-05-26. Archived from the original on 2010-12-03. Retrieved 2010-12-06.
- Duarte JD, Hanson RL, Machado RF (May 2013). "Pharmacologic treatments for pulmonary hypertension: exploring pharmacogenomics". Future Cardiology. 9 (3): 335–349. doi:10.2217/fca.13.6. PMC 3864092. PMID 23668740.
- Forgue ST, Patterson BE, Bedding AW, Payne CD, Phillips DL, Wrishko RE, Mitchell MI (March 2006). "Tadalafil pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 61 (3): 280–288. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02553.x. PMC 1885023. PMID 16487221.
- Arif SA, Poon H (August 2011). "Tadalafil: a long-acting phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension". Clin Ther. 33 (8): 993–1004. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.06.008. PMID 21762988.
- Galiè N, Brundage BH, Ghofrani HA, Oudiz RJ, Simonneau G, Safdar Z, et al. (June 2009). "Tadalafil therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension". Circulation. 119 (22): 2894–2903. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.108.839274. PMID 19470885.
- "Opsynvi (macitentan and tadalafil) Becomes the First and Only Health Canada-Approved Once Daily Fixed Dose Combination Treatment for Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)". Johnson & Johnson (Press release). 15 October 2021. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- "Approval Letter: Opsynvi (macitentan and tadalafil)" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- "U.S. FDA Approves Opsynvi (macitentan and tadalafil) as the First and Only Once-Daily Single-Tablet Combination Therapy for Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)". Johnson & Johnson (Press release). 22 March 2024. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- Lasker GF, Maley JH, Pankey EA, Kadowitz PJ (April 2011). "Targeting soluble guanylate cyclase for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension". Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine. 5 (2): 153–161. doi:10.1586/ers.11.9. PMC 3108035. PMID 21510726.
- George MP, Champion HC, Pilewski JM (2011). "Lung transplantation for pulmonary hypertension". Pulmonary Circulation. 1 (2): 182–191. doi:10.4103/2045-8932.83455. PMC 3198646. PMID 22034605.
- "2006 OPTN/SRTR Annual Report". US Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients. 2006-05-01. Archived from the original on 2010-06-05. Retrieved 2007-03-28.
- Cerveri I, D'Armini AM, Viganò M (April 2003). "Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy almost 50 years after the first surgical attempts". Heart. 89 (4): 369–370. doi:10.1136/heart.89.4.369. PMC 1769265. PMID 12639858.
- American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society (September 2013), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American College of Chest Physicians and American Thoracic Society, archived from the original on 3 November 2013, retrieved 6 January 2013
- Guidelines: Six-minute Walk Test. Accessed: 2015
- "Pulmonary Hypertension. About Pulmonary Hypertension | Patient". Patient. Archived from the original on 2016-01-02. Retrieved 2015-12-30.
- Mouratoglou SA, Bayoumy AA, Noordegraaf AV (2021). "Prediction Models and Scores in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Review". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 27 (10): 1266–1276. doi:10.2174/1381612824999201105163437. PMID 33155897. S2CID 226272078.
- McLaughlin VV, Sitbon O, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Black C, Galiè N, et al. (February 2005). "Survival with first-line bosentan in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension". The European Respiratory Journal. 25 (2): 244–249. doi:10.1183/09031936.05.00054804. PMID 15684287.
- Benza RL, Miller DP, Barst RJ, Badesch DB, Frost AE, McGoon MD (August 2012). "An evaluation of long-term survival from time of diagnosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension from the REVEAL Registry". Chest. 142 (2): 448–456. doi:10.1378/chest.11-1460. PMID 22281797.
- Kaufman MH, Stead L, Feig R (2007). First aid for the obstetrics & gynecology clerkship. New York: McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-07-144874-1.
- Ghosh AK (2008). Mayo Clinic Internal Medicine Review (8th ed.). Informa Healthcare. p. 55. ISBN 978-1-4200-8478-8.
- British Journal of Anaesthesia: "Primary pulmonary hypertension in pregnancy; a role for novel vasodilators" Archived 2011-01-21 at the Wayback Machine March 19, 2011
- Oudiz RJ (6 February 2023). "Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology". Medscape Reference.
- York M, Farber HW (November 2011). "Pulmonary hypertension: screening and evaluation in scleroderma". Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 23 (6): 536–544. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e32834ba6a7. PMID 21934501. S2CID 19528958.
- Nannini C. "Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis". MedScape.com. MedScape. Archived from the original on 8 February 2016. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- Mittoo S, Fell CD (April 2014). "Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus". Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 35 (2). MedScape: 249–254. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1371537. PMID 24668539. S2CID 24654448. Archived from the original on 26 October 2015. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- Lee MT, Rosenzweig EB, Cairo MS (August 2007). "Pulmonary hypertension in sickle cell disease". Clinical Advances in Hematology & Oncology. 5 (8): 585, 645–653. PMID 17982405.
- Minai OA, Chaouat A, Adnot S (June 2010). "Pulmonary hypertension in COPD: epidemiology, significance, and management: pulmonary vascular disease: the global perspective". Chest. 137 (6 Suppl): 39S – 51S. doi:10.1378/chest.10-0087. PMID 20522579.
- Balachandran JS, Masa JF, Mokhlesi B (September 2014). "Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome Epidemiology and Diagnosis". Sleep Medicine Clinics. 9 (3): 341–347. doi:10.1016/j.jsmc.2014.05.007. PMC 4210766. PMID 25360072.
- Reynolds PN (February 2011). "Gene therapy for pulmonary hypertension: prospects and challenges". Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy. 11 (2): 133–143. doi:10.1517/14712598.2011.542139. PMID 21219232. S2CID 23641857.
- "Elaine Kaufman, famed Elaine's restaurateur, dies at age 81". Daily News. 3 December 2010. Archived from the original on 28 August 2016. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- Folkart BA (21 June 1990). "Ina Balin, 52; Movie and TV Actress Sought Lung Implant". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 27 September 2016.
- Phull H (July 26, 2016). "She's tethered to an oxygen tank, but her singing career is soaring". New York Post. Archived from the original on August 14, 2016.
- Insdorf A (November 10, 2013). "The Challenges of Chloe Temtchine". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on September 18, 2016.
- "Autopsy: The Last Hours of Natalie Cole." Autopsy. Nar. Eric Meyers. Exec. Prod. Ed Taylor and Michael Kelpie. Reelz, 27 May 2017. Television.
Further reading
- "Pulmonary arterial hypertension". Genetics: Genetic Conditions. MedlinePlus, National Library of Medicine. 2016.
- "What Is Pulmonary Hypertension?". Health Topics: Pulmonary Hypertension. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. National Library of Medicine. May 2023.
- Rubin LJ, Badesch DB (August 2005). "Evaluation and management of the patient with pulmonary arterial hypertension". Annals of Internal Medicine. 143 (4): 282–292. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.463.8466. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-143-4-200508160-00009. PMID 16103472. S2CID 28841269.
- Abman SH, Hansmann G, Archer SL, Ivy DD, Adatia I, Chung WK, et al. (November 2015). "Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension: Guidelines From the American Heart Association and American Thoracic Society". Circulation. 132 (21): 2037–2099. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000329. PMID 26534956. S2CID 7412370.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Cardiovascular disease (vessels) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arteries, arterioles and capillaries | |||||||||
| Veins |
| ||||||||
| Arteries or veins | |||||||||
| Blood pressure |
| ||||||||
| Diseases of the respiratory system | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper RT (including URTIs, common cold) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lower RT/ lung disease (including LRTIs) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pleural cavity/ mediastinum |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other/general | |||||||||||||||||||||||