This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Materialscientist (talk | contribs) at 09:59, 14 November 2011 (tidy and expand). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 09:59, 14 November 2011 by Materialscientist (talk | contribs) (tidy and expand)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)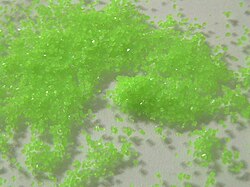 Praseodymium sulfate octahydrate | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Praseodymium sulphate, dipraseodymium trisulphate, praseodymium(III) sulfate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.553 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | Pr2(SO4)3 Pr2(SO4)3·nH2O, n=2,5,8 |
| Molar mass | 570.0031 g/mol 714.12534 g/mol (octahydrate) |
| Appearance | green crystalline solid |
| Density | 3.72 g/cm |
| Melting point | 1010 °C (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | 113.0 g/L (20 °C) 108.8 g/L (25 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Xi |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Praseodymium carbonate Praseodymium chloride |
| Other cations | Neodymium sulfate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Praseodymium sulfate is a Pr compound with formula Pr2(SO4)3. It is an odourless whitish-green crystalline compound. The anhydrous substance readily absorbs water forming pentahydrate and octahydrate.
Properties
Praseodymium sulfate is stable under standard conditions. At elevated temperatures, it gradually loses water and becomes more whitish. Like all rare earth sulfates, its solubility decreases with temperature, a property once used to separate it from other, non-rare earth compounds.
Pentahydrate and octahydrate have monoclinic crystal structures with densities of 3.713 and 2.813 g/cm, respectively. The octahydrate crystals are optically biaxial, with refractive index components of nα = 1.5399, nβ = 1.5494 and nγ = 1.5607. They belong to the space group C12/c1 (No. 15) and have lattice constants a = 13.700(2) Å, b = 6.861(1) Å, c = 18.453(2) Å, β = 102.80(1)° and Z = 4.
Synthesis
Crystals of octahydrate can be grown from solution obtained by dissolving wet Pr2O3 powder with sulfuric acid. This procedure can be optimised by adding a few evaporation/dissolution steps involving organic chemicals.
References
- ^ National Research Council (U.S.) (1919). Bulletin of the National Research Council. National Academies. pp. 3–. NAP:12020. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- ^ Y.-Q. Zheng, Y.-J. Zhu and J.-L. Lin (2002). "Redeterminaton of the crystal structure of praseodymium sulfate octahydrate, Pr2(SO4)3·8H2O". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie. New crystal structures. 217: 299–300. PDF copy
| Praseodymium compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pr(II) | |||
| Pr(III) |
| ||
| Pr(III,IV) | |||
| Pr(IV) | |||
| Pr(V) | |||
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |