This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Graeme Bartlett (talk | contribs) at 23:39, 16 March 2023 (added Category:Methoxy compounds using HotCat). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 23:39, 16 March 2023 by Graeme Bartlett (talk | contribs) (added Category:Methoxy compounds using HotCat)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical used to treat pulmonary issues Pharmaceutical compound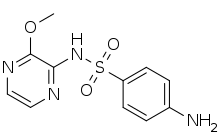 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Eadazine, Kelfizina, Kelfizine W, Longum |
| Other names | Sulfametopyrazine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 60 to 80% |
| Elimination half-life | 60 to 65 hours |
| Excretion | Urinary |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.278 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H12N4O3S |
| Molar mass | 280.30 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Sulfalene (INN, USAN) or sulfametopyrazine (BAN) is a long-acting sulfonamide antibacterial used for the treatment of chronic bronchitis, urinary tract infections and malaria. As of 2014 there were only two countries in which it is currently still marketed: Thailand and Ireland.
It was discovered by researchers at Farmitalia and first published in 1960 and was marketed as Kelfizina.
See also
References
- ^ "Sulfalene". MIMS Drug Information System. Retrieved 26 August 2011.
- DrugBank DB00664
- ^ Brayfield A, ed. (9 May 2013). "Sulfametopyrazine". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- Baruffa G (1966). "Clinical trials in Plasmodium falciparum malaria with a long-acting sulphonamide". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 60 (2): 222–4. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(66)90030-7. PMID 5332105.
- Per prior citation, the first publication: Camerino B, Palamidessi G (1960). "Derivati della parazina II. Sulfonamdopir". Gazz Chim Ital (in Italian). 90: 1802–1815.
| Antibacterials that inhibit nucleic acid (J01E, J01M) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antifolates (inhibit bacterial purine metabolism, thereby inhibiting DNA and RNA synthesis) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Quinolones (inhibit bacterial topoisomerase and/or DNA gyrase, thereby inhibiting DNA replication) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Anaerobic DNA inhibitors |
| ||||||||||||||||
| RNA synthesis |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This systemic antibiotic-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |