| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
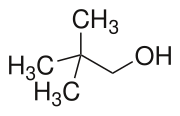
| Preferred IUPAC name 2,2-Dimethylpropan-1-ol | |
| Other names
tert-Butyl carbinol tert-Butylmethanol Neoamyl alcohol Neopentanol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.826 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1325 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C5H12O |
| Molar mass | 88.150 g·mol |
| Density | 0.812 g/mL at 20 °C |
| Melting point | 52.5 °C (126.5 °F; 325.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 113.5 °C (236.3 °F; 386.6 K) |
| Solubility in water | 36 g/L |
| Solubility | very soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
-399.4 kJ·mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H228, H319, H332, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264+P265, P271, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P317, P319, P337+P317, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 |
| Flash point | 37 °C (99 °F; 310 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Neopentyl alcohol is a compound with formula (CH3)3CCH2OH. It is a colorless solid. The compound is one of the eight isomers of pentyl alcohol.
Preparation and reactions
Neopentyl alcohol can be prepared from the hydroperoxide of diisobutylene. It can also be prepared by the reduction of trimethylacetic acid with lithium aluminium hydride. Neopentyl alcohol was the first described in 1891 by L. Tissier, who prepared it by reduction of a mixture of trimethyl acetic acid and trimethylacetyl chloride with sodium amalgam.
Neopentyl alcohol can be converted to neopentyl iodide by treatment with triphenylphosphite/methyl iodide:
- (CH3)3CCH2OH + I → (CH3)3CCH2I + [CH3(C6H5O)2PO + C6H5OH
See also
References
- Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 3–228, 5–42, 8–102, 16–22, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- "Neopentyl alcohol". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Joseph Hoffman (1960). "Neopentyl Alcohol". Organic Syntheses. 40: 76. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.040.0076.
- Comptes Rendus, 1891, 112, p. 1065
- H. N. Rydon (1971). "Alkyl Iodides: Neopentyl Iodide and Iodocyclohexane". Organic Syntheses. 51: 44. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.051.0044.