 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
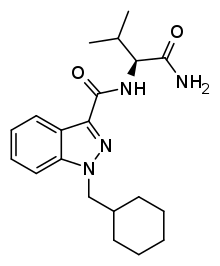
| Formula | C20H28N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 356.470 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
AB-CHMINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid. It is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor (Ki = 0.78 nM) and CB2 receptor (Ki = 0.45 nM) and fully substitutes for Δ-THC in rat discrimination studies, while being 16x more potent. Continuing the trend seen in other cannabinoids of this generation, such as AB-FUBINACA and AB-PINACA, it contains a valine amino acid amide residue as part of its structure, where older cannabinoids contained a naphthyl or adamantane residue.
Side effects
There have been a number of reported cases of seizures, deaths, and psychotic episodes in relation to this synthetic cannabinoid.
Legal status
In 2015, AB-CHMINACA became a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States.
AB-CHMINACA is an Anlage II controlled substance in Germany as of May 2015.
As of October 2015 AB-CHMINACA is a controlled substance in China.
AB-CHMINACA is illegal in Switzerland as of December 2015.
AB-CHMINACA is an illegal substance in Russian Federation.
See also
- 5F-AB-PINACA
- 5F-ADB
- 5F-AMB
- A-CHMINACA
- AB-FUBINACA
- AB-CHFUPYCA
- AB-PINACA
- ADB-CHMINACA
- ADB-FUBINACA
- ADB-PINACA
- ADBICA
- APICA
- APINACA
- MDMB-CHMICA
- MDMB-CHMINACA
- MDMB-FUBINACA
- PX-3
References
- Anvisa (2023-07-24). "RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-07-25). Archived from the original on 2023-08-27. Retrieved 2023-08-27.
- "Substance Details AB-CHMINACA". Retrieved 2024-01-22.
- Wiley JL, Marusich JA, Lefever TW, Antonazzo KR, Wallgren MT, Cortes RA, et al. (September 2015). "AB-CHMINACA, AB-PINACA, and FUBIMINA: Affinity and Potency of Novel Synthetic Cannabinoids in Producing Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol-Like Effects in Mice". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 354 (3): 328–39. doi:10.1124/jpet.115.225326. PMC 4538877. PMID 26105953.
- AB-CHMINACA, Cayman Chemicals
- "N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-CHMINACA), N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-PINACA) and [1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl](naphthalen-1-yl)methanone (THJ-2201). Background Information and Evaluation of 'Three Factor Analysis' (Factors 4, 5, and 6) for Temporary Scheduling" (PDF). Drug Enforcement Administration. December 2014. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
- Merrill J (5 June 2015). "Vertex: Police warn of 'ticking time bomb' of potentially lethal cannabis substitute". The Independent. Archived from the original on 2015-06-05. Retrieved 2 July 2015.
- Trecki J, Gerona RR, Schwartz MD (July 2015). "Synthetic Cannabinoid-Related Illnesses and Deaths". The New England Journal of Medicine. 373 (2): 103–7. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1505328. PMID 26154784.
- Wurita A, Hasegawa K, Minakata K, Gonmori K, Nozawa H, Yamagishi I, et al. (March 2016). "Identification and quantification of metabolites of AB-CHMINACA in a urine specimen of an abuser". Legal Medicine. 19: 113–8. doi:10.1016/j.legalmed.2015.07.011. PMID 26257317.
- Schock B (30 September 2015). "No criminal charges in March death of Terrance Moxley". Richland Source. Retrieved 2 October 2015.
- Tyndall JA, Gerona R, De Portu G, Trecki J, Elie MC, Lucas J, et al. (November 2015). "An outbreak of acute delirium from exposure to the synthetic cannabinoid AB-CHMINACA". Clinical Toxicology. 53 (10): 950–6. doi:10.3109/15563650.2015.1100306. PMC 9128755. PMID 26555732. S2CID 24724258.
- Klavž J, Gorenjak M, Marinšek M (August 2016). "Suicide attempt with a mix of synthetic cannabinoids and synthetic cathinones: Case report of non-fatal intoxication with AB-CHMINACA, AB-FUBINACA, alpha-PHP, alpha-PVP and 4-CMC". Forensic Science International. 265: 121–4. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.01.018. PMID 26890319.
- Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (January 2015). "Schedules of controlled substances: temporary placement of three synthetic cannabinoids into schedule I. Final order" (PDF). Federal Register. 80 (20): 5042–7. PMID 25730924.
- "Gesetz über den Verkehr mit Betäubungsmitteln (Betäubungsmittelgesetz - BtMG) Anlage II (zu § 1 Abs. 1) (verkehrsfähige, aber nicht verschreibungsfähige Betäubungsmittel)". Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- "Verordnung des EDI über die Verzeichnisse der Betäubungsmittel, psychotropen Stoffe, Vorläuferstoffe und Hilfschemikalien". Der Bundesrat.
- Cannaert A, Sparkes E, Pike E, Luo JL, Fang A, Kevin RC, et al. (November 2020). "in Vitro Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Activity of Recently Detected Synthetic Cannabinoids 4F-MDMB-BICA, 5F-MPP-PICA, MMB-4en-PICA, CUMYL-CBMICA, ADB-BINACA, APP-BINACA, 4F-MDMB-BINACA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, A-CHMINACA, 5F-AB-P7AICA, 5F-MDMB-P7AICA, and 5F-AP7AICA". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 11 (24): 4434–4446. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00644. PMID 33253529. S2CID 227246346.
| Cannabinoid receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transporter (modulators) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (modulators) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||