| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Cadmium(II) sulfate | |
| Other names Sulfuric acid, cadmium salt (1:1), | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.288 |
| EC Number |
|
| Gmelin Reference | 8295 |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2570 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | CdSO4 CdSO4·H2O (monohydrate) 3CdSO4·8H2O (octahydrate) |
| Molar mass | 208.47 g/mol (anhydrous) 226.490 g/mol (monohydrate) 769.546 g/mol (octahydrate) |
| Appearance | White hygroscopic solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 4.691 g/cm (anhydrous) 3.79 g/cm (monohydrate) 3.08 g/cm (octahydrate) |
| Melting point | 1,000 °C (1,830 °F; 1,270 K) (anhydrous) 105 °C (monohydrate) 40 °C (octahydrate) |
| Boiling point | (decomposes to basic sulfate and then oxide) |
| Solubility in water | anhydrous: 75 g/100 mL (0 °C) 76.4 g/100 mL (25 °C) 58.4 g/100 mL (99 °C) monohydrate: 76.7 g/100 mL (25 °C) octahydrate: very soluble |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in methanol, ethyl acetate insoluble in ethanol |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -59.2·10 cm/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.565 |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | orthorhombic (anhydrous) monoclinic (hepta & octahydrate) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S298) |
123 J·mol·K |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−935 kJ·mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |   
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H301, H330, H340, H350, H360, H372, H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P201, P202, P260, P264, P270, P271, P273, P281, P284, P301+P310, P304+P340, P308+P313, P310, P314, P320, P321, P330, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 280 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
| PEL (Permissible) | TWA 0.005 mg/m (as Cd) |
| REL (Recommended) | Ca |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | Ca |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Cadmium acetate, Cadmium chloride, Cadmium nitrate |
| Other cations | Zinc sulfate, Calcium sulfate, Magnesium sulfate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Cadmium sulfate is the name of a series of related inorganic compounds with the formula CdSO4·xH2O. The most common form is the monohydrate CdSO4·H2O, but two other forms are known CdSO4·8⁄3H2O and the anhydrous salt (CdSO4). All salts are colourless and highly soluble in water.
Structure, preparation, and occurrence
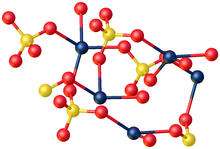
X-ray crystallography shows that CdSO4·H2O is a typical coordination polymer. Each Cd center has octahedral coordination geometry, being surrounded by four oxygen centers provided by four sulfate ligands and two oxygen centers from the bridging water ligands.
Cadmium sulfate hydrate can be prepared by the reaction of cadmium metal or its oxide or hydroxide with dilute sulfuric acid:
- CdO + H2SO4 → CdSO4 + H2O
- Cd + H2SO4 → CdSO4 + H2
The anhydrous material can be prepared using sodium persulfate:
- Cd + Na2S2O8 → CdSO4 + Na2SO4
Cadmium sulfates occur as the following rare minerals drobecite (CdSO4·4H2O), voudourisite (monohydrate), and lazaridisite (the 8/3-hydrate).
Applications
Cadmium sulfate is used widely for the electroplating of cadmium in electronic circuits. It is also a precursor to cadmium-based pigment such as cadmium sulfide. It is also used for electrolyte in a Weston standard cell as well as a pigment in fluorescent screens.
References
- Lide, David R., ed. (2006). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0487-3.
- ^ Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A21. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0087". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Aurivillius, Karin; Stålhandske, Claes (1980). "A Reinvestigation of the Crystal Structures of HgSO4 and CdSO4". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials. 153 (1–2): 121–129. Bibcode:1980ZK....153..121A. doi:10.1524/zkri.1980.0011.
- Theppitak, C.; Chainok, K. (2015). "Crystal Structure of CdSO4(H2O): A Redetermination"". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 71 (10): i8 – pi9. doi:10.1107/S2056989015016904. PMC 4647421. PMID 26594423.
| Cadmium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Cadmium(I) | |
| Cadmium(II) | |