| |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.210 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1469 | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | Pb(NO3)2 | ||
| Molar mass | 331.2 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless or white | ||
| Density | 4.53 g/cm | ||
| Melting point | 470 °C (878 °F; 743 K) decomposes | ||
| Solubility in water | 376.5 g/L (0 °C) 597 g/L (25°C) 1270 g/L (100°C) | ||
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −74·10 cm/mol | ||
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.782 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−451.9 kJ·mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |    
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H302, H317, H318, H332, H360, H373, H410 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P201, P202, P210, P220, P221, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P312, P314, P321, P330, P333+P313, P363, P370+P378, P391, P405, P501 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
| LDLo (lowest published) | 500 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 1000 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |||
Lead(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb(NO3)2. It commonly occurs as a colourless crystal or white powder and, unlike most other lead(II) salts, is soluble in water.
Known since the Middle Ages by the name plumbum dulce, the production of lead(II) nitrate from either metallic lead or lead oxide in nitric acid was small-scale, for direct use in making other lead compounds. In the nineteenth century lead(II) nitrate began to be produced commercially in Europe and the United States. Historically, the main use was as a raw material in the production of pigments for lead paints, but such paints have been superseded by less toxic paints based on titanium dioxide. Other industrial uses included heat stabilization in nylon and polyesters, and in coatings of photothermographic paper. Since around the year 2000, lead(II) nitrate has begun to be used in gold cyanidation.
Lead(II) nitrate is toxic and must be handled with care to prevent inhalation, ingestion and skin contact. Due to its hazardous nature, the limited applications of lead(II) nitrate are under constant scrutiny.
History
Lead nitrate was first identified in 1597 by the alchemist Andreas Libavius, who called the substance plumbum dulce, meaning "sweet lead", because of its taste. It is produced commercially by reaction of metallic lead with concentrated nitric acid in which it is sparingly soluble. It has been produced as a raw material for making pigments such as chrome yellow (lead(II) chromate, PbCrO4) and chrome orange (basic lead(II) chromate, Pb2CrO5) and Naples yellow. These pigments were used for dyeing and printing calico and other textiles. It has been used as an oxidizer in black powder and together with lead azide in special explosives.
Production
Lead nitrate is produced by reaction of lead(II) oxide with concentrated nitric acid:
- PbO + 2 HNO3(concentrated) → Pb(NO3)2↓ + H2O
It may also be obtained evaporation of the solution obtained by reacting metallic lead with dilute nitric acid.
- Pb + 4 HNO3 → Pb(NO3)2 + 2 NO2 + 2 H2O
Solutions and crystals of lead(II) nitrate are formed in the processing of lead–bismuth wastes from lead refineries.
Structure
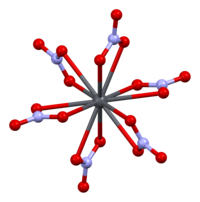
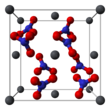
The crystal structure of solid lead(II) nitrate has been determined by neutron diffraction. The compound crystallizes in the cubic system with the lead atoms in a face-centred cubic system. Its space group is Pa3Z=4 (Bravais lattice notation), with each side of the cube with length 784 picometres.
The black dots represent the lead atoms, the white dots the nitrate groups 27 picometres above the plane of the lead atoms, and the blue dots the nitrate groups the same distance below this plane. In this configuration, every lead atom is bonded to twelve oxygen atoms (bond length: 281 pm). All N–O bond lengths are identical, at 127 picometres.
Research interest in the crystal structure of lead(II) nitrate was partly based on the possibility of free internal rotation of the nitrate groups within the crystal lattice at elevated temperatures, but this did not materialise.
Chemical properties and reactions
| Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Lead nitrate decomposes on heating, a property that has been used in pyrotechnics . It is soluble in water and dilute nitric acid.
Basic nitrates are formed in when alkali is added to a solution. Pb2(OH)2(NO3)2 is the predominant species formed at low pH. At higher pH Pb6(OH)5(NO3) is formed. The cation is unusual in having an oxide ion inside a cluster of 3 face-sharing PbO4 tetrahedra. There is no evidence for the formation of the hydroxide, Pb(OH)2, in aqueous solution below pH 12.
Solutions of lead nitrate can be used to form co-ordination complexes. Lead(II) is a hard acceptor; it forms stronger complexes with nitrogen and oxygen electron-donating ligands. For example, combining lead nitrate and pentaethylene glycol (EO5) in a solution of acetonitrile and methanol followed by slow evaporation produced the compound . In the crystal structure for this compound, the EO5 chain is wrapped around the lead ion in an equatorial plane similar to that of a crown ether. The two bidentate nitrate ligands are in trans configuration. The total coordination number is 10, with the lead ion in a bicapped square antiprism molecular geometry.
The complex formed by lead nitrate with a bithiazole bidentate N-donor ligand is binuclear. The crystal structure shows that the nitrate group forms a bridge between two lead atoms. One interesting aspect of this type of complexes is the presence of a physical gap in the coordination sphere; i.e., the ligands are not placed symmetrically around the metal ion. This is potentially due to a lead lone pair of electrons, also found in lead complexes with an imidazole ligand.
Applications
Lead nitrate has been used as a heat stabiliser in nylon and polyesters, as a coating for photothermographic paper, and in rodenticides.
Heating lead nitrate is convenient means of making nitrogen dioxide
In the gold cyanidation process, addition of lead(II) nitrate solution improves the leaching process. Only limited amounts (10 to 100 milligrams lead nitrate per kilogram gold) are required.
In organic chemistry, it may be used in the preparation of isothiocyanates from dithiocarbamates. Its use as a bromide scavenger during SN1 substitution has been reported.
Safety
Main article: Lead poisoningLead(II) nitrate is toxic, and ingestion may lead to acute lead poisoning, as is applicable for all soluble lead compounds. All inorganic lead compounds are classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as probably carcinogenic to humans (Category 2A). They have been linked to renal cancer and glioma in experimental animals and to renal cancer, brain cancer and lung cancer in humans, although studies of workers exposed to lead are often complicated by concurrent exposure to arsenic. Lead is known to substitute for zinc in a number of enzymes, including δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (porphobilinogen synthase) in the haem biosynthetic pathway and pyrimidine-5′-nucleotidase, important for the correct metabolism of DNA and can therefore cause fetal damage.
References
- ^ CRC handbook of chemistry and physics : a ready-reference book of chemical and physical data. William M. Haynes, David R. Lide, Thomas J. Bruno (2016-2017, 97th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida. 2016. ISBN 978-1-4987-5428-6. OCLC 930681942.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Patnaik, Pradyot (2003). Handbook of inorganic chemicals. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 475. ISBN 0-07-049439-8. OCLC 50252041.
- "Lead compounds (as Pb)". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "Lead nitrate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- Libavius, Andreas (1595). Alchemia Andreæ Libavii. Francofurti: Iohannes Saurius.
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Lead" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 16 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 314–320.
- Macgregor, John (1847). Progress of America to year 1846. London: Whittaker & Co. ISBN 0-665-51791-2.
- Partington, James Riddick (1950). A Text-book of Inorganic Chemistry. MacMillan. p. 838.
- ^ Barkley, J. B. (October 1978). "Lead nitrate as an oxidizer in blackpowder". Pyrotechnica. 4. Post Falls, Idaho: Pyrotechnica Publications: 16–18.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 388, 456. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
- Othmer, D. F. (1967). Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Vol. 12 (Iron to Manganese) (second completely revised ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons. p. 272. ISBN 0-471-02040-0.
- "Product catalog; other products". Tilly, Belgium: Sidech. Archived from the original on 2007-07-01. Retrieved 2008-01-05.
- Hamilton, W. C. (1957). "A neutron crystallographic study of lead nitrate". Acta Crystallogr. 10 (2): 103–107. doi:10.1107/S0365110X57000304.
- ^ Nowotny, H.; G. Heger (1986). "Structure refinement of lead nitrate". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 42 (2): 133–35. doi:10.1107/S0108270186097032.
- Nowotny, H.; Heger, G. (15 February 1986). "Cấu trúc của chì nitrat". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 42 (2): 133–135. doi:10.1107/S0108270186097032. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- Ferris, L. M. (1959). "Lead nitrate—Nitric acid—Water system". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 5 (3): 242. doi:10.1021/je60007a002.
- Pauley, J. L.; M. K. Testerman (1954). "Basic Salts of Lead Nitrate Formed in Aqueous Media". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (16): 4220–4222. doi:10.1021/ja01645a062.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8. p. 395
- Rogers, Robin D.; Andrew H. Bond; Debra M. Roden (1996). "Structural Chemistry of Poly (ethylene glycol). Complexes of Lead(II) Nitrate and Lead(II) Bromide". Inorg. Chem. 35 (24): 6964–6973. doi:10.1021/ic960587b. PMID 11666874.
- Mahjoub, Ali Reza; Ali Morsali (2001). "A Dimeric Mixed-Anions Lead(II) Complex: Synthesis and Structural Characterization of (ClO4)3 {BTZ = 4,4'-Bithiazole}". Chemistry Letters. 30 (12): 1234. doi:10.1246/cl.2001.1234.
- Shuang-Yi Wan; Jian Fan; Taka-aki Okamura; Hui-Fang Zhu; Xing-Mei Ouyang; Wei-Yin Sun & Norikazu Ueyama (2002). "2D 4.8 Network with threefold parallel interpenetration from nanometre-sized tripodal ligand and lead(II) nitrate". Chem. Commun. (21): 2520–2521. doi:10.1039/b207568g.
- Habashi, Fathi (1998). "Recent advances in gold metallurgy". Revisa de la Facultad de Ingeniera, Universidad Central de Venezuela. 13 (2): 43–54.
- "Auxiliary agents in gold cyanidation". Gold Prospecting and Gold Mining. Retrieved 2008-01-05.
- Dains, F. B.; Brewster, R. Q.; Olander, C. P. "Phenyl isothiocyanate". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 1, p. 447.
- Rapoport, H.; Jamison, T. (1998). "(S)-N-(9-Phenylfluoren-9-yl)alanine and (S)-Dimethyl-N-(9-phenylfluoren-9-yl)aspartate". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 9, p. 344.
- "Lead nitrate, Chemical Safety Card 1000". International Labour Organization, International Occupational Safety and Health Information Centre. March 1999. Retrieved 2008-01-19.
- "Inorganic and Organic Lead Compounds" (PDF). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Suppl. 7. International Agency for Research on Cancer: 239. 1987. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-03-06. Retrieved 2008-01-19.
- World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer (2006). "Inorganic and Organic Lead Compounds" (PDF). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 87. International Agency for Research on Cancer. ISBN 92-832-1287-8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-10-21. Retrieved 2008-01-01.
- Mohammed-Brahim, B.; Buchet, J.P.; Lauwerys, R. (1985). "Erythrocyte pyrimidine 5'-nucleotidase activity in workers exposed to lead, mercury or cadmium". Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 55 (3): 247–52. doi:10.1007/BF00383757. PMID 2987134. S2CID 40092031.
External links
- Woodbury, William D. (1982). "Lead". Mineral Yearbook Metals and Minerals. Bureau of Mines: 515–42. Retrieved 2008-01-18.
- "Lead". NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. September 2005. NIOSH 2005-149. Retrieved 2008-01-19.
- "Lead and Lead Compounds Fact Sheet". National Pollutant Inventory. Australian Government, Department of the Environment and Water Resources. July 2007. Archived from the original on January 11, 2008. Retrieved 2008-01-19.
- "Lead". A Healthy Home Environment, Health Hazards. US Alliance for healthy homes. Archived from the original on 2008-02-20. Retrieved 2008-01-19.
- Material Safety Data Sheets
- MSDS for lead nitrate, PTCL, Oxford University
- MSDS for lead nitrate, Science Stuff Inc
- MSDS for lead nitrate, Iowa State University
| Lead compounds | |
|---|---|
| Pb(II) | |
| Pb(II,IV) | |
| Pb(IV) | |
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the nitrate ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||