| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.222.600 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | Sn(NO3)4 |
| Molar mass | 366.73 g/mol |
| Appearance | Silky Crystals |
| Density | 2.65 g/cm |
| Melting point | 91 °C (196 °F; 364 K) |
| Boiling point | 98 °C (208 °F; 371 K) (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | Reacts |
| Solubility | Soluble in carbon tetrachloride, chloroform |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/c |
| Lattice constant | a = 7.80 Å, b = 13.85 Å, c = 10.23 Å |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H272, H314 |
| Precautionary statements | P220, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Tin(IV) nitrate is a salt of tin with nitric acid. It is a volatile white solid, subliming at 40 °C under a vacuum. Unlike other nitrates, it reacts with water to produce nitrogen dioxide.
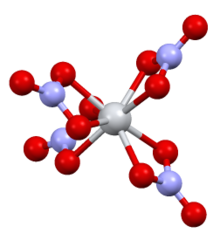
Structure
It is structurally very similar to titanium(IV) nitrate, with the only major difference being the Sn–O bond(2.161 Å) being slightly longer than the Ti–O bond(2.068 Å).
Production
It was first prepared in the 1960s. Tin(IV) chloride was added to dinitrogen pentoxide at -78 °C, which produced tin(IV) nitrate and nitryl chloride:
- SnCl4 + 4 N2O5 → Sn(NO3)4 + 4 NO2Cl
Attempts to prepare this compound by reacting tin(II) oxide and nitric acid resulted in a formation of tin(II) nitrate hydroxide.
Reactions
This compound is sensitive to water, it hydrolyzes into tin(IV) oxide and nitrogen dioxide. Tin(IV) nitrate reacts with trifloroacetic acid anhydride to yield (NO2)2 which is a nitronium salt. With trifluoroacetic acid a similar compound solvated with trifluoroacetic acid is produced.
It also reacts with acetic anhydride or acetic acid to produce tin(IV) acetate and with nitric oxide to produce tin(IV) oxynitrate.
The reaction of tin(IV) nitrate with triphenylphosphine and triphenylarsine yields dinitratotin(IV)bis(diphenylphosphonate) and dinitratotin(IV)bis(diphenylarsonate).
References
- "Tin(IV) Nitrate". American Elements. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- "Tin(IV) nitrate". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ C. D. Garner; D. Sutton; S. C. Wallwork (1967). "The crystal structures of anhydrous nitrates and their complexes. Part IV. Tin(IV) nitrate". Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical: 1949–1954. doi:10.1039/J19670001949.
- C. C. Addison; W. B. Simpson (1965). "Tin(IV) nitrate: the relation between structure and reactivity of metal nitrates". Journal of the Chemical Society: 598–602. doi:10.1039/JR9650000598.
- J. D. Donaldson; W. Moser (1961). "Basic tin(II) nitrate". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed). 381: 1996–2000. doi:10.1039/JR9610001996.
- ^ Harrison, Philip G.; Khalil, Mutassim I.; Logan, Norman (January 1978). "A contribution to the chemistry of tin(IV) nitrate". Inorganica Chimica Acta. 30: 165–170. doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(00)89031-3.
| Tin compounds | |
|---|---|
| Sn(II) | |
| Sn(IV) | |
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the nitrate ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||