This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 64.229.178.246 (talk) at 00:36, 27 March 2005 (→Effects and health issues). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 00:36, 27 March 2005 by 64.229.178.246 (talk) (→Effects and health issues)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |
| General | |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | Template:Carbon17Template:Hydrogen21Template:NitrogenTemplate:Oxygen4 |
| Molecular weight | 303.35 amu |
| CAS number | 50-36-2 |
| Other names | |
| |
Cocaine is a crystalline alkaloid that is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant. It is a stimulant of the central nervous system and an appetite suppressant, creating a euphoric sense of happiness and increased energy. Though most often used recreationally for this effect, cocaine is also a topical anesthetic that is used in eye and nasal surgery.
History
The coca leaf
For thousands of years, South American indigenous peoples chewed the coca leaf, a plant which contains vital nutrients as well as numerous alkaloids including cocaine. The leaf was chewed almost universally by some indigenous communities, but there is no evidence that its habitual use ever led to any of the negative consequences generally associated with habitual cocaine use today. It was an important source of nutrition and energy in a region that was lacking in other food sources and oxygen; the vitamins and protein present in the leaves, as much as the cocaine alkaloid, helped provide the energy and strength necessary for steep walks in this mountainous area.
When the Spaniards conquered South America, they at first ignored Aboriginal claims that the leaf gave them strength and energy, and declared the practice of chewing it the work of the Devil. But after discovering that these claims were true, they legalized and taxed the leaf, taking 10% of the value of each crop. These taxes were for a time the main source of support for the Roman Catholic Church in the region.
In 1609 Padre Blas Valera wrote:
"Coca protects the body from many ailments, and our doctors use it in powdered form to reduce the swelling of wounds, to strengthen broken bones, to expel cold from the body or prevent it from entering, and to cure rotten wounds or sores that are full of maggots. And if it does so much for outward ailments, will not its singular virtue have even greater effect in the entrails of those who eat it?"
Isolation
Although the stimulant and hunger-suppressant properties of coca had been known for many centuries, the isolation of the cocaine alkaloid was not achieved until 1855. Although many scientists had attempted to isolate cocaine, no one had been successful for two reasons: the knowledge of chemistry required was insufficient at the time, and coca does not grow in Europe and is easily ruined during travel.
The cocaine alkaloid was first isolated by the German chemist Friedrich Gaedcke in 1855. Gaedcke named the alkaloid "erythroxyline", and published a description in the journal Archives de Pharmacie.
In 1856 Friederich Wöhler asked Dr. Carl Scherzer, a scientist aboard the Novara (an Austrian frigate sent by Emperor Franz Joseph to circle the globe), to bring him a large amount of coca leaves from South America. In 1859 the ship finished its travels and Wöhler received a trunk full of coca. Wöhler passed on the leaves to Albert Niemann, a Ph.D. student at the University of Göttingen in Germany, who then developed an improved purification process.
Niemann described every step he took to isolate cocaine in a his dissertation entitled On a New Organic Base in the Coca Leaves, which was published in 1860 — it also earned him his Ph.D. and is now in the British Library. He wrote of the alkaloid's "colourless transparent prisms" and said that, "Its solutions have an alkaline reaction, a bitter taste, promote the flow of saliva and leave a peculiar numbness, followed by a a sense of cold when applied to the tongue." Niemann named the alkaloid "cocaine" — as with other alkaloids its name carried the "-ine" suffix.
Popularization
In 1859 an Italian doctor Paolo Mantegazza returned from Peru, where he had witnessed first-hand the use of coca by the natives. He proceeded to experiment on himself and upon his return to Milan he wrote a paper in which he described the effects. In this paper he declared coca and cocaine (at the time they were assumed to be the same) as being useful medicinally, in the treatment of "a furred tongue in the morning, flatulence, whitening of the teeth."

A chemist named Angelo Mariani who read Mantegazza's paper became immediately intrigued with coca, and its economic potential. In 1863 Mariani started marketing a wine called Vin Mariani which had been treated with coca leaves. The ethanol in the wine acted as a solvent and extracted the cocaine from the coca leaves, altering the drink's effect. It contained 6 mg cocaine per ounce of wine, but Vin Mariani, which was to be exported, contained 7.2 mg per ounce in order to compete with the higher cocaine content of similar drinks in the United States. Later when Coca Cola was invented, cocaine was included in its ingredients. The only known measure of the amount of cocaine in Coca Cola was determined in 1902 as being as little as 1/400 of a grain (0.2 mg) per ounce of syrup. (6 ppm.) The actual amount of cocaine that Coca Cola contained is impossible to determine. (Cocaine was removed from the drink using a chemical process as of 1929.)
Cocaine use became very popular in the late 19th century, with many prominent figures praising its therapeutic and even recreational usage. Satisfied consumers of Mariani's cocaine-wine products included Ulysses S. Grant, whom Mariani claimed drank the elixir daily; Pope Leo XIII, who appeared on a poster promoting the wine; Frédéric Bartholdi, who designed the Statue of Liberty and remarked that if Vin Mariani had been available earlier he would have made the statue taller; and "physicians to all the royal households of Europe".
In 1879 cocaine began to be used to treat morphine addiction. Cocaine was introduced into clinical use as a local anaesthetic in Germany in 1884, about the same time as Sigmund Freud published his work Über Coca, in which he wrote that cocaine causes:
"...exhilaration and lasting euphoria, which in no way differs from the normal euphoria of the healthy person...You perceive an increase of self-control and possess more vitality and capacity for work....In other words, you are simply normal, and it is soon hard to believe you are under the influence of any drug....Long intensive physical work is performed without any fatigue...This result is enjoyed without any of the unpleasant after-effects that follow exhilaration brought about by alcohol....Absolutely no craving for the further use of cocaine appears after the first, or even after repeated taking of the drug..."
Although synthetic local anaesthetics are much more widely used today, cocaine is, to some degree, still in use in dentistry and ophthalmology.
In 1885 the U.S. manufacturer Parke Davis and Co. sold cocaine in various forms, including cigarettes, powder, and even a cocaine mixture that could be injected directly into the user's veins with the included needle. The company promised that its cocaine products would "supply the place of food, make the coward brave, the silent eloquent and ... render the sufferer insensitive to pain."
By late Victorian era cocaine use had appeared as a vice in literature, for example as the cucaine injected by Arthur Conan Doyle's fictional Sherlock Holmes.
In 1909 Ernest Shackleton took "Forced March" brand cocaine tablets to Antarctica, as did Captain Scott a year later on his ill-fated journey to the south pole.
Prohibition
By the turn of the twentieth century, the addictive properties of cocaine had become clear to many, and the problem of cocaine abuse began to capture public attention in the United States. The dangers of cocaine abuse became part of a moral panic that was tied to the dominant racial and social anxieties of the day. In 1903 the American Journal of Pharmacy stressed that most cocaine abusers were "bohemians, gamblers, high- and low-class prostitutes, night porters, bell boys, burglars, racketeers, pimps, and casual laborers." In 1914 Dr. Christopher Koch of Pennsylvania's State Pharmacy Board made the racial innuendo explicit, testifying that, "Most of the attacks upon the white women of the South are the direct result of a cocaine-crazed Negro brain." In the same year, the Harrison Narcotics Act heavily regulated cocaine, and it was officially outlawed as a narcotic in 1922.
Modern usage

In most Western countries, cocaine is a popular recreational drug. In the United States, the introduction of "crack" cocaine introduced it to a generally poorer inner-city market. Use of the powder form has stayed relatively constant, experiencing a new height of use during the late 1990s and early 2000s in the USA, and has become much more popular in the last few years in the UK.
The stereotypical powder cocaine user is a frequenter of bars and clubs in his or her 20s or 30s, often employed in an office or professional environment. Average users of "crack" cocaine are 30 years or older inner-city residents of a lower income bracket. Exceptions to both rules exist in large numbers due to the immense popularity of the drug. Notwithstanding these averages, cocaine use is prevalent across all socioeconomic strata, including age, demographics, economic, social, political, religious, and livelihood; even President George Bush has refused to deny prior cocaine usage. Cocaine in its various forms comes in second only to cannabis as the most popular illegal recreational drug in the United States, and is number one in street value sold each year.
The estimated U.S. cocaine market exceeded $35 billion in street value for the year 2003, exceeding revenues by corporations such as AT&T and Starbucks. There is a tremendous demand for cocaine in the U.S. market, particularly among those who are making incomes affording luxury spending, such as single adults and various professionals. Cocaine's status as a club drug shows its immense popularity among the "party crowd". Cocaine's high revenues may be due to the drug's psychologically addictive nature, which makes the cessation of use quite difficult when compared to less addictive drugs such as marijuana or alcohol. It has become much more popular as a middle class drug in the United Kingdom in recent years.
Pharmacology
Appearance

Cocaine in its purest form is an off-white or pink chunky product. Cocaine appearing in powder form is a salt, typically cocaine hydrochloride (CAS 53-21-4). Cocaine is frequently adulterated or "cut" with various powdery fillers to increase its volume; the substances most commonly used in this process are baking soda, sugars, such as lactose, inositol, and mannitol, and local anesthetics, such as lidocaine. Adulterated cocaine is often a white or off-white powder.
The color of "crack" cocaine depends upon several factors including the origin of the cocaine used, the method of preparation — with ammonia or sodium bicarbonate, and the presence of impurities, but will generally range from a light brown to a pale brown. Its texture will also depend on the factors which affect color, but will range from a crumbly texture, which is usually the lighter variety, to hard, almost crystalline nature, which is usually the darker variety.
Forms of cocaine
Cocaine sulfate
Cocaine sulfate is produced by crushing coca leaves along with water and dilute sulfuric acid. This is often accomplished by putting the ingredients into a vat and stamping on it, in a manner not dissimilar to the traditional method for crushing grapes.
The sulfate itself is an intermediate step to producing cocaine hydrochloride. In South America it is commonly smoked along with tobacco, and is known as pasta, basuco, basa, pitillo, or simply paste.
Cocaine hydrochloride
This is the basic form of cocaine. It is very stable, and soluble in water, which makes it suitable for snorting or injecting.
Freebase
As the name implies, "freebase" is the base form of cocaine, as opposed to the salt form of cocaine hydrochloride. Whereas cocaine hydrochloride is extremely soluble in water, cocaine base is insoluble in water and is therefore not suitable for drinking, snorting or injecting. Cocaine hydrochloride is not well-suited for smoking because the temperature at which it vaporizes is very high, and close to the temperature at which it burns; however, cocaine base vaporizes at a low temperature, which makes it suitable for smoking.
Smoking freebase is preferred by many users because the cocaine is absorbed immediately into blood via the lungs, where it reaches the brain in about five seconds. The rush is much more intense than sniffing the same amount of cocaine nasally, but the effects do not last as long. The peak of the freebase rush is over almost as soon as the user exhales the vapor, but the high typically lasts 5–10 minutes afterwards. What makes freebase a particularly dangerous drug is that users typically don't wait that long for their next hit and will continue to smoke freebase until none is left. These effects are similar to those that can be achieved by injecting or "slamming" cocaine hydrochloride, but without the risks associated with intravenous drug use (although there are other serious risks associated with smoking freebase).
Freebase cocaine is produced by first dissolving cocaine hydrochloride in water. Once dissolved in water, cocaine hydrochloride (Coc HCl) disassociates into protonated cocaine ion (HCoc) and chloride ion (Cl). Any solids that remain in the solution are not cocaine (they are part of the cut) and are removed by filtering. A base, typically ammonia (NH3), is added to the solution to remove the extra proton from the cocaine. The following net chemical reaction takes place: -
As freebase cocaine (Coc) is insoluble in water, it precipitates out and the solution becomes cloudy. To recover the freebase, ether is added to the solution: Since freebase is highly soluble in ether, a vigorous shaking of the mixture results in the freebase being dissolved in the ether. As ether is insoluble in water, it can be siphoned off. The ether is then left to evaporate, leaving behind the nearly pure freebase.
This procedure is dangerous because of the hazards of handling ether: it is extremely flammable, its vapors are heavier than air and can "creep" from an open bottle, and in the presence of oxygen it can form peroxides which can spontaneously combust.
Crack cocaine
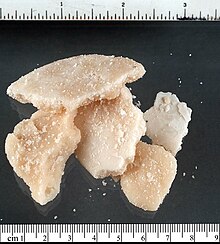
Because of the dangers of using ether to produce pure freebase cocaine, cocaine producers began to omit the step of removing the freebase cocaine precipitate from the ammonia mixture. Typically, filtration processes are also omitted. The end result of this process is that the cut, in addition to the ammonium salt (NH4Cl), remains in the freebase cocaine after the mixture is evaporated. The "rock" which is thus formed also contains a small amount of water. When the rock is heated this water boils, making a crackling sound (hence the name "crack"). Baking soda is now most often used as a base rather than ammonia for reasons of lowered stench and toxicity; however, any base can be used to make crack cocaine.
The net reaction when using baking soda (also called sodium bicarbonate, with a chemical formula of NaHCO3) is:
Crack is unique because it offers a strong cocaine experience in small, low-priced packages. In the United States, crack cocaine is often sold in small, inexpensive dosage units frequently known as "nickels" or "nickel rocks" (referring to the price of $5.00), and also "dimes" or "dime rocks" ($10.00) and sometimes as "twenties" or "forties". The quantity provided by such a purchase varies depending upon many factors, such as local availability, which is affected by geographic location. A twenty may yield a quarter gram or half gram on average, yielding 30 minutes to an hour of effect if hits are taken every few minutes. After the $20 or $40 mark, crack and powder cocaine are sold in grams or fractions of ounces. Many inner-city addicts with a regular dealer will "work a corner", taking money from anyone who wants crack, making a buy from the dealer, then delivering part of the product while keeping some for themselves. Street names for crack include "Devil's dandruff", "Devilsmoke", "Devil drug" and simply "rock".
Methods of administration
Chewed/eaten
The simplest way to administer cocaine is to chew on the leaves of the plant. Physical restrictions mean when taken this way, only small amounts of cocaine make it into the bloodstream and the effect is that of a mild stimulant. Mate de coca or coca-leaf tea (cf. Yerba mate) is also a traditional method of consumption and is often recommended to treat altitude sickness.
In 1986 an article in the Journal of the American Medical Association revealed that health food stores were selling coca-leaf tea as "Health Inca Tea". While the packaging claimed it had been "decocainized", no such process had taken place—they were selling a controlled substance off the shelves. The article stated that drinking two cups of the tea per day gave a mild stimulation, increased heart rate, and mood elevation, and the tea was essentially harmless. Despite this, the DEA seized several shipments in Hawaii, Chicago, Georgia, and several locations on the East Coast of the United States, and the product was removed from the shelves.
Snorted/sniffed
Absorption is approximately 80% through the nasal membranes when cocaine powder is "snorted". The blood vessels limit absorption. Chronic use results in ongoing rhinitis and necrosis of the nasal membranes. Cellulose granulomas from adulterants have also been found in the lungs of recreational "sniffers".
Prior to inhalation, cocaine powder must be divided into very fine particles. The cliché is that the user prepares his or her dose by putting some cocaine powder on a flat, hard surface such as a mirror, then uses a razor blade or credit card to finely chop the powder.
Injected
The intravenous route of administration provides the highest blood levels of drug in the shortest time. Injection of cocaine produces an exhilarating rush, although the euphoria passes quickly as the liver rapidly metabolizes the drug. Aside from the toxic effects of cocaine, there is also danger of circulatory emboli from the insoluble substances that may be used to cut the drug. Obviously, there is also a risk of serious infection associated with the use of contaminated needles.
Smoked
Smoking freebase or crack cocaine is most often accomplished using a pipe made from a small glass tube about one quarter-inch (about 6 mm) in diameter and up to several inches long. These are sometimes called "straight shooters"; readily available in convenience stores or smoke shops. They will sometimes contain a small paper flower and are promoted as a romantic gift. Buyers usually ask for a "rose" or a "flower".
A small piece of steel or copper scouring pad — often called a "brillo" or "chore", from the scouring pads of the same name — is placed into one end of the tube after having the bad-smelling coating burned off the metal. It then serves as a crude filter in which the "rock" can melt and boil to vapor.
The "rock" is placed at the end of the pipe closest to the filter and the other end of the pipe is placed in the mouth. A flame from a cigarette lighter or handheld torch is then held under the rock. As the rock is heated, it melts and burns away to vapor which the user inhales as smoke.
The effects are felt almost immediately after smoking, are very intense, and do not last long — usually five to fifteen minutes. Most users will want more after this time, especially frequent users. "Crack houses" depend on these cravings by providing users a place to smoke, and a ready supply of small bags for sale. Crack users will purchase a quantity and smoke it at the house, often buying and smoking more and more until they are out of money.
A heavily used crackpipe tends to break at the ends as the user "pushes" the pipe. "Pushing" is a technique used to partially recover crack which hardens on the inside wall of the pipe as the pipe cools. The user pushes the metal wool filter through the pipe from one end to the other to collect the build-up inside the pipe. The ends of the pipe can be broken by the object used to push the filter, frequently a small screwdriver or stiff piece of wire. The user will often remove the most jagged edges and continue using the pipe until it becomes so short that it burns the lips and fingers.
The tell-tale signs of a used crack pipe are a glass tube with burn marks at one or both ends and a clump of metal wool inside.
When smoked, cocaine is sometimes combined with other drugs, such as cannabis; often rolled into a joint or blunt. This combination is known as "primo". Cocaine and heroin combined is known as "speedball" or "moonrock" and has caused many deaths, particularly in and around Los Angeles. Crack smokers who are being drug tested may also make their "primo" with cigarette tobacco instead of cannabis, since a crack smoker can test clean within 2 to 3 days of use, if only urine (and not hair) is being tested.
Mechanism of action
Cocaine is a potent blocker of the dopamine transporter (DAT) and a less potent blocker of the norepinephrine transporter (NET) and serotonin transporter (SERT). Cocaine also blocks sodium channels, thereby interfering with the propagation of action potentials; thus, like lidocaine and novocaine, it acts as a local anaesthetic. The locomotor enhancing properties of cocaine may be attributable to its enhancement of dopaminergic transmission from the substantia nigra.
After cocaine is introduced to the body it travels to reward areas of the brain: the ventral tegmental area (VTA), the nucleus accumbens and the prefrontal cortex. These areas are saturated with dopamine synapses. Normally, after dopamine is released in the synaptic cleft, it binds to the dopamine receptors; reuptake sites (protein transported structures) will utilize the rest of the neurotransmitter (dopamine). In the presence of cocaine the normal process of reuptaking is breached. Cocaine binds to the uptake sites, which leaves a higher concentration of dopamine in the synaptic cleft. The higher activation of dopamine receptors in the post-synaptic cell causes various intracellular changes, which ultimately lead to changes in firing patterns.
Metabolism and excretion
Cocaine is extensively metabolized, primarily in the liver, with only about 1% excreted unchanged in the urine. It is mostly eliminated as benzoylecgonine, the major metabolite of cocaine, and is also excreted in lesser amounts as ecgonine methyl ester and ecgonine.
If taken with alcohol, cocaine combines with the ethanol in the liver to form cocaethylene, which is both more euphorigenic and has higher cardiovascular toxicity than cocaine by itself.
Cocaine metabolites are detectable in urine for up to two days after cocaine is used. Benzoylecgonine can be detected in urine within four hours after cocaine inhalation and remains detectable in concentrations greater than 1000 ng/ml for as long as 48 hours. Detection in hair is possible in regular users until the sections of hair grown during use are cut or fall out.
Effects and health issues
Cocaine is a potent central nervous system stimulant. Its effects last from 20 minutes to several hours, dependent upon the dosage of cocaine taken and its purity.
The initial signs of stimulation are hyperactivity, restlessness, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, increased heart rate and euphoria. The euphoria is quickly followed by feelings of discomfort and depression and a craving to re-experience the drug. Side effects can include twitching and paranoia, which usually increase with frequent usage.
With excessive dosage the drug can produce hallucinations, paranoid delusions, itching, and formication.
Overdose causes tachyarrhythmias and a marked elevation of blood pressure. These can be life threatening, especially if the user has existing cardiac problems.
Toxicity results in seizures, followed by respiratory and circulatory depression of medullar origin. This may lead to death from respiratory failure, stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, or heart-failure. Cocaine is also highly pyrogenic, because the stimulation and increased muscular activity cause greater heat production. Heat loss is inhibited by the intense vasoconstriction. Cocaine-induced hyperthermia may cause muscle cell destruction and myoglobinuria resulting in renal failure. There is no specific antidote for cocaine overdose.
Cocaine abuse is associated with a lifetime risk of heart attack that is seven times that of non-users. During the hour after cocaine is used, heart attack risk rises 24-fold. It accounts for 25% of the heart attacks in the 18–45 year-old age group.
Side effects from chronic smoking of cocaine include chest pain, lung trauma, shortness of breath, sore throat, hoarse voice, dyspnea, and an aching, flu-like syndrome. A common misconception is that the smoking of cocaine breaks down tooth enamel and causes tooth decay. Although this isn't true, the lifestyle of frequent cocaine users may include poor dental hygeine, which often results in tooth decay. In addition, cocaine often causes involuntary tooth grinding, known as bruxism, which can deteriorate tooth enamel and lead to gingivitis.
Chronic intranasal usage can degrade the cartilage separating the nostrils (the Septum nasi), leading eventually to its complete disappearance.
Cocaine as a local anesthetic
Cocaine is used as a topical anesthetic in eye and nasal surgery. The major disadvantages of this use are cocaine's intense vasoconstrictor activity and potential for cardiovascular toxicity. Although the vasoconstriction is sometimes an advantage (as it reduces bleeding), cocaine has now been largely replaced in medicine by local anaesthetics that are simply combined with a vasoconstrictor such as phenylephrine or epinephrine.
Cocaine addiction
Cocaine addiction is obsessive or uncontrollable abuse of cocaine. Twelve-step programs such as Cocaine Anonymous (modeled on Alcoholics Anonymous) exist to combat this problem. A cocaine vaccine is also being tested which may prevent the recipient from feeling the desirable effects of the drug, although it only works when given to young children.
Cocaine has positive reinforcement effects, which refers to the effect that certain stimuli have on behavior. Good feelings become associated with the drug, causing a frequent user to take the drug as a response to bad news or mild depression. This activation strengthens the response that was just made. If the drug was taken by a fast acting route such as injection or inhalation, the response will be the act of taking more cocaine, so the response will be reinforced. Powder cocaine, being a club drug is most commonly available in the evening and night hours. Since cocaine is a stimulant, a user will often drink large amounts of alcohol during and after usage in order to sleep. These several hours of temporary relief and pleasure will further reinforce the positive response. Other downers such as heroin and various pharmaceuticals are often used for the same purpose, further increasing addiction potential and harmfulness.
It is speculated that cocaine's addictive properties stem from its DAT-blocking effects (in particular, increasing the dopaminergic transmission from ventral tegmental area neurons). However, a study has shown that mice with no dopamine transporters still exhibit the rewarding effects of cocaine administration . Later work demonstrated that a combined DAT/SERT knockout eliminated the rewarding effects .
Treatment
GVG
Studies have shown that gamma vinyl-gamma-aminobutyric acid (gamma vinyl-GABA, or GVG), a drug normally used to treat epilepsy, blocks cocaine's action in the brains of primates. GVG increases the amount of the neurotransmitter GABA in the brain and reduces the level of dopamine in the region of the brain which is thought to be involved in addiction. In January 2005 the US Food and Drug Administration gave permission for a Phase I clinical trial of GVG for the treatment of addiction. Another drug currently tested for anti-addictive properties is the cannabinoid antagonist rimonabant.
GBR 12909
GBR 12909 (Vanoxerine) is a selective dopamine uptake inhibitor. Because of this, it reduces cocaine's effect on the brain, and may help to treat cocaine addiction. Studies have shown that GBR, when given to primates, suppresses cocaine self-administration.
Legal status
The production, the distribution and the sales of cocaine products are restricted (and illegal in most contexts) in most countries.
Africa
Asia
Australasia and the Pacific
- New Zealand: Cocaine is a Class A drug. The coca leaf and preparations of cocaine containing no more than 0.1% cocaine base, in such a way that the cocaine cannot be recovered, are both classified as Class C.
Europe
- The United Kingdom: Cocaine is a Schedule 2/Class A drug.
North America
- Canada: Cocaine is a Schedule I drug.
- The United States of America: Cocaine is classified as a Schedule II stimulant.
South America
Usage
In the United States
Overall usage
The National Household Survey on Drug Abuse (NHSDA) reported in 1999 that cocaine was used by 3.7 million Americans, or 1.7 percent of the household population aged 12 and over. To put this into perspective, this is about 3 times the number of nurses in the United States. Estimates of the current number of those who use cocaine regularly (at least once per month) vary, but 1.5 million is a widely accepted figure within the research community.
Although cocaine use had not significantly changed over the six years prior to 1999, the number of first-time users went from 574,000 in 1991, to 934,000 in 1998 — an increase of 63%. While these numbers indicated that cocaine is still widely present in the United States, cocaine use was significantly less prevalent than it was during the early 1980s. Cocaine use peaked in 1982 when 10.4 million Americans (5.6 percent of the population) reportedly used cocaine.
Usage among youth
The 1999 Monitoring the Future (MTF) survey found the proportion of American students reporting use of powder cocaine rose during the 1990s. In 1991, 2.3 percent of eighth-graders stated that they had used cocaine in their lifetime. This figure rose to 4.7 percent in 1999. For the older grades, increases began in 1992 and continued through the beginning of 1999. Between those years, lifetime use of cocaine went from 3.3 percent to 7.7 percent for tenth-graders and from 6.1 percent to 9.8 percent for twelfth-graders. Lifetime use of crack cocaine, according to MTF, also increased among eighth-, tenth-, and twelfth-graders, from an average of 2 percent in 1991 to 3.9 percent in 1999.
Perceived risk and disapproval of cocaine and crack use both decreased during the 1990s at all three grade levels. The 1999 NHSDA found the highest rate of monthly cocaine use was for those aged 18–25 at 1.7 percent, an increase from 1.2 percent in 1997. Rates declined between 1996 and 1998 for ages 26–34, while rates slightly increased for the 12–17 and 35+ age groups. Studies also show people are experimenting with cocaine at younger ages. NHSDA found a steady decline in the mean age of first use from 23.6 years in 1992 to 20.6 years in 1998.
Availability
Cocaine is readily available in all major U.S. metropolitan areas. According to the Summer 1998 Pulse Check, published by the U.S. Office of National Drug Control Policy, cocaine use had stabilized across the country, with a few increases reported in San Diego, Bridgeport, Miami, and Boston. In the West, cocaine usage was lower, which was thought to be because some users were switching to methamphetamine, which was cheaper and provides a longer-lasting high. Numbers of cocaine users are still very large, with a concentration among city-dwelling youth.
Sources
In 1999, Colombia was the world's leading producer of cocaine. Three-quarters of the world's annual yield of cocaine was produced there, both from cocaine base imported from Peru and Bolivia, and from locally grown coca. There was a 28 percent increase in the amount of potentially harvestable coca plants in Colombia in 1998. This, combined with crop reductions in Bolivia and Peru, made Colombia the nation with the largest area of coca under cultivation.
Distribution
Cocaine shipments from South America transported through Mexico or Central America are generally moved over land or by air to staging sites in northern Mexico. The cocaine is then broken down into smaller loads for smuggling across the U.S.–Mexico border. The primary cocaine importation points in the United States are in Arizona, southern California, southern Florida, and Texas. Typically, land vehicles are driven across the U.S.-Mexico border.
Cocaine is also carried in small, concealed, kilogram quantities across the border by couriers known as "mules", who enter the United States either legally through ports of entry or illegally through undesignated points along the border. Colombian traffickers have also started using a new concealment method whereby they add chemical compounds to cocaine hydrochloride to produce "black cocaine". The cocaine in this substance is not detected by standard chemical tests or drug-sniffing canines.
Cocaine traffickers from Colombia, and recently Mexico, have also established a labyrinth of smuggling routes throughout the Caribbean, the Bahama Island chain, and South Florida. They often hire traffickers from Mexico or the Dominican Republic to transport the drug. The traffickers use a variety of smuggling techniques to transfer their drug to U.S. markets. These include airdrops of 500–700 kg in the Bahama Islands or off the coast of Puerto Rico, mid-ocean boat-to-boat transfers of 500–2,000 kg, and the commercial shipment of tonnes of cocaine through the port of Miami.
Bulk cargo ships are also used to smuggle cocaine to staging sites in the western Caribbean–Gulf of Mexico area. These vessels are typically 150–250 foot (50–80 m) coastal freighters that carry an average cocaine load of approximately 2.5 tonnes. Commercial fishing vessels are also used for smuggling operations. In areas with a high volume of recreational traffic, smugglers use the same types of vessels, such as go-fast boats, as those used by the local populations.
Books and other works about cocaine
- Cocaine: an unauthorized biography by Dominic Streatfeild
- The Pleasures of Cocaine by Adam Gottlieb
- Ūber Coca by Sigmund Freud
See also
- Benzocaine
- Coca eradication
- Cuscohygrine
- Dihydrocuscohygrine
- Drug addiction
- Ecgonine benzoate
- Hydroxytropacocaine
- Hygrine
- Methylecgonine cinnamate
- Novocain
- Tropacocaine
- Truxilline
- New London police commissioner blames middle-class cocaine users for violence in Colombia and on British housing estates
External links
- Self-test – from Cocaine Addicts Anonymous
- Cocaine User Helping Hand – Internet Portal dedicated to help crack- and cocaine-addicted people. Contains wide variety of information on drug abuse, available treatment, and recovery issues.
- Good Drugs Guide
- The Erowid Cocaine Vault
- Urban Legends Reference Pages: Cokelore (Cocaine-Cola) – information about cocaine in Coke
- Addictive properties
- The Mystery of the Coca Plant that Wouldn't Die - Wired Magazine