 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H13N3O |
| Molar mass | 203.245 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Feprosidnine, sold under the brand name Sydnophen, is a stimulant drug which was developed in the USSR in the 1970s. It is structurally related to another Russian drug mesocarb but unlike mesocarb, was withdrawn earlier from production. In comparison with mesocarb it has own antidepressant activity, which makes it useful in treating depressions. Indications of feprosidnine included apathic, asthenic depressions, fatigue, apathic syndrome, narcolepsy and other similar conditions. Therapeutic range of doses: 10-50mg a day. Sydnophen has multiple mechanisms of action, the relative importance of which has not been clearly established. Effects on the body include reversible monoamine oxidase inhibition, cholinergic, adrenergic, opioid and nitric oxide donating actions, all of which may contribute to its pharmacological effects to some extent.
Chemistry
Feprosidnine is a mesoionic sydnone imine.
A similar agent is described in the Amfetaminil article.
Synthesis
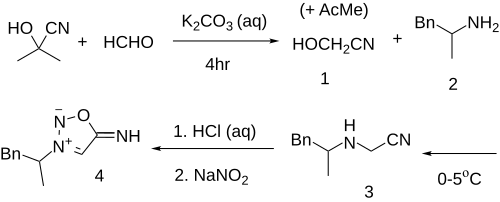
Base catalyzed reaction between acetone cyanohydrin and 40% formaldehyde solution gives glycolonitrile (1) & some acetone by-product. The amphetamine (2) is then added and this is allowed to react overnight to give N-(1-phenyl-2-propylamine)-acetonitrile (3). Nitrosylation of the amino group by in situ creation of nitrous acid from hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite results in a 51.5% yield of feprosidnine based on the initial weight of the amine (4).
See also
References
- Veksler IG, Riabukha VN, Balitskiĭ KP, Al'tshuler RA, Mashkovskiĭ MD (1980). "". Farmakologiia I Toksikologiia (in Russian). 43 (3): 349–52. PMID 7449977.
- Koniaeva EI, Beketov AI (1987). "". Farmakologiia I Toksikologiia (in Russian). 50 (3): 39–42. PMID 3609274.
- Samonina GE, Mandriko EV (April 1989). "". Biulleten' Eksperimental'noi Biologii I Meditsiny (in Russian). 107 (4): 449–51. PMID 2720163.
- Babskaia NE (1992). "". Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia (in Russian). 55 (5): 21–5. PMID 1339046.
- D'iakonova TL, Samonina GE (1994). "". Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deiatelnosti Imeni I P Pavlova (in Russian). 44 (4–5): 786–95. PMID 7810220.
- Arzamastsev AP, Severina IS, Grigor'ev NB, Granik VG (2003). "". Vestnik Rossiiskoi Akademii Meditsinskikh Nauk (in Russian) (12): 88–95. PMID 14724985.
- Mashkovsky Mikhail Davydovich & Yashunsky Vladimir Genrikhovic; GB1242743 (1971 to Vni Khim Farmatsevtichesky I I ).
| Nitric oxide signaling modulators | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forms | |||||||||||||||
| Targets |
| ||||||||||||||
| NO donors (prodrugs) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators | |||||||||||||||