Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) is a general linear model that blends ANOVA and regression. ANCOVA evaluates whether the means of a dependent variable (DV) are equal across levels of one or more categorical independent variables (IV) and across one or more continuous variables. For example, the categorical variable(s) might describe treatment and the continuous variable(s) might be covariates (CV)'s, typically nuisance variables; or vice versa. Mathematically, ANCOVA decomposes the variance in the DV into variance explained by the CV(s), variance explained by the categorical IV, and residual variance. Intuitively, ANCOVA can be thought of as 'adjusting' the DV by the group means of the CV(s).
The ANCOVA model assumes a linear relationship between the response (DV) and covariate (CV):
In this equation, the DV, is the jth observation under the ith categorical group; the CV, is the jth observation of the covariate under the ith group. Variables in the model that are derived from the observed data are (the grand mean) and (the global mean for covariate ). The variables to be fitted are (the effect of the ith level of the categorical IV), (the slope of the line) and (the associated unobserved error term for the jth observation in the ith group).
Under this specification, the categorical treatment effects sum to zero The standard assumptions of the linear regression model are also assumed to hold, as discussed below.
Example
In an agricultural study, ANCOVA can be used to analyze the effect of different fertilizers () on crop yield (), while accounting for soil quality () as a covariate. Soil quality, a continuous variable, influences crop yield and may vary across plots, potentially confounding the results.
The model adjusts yield measurements for soil quality differences and evaluates whether fertilizer types differ significantly. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
where:
- is the crop yield for the -th plot under the -th fertilizer type,
- is the grand mean crop yield,
- represents the effect of the -th fertilizer type, subject to the constraint for identifiability,
- is the slope of the regression line representing the relationship between soil quality and crop yield,
- is the soil quality for the -th plot under the -th fertilizer type, and is the global mean soil quality,
- is the residual error term, assumed to be normally distributed with mean 0 and variance .
In this setup, ANCOVA partitions the total variance in crop yield into variance explained by soil quality (covariate), variance explained by fertilizer type (categorical IV), and residual variance. By adjusting for soil quality, ANCOVA provides a more precise estimate of the fertilizer effect on crop yield. The constraint ensures that the categorical variable's effects are centered around zero, allowing for meaningful interpretation of group differences. It is standard in ANOVA and ANCOVA with categorical variables.
Uses
Increase power
ANCOVA can be used to increase statistical power (the probability a significant difference is found between groups when one exists) by reducing the within-group error variance. In order to understand this, it is necessary to understand the test used to evaluate differences between groups, the F-test. The F-test is computed by dividing the explained variance between groups (e.g., medical recovery differences) by the unexplained variance within the groups. Thus,
If this value is larger than a critical value, we conclude that there is a significant difference between groups. Unexplained variance includes error variance (e.g., individual differences), as well as the influence of other factors. Therefore, the influence of CVs is grouped in the denominator. When we control for the effect of CVs on the DV, we remove it from the denominator making F larger, thereby increasing our power to find a significant effect if one exists at all.
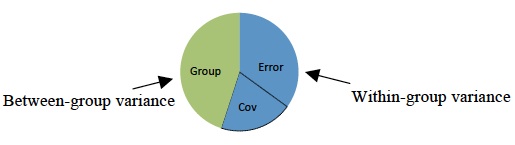
Adjusting preexisting differences
Another use of ANCOVA is to adjust for preexisting differences in nonequivalent (intact) groups. This controversial application aims at correcting for initial group differences (prior to group assignment) that exists on DV among several intact groups. In this situation, participants cannot be made equal through random assignment, so CVs are used to adjust scores and make participants more similar than without the CV. However, even with the use of covariates, there are no statistical techniques that can equate unequal groups. Furthermore, the CV may be so intimately related to the categorical IV that removing the variance on the DV associated with the CV would remove considerable variance on the DV, rendering the results meaningless.
Assumptions
There are several key assumptions that underlie the use of ANCOVA and affect interpretation of the results. The standard linear regression assumptions hold; further we assume that the slope of the covariate is equal across all treatment groups (homogeneity of regression slopes).
Assumption 1: linearity of regression
The regression relationship between the dependent variable and concomitant variables must be linear.
Assumption 2: homogeneity of error variances
The error is a random variable with conditional zero mean and equal variances for different treatment classes and observations.
Assumption 3: independence of error terms
The errors are uncorrelated. That is, the error covariance matrix is diagonal.
Assumption 4: normality of error terms
The residuals (error terms) should be normally distributed ~ .
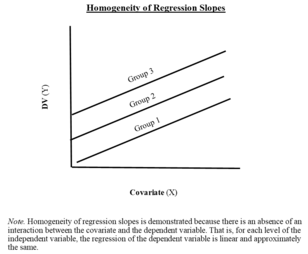
Assumption 5: homogeneity of regression slopes
The slopes of the different regression lines should be equivalent, i.e., regression lines should be parallel among groups.
The fifth issue, concerning the homogeneity of different treatment regression slopes is particularly important in evaluating the appropriateness of ANCOVA model. Also note that we only need the error terms to be normally distributed. In fact both the independent variable and the concomitant variables will not be normally distributed in most cases.
Conducting an ANCOVA
Test multicollinearity
If a CV is highly related to another CV (at a correlation of 0.5 or more), then it will not adjust the DV over and above the other CV. One or the other should be removed since they are statistically redundant.
Test the homogeneity of variance assumption
Tested by Levene's test of equality of error variances. This is most important after adjustments have been made, but if you have it before adjustment you are likely to have it afterwards.
Test the homogeneity of regression slopes assumption
To see if the CV significantly interacts with the categorical IV, run an ANCOVA model including both the IV and the CVxIV interaction term. If the CVxIV interaction is significant, ANCOVA should not be performed. Instead, Green & Salkind suggest assessing group differences on the DV at particular levels of the CV. Also consider using a moderated regression analysis, treating the CV and its interaction as another IV. Alternatively, one could use mediation analyses to determine if the CV accounts for the IV's effect on the DV.
Run ANCOVA analysis
If the CV×IV interaction is not significant, rerun the ANCOVA without the CV×IV interaction term. In this analysis, you need to use the adjusted means and adjusted mean squared error. The adjusted means (also referred to as least squares means, LS means, estimated marginal means, or EMM) refer to the group means after controlling for the influence of the CV on the DV.

Follow-up analyses
If there was a significant main effect, it means that there is a significant difference between the levels of one categorical IV, ignoring all other factors. To find exactly which levels are significantly different from one another, one can use the same follow-up tests as for the ANOVA. If there are two or more IVs, there may be a significant interaction, which means that the effect of one IV on the DV changes depending on the level of another factor. One can investigate the simple main effects using the same methods as in a factorial ANOVA.
Power considerations
While the inclusion of a covariate into an ANOVA generally increases statistical power by accounting for some of the variance in the dependent variable and thus increasing the ratio of variance explained by the independent variables, adding a covariate into ANOVA also reduces the degrees of freedom. Accordingly, adding a covariate which accounts for very little variance in the dependent variable might actually reduce power.
See also
- MANCOVA (Multivariate analysis of covariance)
References
- Keppel, G. (1991). Design and analysis: A researcher's handbook (3rd ed.). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
- ^ Montgomery, Douglas C. "Design and analysis of experiments" (8th Ed.). John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
- Tabachnick, B. G.; Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using Multivariate Statistics (5th ed.). Boston: Pearson Education.
- Miller, G. A.; Chapman, J. P. (2001). "Misunderstanding Analysis of Covariance". Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 110 (1): 40–48. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.110.1.40. PMID 11261398.
- Green, S. B., & Salkind, N. J. (2011). Using SPSS for Windows and Macintosh: Analyzing and Understanding Data (6th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Howell, D. C. (2009) Statistical methods for psychology (7th ed.). Belmont: Cengage Wadsworth.
External links
- Examples of all ANOVA and ANCOVA models with up to three treatment factors, including randomized block, split plot, repeated measures, and Latin squares, and their analysis in R (University of Southampton)
- One-Way Analysis of Covariance for Independent Samples
- What is analysis of covariance used for?
- Use of covariates in randomized controlled trials by G.J.P. Van Breukelen and K.R.A. Van Dijk (2007)
| Design of experiments | |
|---|---|
| Scientific method | |
| Treatment and blocking | |
| Models and inference | |
| Designs Completely randomized | |
| Least squares and regression analysis | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computational statistics | |||||||||
| Correlation and dependence | |||||||||
| Regression analysis | |||||||||
| Regression as a statistical model |
| ||||||||
| Decomposition of variance | |||||||||
| Model exploration | |||||||||
| Background | |||||||||
| Design of experiments | |||||||||
| Numerical approximation | |||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||

 is the jth observation under the ith categorical group; the CV,
is the jth observation under the ith categorical group; the CV,  is the jth observation of the covariate under the ith group. Variables in the model that are derived from the observed data are
is the jth observation of the covariate under the ith group. Variables in the model that are derived from the observed data are  (the grand mean) and
(the grand mean) and  (the global mean for covariate
(the global mean for covariate  ). The variables to be fitted are
). The variables to be fitted are  (the effect of the ith level of the categorical IV),
(the effect of the ith level of the categorical IV),  (the slope of the line) and
(the slope of the line) and  (the associated unobserved error term for the jth observation in the ith group).
(the associated unobserved error term for the jth observation in the ith group).
 The standard assumptions of the linear regression model are also assumed to hold, as discussed below.
The standard assumptions of the linear regression model are also assumed to hold, as discussed below.

 -th plot under the
-th plot under the  -th fertilizer type,
-th fertilizer type, for identifiability,
for identifiability, is the slope of the regression line representing the relationship between soil quality and crop yield,
is the slope of the regression line representing the relationship between soil quality and crop yield, .
.
 .
.