The survival function is a function that gives the probability that a patient, device, or other object of interest will survive past a certain time. The survival function is also known as the survivor function or reliability function. The term reliability function is common in engineering while the term survival function is used in a broader range of applications, including human mortality. The survival function is the complementary cumulative distribution function of the lifetime. Sometimes complementary cumulative distribution functions are called survival functions in general.
Definition
Let the lifetime be a continuous random variable describing the time to failure. If has cumulative distribution function and probability density function on the interval , then the survival function or reliability function is:
Examples of survival functions
The graphs below show examples of hypothetical survival functions. The x-axis is time. The y-axis is the proportion of subjects surviving. The graphs show the probability that a subject will survive beyond time t.

For example, for survival function 1, the probability of surviving longer than t = 2 months is 0.37. That is, 37% of subjects survive more than 2 months.

For survival function 2, the probability of surviving longer than t = 2 months is 0.97. That is, 97% of subjects survive more than 2 months.

Median survival may be determined from the survival function: The median survival is the point where the survival function intersects the value 0.5. For example, for survival function 2, 50% of the subjects survive 3.72 months. Median survival is thus 3.72 months.
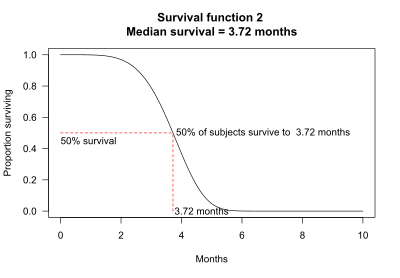
Median survival cannot always be determined from the graph alone. For example, in survival function 4, more than 50% of the subjects survive longer than the observation period of 10 months.

The survival function is one of several ways to describe and display survival data. Another useful way to display data is a graph showing the distribution of survival times of subjects. Olkin, page 426, gives the following example of survival data. The number of hours between successive failures of an air-conditioning (AC) system were recorded. The time in hours, t, between successive failures are 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 11,
11, 12, 14, 14, 14, 16, 16, 20, 21, 23, 42,
47, 52, 62, 71,
71, 87, 90, 95, 120, 120, 225, 246, and 261. The mean time between failures is 59.6. The figure below shows the distribution of the time between failures. The blue tick marks beneath the graph are the actual hours between successive AC failures.
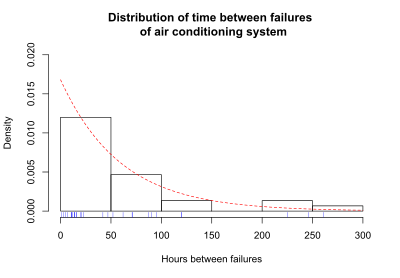
In this example, a curve representing the exponential distribution overlays the distribution of AC failure times; the exponential distribution approximates the distribution of AC failure times. This particular exponential curve is specified by the parameter lambda, λ:
λ = 1/(mean time between failures) = 1/59.6 = 0.0168.
The distribution of failure times is the probability density function (PDF), since time can take any positive value. In equations, the PDF is specified as fT. If time can only take discrete values (such as 1 day, 2 days, and so on), the distribution of failure times is called the probability mass function. Most survival analysis methods assume that time can take any positive value, and fT is the PDF. If the time between observed AC failures is approximated using the exponential function, then the exponential curve gives the probability density function, fT, for AC failure times.
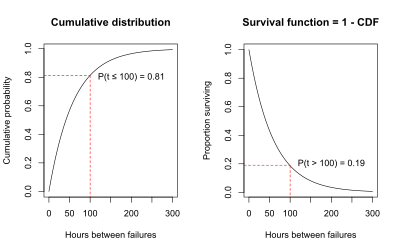
Another useful way to display the survival data is a graph showing the cumulative failures up to each time point. These data may be displayed as either the cumulative number or the cumulative proportion of failures up to each time. The graph below shows the cumulative probability (or proportion) of failures at each time for the air conditioning system. The stairstep line in black shows the cumulative proportion of failures. For each step there is a blue tick at the bottom of the graph indicating an observed failure time. The smooth red line represents the exponential curve fitted to the observed data.
A graph of the cumulative probability of failures up to each time point is called the cumulative distribution function (CDF). In survival analysis, the cumulative distribution function gives the probability that the survival time is less than or equal to a specific time, t.
Let T be survival time, which is any positive number. A particular time is designated by the lower case letter t. The cumulative distribution function of T is the function
where the right-hand side represents the probability that the random variable T is less than or equal to t. If time can take on any positive value, then the cumulative distribution function F(t) is the integral of the probability density function f(t).
For the air-conditioning example, the graph of the CDF below illustrates that the probability that the time to failure is less than or equal to 100 hours is 0.81, as estimated using the exponential curve fit to the data.
An alternative to graphing the probability that the failure time is less than or equal to 100 hours is to graph the probability that the failure time is greater than 100 hours. The probability that the failure time is greater than 100 hours must be 1 minus the probability that the failure time is less than or equal to 100 hours, because total probability must sum to 1.
This gives:
- P(failure time > 100 hours) = 1 – P(failure time < 100 hours) = 1 – 0.81 = 0.19.
This relationship generalizes to all failure times:
- P(T > t) = 1 – P(T < t) = 1 – cumulative distribution function.
This relationship is shown on the graphs below. The graph on the left is the cumulative distribution function, which is P(T < t). The graph on the right is P(T > t) = 1 - P(T < t). The graph on the right is the survival function, S(t). The fact that the S(t) = 1 – CDF is the reason that another name for the survival function is the complementary cumulative distribution function.
Parametric survival functions
In some cases, such as the air conditioner example, the distribution of survival times may be approximated well by a function such as the exponential distribution. Several distributions are commonly used in survival analysis, including the exponential, Weibull, gamma, normal, log-normal, and log-logistic. These distributions are defined by parameters. The normal (Gaussian) distribution, for example, is defined by the two parameters mean and standard deviation. Survival functions that are defined by parameters are said to be parametric.
In the four survival function graphs shown above, the shape of the survival function is defined by a particular probability distribution: survival function 1 is defined by an exponential distribution, 2 is defined by a Weibull distribution, 3 is defined by a log-logistic distribution, and 4 is defined by another Weibull distribution.
Exponential survival function
For an exponential survival distribution, the probability of failure is the same in every time interval, no matter the age of the individual or device. This fact leads to the "memoryless" property of the exponential survival distribution: the age of a subject has no effect on the probability of failure in the next time interval. The exponential may be a good model for the lifetime of a system where parts are replaced as they fail. It may also be useful for modeling survival of living organisms over short intervals. It is not likely to be a good model of the complete lifespan of a living organism. As Efron and Hastie (p. 134) note, "If human lifetimes were exponential there wouldn't be old or young people, just lucky or unlucky ones".
Weibull survival function
A key assumption of the exponential survival function is that the hazard rate is constant. In an example given above, the proportion of men dying each year was constant at 10%, meaning that the hazard rate was constant. The assumption of constant hazard may not be appropriate. For example, among most living organisms, the risk of death is greater in old age than in middle age – that is, the hazard rate increases with time. For some diseases, such as breast cancer, the risk of recurrence is lower after 5 years – that is, the hazard rate decreases with time. The Weibull distribution extends the exponential distribution to allow constant, increasing, or decreasing hazard rates.
Other parametric survival functions
There are several other parametric survival functions that may provide a better fit to a particular data set, including normal, lognormal, log-logistic, and gamma. The choice of parametric distribution for a particular application can be made using graphical methods or using formal tests of fit. These distributions and tests are described in textbooks on survival analysis. Lawless has extensive coverage of parametric models.
Parametric survival functions are commonly used in manufacturing applications, in part because they enable estimation of the survival function beyond the observation period. However, appropriate use of parametric functions requires that data are well modeled by the chosen distribution. If an appropriate distribution is not available, or cannot be specified before a clinical trial or experiment, then non-parametric survival functions offer a useful alternative.
Non-parametric survival functions
A parametric model of survival may not be possible or desirable. In these situations, the most common method to model the survival function is the non-parametric Kaplan–Meier estimator. This estimator requires lifetime data. Periodic case (cohort) and death (and recovery) counts are statistically sufficient to make non-parametric maximum likelihood and least squares estimates of survival functions, without lifetime data.
Properties
- Every survival function is monotonically decreasing, i.e. for all .
- It is a property of a random variable that maps a set of events, usually associated with mortality or failure of some system, onto time.
- The time, , represents some origin, typically the beginning of a study or the start of operation of some system. is commonly unity but can be less to represent the probability that the system fails immediately upon operation.
- Since the CDF is a right-continuous function, the survival function is also right-continuous.
- The survival function can be related to the probability density function and the hazard function
So that
- The expected survival time
| Proof of expected survival time formula |
|---|
| The expected value of a random variable is defined as:
where is the probability density function. Using the relation , the expected value formula may be modified: This may be further simplified by employing integration by parts: By definition, , meaning that the boundary terms are identically equal to zero. Therefore, we may conclude that the expected value is simply the integral of the survival function: |
See also
- Failure rate
- Frequency of exceedance
- Kaplan–Meier estimator
- Mean time to failure
- Residence time (statistics)
- Survivorship curve
References
- ^ Kleinbaum, David G.; Klein, Mitchel (2012), Survival analysis: A Self-learning text (Third ed.), Springer, ISBN 978-1441966452
- Tableman, Mara; Kim, Jong Sung (2003), Survival Analysis Using S (First ed.), Chapman and Hall/CRC, ISBN 978-1584884088
- ^ Ebeling, Charles (2010), An Introduction to Reliability and Maintainability Engineering (Second ed.), Waveland Press, ISBN 978-1577666257
- Machin, D., Cheung, Y. B., Parmar, M. (2006). Survival Analysis: A Practical Approach. Deutschland: Wiley. Page 36 and following Google Books
- Olkin, Ingram; Gleser, Leon; Derman, Cyrus (1994), Probability Models and Applications (Second ed.), Macmillan, ISBN 0-02-389220-X
- Klein, John; Moeschberger, Melvin (2005), Survival Analysis: Techniques for Censored and Truncated Data (Second ed.), Springer, ISBN 978-0387953991
- Mendenhall, William; Terry, Sincich (2007), Statistics for Engineering and the Sciences (Fifth ed.), Pearson / Prentice Hall, ISBN 978-0131877061
- Brostrom, Göran (2012), Event History Analysis with R (First ed.), Chapman & Hall/CRC, ISBN 978-1439831649
- Efron, Bradley; Hastie, Trevor (2016), Computer Age Statistical Inference: Algorithms, Evidence, and Data Science (First ed.), Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-1107149892
- Lawless, Jerald (2002), Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data (Second ed.), Wiley, ISBN 978-0471372158
 be a continuous random variable describing the time to failure. If
be a continuous random variable describing the time to failure. If  and
and  on the interval
on the interval  , then the survival function or reliability function is:
, then the survival function or reliability function is:




 is
is  for all
for all  .
.
 , represents some origin, typically the beginning of a study or the start of operation of some system.
, represents some origin, typically the beginning of a study or the start of operation of some system.  is commonly unity but can be less to represent the
is commonly unity but can be less to represent the  is also right-continuous.
is also right-continuous.




 is defined as:
is defined as:



 , meaning that the boundary terms are identically equal to zero. Therefore, we may conclude that the expected value is simply the integral of the survival function:
, meaning that the boundary terms are identically equal to zero. Therefore, we may conclude that the expected value is simply the integral of the survival function: