| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Dysprosium nitrate, Dysprosium trinitrate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.360 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | Dy(NO3)3 |
| Molar mass | 348.51 |
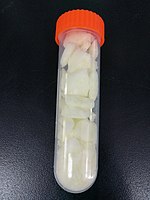
| Appearance | Yellowish crystals |
| Melting point | 88.6 °C (191.5 °F; 361.8 K) |
| Solubility in water | Soluble |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H272, H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P220, P221, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Terbium(III) nitrate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Dysprosium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of dysprosium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Dy(NO3)3. The compound forms yellowish crystals, dissolves in water, forms a crystalline hydrate.
Synthesis
Anhydrous salt is obtained by the action of nitrogen dioxide on dysprosium(III) oxide:
The action of nitrogen dioxide on metallic dysprosium:
Physical properties
Dysprosium(III) nitrate forms yellowish crystals.
The anhydrous nitrate forms a crystalline hydrate in wet air with the ideal composition of Dy(NO3)3·5H2O, which melts in its own crystallization water at 88.6 °C.
All hydrates (anhydrous, pentahydrate, and hexahydrate) are soluble in water and ethanol, hygroscopic.
Chemical properties
Hydrated dysprosium nitrate thermally decomposes to form DyONO3, and further heating produces dysprosium oxide.
Application
Dysprosium(III) nitrate is used as a catalyst.
References
- "Dysprosium(III) nitrate | CAS 10031-49-9". scbt.com. Retrieved 18 August 2021.
- Macintyre, Jane E. (23 July 1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 3117. ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9. Retrieved 18 August 2021.
- Edelmann, Frank T.; Herrmann, Wolfgang A. (14 May 2014). Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry, Volume 6, 1997: Volume 6: Lanthanides and Actinides. Georg Thieme Verlag. p. 23. ISBN 978-3-13-179221-1. Retrieved 18 August 2021.
- "Dysprosium(III) nitrate - Hazardous Agents | Haz-Map". haz-map.com. Retrieved 18 August 2021.
- "Dysprosium(III) nitrate hydrate". Sigma Aldrich. Retrieved 18 August 2021.
- "10031-49-9 - Dysprosium(III) nitrate pentahydrate, 99.9% (REO) - 12922 - Alfa Aesar". Alfa Aesar. Retrieved 18 August 2021.
| Dysprosium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Dy(II) | |
| Dy(III) | |
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the nitrate ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

