Pharmaceutical compound
 | |
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Empagliflozin | SGLT2 inhibitor |
| Linagliptin | DPP-4 inhibitor |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Glyxambi |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
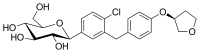
| Formula | C48H55ClN8O9 |
| Molar mass | 923.47 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Empagliflozin/linagliptin, sold under the brand name Glyxambi, is a fixed-dose combination anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is a combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin. It is taken by mouth.
The most common side effects include urinary infections, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infections .
It was approved for use in the United States in January 2015, for use in the European Union in November 2016, and for use in Australia in December 2016.
Medical uses
In the United States empagliflozin/linagliptin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease.
In the European Union empagliflozin/linagliptin is indicated in adults aged 18 years and older with type 2 diabetes mellitus:
- to improve glycemic control when metformin and/or sulphonylurea (SU) and empagliflozin or linagliptin do not provide adequate glycemic control;
- when already being treated with the free combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin.
Adverse effects
The most common side effects include urinary infections, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infections . The most serious side effects include ketoacidosis (high blood levels of acids called ‘ketoacids’), pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), hypersensitivity (allergic reactions) and hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar levels).
History
The combination preparation was developed and is marketed by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly and Company under the brand name Glyxambi.
References
- "Empagliflozin / linagliptin (Glyxambi) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 29 November 2018. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ "Summary for ARTG Entry: 263557 Glyxambi 25 mg/5 mg empagliflozin/linagliptin 25mg/5mg film coated tablet blister pack". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA).
- "Glyxambi 10 mg/5 mg Film-coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 18 December 2019. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- "Glyxambi 25 mg/5 mg Film-coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 18 December 2019. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ "Glyxambi- empagliflozin and linagliptin tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 22 January 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- ^ "Glyxambi EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Retrieved 3 April 2020. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- "Glyxambi (empagliflozin and linagliptin) tablets". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 11 April 2016. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- "Glyxambi: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- Raedler LA (March 2015). "Glyxambi (Empagliflozin/Linagliptin): A Dual-Acting Oral Medication Approved for the Treatment of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes". Am Health Drug Benefits. 8 (Spec Feature): 171–5. PMC 4665058. PMID 26629285.
Further reading
- Kim ES, Deeks ED (September 2015). "Empagliflozin/Linagliptin: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes". Drugs. 75 (13): 1547–57. doi:10.1007/s40265-015-0457-z. PMID 26323340. S2CID 27675087.
| Eli Lilly and Company | |
|---|---|
| Corporate directors | |
| Products |
|