 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.841 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
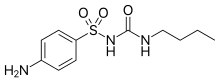
| Formula | C11H17N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 271.33 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Carbutamide (brand name Glucidoral) is an anti-diabetic drug of the sulfonylurea class, developed by Servier.
It is classified as first-generation.
It was patented in 1953 and approved for medical use in 1956.
See also
- Hellmuth Kleinsorge (1920-2001) German medical doctor
References
- Ballagi-Pordány G, Köszeghy A, Koltai MZ, Aranyi Z, Pogátsa G (January 1990). "Divergent cardiac effects of the first and second generation hypoglycemic sulfonylurea compounds". Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 8 (2): 109–114. doi:10.1016/0168-8227(90)90020-T. PMID 2106423.
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 449. ISBN 9783527607495.
| Ion channel modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Potassium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chloride |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Transient receptor potential channel modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
This drug article relating to the gastrointestinal system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |