| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Mercury dinitrate Mercury(II) nitrate | |
| Other names Mercuric nitrate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.126 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1625 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
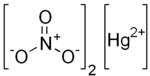
| Chemical formula | Hg(NO3)2 |
| Molar mass | 324.60 g/mol (anhydrous) |
| Appearance | colorless crystals or white powder |
| Odor | sharp |
| Density | 4.3 g/cm (monohydrate) |
| Melting point | 79 °C (174 °F; 352 K) (monohydrate) |
| Solubility in water | soluble |
| Solubility | soluble in nitric acid, acetone, ammonia insoluble in ethanol |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −74.0·10 cm/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |    
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H272, H300, H310, H330, H373, H410 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | Nonflammable |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0980 |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Mercury(II) sulfate Mercury(II) chloride |
| Other cations | Zinc nitrate Cadmium nitrate |
| Related compounds | Mercury(I) nitrate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Mercury(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Hg(NO3)2. It is the mercury(II) salt of nitric acid HNO3. It contains mercury(II) cations Hg and nitrate anions NO−3, and water of crystallization H2O in the case of a hydrous salt. Mercury(II) nitrate forms hydrates Hg(NO3)2·xH2O. Anhydrous and hydrous salts are colorless or white soluble crystalline solids that are occasionally used as a reagents. Mercury(II) nitrate is made by treating mercury with hot concentrated nitric acid. Neither anhydrous nor monohydrate has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The anhydrous material is more widely used.
Uses
Mercury(II) nitrate is used as an oxidizing agent in organic synthesis, as a nitrification agent, as an analytical reagent in laboratories, in the manufacture of felt, and in the manufacture of mercury fulminate. An alternative qualitative Zeisel test can be done with the use of mercury(II) nitrate instead of silver nitrate, leading to the formation of scarlet red mercury(II) iodide.
Health information
Mercury compounds are highly toxic. The use of this compound by hatters and the subsequent mercury poisoning of said hatters is a common theory of where the phrase "mad as a hatter" came from.
See also
References
- Nolte, M.; Pantenburg, I.; Meyer, G. (9 December 2005). "The Monohydrate of Basic Mercuric Nitrate, [Hg(OH)](NO3)(H2O)". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie (in German). 632 (1). Wiley Publishing: 111–113. doi:10.1002/zaac.200500344. ISSN 0044-2313. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- "Mercury nitrate monohydrate". Chemical Book. 2023. Retrieved June 30, 2024.
- Wang, Zerong (2010). "Zeisel Determination". Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 3115–3118. doi:10.1002/9780470638859.conrr689. ISBN 9780470638859.
External links
- ATSDR - Toxic Substances Portal - Mercury (11/14/2013)
- ATSDR - Public Health Statement: Mercury (11/14/2013)
- ATSDR - ALERT! Patterns of Metallic Mercury Exposure, 6/26/97 (link not traceable 11/14/2013)
- ATSDR - Medical Management Guidelines for Mercury (11/14/2013)
- ATSDR - Toxicological Profile: Mercury (11/14/2013)
- Safety data (MSDS) (link not traceable 11/14/2013)
- Mercuric Nitrate (ICSC)
- Mercury Archived 2018-02-17 at the Wayback Machine
- Mercury Information Packages
- How to Make Good Mercury Electrical Connections, Popular Science monthly, February 1919, Unnumbered page, Scanned by Google Books: https://books.google.com/books?id=7igDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PT14
| Mercury compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury(I) | |||
| Mercury(II) |
| ||
| Mercury(IV) |
| ||
| Amalgams | |||
| Mercury cations | |||
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the nitrate ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||