 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Wei Ni An |
| Other names | Nylestriol; LY-49825; Ethinylestriol cyclopentyl ether; EE3CPE; 17α-Ethynylestriol 3-cyclopentyl ether |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ether |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 380.528 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
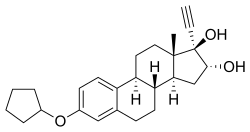
Nilestriol (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name) (brand name Wei Ni An; developmental code name LY-49825), also known as nylestriol (USANTooltip United States Adopted Name, BANTooltip British Approved Name), is a synthetic estrogen which was patented in 1971 and is marketed in China. It is the 3-cyclopentyl ether of ethinylestriol, and is also known as ethinylestriol cyclopentyl ether (EE3CPE). Nilestriol is a prodrug of ethinylestriol, and is a more potent estrogen in comparison. It is described as a slowly-metabolized, long-acting estrogen and derivative of estriol. Nilestriol was assessed in combination with levonorgestrel for the potential treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, but this formulation ultimately was not marketed.
See also
References
- Official Gazette of the United States Patent and Trademark Office: Patents. U.S. Department of Commerce, Patent and Trademark Office. 1975. p. 1677.
- Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 891–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- "Nilestriol". Drugs.com.
- ^ McGuire W (14 December 2013). Experimental Biology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 161–. ISBN 978-1-4757-4673-0.
- Schoenberg DR (1977). Biochemical Properties of the Cytoplasmic Estrogen Receptors from Immature Rat and Mature Rabbit Uteri (Ph.D. thesis). University of Wisconsin. p. A-17.
- "Section 10: Obstetrics and gynecology". Excerpta Medica. 1978.
- Aronson JK (21 February 2009). Meyler's Side Effects of Endocrine and Metabolic Drugs. Elsevier. pp. 173–. ISBN 978-0-08-093292-7.
| Estrogen receptor modulators | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERTooltip Estrogen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPERTooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor |
| ||||||
This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |