You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Chinese. (June 2023) Click for important translation instructions.
|
| Examples of pentadecahedra | |
|---|---|
 Dual elongated triangular cupola |
 Elongated pentagonal bipyramid |
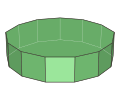 Tridecagonal prism |
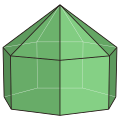 Elongated heptagonal pyramid |
A pentadecahedron (or pentakaidecahedron) is a polyhedron with 15 faces. No pentadecahedron is regular; hence, the name is ambiguous. There are numerous topologically distinct forms of a pentadecahedron, for example the tetradecagonal pyramid, and tridecagonal prism. In the pentadecahedron, none of the shapes are regular polyhedra. In other words, a regular pentadecahedron does not exist, and the pentadecahedron cannot fill space; a space-filling pentadecahedron does not exist.
In chemistry, some clusters of atoms are in the form of pentadecahedra. Calculations have shown that there is a unit cell of the pentadecahedron that is stable in the crystal.
Convex
There are 23,833,988,129 topologically distinct convex pentadecahedra, excluding mirror images, having at least 10 vertices. (Two polyhedra are "topologically distinct" if they have intrinsically different arrangements of faces and vertices, such that it is impossible to distort one into the other simply by changing the lengths of edges or the angles between edges or faces.)
Common pentadecahedra
| Name | Type | Image | Symbol | Vertices | Sides | Faces | χ | Face type | Symmetry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tridecagonal prism | prism | 
|
t{2,13} {13}x{} |
26 | 39 | 15 | 2 | 2 tridecagons 13 rectangles |
D13h, , (*13 2 2) |
| Tetradecagonal pyramid | pyramid | 
|
( )∨{14} | 15 | 28 | 15 | 2 | 1 tetradecagon 14 triangles |
C14v, , (*14 14) |
| Elongated heptagonal pyramid | pyramid | 
|
15 | 28 | 15 | 2 | 7 triangles 7 rectangles 1 heptagon |
D7h, , (*227), order 28 | |
| Heptagonal truncated cone | truncated cone | 
|
15 | 28 | 15 | 2 | 7 triangles 7 kites 1 heptagon |
D7h, , (*227), order 28 | |
| Elongated pentagonal bipyramid | Bipyramid Johnson solid |

|
12 | 25 | 15 | 2 | 10 triangles 5 squares |
D5h, , (*225) |
References
- Parker), 麥特‧帕克(Matt (2020-06-11). 數學大觀念2:從掐指一算到穿越四次元的數學魔術 (in Chinese (Taiwan)). 貓頭鷹. ISBN 978-986-262-426-5.
- Montejano, JM and Rodríguez, JL and Gutierrez-Wing, C and Miki, M and José-Yacamán, M (2004). "Crystallography and Shape of Nanoparticles and Clusters" (PDF). Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology X: 1–44. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-08-28. Retrieved 2023-06-26.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Lagunov, VA and Sinani, AB (1998). "Formation of a bistructure of a solid in a computer experiment". Physics of the Solid State. 40 (10). Springer: 1742–1747. Bibcode:1998PhSS...40.1742L. doi:10.1134/1.1130648. S2CID 121047989.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Counting polyhedra
- What Are Polyhedra?, with Greek Numerical Prefixes
External links
| Polyhedra | |
|---|---|
| Listed by number of faces and type | |
| 1–10 faces | |
| 11–20 faces | |
| >20 faces |
|
| elemental things |
|
| convex polyhedron |
|
| non-convex polyhedron |
|
| prismatoids | |
This polyhedron-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |