In geometry, a skew apeirohedron is an infinite skew polyhedron consisting of nonplanar faces or nonplanar vertex figures, allowing the figure to extend indefinitely without folding round to form a closed surface.
Skew apeirohedra have also been called polyhedral sponges.
Many are directly related to a convex uniform honeycomb, being the polygonal surface of a honeycomb with some of the cells removed. Characteristically, an infinite skew polyhedron divides 3-dimensional space into two halves. If one half is thought of as solid the figure is sometimes called a partial honeycomb.
Regular skew apeirohedra
Main article: Regular skew apeirohedronAccording to Coxeter, in 1926 John Flinders Petrie generalized the concept of regular skew polygons (nonplanar polygons) to regular skew polyhedra (apeirohedra).
Coxeter and Petrie found three of these that filled 3-space:
| Regular skew apeirohedra | ||
|---|---|---|
 {4,6|4} mucube |
 {6,4|4} muoctahedron |
 {6,6|3} mutetrahedron |
There also exist chiral skew apeirohedra of types {4,6}, {6,4}, and {6,6}. These skew apeirohedra are vertex-transitive, edge-transitive, and face-transitive, but not mirror symmetric (Schulte 2004).
Beyond Euclidean 3-space, in 1967 C. W. L. Garner published a set of 31 regular skew polyhedra in hyperbolic 3-space.
Gott's regular pseudopolyhedrons
J. Richard Gott in 1967 published a larger set of seven infinite skew polyhedra which he called regular pseudopolyhedrons, including the three from Coxeter as {4,6}, {6,4}, and {6,6} and four new ones: {5,5}, {4,5}, {3,8}, {3,10}.
Gott relaxed the definition of regularity to allow his new figures. Where Coxeter and Petrie had required that the vertices be symmetrical, Gott required only that they be congruent. Thus, Gott's new examples are not regular by Coxeter and Petrie's definition.
Gott called the full set of regular polyhedra, regular tilings, and regular pseudopolyhedra as regular generalized polyhedra, representable by a {p,q} Schläfli symbol, with by p-gonal faces, q around each vertex. However neither the term "pseudopolyhedron" nor Gott's definition of regularity have achieved wide usage.
Crystallographer A.F. Wells in 1960's also published a list of skew apeirohedra. Melinda Green published many more in 1998.
| {p,q} | Cells around a vertex |
Vertex faces |
Larger pattern |
Space group | Related H orbifold notation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cubic space group |
Coxeter notation |
Fibrifold notation | |||||
| {4,5} | 3 cubes |  |
 |
Im3m | ] | 8°:2 | *4222 |
| {4,5} | 1 truncated octahedron 2 hexagonal prisms |
 |
I3 | ] | 8°:2 | 2*42 | |
| {3,7} | 1 octahedron 1 icosahedron |
 |
 |
Fd3 | ] | 2° | 3222 |
| {3,8} | 2 snub cubes |  |
 |
Fm3m | 2 | 32* | |
| {3,9} | 1 tetrahedron 3 octahedra |
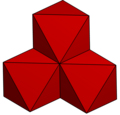 |
 |
Fd3m | ] | 2:2 | 2*32 |
| {3,9} | 1 icosahedron 2 octahedra |
 |
I3 | ] | 8°:2 | 22*2 | |
| {3,12} | 5 octahedra | 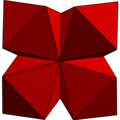 |
 |
Im3m | ] | 8°:2 | 2*32 |
Prismatic forms
 Prismatic form: {4,5} |
There are two prismatic forms:
- {4,5}: 5 squares on a vertex (Two parallel square tilings connected by cubic holes.)
- {3,8}: 8 triangles on a vertex (Two parallel triangle tilings connected by octahedral holes.)
Other forms
{3,10} is also formed from parallel planes of triangular tilings, with alternating octahedral holes going both ways.
{5,5} is composed of 3 coplanar pentagons around a vertex and two perpendicular pentagons filling the gap.
Gott also acknowledged that there are other periodic forms of the regular planar tessellations. Both the square tiling {4,4} and triangular tiling {3,6} can be curved into approximating infinite cylinders in 3-space.
Theorems
He wrote some theorems:
- For every regular polyhedron {p,q}: (p-2)*(q-2)<4. For Every regular tessellation: (p-2)*(q-2)=4. For every regular pseudopolyhedron: (p-2)*(q-2)>4.
- The number of faces surrounding a given face is p*(q-2) in any regular generalized polyhedron.
- Every regular pseudopolyhedron approximates a negatively curved surface.
- The seven regular pseudopolyhedron are repeating structures.
Uniform skew apeirohedra
There are many other uniform (vertex-transitive) skew apeirohedra. Wachmann, Burt and Kleinmann (1974) discovered many examples but it is not known whether their list is complete.
A few are illustrated here. They can be named by their vertex configuration, although it is not a unique designation for skew forms.
| 4.4.6.6 | 6.6.8.8 | |
|---|---|---|

|

|
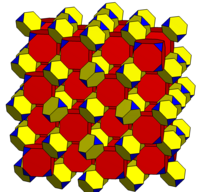
|
| Related to cantitruncated cubic honeycomb, |
Related to runcicantic cubic honeycomb, | |
| 4.4.4.6 | 4.8.4.8 | 3.3.3.3.3.3.3 |

|

|
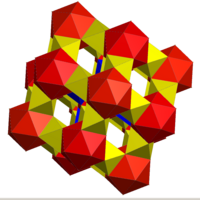
|
| Related to the omnitruncated cubic honeycomb: | ||
| 4.4.4.6 | 4.4.4.8 | 3.4.4.4.4 |

|
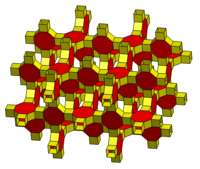
|
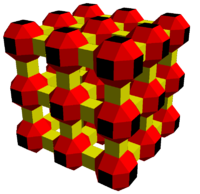 Related to the runcitruncated cubic honeycomb. |
| 4.4.4.4.4 | 4.4.4.6 |
|---|---|
 Related to |
 Related to |
Others can be constructed as augmented chains of polyhedra:
 
|

|
| Uniform Boerdijk–Coxeter helix |
Stacks of cubes |
|---|
See also
References
- Coxeter, H. S. M. Regular Skew Polyhedra in Three and Four Dimensions. Proc. London Math. Soc. 43, 33-62, 1937.
- Garner, C. W. L. Regular Skew Polyhedra in Hyperbolic Three-Space. Can. J. Math. 19, 1179-1186, 1967. Archived 2015-04-02 at the Wayback Machine
- J. R. Gott, Pseudopolyhedrons, American Mathematical Monthly, Vol 74, p. 497-504, 1967.
- The Symmetries of things, Pseudo-platonic polyhedra, p.340-344
- Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, Third edition, (1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6
- (Paper 2) H.S.M. Coxeter, "The Regular Sponges, or Skew Polyhedra", Scripta Mathematica 6 (1939) 240-244.
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, (2008) The Symmetries of Things, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 23, Objects with prime symmetry, pseudo-platonic polyhedra, p340-344)
- Schulte, Egon (2004), "Chiral polyhedra in ordinary space. I", Discrete and Computational Geometry, 32 (1): 55–99, doi:10.1007/s00454-004-0843-x, MR 2060817. Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine
- A. F. Wells, Three-Dimensional Nets and Polyhedra, Wiley, 1977.
- A. Wachmann, M. Burt and M. Kleinmann, Infinite polyhedra, Technion, 1974. 2nd Edn. 2005.
- E. Schulte, J.M. Wills On Coxeter's regular skew polyhedra, Discrete Mathematics, Volume 60, June–July 1986, Pages 253–262
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Regular Skew Polyhedron". MathWorld.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Honeycombs and sponges". MathWorld.
- Olshevsky, George. "Skew polytope". Glossary for Hyperspace. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007.
- "Hyperbolic" Tessellations
- Infinite Regular Polyhedra Archived 2016-03-12 at the Wayback Machine
- Infinite Repeating Polyhedra - Partial Honeycombs in 3-Space
- 18 SYMMETRY OF POLYTOPES AND POLYHEDRA, Egon Schulte: 18.3 REGULAR SKEW POLYHEDRA
- Infinite Polyhedra, T.E. Dorozinski
| Polyhedra | |
|---|---|
| Listed by number of faces and type | |
| 1–10 faces | |
| 11–20 faces | |
| >20 faces |
|
| elemental things |
|
| convex polyhedron |
|
| non-convex polyhedron |
|
| prismatoids | |