 Powdered promethium oxide in a metal tray | |
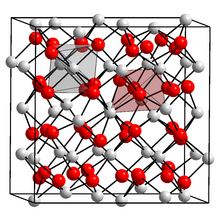 Cubic form | |
 Hexagonal form | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Promethium(III) oxide | |
| Other names Promethium sesquioxide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| PubChem CID | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | Pm2O3 |
| Molar mass | 337.824 g/mol |
| Melting point | ~2320 °C |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Cubic |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Promethium(III) chloride |
| Other cations | Neodymium(III) oxide, Samarium(III) oxide, Neptunium(III) oxide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Promethium(III) oxide is a compound with the formula Pm2O3. It is the most common form of promethium.
Crystal structure
Promethium oxide exists in three major crystalline forms:
| Form | Pearson symbol | Space group | No. | a,b,c (nm) | β(deg) | Z | Density (g/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cubic | cI80 | Ia3 | 206 | 1.099 | 16 | 6.85 | |
| Monoclinic | mS30 | C2/m | 12 | 1.422; 0.365; 0.891 | 100.1 | 6 | 7.48 |
| Hexagonal | hP5 | P3m1 | 164 | 0.3802; 0.3802; 0.5954 | 1 | 7.62 |
*a, b and c are lattice parameters, Z is the number of formula units per unit cell, density is calculated from X-ray data.
The low-temperature cubic form converts to the monoclinic structure upon heating to 750–800 °C, and this transition can only be reversed by melting the oxide. The transition from the monoclinic to hexagonal form occurs at 1740 °C.
References
- ^ Chikalla, T. D.; McNeilly, C. E.; Roberts, F. P. (1972). "Polymorphic Modifications of Pm2O3". Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 55 (8): 428. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1972.tb11329.x.
| Promethium compounds | |
|---|---|
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |