| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Strontium monosulfide C.I. 77847 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.864 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | SrS |
| Molar mass | 119.68 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid (spoiled samples are colored) |
| Odor | none (degraded samples smell of hydrogen sulfide) |
| Density | 3.70 g/cm |
| Melting point | 2,002 °C (3,636 °F; 2,275 K) |
| Solubility in water | slightly soluble |
| Solubility in acids | decomposes |
| Refractive index (nD) | 2.107 |
| Structure | |
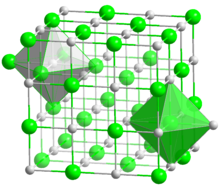
| Crystal structure | Halite (cubic), cF8 |
| Space group | Fm3m, No. 225 |
| Coordination geometry | Octahedral (Sr); octahedral (S) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Strontium oxide |
| Other cations | Magnesium sulfide Calcium sulfide Barium sulfide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Strontium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula SrS. It is a white solid. The compound is an intermediate in the conversion of strontium sulfate, the main strontium ore called celestite (or, more correctly, celestine), to other more useful compounds.
Production and reactions
Strontium sulfide is produced by roasting celestine with coke at 1100–1300 °C. The sulfate is reduced, leaving the sulfide:
- SrSO4 + 2 C → SrS + 2 CO2
About 300,000 tons are processed in this way annually. Both luminous and nonluminous sulfide phases are known, impurities, defects, and dopants being important.
As expected for a sulfide salt of alkaline earth, the sulfide hydrolyzes readily:
- SrS + 2 H2O → Sr(OH)2 + H2S
For this reason, samples of SrS have an odor of rotten eggs.
Similar reactions are used in the production of commercially useful compounds, including the most useful strontium compound, strontium carbonate: a mixture of strontium sulfide with either carbon dioxide gas or sodium carbonate leads to formation of a precipitate of strontium carbonate.
- SrS + H2O + CO2 → SrCO3 + H2S
- SrS + Na2CO3 → SrCO3 + Na2S
Strontium nitrate can also be prepared in this way.
References
- Strontium sulfide, cameochemicals.noaa.gov
- ^ J. Paul MacMillan, Jai Won Park, Rolf Gerstenberg, Heinz Wagner, Karl Köhler, Peter Wallbrecht “Strontium and Strontium Compounds” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a25_321.
- "Celestine".
- "List of Minerals". 21 March 2011.
- ^ Aydoğan, Salih; Erdemoğlu, Murat; Aras, Ali; Uçar, Gökhan; Özkan, Alper (2006). "Dissolution kinetics of celestite (SrSO4) in HCl solution with BaCl2". Hydrometallurgy. 84 (3–4): 239–246. Bibcode:2006HydMe..84..239A. doi:10.1016/j.hydromet.2006.06.001.
- R. Ward, R. K. Osterheld, R. D. Rosenstein "Strontium Sulfide and Selenide Phosphors" Inorganic Syntheses, 1950, vol. III, pp. 11–24. doi:10.1002/9780470132340.ch4
External links
| Strontium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Sulfides (S) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||