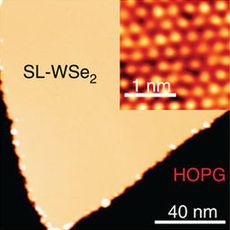
 WSe2 monolayer on graphene (yellow) and its atomic image (inset) | |
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.877 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | WSe2 |
| Molar mass | 341.76 g/mol |
| Appearance | grey to black solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 9.32 g/cm |
| Melting point | > 1200 °C |
| Solubility in water | insoluble |
| Band gap | ~1 eV (indirect, bulk) ~1.7 eV (direct, monolayer) |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | hP6, space group P6 3/mmc, No 194 |
| Lattice constant | a = 0.3297 nm, c = 1.2982 nm |
| Coordination geometry | Trigonal prismatic (W) Pyramidal (Se) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
-185.3 kJ mol |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Tantalum diselenide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
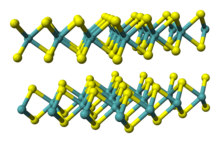
Tungsten diselenide is an inorganic compound with the formula WSe2. The compound adopts a hexagonal crystalline structure similar to molybdenum disulfide. The tungsten atoms are covalently bonded to six selenium ligands in a trigonal prismatic coordination sphere while each selenium is bonded to three tungsten atoms in a pyramidal geometry. The tungsten–selenium bond has a length of 0.2526 nm, and the distance between selenium atoms is 0.334 nm. It is a well studied example of a layered material. The layers stack together via van der Waals interactions. WSe2 is a very stable semiconductor in the group-VI transition metal dichalcogenides.
Structure and properties
The hexagonal (P63/mmc) polymorph 2H-WSe2 is isotypic with hexagonal MoS2. The two-dimensional lattice structure has W and Se arranged periodically in layers with hexagonal symmetry. Similar to graphite, van der Waals interactions hold the layers together; however, the 2D-layers in WSe2 are not atomically thin. The large size of the W cation renders the lattice structure of WSe2 more sensitive to changes than MoS2.
In addition to the typical semiconducting hexagonal structure, a second metallic polymorph of WSe2 exists. This phasem 1T-WSe2, is based on a tetragonal symmetry with one WSe2 layer per repeating unit. The 1T-WSe2 phase is less stable and transitions to the 2H-WSe2 phase. WSe2 can form a fullerene-like structure.
The Young’s modulus vary greatly as a function of the number of layers in a flake. For a single monolayer, the reported Young’s modulus is 258.6 ± 38.3 GPa.
Synthesis
Heating thin films of tungsten under pressure from gaseous selenium and high temperatures (>800 K) using the sputter deposition technique leads to the films crystallizing in hexagonal structures with the correct stoichiometric ratio.
- W + 2 Se → WSe2
Potential applications
The potential applications of transition metal dichalcogenides in solar cells and photonics are often discussed. Bulk WSe
2 has an optical band gap of ~1.35 eV with a temperature dependence of −4.6×10 eV/K. WSe
2 photoelectrodes are stable in both acidic and basic conditions, making them potentially useful in electrochemical solar cells.
The properties of WSe
2 monolayers differ from those of the bulk state, as is typical for semiconductors. Mechanically exfoliated monolayers of WSe
2 are transparent photovoltaic materials with LED properties. The resulting solar cells pass 95 percent of the incident light, with one tenth of the remaining five percent converted into electrical power. The material can be changed from p-type to n-type by changing the voltage of an adjacent metal electrode from positive to negative, allowing devices made from it to have tunable bandgaps.
See also
References
- Chiu, Ming-Hui; Zhang, Chendong; Shiu, Hung-Wei; Chuu, Chih-Piao; Chen, Chang-Hsiao; Chang, Chih-Yuan S.; Chen, Chia-Hao; Chou, Mei-Yin; Shih, Chih-Kang; Li, Lain-Jong (2015). "Determination of band alignment in the single-layer MoS2/WSe2 heterojunction". Nature Communications. 6: 7666. arXiv:1406.5137. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.7666C. doi:10.1038/ncomms8666. PMC 4518320. PMID 26179885.
- ^ Agarwal, M. K.; Wani, P. A. (1979). "Growth conditions and crystal structure parameters of layer compounds in the series Mo1−xWxSe2". Materials Research Bulletin. 14 (6): 825–830. doi:10.1016/0025-5408(79)90144-2.
- Prakash, Abhijith; Appenzeller, Joerg (2017-02-28). "Bandgap Extraction and Device Analysis of Ionic Liquid Gated WSe2 Schottky Barrier Transistors". ACS Nano. 11 (2): 1626–1632. doi:10.1021/acsnano.6b07360. ISSN 1936-0851. PMID 28191930.
- Yun, Won Seok; Han, S. W.; Hong, Soon Cheol; Kim, In Gee; Lee, J. D. (2012). "Thickness and strain effects on electronic structures of transition metal dichalcogenides: 2H-MX2 semiconductors (M = Mo, W; X = S, Se, Te)". Physical Review B. 85 (3): 033305. Bibcode:2012PhRvB..85c3305Y. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.85.033305.
- O'Hare, P.A.G.; Lewis, Brett M.; parkinson, B.A. (June 1988). "Standard molar enthalpy of formation by fluorine-combustion calorimetry of tungsten diselenide (WSe2). Thermodynamics of the high-temperature vaporization of WSe2. Revised value of the standard molar enthalpy of formation of molybdenite (MoS2)". The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 20 (6): 681–691. doi:10.1016/0021-9614(88)90019-5.
- Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- Schutte, W.J.; De Boer, J.L.; Jellinek, F. (1986). "Crystal Structures of Tungsten Disulfide and Diselenide". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 70 (2): 207–209. Bibcode:1987JSSCh..70..207S. doi:10.1016/0022-4596(87)90057-0.
- ^ Eftekhari, Ali (2017). "Tungsten dichalcogenides (WS 2 , WSe 2 , and WTe 2 ): materials chemistry and applications". Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 5 (35): 18299–18325. doi:10.1039/C7TA04268J. ISSN 2050-7488.
- Ma, Yuqiang; Liu, Bilu; Zhang, Anyi; Chen, Liang; Fathi, Mohammad; Shen, Chenfei; Abbas, Ahmad N.; Ge, Mingyuan; Mecklenburg, Matthew; Zhou, Chongwu (2015-07-28). "Reversible Semiconducting-to-Metallic Phase Transition in Chemical Vapor Deposition Grown Monolayer WSe 2 and Applications for Devices". ACS Nano. 9 (7): 7383–7391. doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b02399. ISSN 1936-0851. PMID 26125321.
- Falin, Alexey; Holwill, Matthew; Lv, Haifeng; Gan, Wei; Cheng, Jun; Zhang, Rui; Qian, Dong; Barnett, Matthew R.; Santos, Elton J. G.; Novoselov, Konstantin S.; Tao, Tao; Wu, Xiaojun; Li, Lu Hua (23 February 2021). "Mechanical Properties of Atomically Thin Tungsten Dichalcogenides: WS 2 , WSe 2 , and WTe 2". ACS Nano. 15 (2): 2600–2610. arXiv:2101.11869. doi:10.1021/acsnano.0c07430. PMID 33503379. S2CID 231719536.
- Pouzet, J.; Bernede, J.C.; Khellil, A.; Essaidi, H.; Benhida, S. (1992). "Preparation and characterization of tungsten diselenide thin films". Thin Solid Films. 208 (2): 252–259. Bibcode:1992TSF...208..252P. doi:10.1016/0040-6090(92)90652-R.
- Lin, Y. C.; Björkman, T. R.; Komsa, H. P.; Teng, P. Y.; Yeh, C. H.; Huang, F. S.; Lin, K. H.; Jadczak, J.; Huang, Y. S.; Chiu, P. W.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Suenaga, K. (2015). "Three-fold rotational defects in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides". Nature Communications. 6: 6736. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.6736L. doi:10.1038/ncomms7736. PMC 4396367. PMID 25832503.
- Mak, Kin Fai; Shan, Jie (2016). "Photonics and optoelectronics of 2D semiconductor transition metal dichalcogenides". Nature Photonics. 10 (4): 216–226. Bibcode:2016NaPho..10..216M. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2015.282. S2CID 124091327.
- Upadhyayula, L.C.; Loferski, J.J.; Wold, A.; Giriat, W.; Kershaw, R. (1968). "Semiconducting Properties of Single Crystals of n- and p-Type Tungsten Diselenide (WSe2)". Journal of Applied Physics. 39 (10): 353–358. Bibcode:1968JAP....39.4736U. doi:10.1063/1.1655829.
- Gobrecht, J.; Gerischer, H.; Tributsch, H. (1978). "Electrochemical Solar Cell Based on the d-Band Semiconductor Tungsten-Diselenide". Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische Chemie. 82 (12): 1331–1335. doi:10.1002/bbpc.19780821212.
- Xia, Fengnian; Wang, Han; Xiao, Di; Dubey, Madan; Ramasubramaniam, Ashwin (2014). "Two-dimensional material nanophotonics". Nature Photonics. 8 (12): 899–907. arXiv:1410.3882. Bibcode:2014NaPho...8..899X. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2014.271. S2CID 14682447.
- Zhang, Xin; Qiao, Xiao-Fen; Shi, Wei; Wu, Jiang-Bin; Jiang, De-Sheng; Tan, Ping-Heng (2015). "Phonon and Raman scattering of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides from monolayer, multilayer to bulk material". Chem. Soc. Rev. 44 (9): 2757–85. arXiv:1502.00701. Bibcode:2015arXiv150200701Z. doi:10.1039/C4CS00282B. PMID 25679474. S2CID 3215062.
- Li, Hai; Wu, Jumiati; Yin, Zongyou; Zhang, Hua (2014). "Preparation and Applications of Mechanically Exfoliated Single-Layer and Multilayer MoS2 and WSe2 Nanosheets". Accounts of Chemical Research. 47 (4): 1067–1075. doi:10.1021/ar4002312. PMID 24697842.
- "Tungsten diselenide shows potential for ultrathin, flexible, semi-transparent solar cells". Gizmag.com. 11 March 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- Florian Aigenr (10 March 2014). "Atomically thin solar cells" (Press release). Vienna University of Technology. Retrieved 18 August 2014.
- Lee, Sung-Joon; Lin, Zhaoyang; Huang, Jin; Choi, Christopher; Chen, Peng; Liu, Yuan; Guo, Jian; Jia, Chuancheng; Wang, Yiliu; Liao, Qingliang; Shakir, Imran; Duan, Xidong; Dunn, Bruce; Zhang, Yue; Huang, Yu; Duan, Xiangfeng (2020). "Programmable devices based on reversible solid-state doping of two-dimensional semiconductors with superionic silver iodide". Nature Electronics. 3 (10): 630–637. doi:10.1038/s41928-020-00472-x. S2CID 224896469.
| Tungsten compounds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten(0) | |||||
| Tungsten(II) | |||||
| Tungsten(III) | |||||
| Tungsten(IV) | |||||
| Tungsten(V) | |||||
| Tungsten(VI) |
| ||||
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the selenide ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||