| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | WBr6 |
| Molar mass | 663.264 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark grey solid |
| Density | 5.32 g/cm |
| Melting point | 232 °C (450 °F; 505 K) (decomposition) |
| Solubility in water | Hydrolysis |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, ether, carbon disulfide, and ammonia |
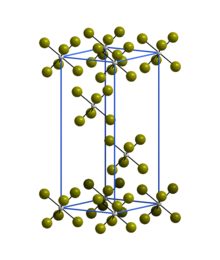
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Rhombohedral |
| Space group | R3 |
| Lattice constant | a = 6.39 Å, c = 17.53 Å |
| Lattice volume (V) | 620.8 Å |
| Formula units (Z) | 3 |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Tungsten hexafluoride Tungsten hexachloride |
| Related compounds | Tungsten(V) bromide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Tungsten hexabromide, also known as tungsten(VI) bromide, is a chemical compound of tungsten and bromine with the formula WBr6. It is an air-sensitive dark grey powder that decomposes above 200 °C to tungsten(V) bromide and bromine.
Production and reactions

Tungsten hexabromide is mainly produced by the reaction of metallic tungsten and bromine at temperatures around 100 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere:
- W + 3 Br2 → WBr6
Another method of producing this compound is by the reaction of tungsten hexacarbonyl and bromine at room temperature, releasing carbon monoxide. It can also be produced by the metathesis reaction of boron tribromide and tungsten hexachloride.
WBr6 is reduced with elemental antimony at elevated temperatrues, consecutively producing, WBr5, WBr4, W4Br10, W5Br12, then finally WBr2 at 350 °C. This reaction produces antimony tribromide as a side product. Any of these bromides can be reverted to the hexabromide by oxidation with bromine at 160 °C.
Tungsten hexabromide is hydrolyzed in water, producing tungsten pentoxide and releasing bromine.
Tungsten(VI) oxytetrabromide is produced by the reaction of tungsten hexabromide and tungsten(VI) oxide:
- 2 WBr6 + WO3 → 3 WOBr4
Structure
The trigonal crystal structure of WBr6 consists of isolated WBr6 octahedra and is isostructural with α-WCl6.
References
- ^ Herbert A. Schaffer; Edgar F. Smith (1896). "Tungsten Hexabromide". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 18 (12): 1098–1100. doi:10.1021/ja02098a015.
- ^ W. Willing; U. Müller (1987). "Wolframhexabromid". Acta Crystallogr. C (in German). 43 (7): 1425–1426. Bibcode:1987AcCrC..43.1425W. doi:10.1107/S0108270187091625.
- O. Kaposi; A. Popović; J. Marsel (1977). "Mass spectrometric studies of tungsten bromides and oxybromides". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. 39 (10): 1809–1815. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(77)80206-6.
- ^ M. Ströbele; H. -J. Meyer (2012). "Low-temperature preparation of tungsten halide clusters: Crystal structure of the adduct W5Br12 · SbBr3". Russian Journal of Coordination Chemistry. 38 (3): 178–182. doi:10.1134/S1070328412020078. S2CID 94477859.
- P. M. Druce; M. F. Lappert (1971). "Boron halides as reagents in inorganic syntheses. Part II. A further general method for the preparation of anhydrous bromides and iodides: halogen exchange reactions". Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical: 3595–3599. doi:10.1039/J19710003595.
- Markus Ströbele; H.-Jürgen Meyer (2012). "W4Br10 Cluster Intermediates in the Solid State Nucleation of W6Br12". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 638 (6): 945–949. doi:10.1002/zaac.201200010.
- ^ P.C. Crouch; G.W.A. Fowles; R.A. Walton (1970). "The high yield synthesis of the tungsten (VI) oxyhalides WOCl4, WOBr4 and WO2Cl2 and some observations on tungsten(VI) bromide and tungsten(V) chloride". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. 32 (1): 329–333. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(70)80475-4.
| Tungsten compounds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten(0) | |||||
| Tungsten(II) | |||||
| Tungsten(III) | |||||
| Tungsten(IV) | |||||
| Tungsten(V) | |||||
| Tungsten(VI) |
| ||||
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the bromide ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||